Содержание
- 2. Lecture Outline The Law of Sines The Law of Cosines Harmonic motion
- 3. Introduction Triangles are everywhere, and we often need to find unknown angles or the side lengths.
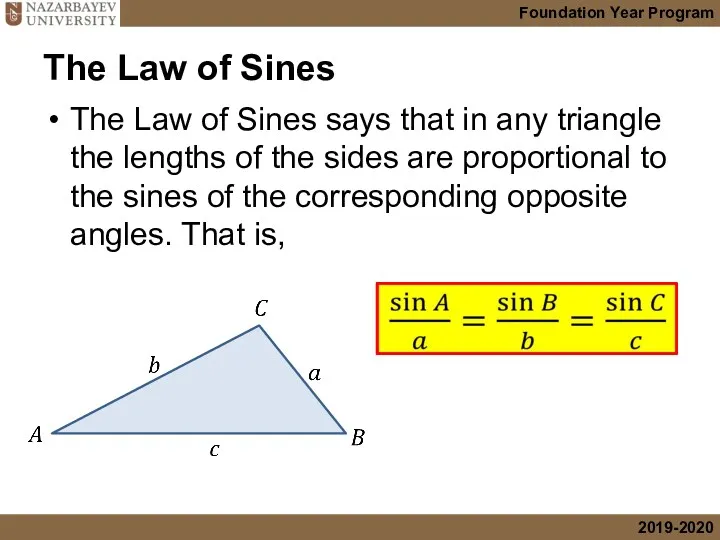
- 4. The Law of Sines The Law of Sines says that in any triangle the lengths of
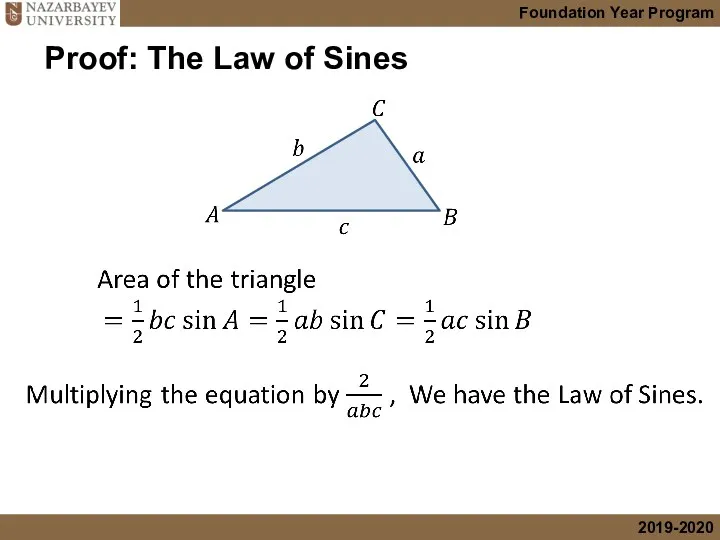
- 5. Proof: The Law of Sines
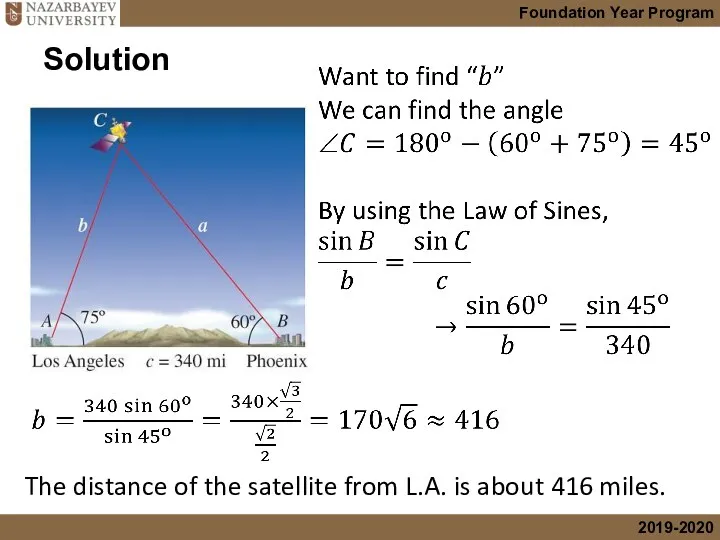
- 6. Example 1. A satellite orbiting the earth passes directly overhead at observation stations in Phoenix and
- 7. Solution The distance of the satellite from L.A. is about 416 miles.
