Содержание
- 2. Section 6-1 Objectives Interpret graphs of normal probability distributions Find areas under the standard normal curve
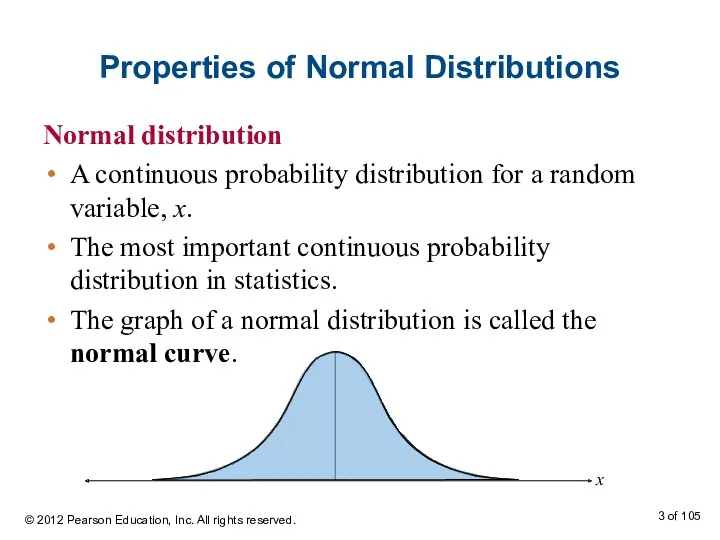
- 3. Properties of Normal Distributions Normal distribution A continuous probability distribution for a random variable, x. The
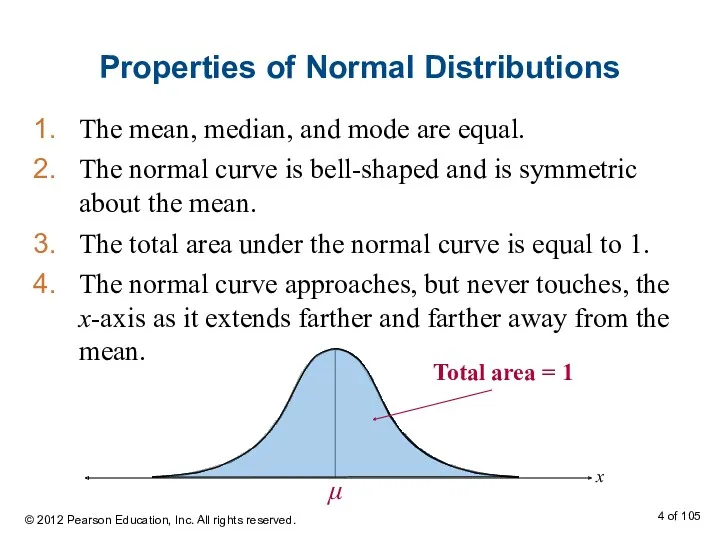
- 4. Properties of Normal Distributions The mean, median, and mode are equal. The normal curve is bell-shaped
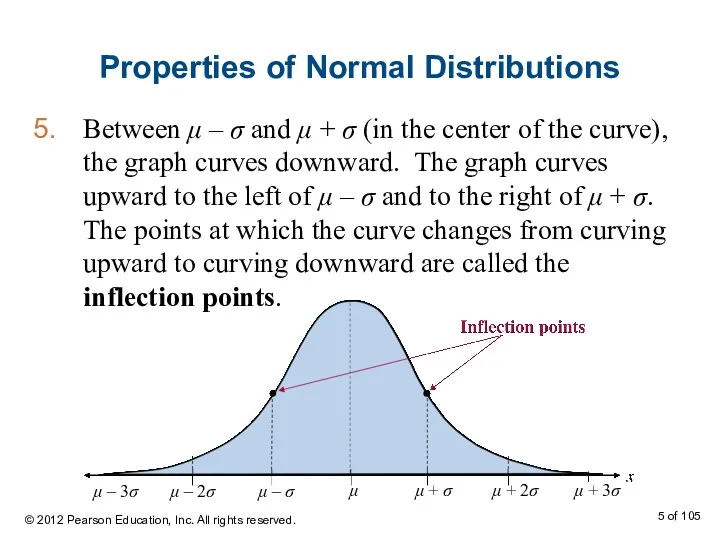
- 5. Properties of Normal Distributions Between μ – σ and μ + σ (in the center of
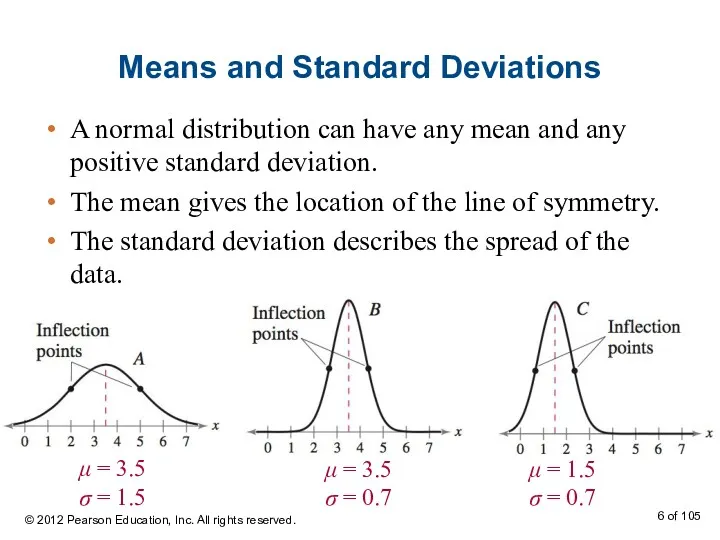
- 6. Means and Standard Deviations A normal distribution can have any mean and any positive standard deviation.
