- Главная
- Математика
- Common Probability Distributions

Содержание
- 2. DISCRETE RANDOM VARIABLES A discrete random variable can take on at most a countable number of
- 3. The Discrete Uniform Distribution The discrete uniform and the continuous uniform distributions are the distributions of
- 4. A binomial random variable has an expected value or mean equal to np and variance equal
- 5. CONTINUOUS RANDOM VARIABLES The Normal Distribution
- 7. Shortfall risk and Safety-first Ratio
- 8. Lognormal distribution
- 10. Скачать презентацию
Слайд 2
DISCRETE RANDOM VARIABLES
A discrete random variable can take on at most
DISCRETE RANDOM VARIABLES
A discrete random variable can take on at most
a countable number of possible values. For example, a discrete random variable X can take on a limited number of outcomes x1, x2, …, xn (n possible outcomes), or a discrete random variable Y can take on an unlimited number of outcomes y1, y2, … (without end).1 Because we can count all the possible outcomes of X and Y (even if we go on forever in the case of Y), both X and Y satisfy the definition of a discrete random variable
We can view a probability distribution in two ways:
The probability function specifies the probability that the random variable will take on a specific value. The probability function is denoted p(x) for a discrete random variable and f(x) for a continuous random variable. For any probability function p(x), 0 ≤ p(x) ≤ 1, and the sum of p(x) over all values of X equals 1.
2. The cumulative distribution function, denoted F(x) for both continuous and discrete random variables, gives the probability that the random variable is less than or equal to x.
We can view a probability distribution in two ways:
The probability function specifies the probability that the random variable will take on a specific value. The probability function is denoted p(x) for a discrete random variable and f(x) for a continuous random variable. For any probability function p(x), 0 ≤ p(x) ≤ 1, and the sum of p(x) over all values of X equals 1.
2. The cumulative distribution function, denoted F(x) for both continuous and discrete random variables, gives the probability that the random variable is less than or equal to x.
Слайд 3
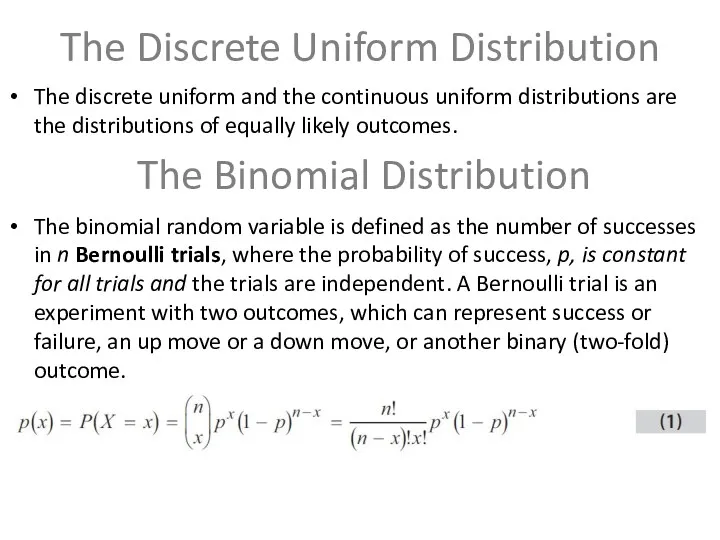
The Discrete Uniform Distribution
The discrete uniform and the continuous uniform distributions
The Discrete Uniform Distribution
The discrete uniform and the continuous uniform distributions
are the distributions of equally likely outcomes.
The binomial random variable is defined as the number of successes in n Bernoulli trials, where the probability of success, p, is constant for all trials and the trials are independent. A Bernoulli trial is an experiment with two outcomes, which can represent success or failure, an up move or a down move, or another binary (two-fold) outcome.
The binomial random variable is defined as the number of successes in n Bernoulli trials, where the probability of success, p, is constant for all trials and the trials are independent. A Bernoulli trial is an experiment with two outcomes, which can represent success or failure, an up move or a down move, or another binary (two-fold) outcome.
The Binomial Distribution
Слайд 4
A binomial random variable has an expected value or mean equal
A binomial random variable has an expected value or mean equal
to np and variance equal to np(1 − p).
A binomial tree is the graphical representation of a model of asset price dynamics in which, at each period, the asset moves up with probability p or down with probability (1 − p). The binomial tree is a flexible method for modelling asset price movement and is widely used in pricing options.
A binomial tree is the graphical representation of a model of asset price dynamics in which, at each period, the asset moves up with probability p or down with probability (1 − p). The binomial tree is a flexible method for modelling asset price movement and is widely used in pricing options.