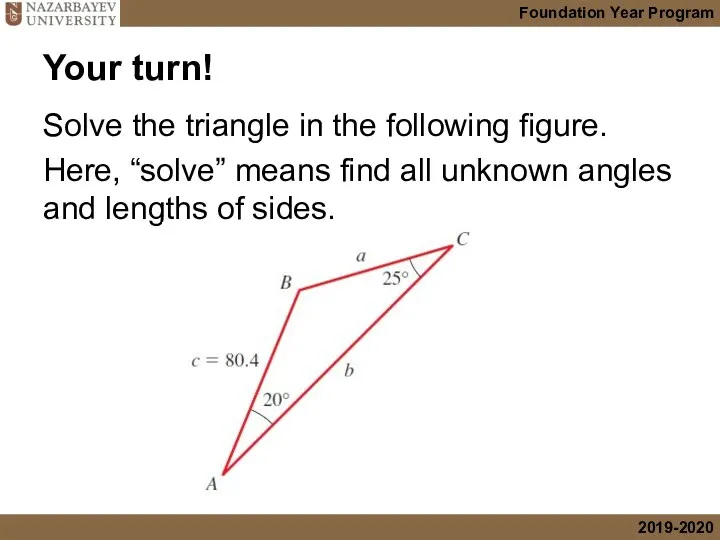
- 8. Your turn! Solve the triangle in the following figure. Here, “solve” means find all unknown angles
- 10. Example 2
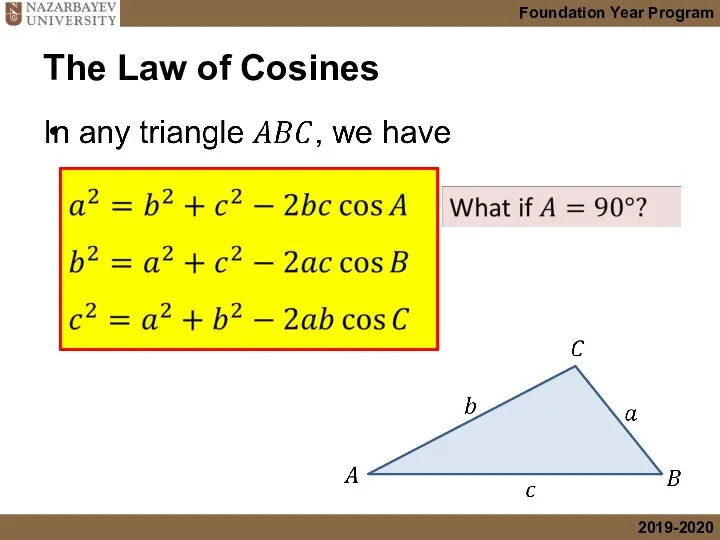
- 11. The Law of Cosines
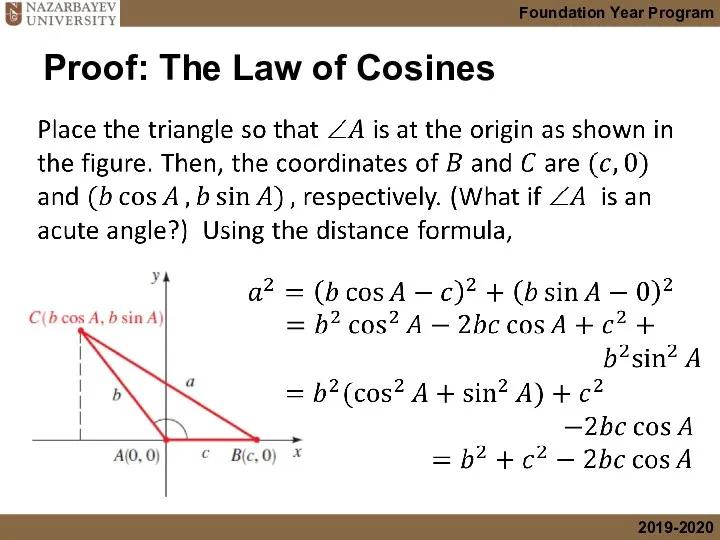
- 12. Proof: The Law of Cosines