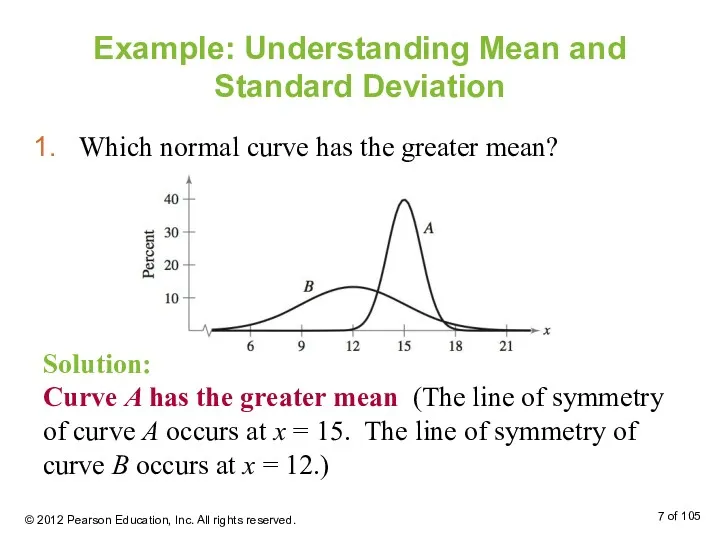
- 7. Example: Understanding Mean and Standard Deviation Which normal curve has the greater mean? Solution: Curve A
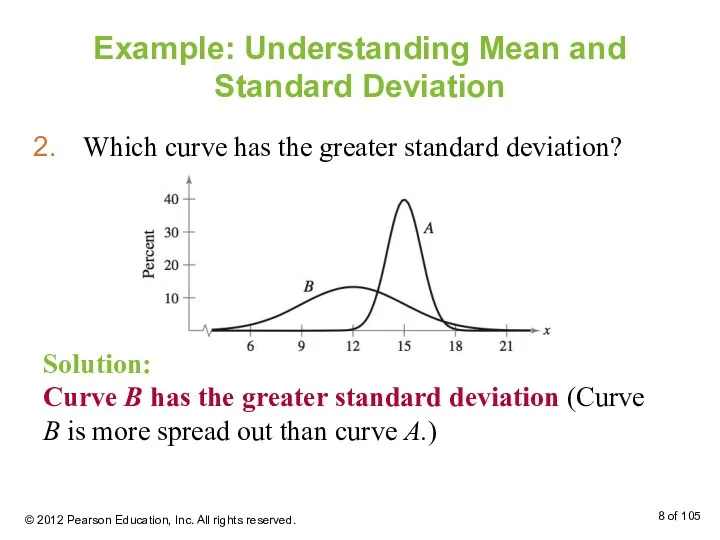
- 8. Example: Understanding Mean and Standard Deviation Which curve has the greater standard deviation? Solution: Curve B
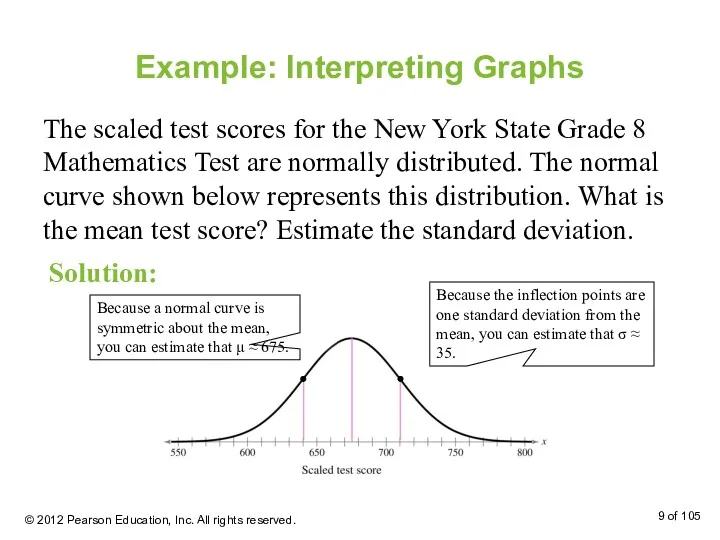
- 9. Example: Interpreting Graphs The scaled test scores for the New York State Grade 8 Mathematics Test
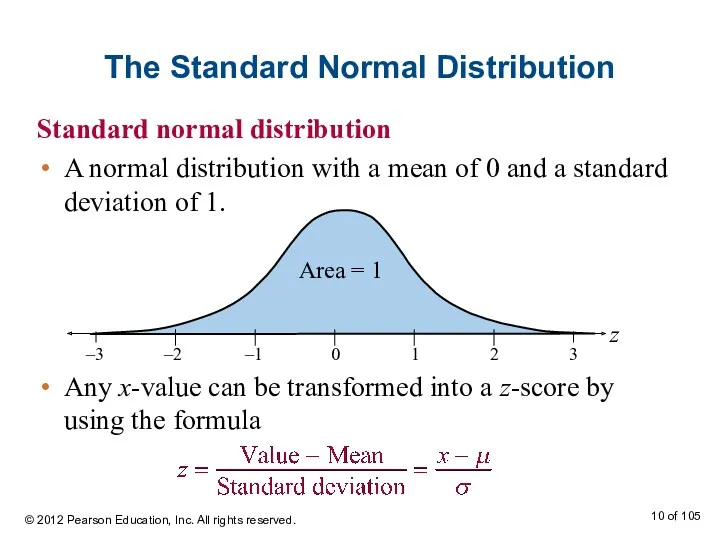
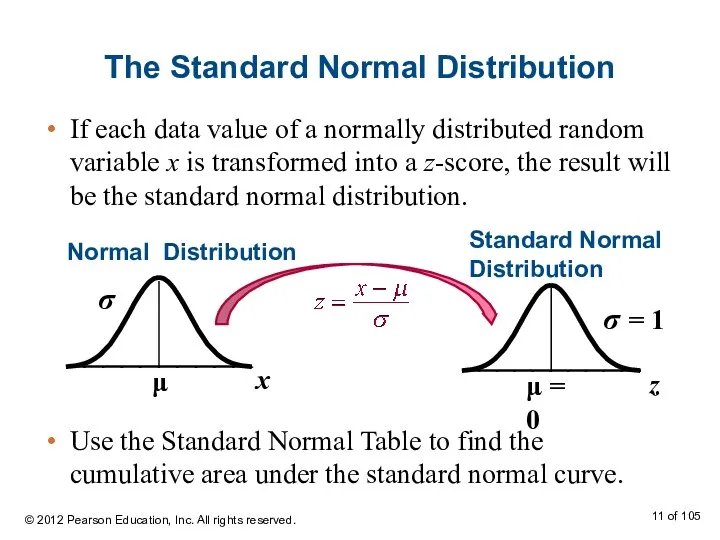
- 10. The Standard Normal Distribution Standard normal distribution A normal distribution with a mean of 0 and
