Содержание
- 2. Outline Different number systems Why use different ones? Binary / Octal / Hexadecimal Conversions Negative number
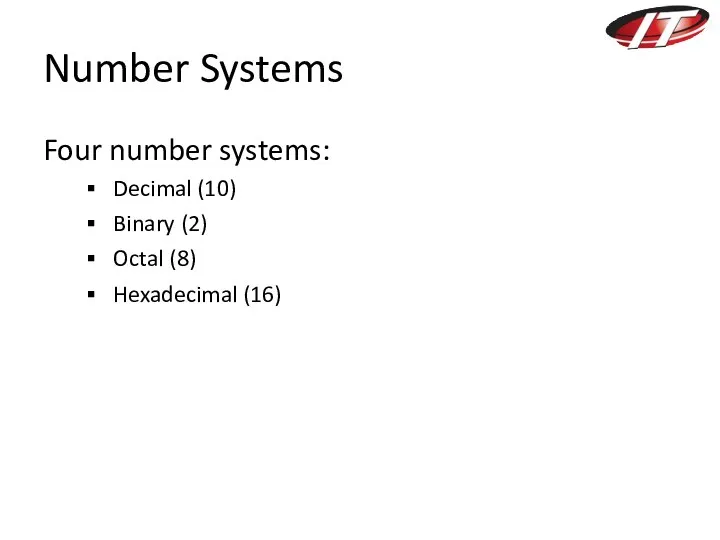
- 3. Number Systems Four number systems: Decimal (10) Binary (2) Octal (8) Hexadecimal (16)
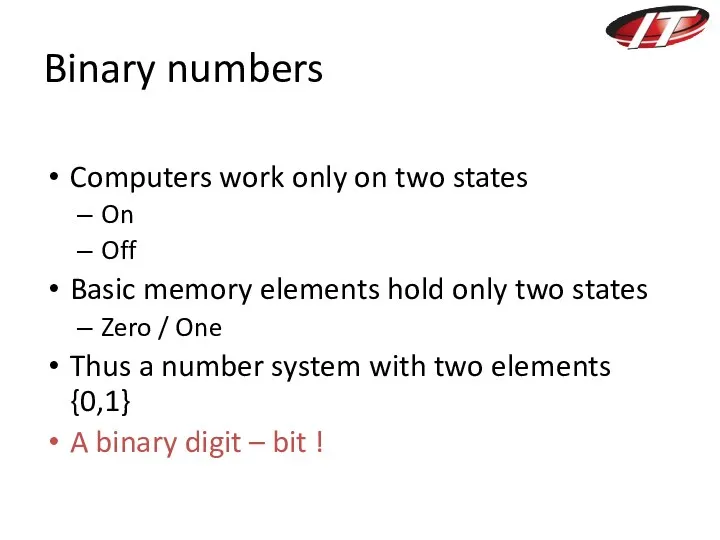
- 4. Binary numbers Computers work only on two states On Off Basic memory elements hold only two
- 5. Decimal numbers 1439 = 1 x 103 + 4 x 102 + 3 x 101 +
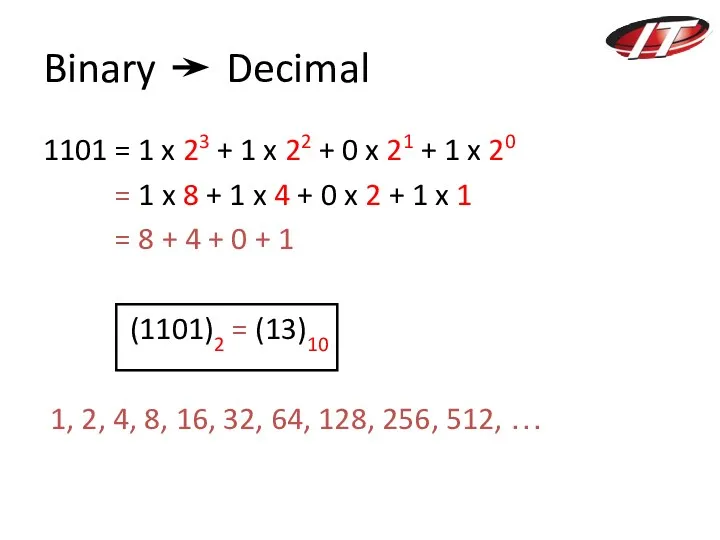
- 6. Binary Decimal 1101 = 1 x 23 + 1 x 22 + 0 x 21 +
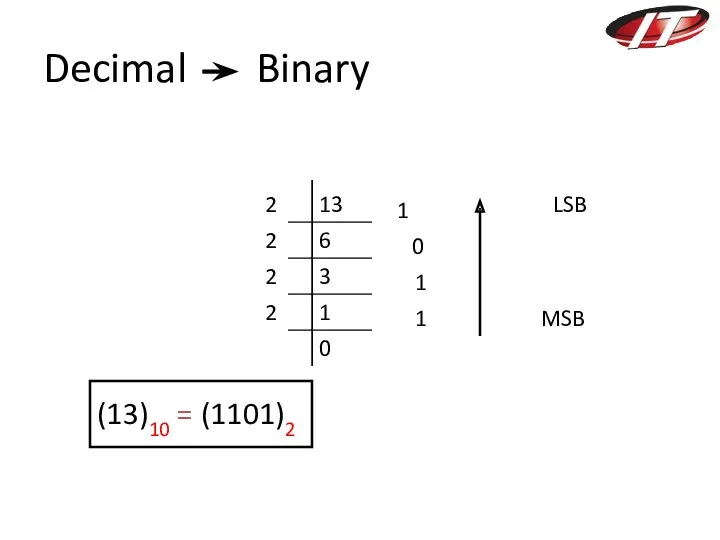
- 7. Decimal Binary 13 6 3 1 0 2 2 2 2 1 0 1 1 (13)10
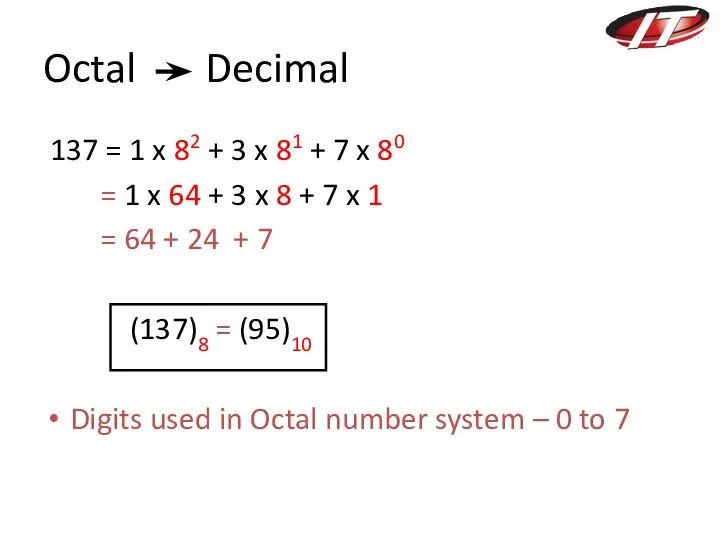
- 8. Octal Decimal 137 = 1 x 82 + 3 x 81 + 7 x 80 =
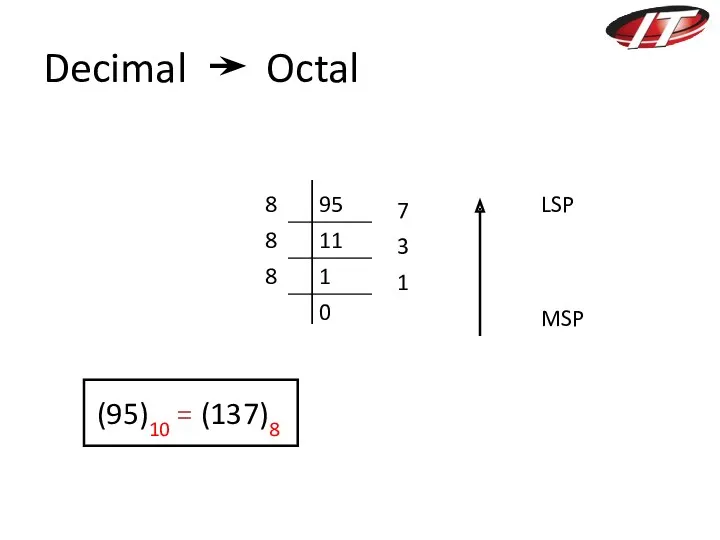
- 9. Decimal Octal 95 11 1 0 8 8 8 7 3 1 (95)10 = (137)8 MSP
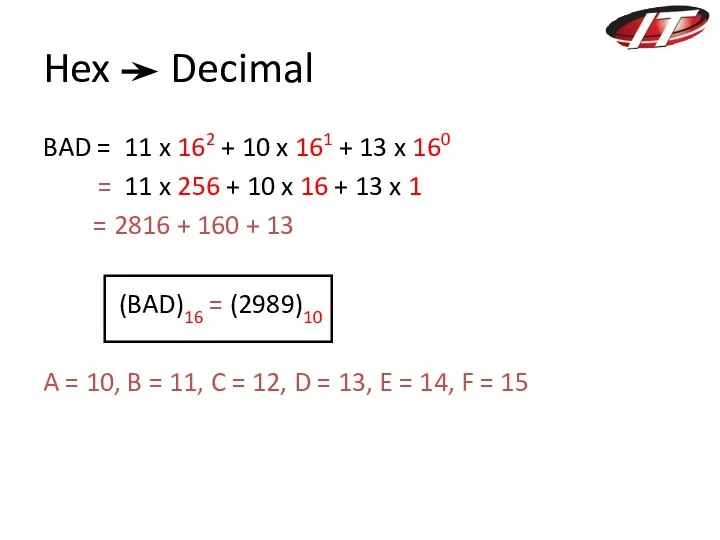
- 10. Hex Decimal BAD = 11 x 162 + 10 x 161 + 13 x 160 =
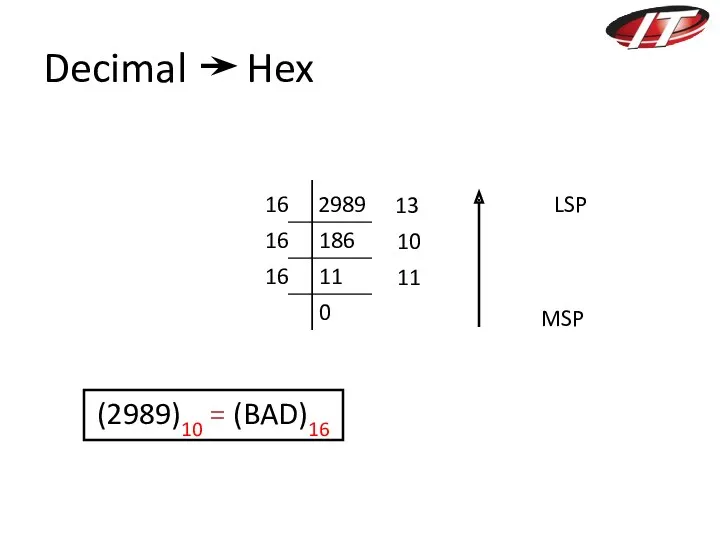
- 11. Decimal Hex 2989 186 11 0 16 16 16 13 10 11 (2989)10 = (BAD)16 MSP
- 12. Why octal or hex? Ease of use and conversion Three bits make one octal digit 111
- 13. Roman Numerals
- 14. A Brief History of Roman Numerals Roman numerals originated in ancient Rome. This ancient counting system
