Содержание
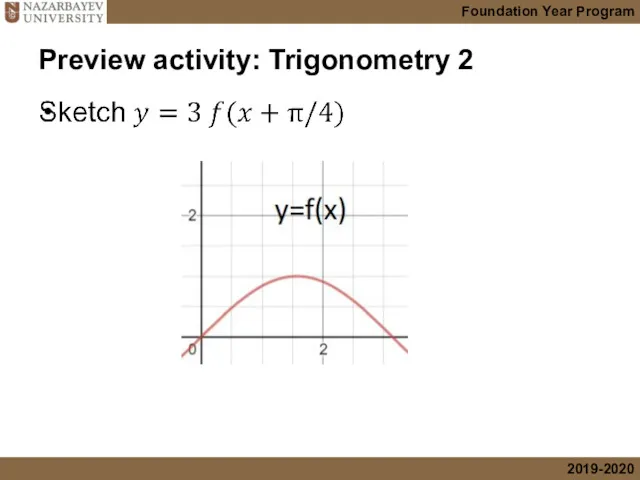
- 2. Preview activity: Trigonometry 2
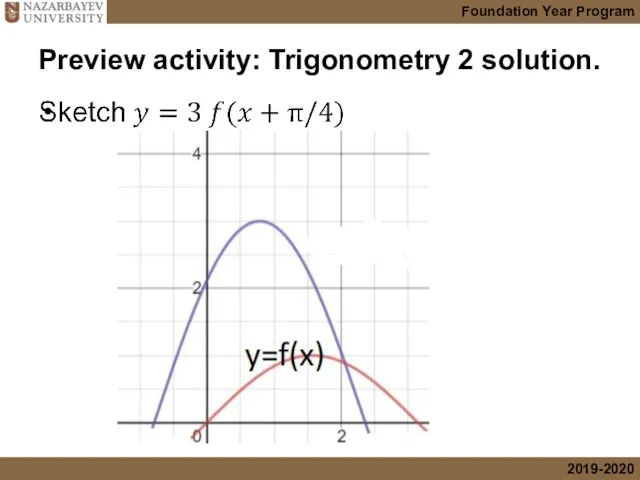
- 3. Preview activity: Trigonometry 2 solution.
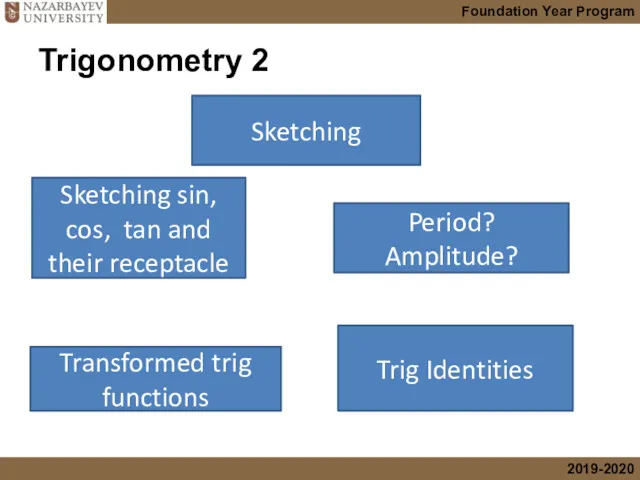
- 4. Trigonometry 2 Sketching sin, cos, tan and their receptacle Period? Amplitude? Trig Identities Transformed trig functions
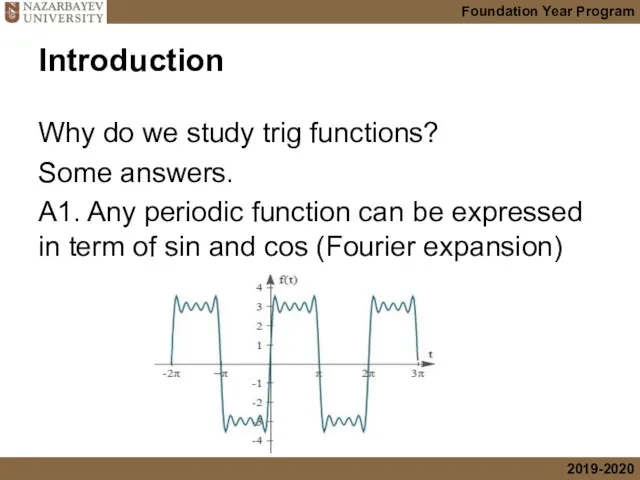
- 5. Introduction Why do we study trig functions? Some answers. A1. Any periodic function can be expressed
- 6. Introduction Why do we study trig functions? A2. Harmonic motions (Hooke’s law) can be written as
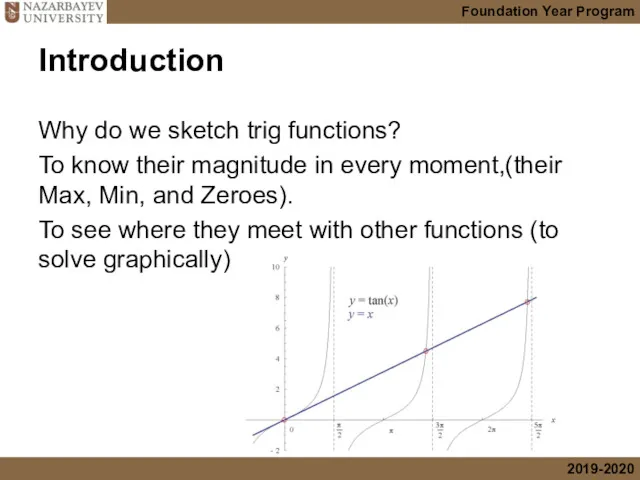