- 11. The Standard Normal Distribution If each data value of a normally distributed random variable x is
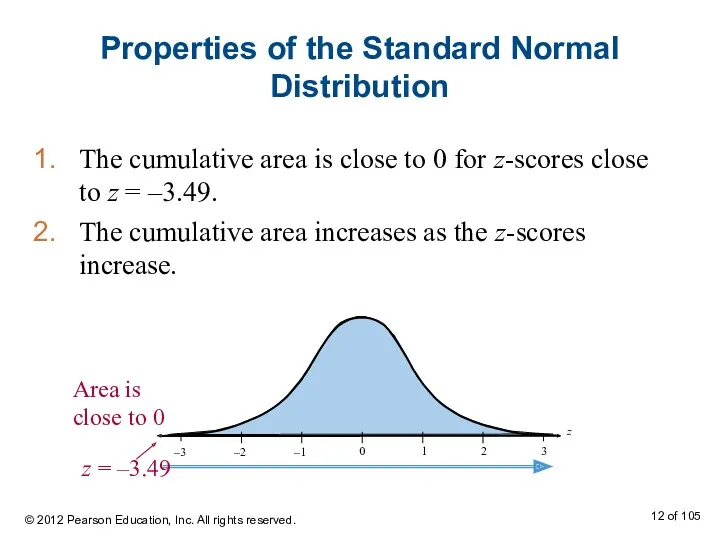
- 12. Properties of the Standard Normal Distribution The cumulative area is close to 0 for z-scores close
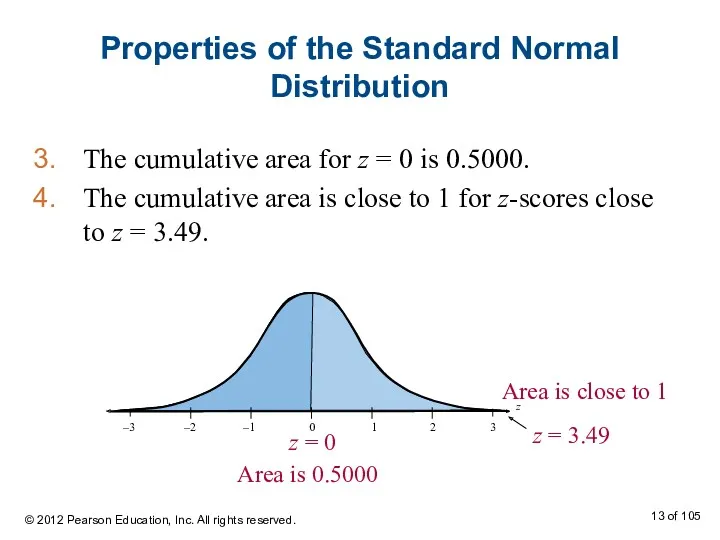
- 13. Properties of the Standard Normal Distribution The cumulative area for z = 0 is 0.5000. The
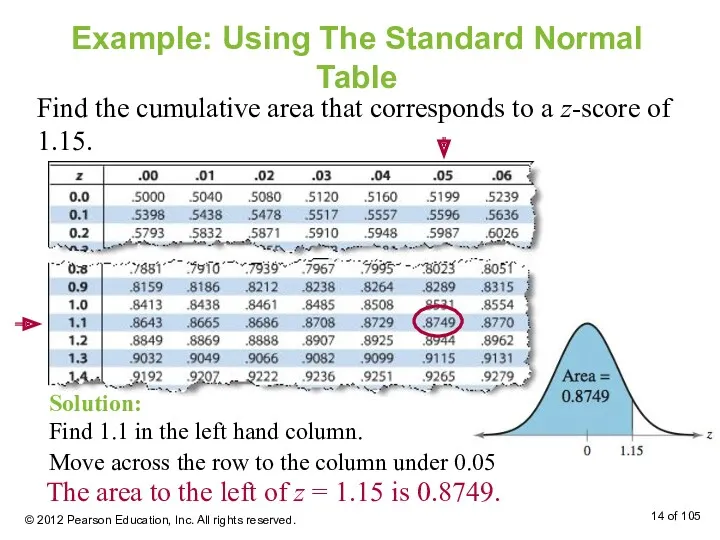
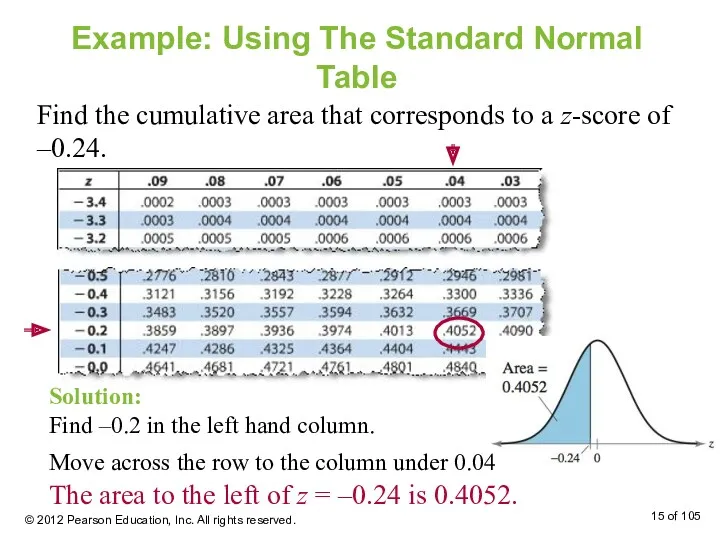
- 14. Example: Using The Standard Normal Table Find the cumulative area that corresponds to a z-score of
- 15. Example: Using The Standard Normal Table Find the cumulative area that corresponds to a z-score of
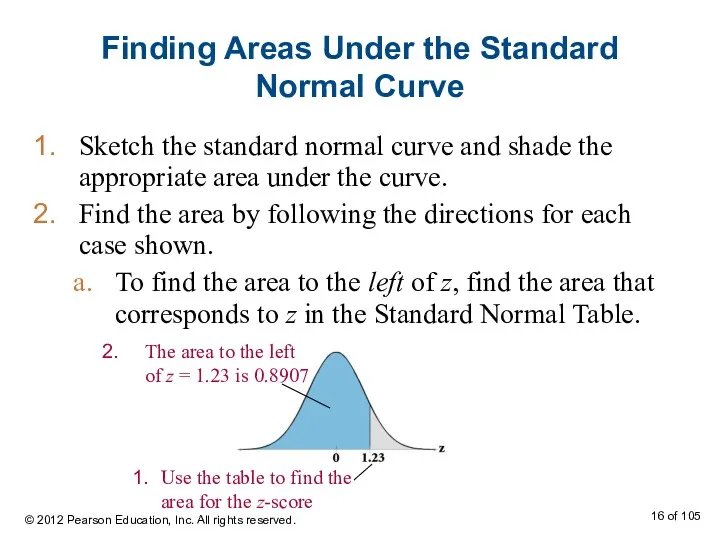