- 15. Arabic numbers → Roman numerals conversion Roman numerals are written as combinations of seven letters. I
- 16. As a general guide Roman Numerals are made up by adding or subtracting numbers like this:-
- 17. VIII = 5+3 = 8 XIX = 10+ 9 = 19 (Remember 9 is always =
- 18. Check your answers. 7 = VII 12 = XII 15 = XV 20 = XX
- 19. Can you convert these numbers to Roman Numerals? 17 = 22 = 26 = 29 =
- 20. Were you correct? 17=XVII 22=XXII 26=XXVI 29=XXIX 30=XXX 32=XXXII 35=XXXV 50=L 40=XL 44=XLIV 49=XLIX 58=LVIII 60=LX
- 21. Some more large numbers to try: 600 = 700 = 800 = 1000 = 900 =
- 22. Check your answers. 600 = DC 700 = DCC 800 = DCCC 1000 = M 900
- 23. The last one Can you convert 2017? MMXVII Now try to write today’s date. Day /
- 24. Binary Arithmetic Addition Subtraction
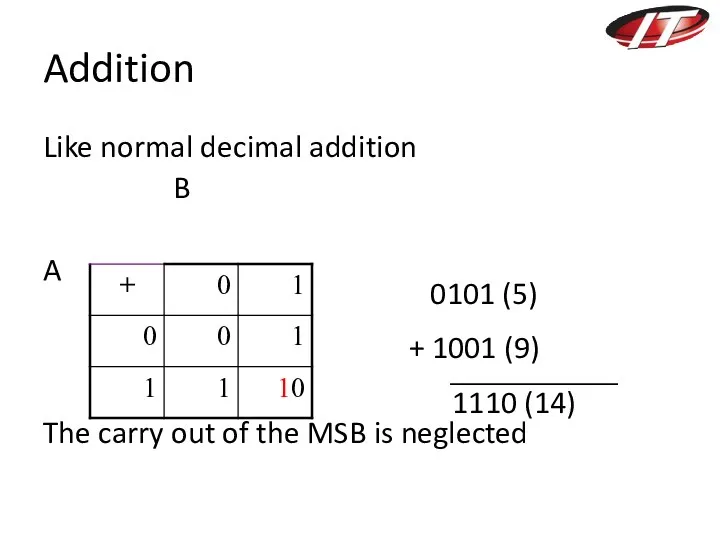
- 25. Addition Like normal decimal addition B A The carry out of the MSB is neglected 0101
- 27. Скачать презентацию







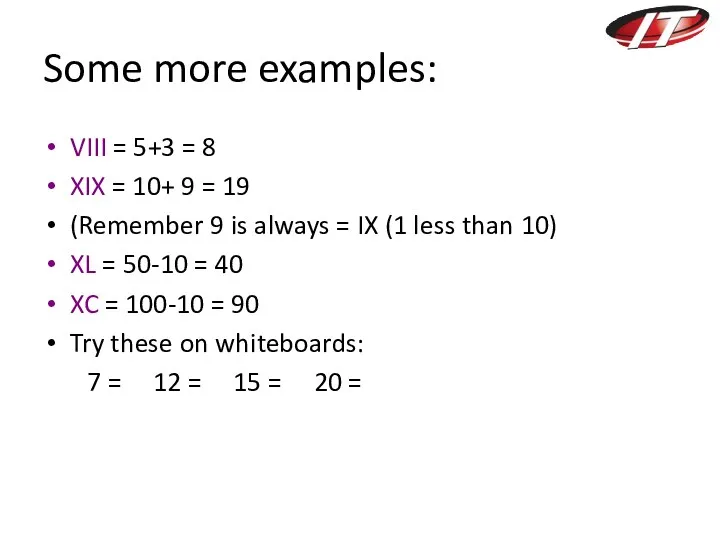






 Геометричні фігури
Геометричні фігури Теория вероятностей. Введение. Урок №2. 9 класс
Теория вероятностей. Введение. Урок №2. 9 класс Что такое цилиндр?
Что такое цилиндр? Соотношение между сторонами и углами треугольника. Решение задач