Слайд 5
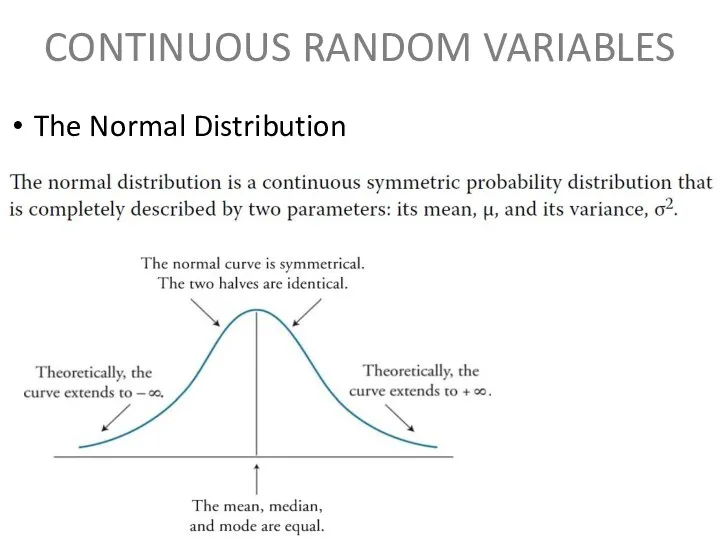
CONTINUOUS RANDOM VARIABLES
The Normal Distribution
CONTINUOUS RANDOM VARIABLES
The Normal Distribution
Слайд 6
Слайд 7
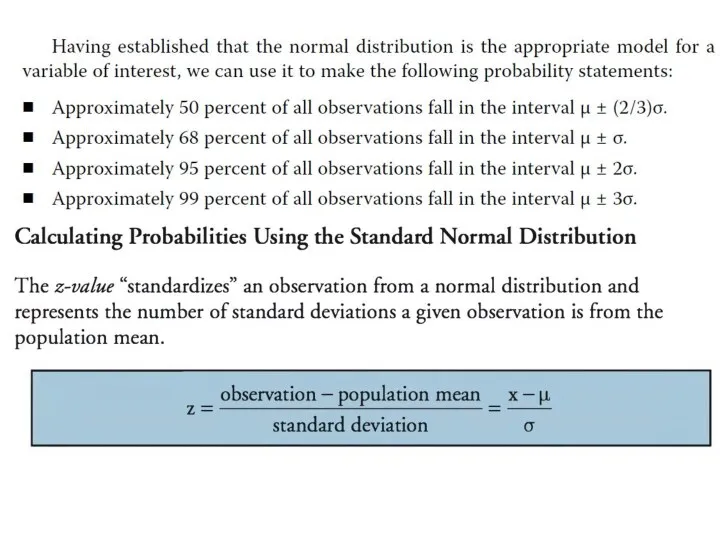
Shortfall risk and Safety-first Ratio
Shortfall risk and Safety-first Ratio
Слайд 8
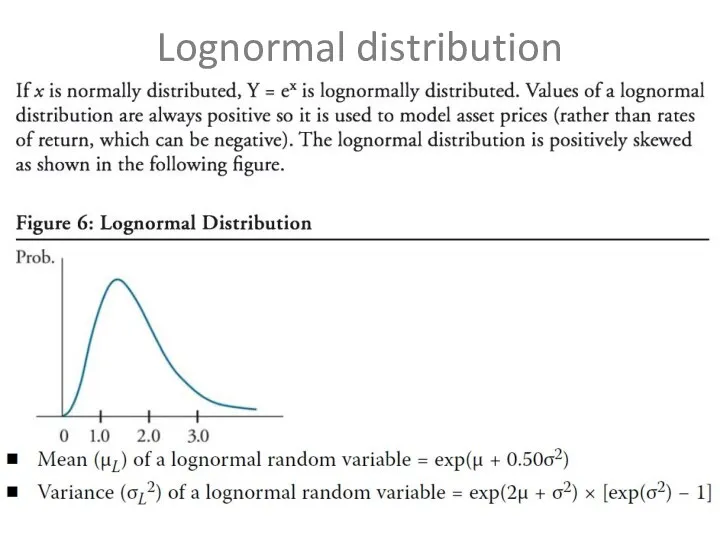
Lognormal distribution
Lognormal distribution
- Предыдущая
Finance and the Financial ManagerСледующая -
Training at Nalco


 Урок и презентация по математике 4 класс Движение. Решение задач
Урок и презентация по математике 4 класс Движение. Решение задач Формулы. 5 класс
Формулы. 5 класс Правильные многогранники. Метапредмет – хаос и порядок
Правильные многогранники. Метапредмет – хаос и порядок урок_23
урок_23 Решение задач на одновременное движение всех видов
Решение задач на одновременное движение всех видов Решение примеров. Прибавление числа 10
Решение примеров. Прибавление числа 10 Стандартный вид числа
Стандартный вид числа Множества и операции с ними
Множества и операции с ними Медианы, биссектрисы, высоты треугольника
Медианы, биссектрисы, высоты треугольника Внеклассное мероприятие по математике Своя игра
Внеклассное мероприятие по математике Своя игра Урок-презентация по математике для 2 кл. Сложение и вычитание в пределах 9. Урок-повторение материала.
