Содержание
- 2. What is Statistics? The science of collecting, analyzing and making inference from the collected data. It
- 3. Statistic vs Statistics Statistic: It means a measured (or) counted fact (or) piece of information stated
- 4. Why Statistics? Statistics is used in many fields: Medical statistics Agricultural statistics Educational statistics Mathematical statistics
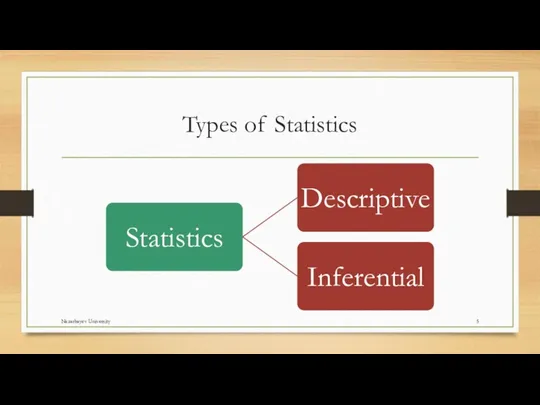
- 5. Types of Statistics Nazarbayev University
- 6. Descriptive vs Inferential Descriptive Statistics: Once the data have been collected, we can organize and summaries
- 7. Sample vs Population Information is gathered in the form of samples, or collections of observations. Samples
- 8. The Role of Probability Elements of probability allow us to quantify the strength or “confidence” in
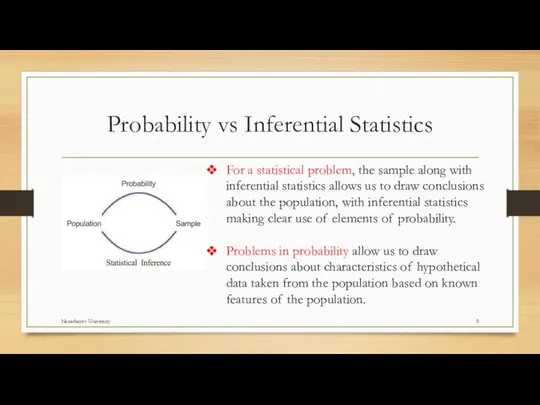
- 9. Probability vs Inferential Statistics For a statistical problem, the sample along with inferential statistics allows us
- 10. Sampling Procedures Simple Random Sampling Experimental Design Nazarbayev University
- 11. Simple Random Sampling Implies that any particular sample of a specified sample size has the same
- 12. Experimental Design A set of treatments or treatment combinations becomes the populations to be studied or
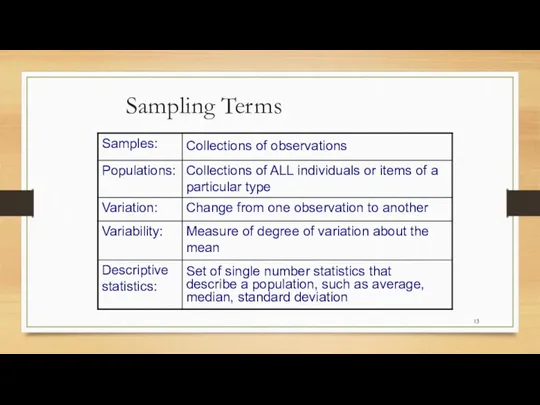
- 13. Sampling Terms Collections of observations Set of single number statistics that describe a population, such as
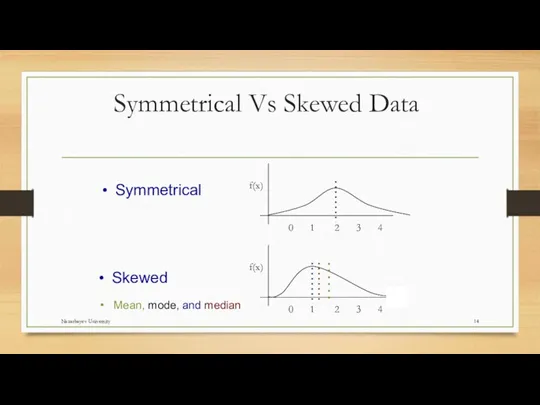
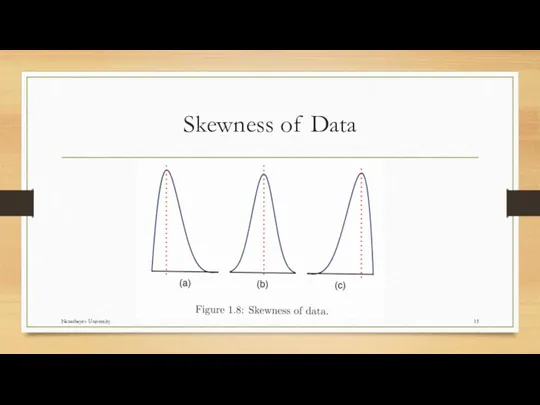
- 14. Symmetrical Vs Skewed Data Skewed Mean, mode, and median Symmetrical Nazarbayev University
- 15. Skewness of Data Nazarbayev University
- 16. Skewness? Nazarbayev University
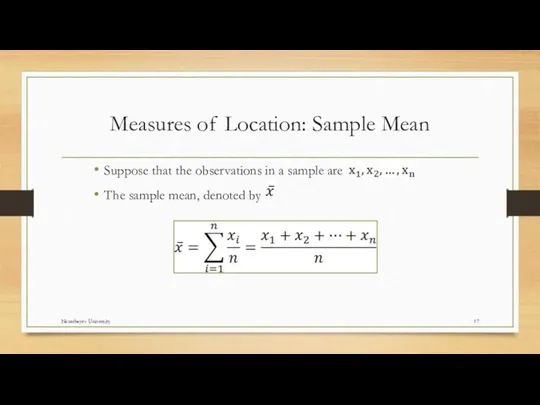
- 17. Measures of Location: Sample Mean Suppose that the observations in a sample are . The sample