Соотношение между сторонами и углами треугольника. Решение задач Комбинаторика и элементы теории вероятностей и статистики в задачах ГИА
Комбинаторика и элементы теории вероятностей и статистики в задачах ГИА Десятичные дроби. Повторение. Действия с десятичными дробями
Десятичные дроби. Повторение. Действия с десятичными дробями Метод главных элементов для решения системы линейных уравнений
Метод главных элементов для решения системы линейных уравнений Задачи а составление уравнения
Задачи а составление уравнения Понятие обратной функции. Определение обратных тригонометрических функций
Понятие обратной функции. Определение обратных тригонометрических функций Проект по математике
Проект по математике Урок 1 класс Решаем задачи.
Урок 1 класс Решаем задачи. Соотношения между сторонами и углами прямоугольного треугольника
Соотношения между сторонами и углами прямоугольного треугольника Площадь многоугольников
Площадь многоугольников Подобные треугольники
Подобные треугольники Компьютерное моделирование физических процессов, как средство формирования математических понятий
Компьютерное моделирование физических процессов, как средство формирования математических понятий Умножение и деление обыкновенных дробей. Проект. Реализация требований ФГОС ООО при обучении учащихся 5 класса
Умножение и деление обыкновенных дробей. Проект. Реализация требований ФГОС ООО при обучении учащихся 5 класса Измерение отрезков
Измерение отрезков Нахождение числа по заданному значению его дроби. Правило нахождения числа по его дроби
Нахождение числа по заданному значению его дроби. Правило нахождения числа по его дроби Сечения тетраэдра
Сечения тетраэдра Преобразование выражений, содержащих квадратные корни. 8 класс
Преобразование выражений, содержащих квадратные корни. 8 класс Урок математики Арифметические действия над числами
Урок математики Арифметические действия над числами Степень с натуральным показателем
Степень с натуральным показателем Среднее арифметическое
Среднее арифметическое Обыкновенные дроби
Обыкновенные дроби Умножение десятичных дробей
Умножение десятичных дробей Расстояние между прямыми в пространстве
Расстояние между прямыми в пространстве Геометрическая интерпретация комплексных чисел
Геометрическая интерпретация комплексных чисел Презентация открытого урока по математике в третьем классе на темуПлощадь прямоугольников
Презентация открытого урока по математике в третьем классе на темуПлощадь прямоугольников