Урок-презентация по математике для 2 кл. Сложение и вычитание в пределах 9. Урок-повторение материала. Таблица умножения
Таблица умножения Введение в математический анализ. Теория пределов
Введение в математический анализ. Теория пределов Математические загадки
Математические загадки Теория кривых. Формулы Сере-Френе
Теория кривых. Формулы Сере-Френе Математический досуг Весёлые задачи в форме игры КВН для детей подготовительной группы.
Математический досуг Весёлые задачи в форме игры КВН для детей подготовительной группы. Сфера и шар
Сфера и шар Специальная теория относительности
Специальная теория относительности Устный счёт в пределах 1000 для 3 класса
Устный счёт в пределах 1000 для 3 класса Математический диктант, 2 класс.
Математический диктант, 2 класс. Определение производной
Определение производной Пирамида. Большая пирамида Хеопса
Пирамида. Большая пирамида Хеопса Кривые второго порядка
Кривые второго порядка Wide-angle X-ray scattering (WAXS) geometries. In-plane diffraction geometry
Wide-angle X-ray scattering (WAXS) geometries. In-plane diffraction geometry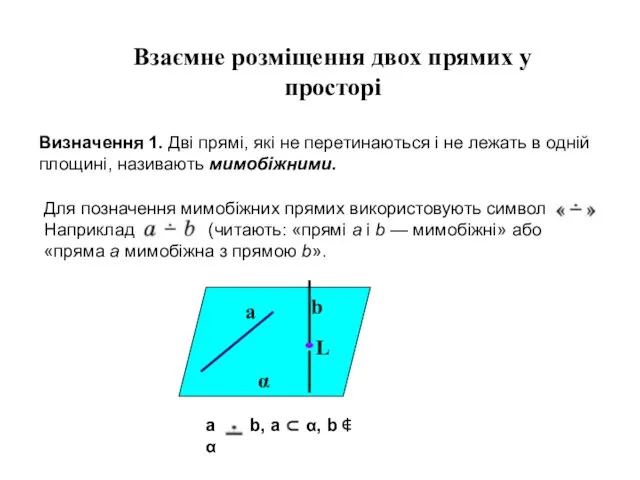 Взаємне розміщення двох прямих у просторі
Взаємне розміщення двох прямих у просторі Умножение обыкновенных дробей
Умножение обыкновенных дробей Круг. Сектор. Сегмент
Круг. Сектор. Сегмент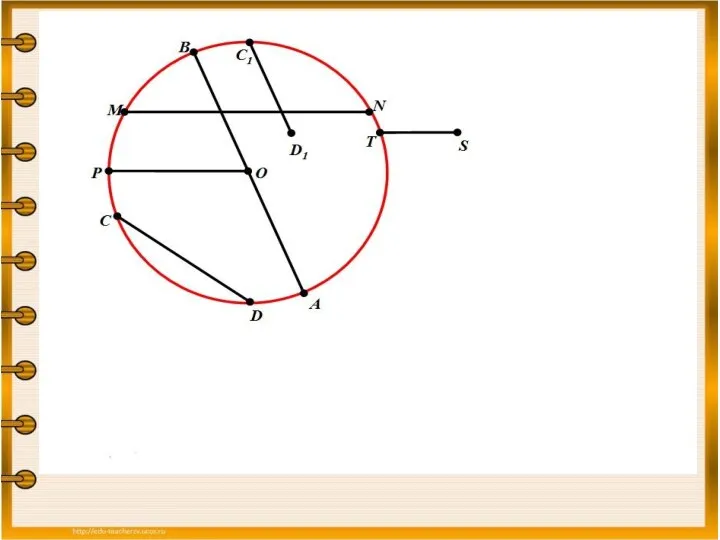 Взаимное расположение прямой и окружности
Взаимное расположение прямой и окружности