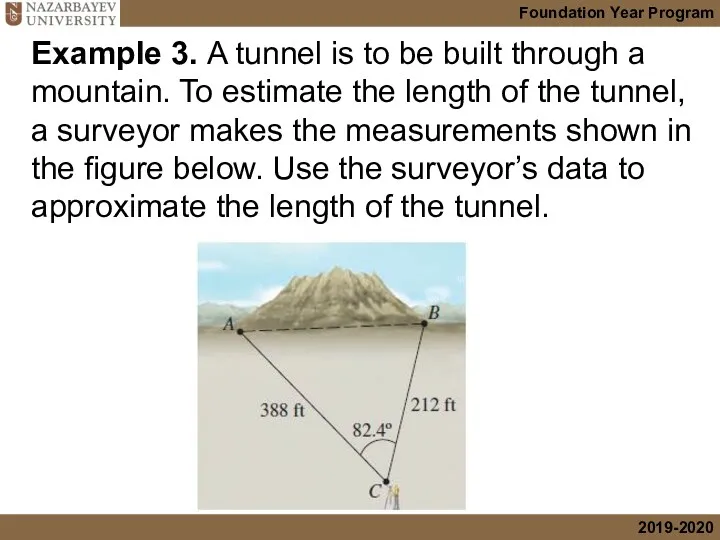
- 13. Example 3. A tunnel is to be built through a mountain. To estimate the length of
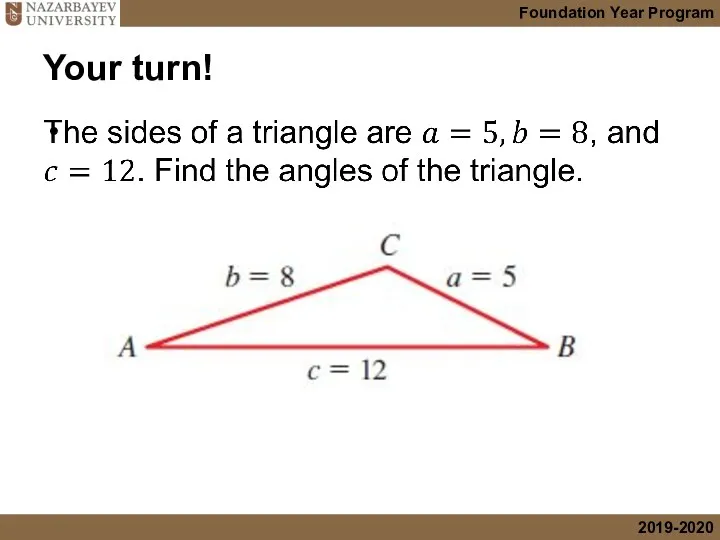
- 15. Your turn!
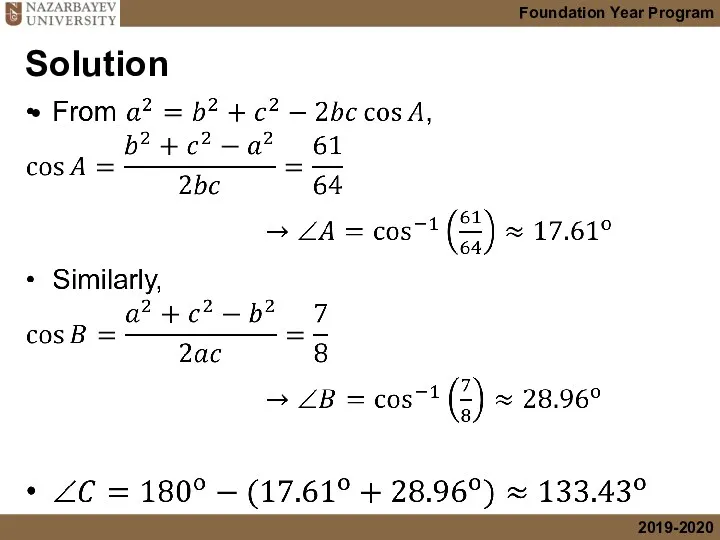
- 16. Solution
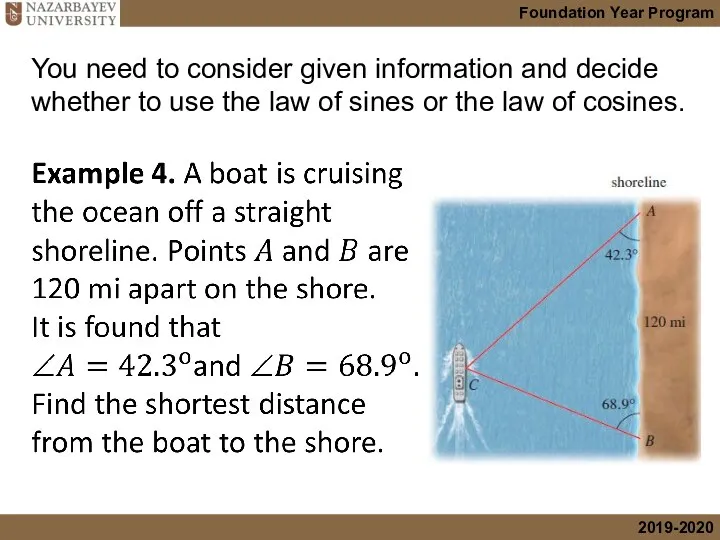