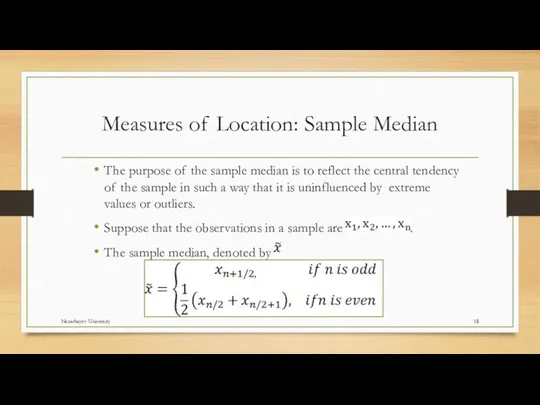
- 18. Measures of Location: Sample Median The purpose of the sample median is to reflect the central
- 19. Measures of Location: Trimmed Means A trimmed mean is computed by “trimming away” a certain percent
- 20. Sample Range Q: What is the sample range for the following data? Nazarbayev University
- 21. Sample Standard Deviation Suppose that the observations in a sample are . The sample variance, denoted
- 22. Nazarbayev University
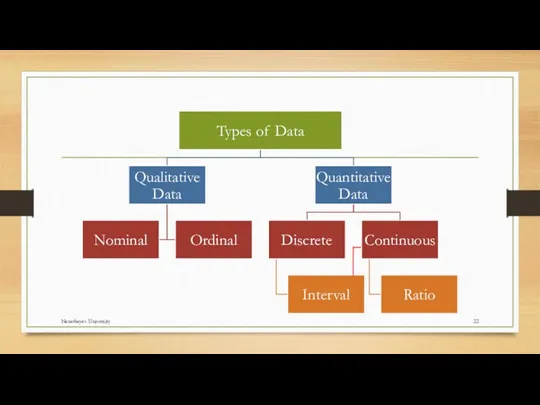
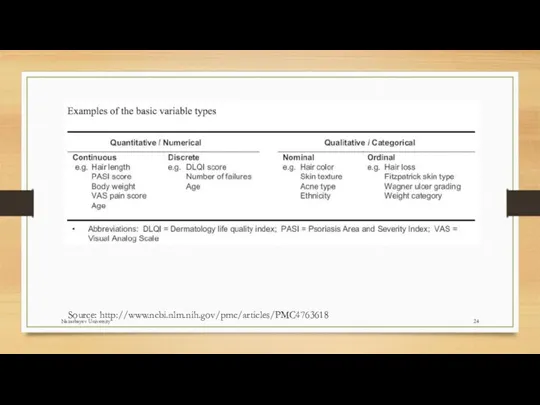
- 23. Level of Measurement Categorical (entities are divided into distinct categories): Binary variable: There are only two
- 24. Source: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4763618 Nazarbayev University
- 26. Скачать презентацию














 Векторы. Тест. (Вариант 2)
Векторы. Тест. (Вариант 2) Правописание числительных – орфография на уроках математики (Интегрированный урок: русский язык + математика)
Правописание числительных – орфография на уроках математики (Интегрированный урок: русский язык + математика) Умножение десятичных дробей. Свойства умножения
Умножение десятичных дробей. Свойства умножения Решение тригонометрических уравнений
Решение тригонометрических уравнений Чётные и нечётные функции
Чётные и нечётные функции Осевая и центральная симметрия. Симметричность точек относительно прямой
Осевая и центральная симметрия. Симметричность точек относительно прямой Урок – космическое путешествие по математике в 1 классе на тему: Решение примеров вида 15-
Урок – космическое путешествие по математике в 1 классе на тему: Решение примеров вида 15- Цифра и число 9
Цифра и число 9 Элементы математической статистики, комбинаторики и теории вероятностей. Формула бинома Ньютона
Элементы математической статистики, комбинаторики и теории вероятностей. Формула бинома Ньютона Треугольник. Тест. Задания в группах