- 16. Finding Areas Under the Standard Normal Curve Sketch the standard normal curve and shade the appropriate
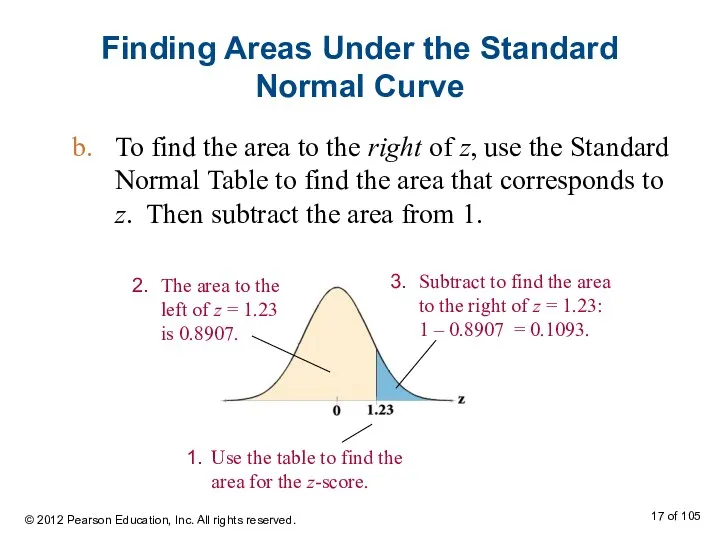
- 17. Finding Areas Under the Standard Normal Curve To find the area to the right of z,
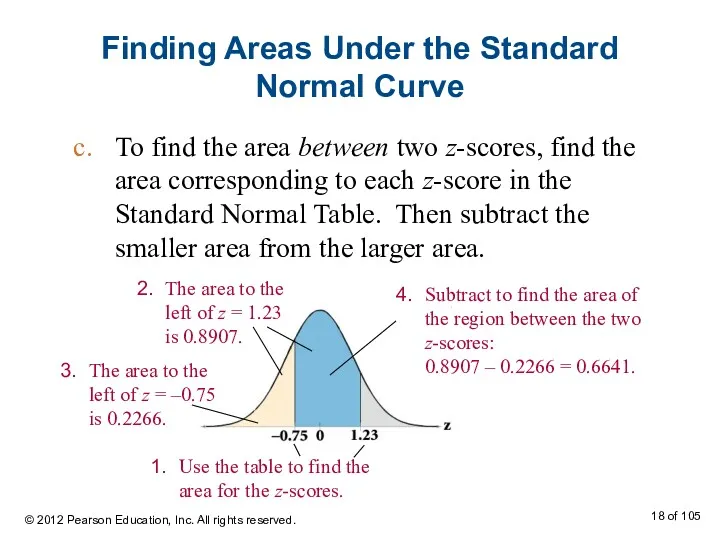
- 18. Finding Areas Under the Standard Normal Curve To find the area between two z-scores, find the
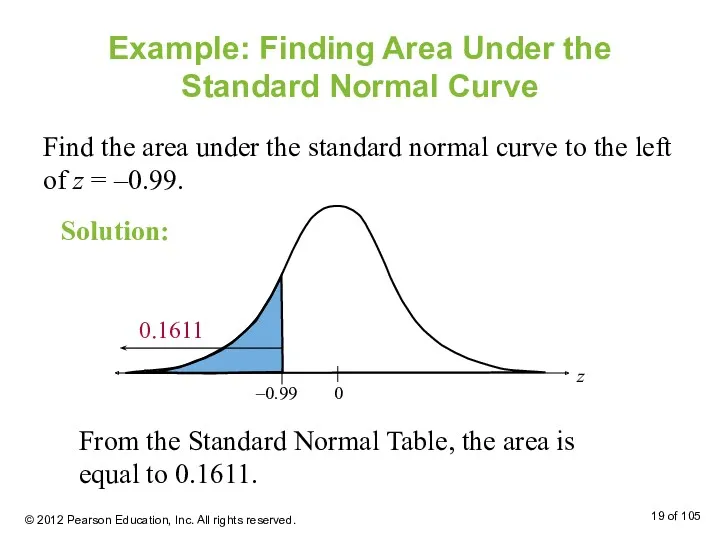
- 19. Example: Finding Area Under the Standard Normal Curve Find the area under the standard normal curve
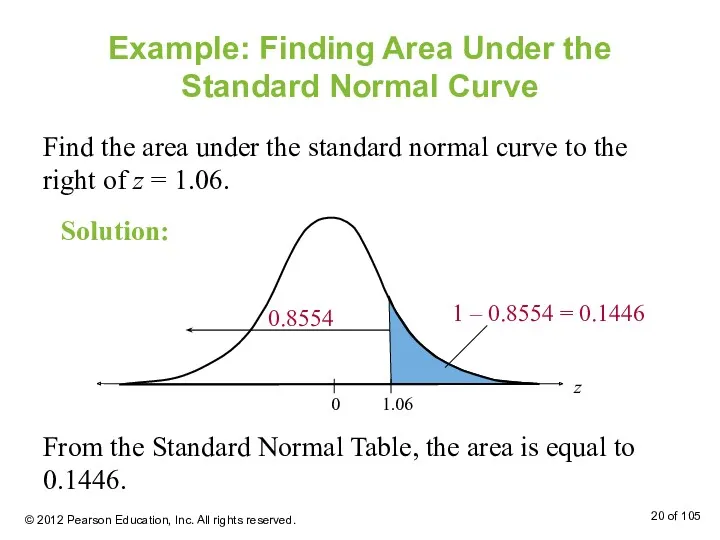
- 20. Example: Finding Area Under the Standard Normal Curve Find the area under the standard normal curve
- 22. Скачать презентацию

 Марковские цепи
Марковские цепи Умножение трёхзначного числа на однозначное