- 17. You need to consider given information and decide whether to use the law of sines or
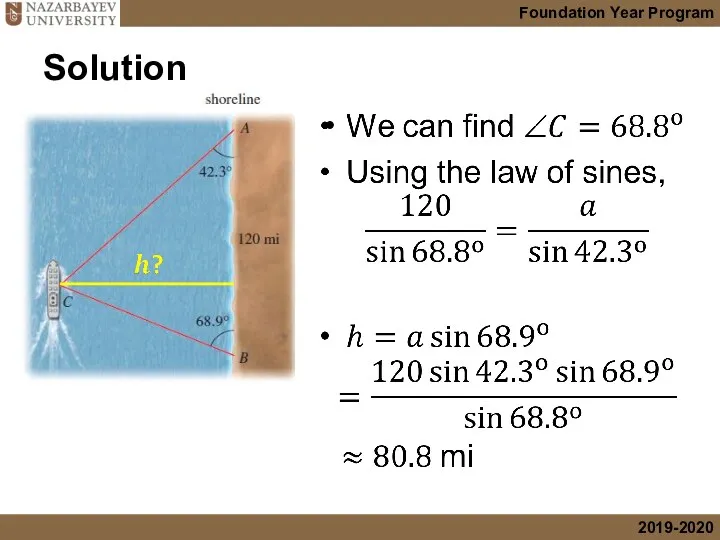
- 18. Solution
- 19. Your turn!
- 20. Solution
- 21. Harmonic motion Periodic behavior – behavior that repeats over and over again – is common in
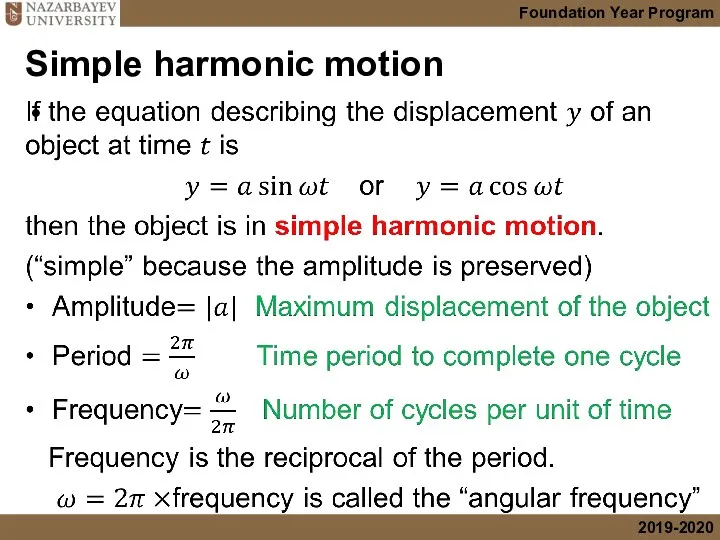
- 22. Simple harmonic motion