Треугольник. Тест. Задания в группах Системы линейных неравенств с одним неизвестным. 9 класс
Системы линейных неравенств с одним неизвестным. 9 класс Урок по математике в 1 классе. Части величин. Школа 2000 (автор учебника Л.Г. Петерсон)
Урок по математике в 1 классе. Части величин. Школа 2000 (автор учебника Л.Г. Петерсон) Мир фракталов. Творческий проект
Мир фракталов. Творческий проект Перпендикулярные прямые
Перпендикулярные прямые открытый урок по математике на тему Площадь фигур 4 класс
открытый урок по математике на тему Площадь фигур 4 класс Число 10
Число 10 Метрологическое обеспечение производства
Метрологическое обеспечение производства презентация к уроку математики Цифра 1 и чичла 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
презентация к уроку математики Цифра 1 и чичла 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, Рациональные числа
Рациональные числа Второй и третий признаки равенства треугольников. 7 класс
Второй и третий признаки равенства треугольников. 7 класс Числовые ряды. Общие определения и свойства. Сходимость рядов. Признаки сходимости. (Семинар 25)
Числовые ряды. Общие определения и свойства. Сходимость рядов. Признаки сходимости. (Семинар 25) Открытый урок математики во 2 классе и отчет за аттестационный период
Открытый урок математики во 2 классе и отчет за аттестационный период Урок математики в 1 классе по теме Вычитание
Урок математики в 1 классе по теме Вычитание Сложение отрицательных чисел
Сложение отрицательных чисел Степени и корни
Степени и корни Площадь фигуры
Площадь фигуры Квадратные уравнения
Квадратные уравнения Презентация отчёта плана по самообразованию на тему: Занимательные математические игры в старшем дошкольном возрасте
Презентация отчёта плана по самообразованию на тему: Занимательные математические игры в старшем дошкольном возрасте