Умножение трёхзначного числа на однозначное Использование координат и векторов при решении прикладных задач
Использование координат и векторов при решении прикладных задач Золотое сечение
Золотое сечение Правильные и неправильные дроби. Понятия
Правильные и неправильные дроби. Понятия Производная в химии
Производная в химии Презентация Волшебный мир геометрических фигур
Презентация Волшебный мир геометрических фигур Статистические показатели
Статистические показатели Десятичная система счисления. Римские цифры
Десятичная система счисления. Римские цифры Тренажёр. Умножение и деление на 5
Тренажёр. Умножение и деление на 5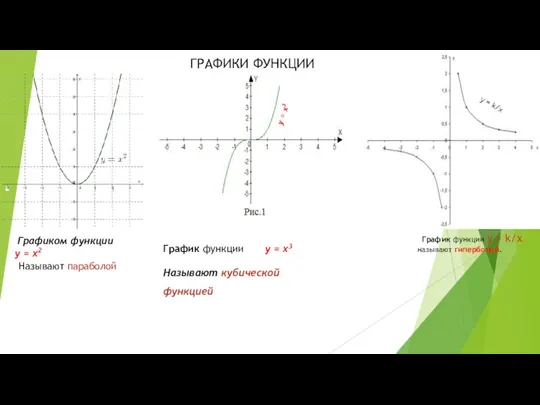 Графики функции. Кубическая парабола