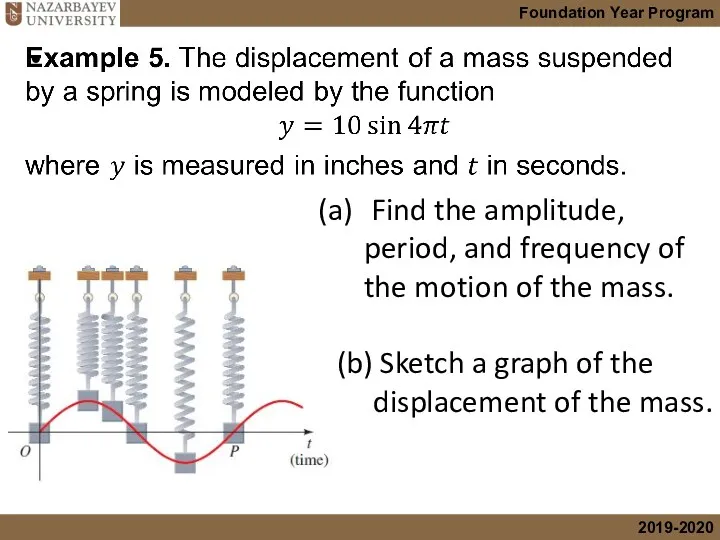
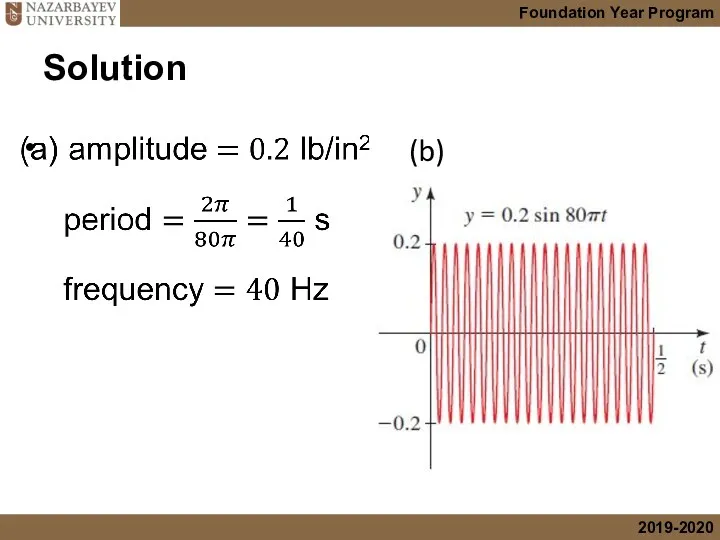
- 23. Find the amplitude, period, and frequency of the motion of the mass. (b) Sketch a graph
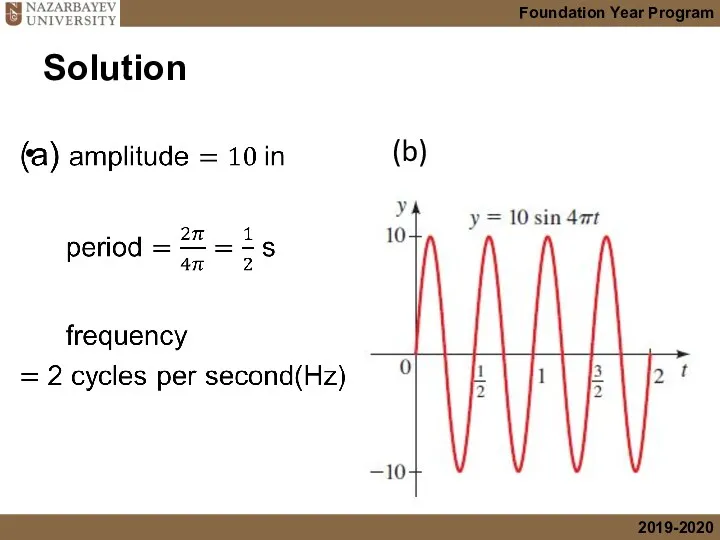
- 24. Solution (b)
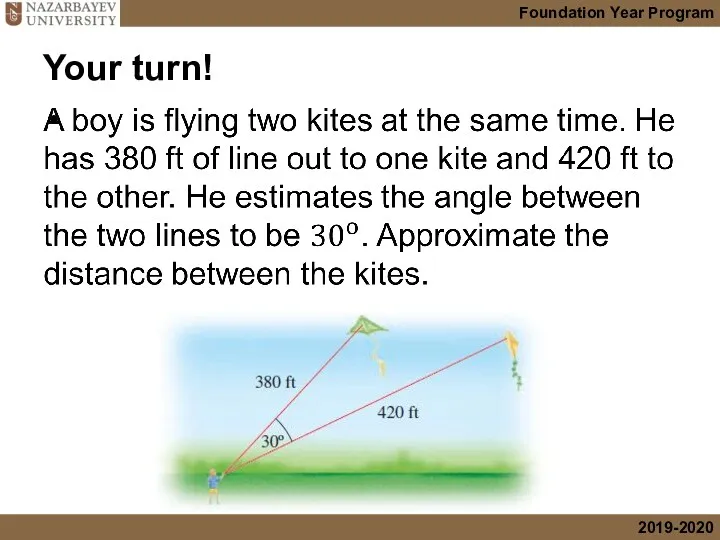
- 25. Your turn!
- 26. Solution (b)
- 27. The tone of the sound depends on the frequency, and the loudness depends on the amplitude.
- 29. Solution The amplitude will increase, so the number 0.2 is replaced by a larger number.
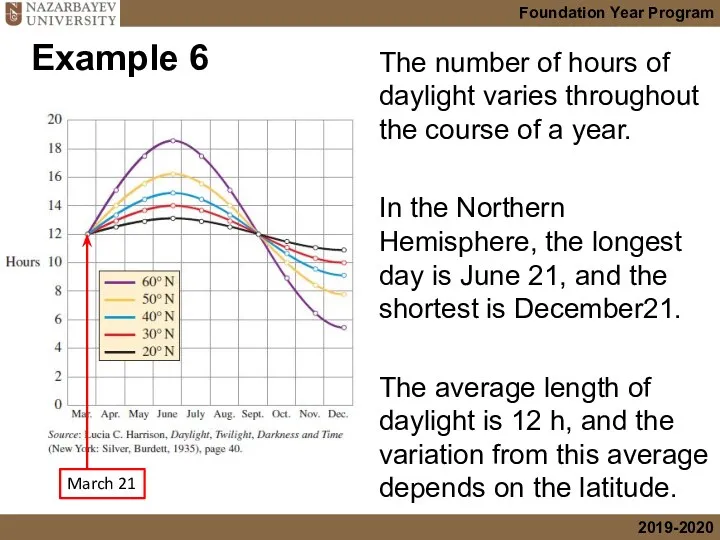
- 31. Example 6 The number of hours of daylight varies throughout the course of a year. In
- 33. Solution
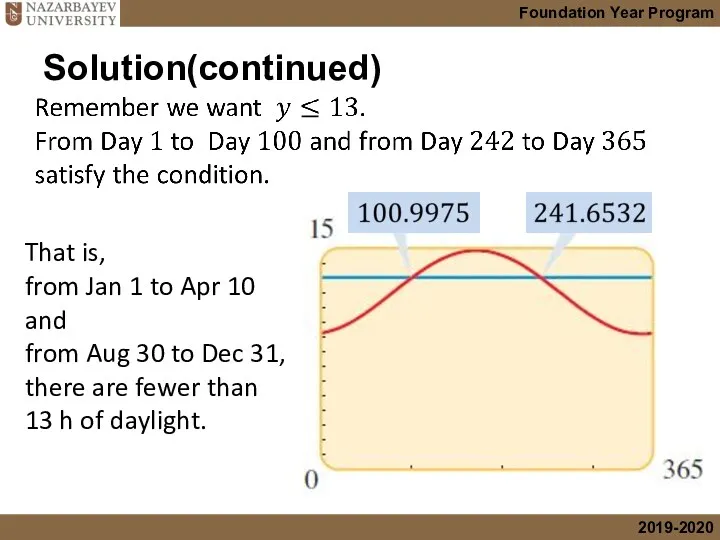
- 34. Solution(continued)
- 35. Solution(continued) That is, from Jan 1 to Apr 10 and from Aug 30 to Dec 31,
- 37. Solution
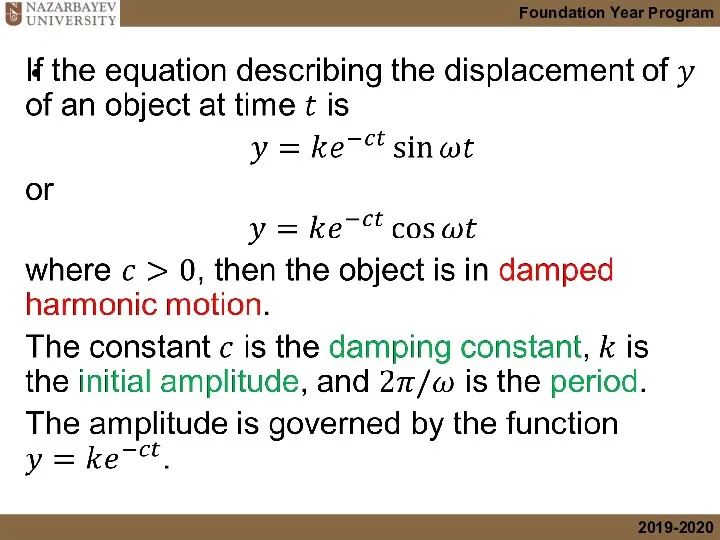
- 38. Damped harmonic motion The amplitude of a spring in a frictionless environment will not change. The
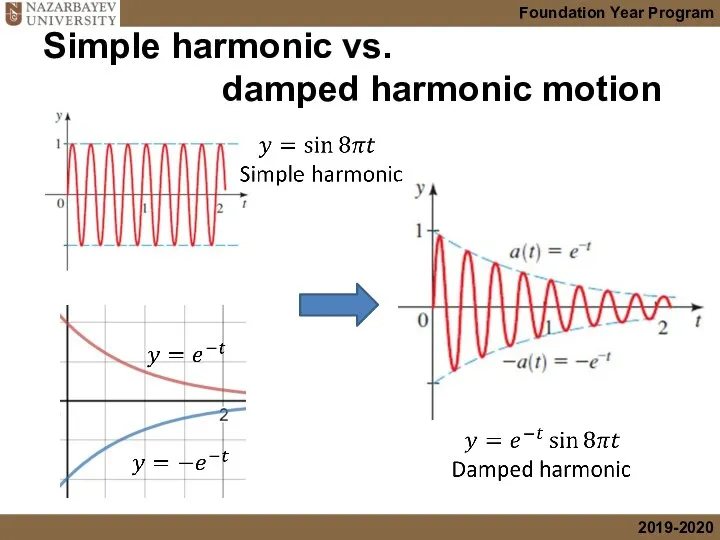
- 40. Simple harmonic vs. damped harmonic motion
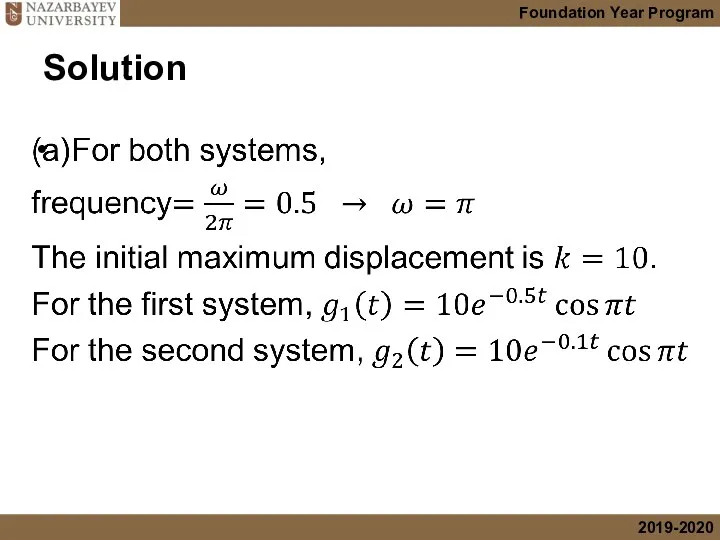
- 41. Example 7
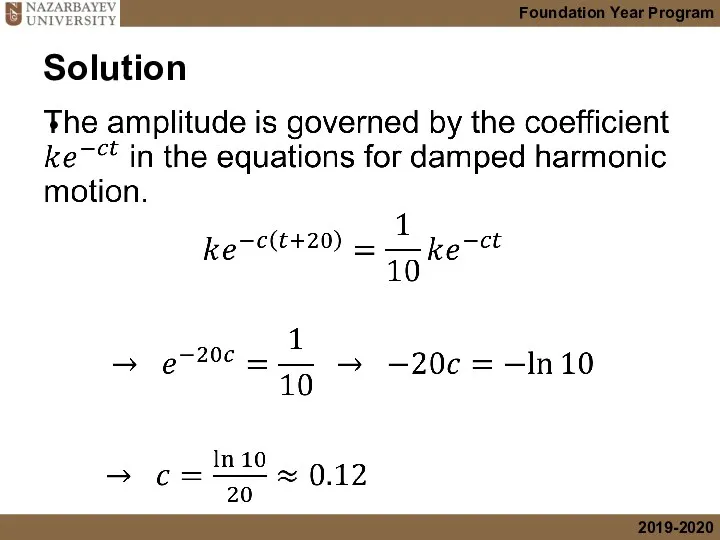
- 42. Solution
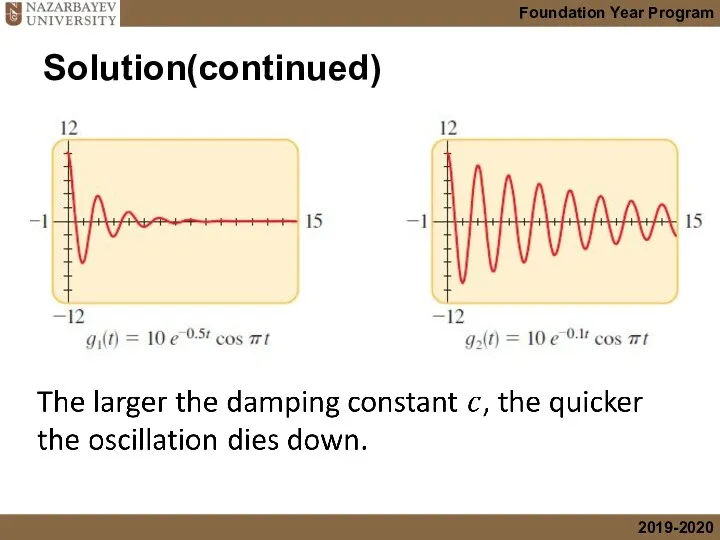
- 43. Solution(continued)
- 44. Example 8
- 45. Solution
- 46. Learning outcomes 3.5.1. Solve triangles by using the law of sines and the law of cosines
- 48. Скачать презентацию





















 Презентация к уроку Формула одновременного движения