Графики функции. Кубическая парабола Divide et impera. Metodei şi aplicaţii
Divide et impera. Metodei şi aplicaţii Дәрес планы
Дәрес планы Двугранный угол. Признак перпендикулярности двух плоскостей
Двугранный угол. Признак перпендикулярности двух плоскостей Презентация к уроку математики Прямой и обратный порядок Диск
Презентация к уроку математики Прямой и обратный порядок Диск Открытый урок математики во 2 классе. Тема Вычитание суммы из числа
Открытый урок математики во 2 классе. Тема Вычитание суммы из числа Геометрические тела
Геометрические тела Решение треугольников
Решение треугольников Определение угла. Развернутый угол. Сравнение углов наложением
Определение угла. Развернутый угол. Сравнение углов наложением Числовые выражения
Числовые выражения Знакомство с архитектоникой здания
Знакомство с архитектоникой здания Деление дробей. 8 класс
Деление дробей. 8 класс Сложная функция. Производная сложной функции
Сложная функция. Производная сложной функции Әй, осы математика
Әй, осы математика Применение методов статистического анализа для изучения общественного здоровья
Применение методов статистического анализа для изучения общественного здоровья Равномерно темперированный строй. Математиечская модель
Равномерно темперированный строй. Математиечская модель Независимые повторные испытания
Независимые повторные испытания Таблица вариантов и правило произведения
Таблица вариантов и правило произведения