Презентация к уроку Формула одновременного движения презентация к уроку математики 2 класса
презентация к уроку математики 2 класса Системы двух линейных уравнений с двумя переменными. 7 класс
Системы двух линейных уравнений с двумя переменными. 7 класс Презентация к уроку математики Взаимосвязь между величинами V,t,S
Презентация к уроку математики Взаимосвязь между величинами V,t,S Дастурланувчи мантиқий матрица
Дастурланувчи мантиқий матрица График функции. Готовимся к ЕГЭ
График функции. Готовимся к ЕГЭ Однородные тригонометрические уравнения
Однородные тригонометрические уравнения Примеры решения простейших тригонометрических неравенств
Примеры решения простейших тригонометрических неравенств Решение задач. Признаки равенства треугольников
Решение задач. Признаки равенства треугольников Движение по воде. Задачи
Движение по воде. Задачи Сравнение предметов по различным признакам. 1 класс
Сравнение предметов по различным признакам. 1 класс Приближение чисел
Приближение чисел Аксиомы стереометрии
Аксиомы стереометрии Марковские процессы (Лекция 9)
Марковские процессы (Лекция 9) Тренажер по математике для 1 класса. Сложение и вычитание в пределах 10
Тренажер по математике для 1 класса. Сложение и вычитание в пределах 10 Арифметический диктант к уроку математика 4 класс
Арифметический диктант к уроку математика 4 класс Різницеве порівняння чисел. Задачі. Урок №60
Різницеве порівняння чисел. Задачі. Урок №60 Трапеция. 8 класс
Трапеция. 8 класс Методы решения тригонометрических уравнений
Методы решения тригонометрических уравнений The discoveries of Pythagoras
The discoveries of Pythagoras Умножение в случаях вида 23х40
Умножение в случаях вида 23х40 Презентация по математике Сложение и вычитание числа 1 и 2
Презентация по математике Сложение и вычитание числа 1 и 2 Треугольник, многоугольник. Плоскость, прямая, луч
Треугольник, многоугольник. Плоскость, прямая, луч Математическая лужайка
Математическая лужайка Методы проецирования. Проекции точки, проекции прямой (1 лекция)
Методы проецирования. Проекции точки, проекции прямой (1 лекция) Компланарные векторы
Компланарные векторы Положительные и отрицательные числа в истории
Положительные и отрицательные числа в истории Визначні математичні задачі
Визначні математичні задачі