- 7. Introduction Why do we sketch trig functions? To know their magnitude in every moment,(their Max, Min,
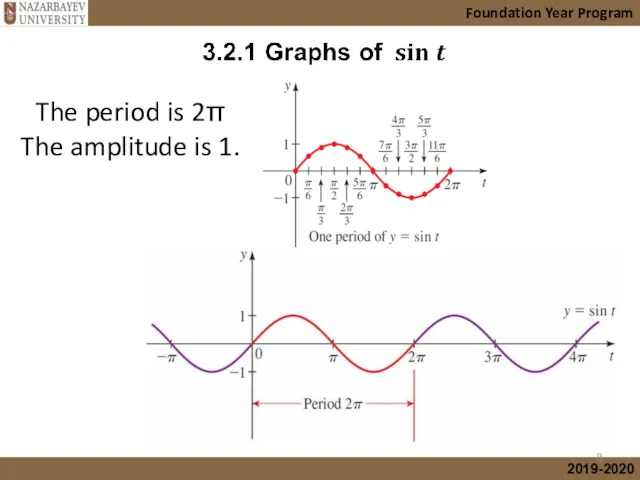
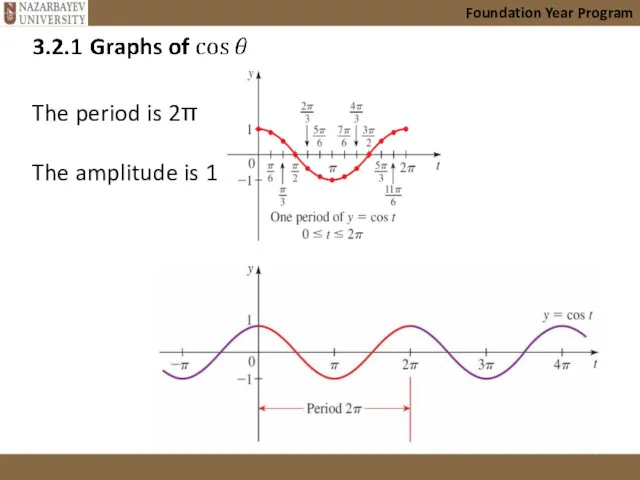
- 8. Foundation Year Program The period is 2π The amplitude is 1.
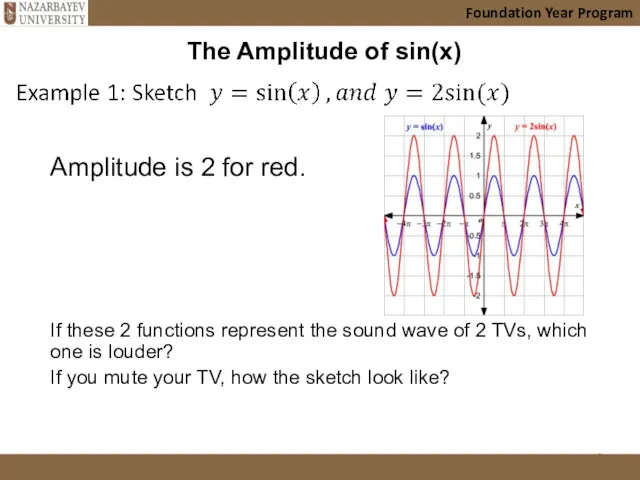
- 9. The Amplitude of sin(x) Amplitude is 2 for red. If these 2 functions represent the sound
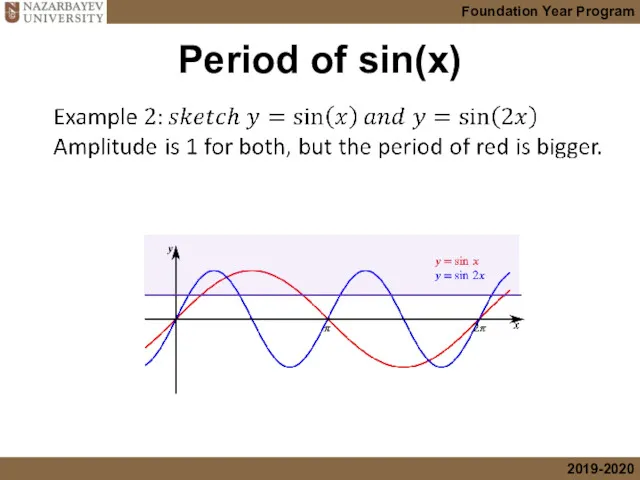
- 10. Period of sin(x)
- 11. Foundation Year Program The period is 2π The amplitude is 1
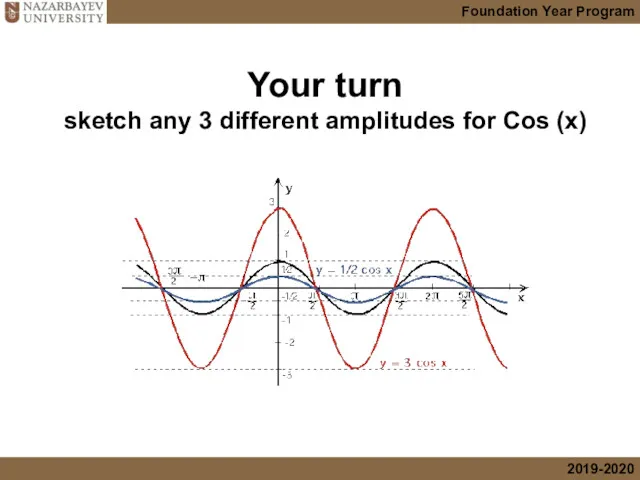
- 12. Your turn sketch any 3 different amplitudes for Cos (x)
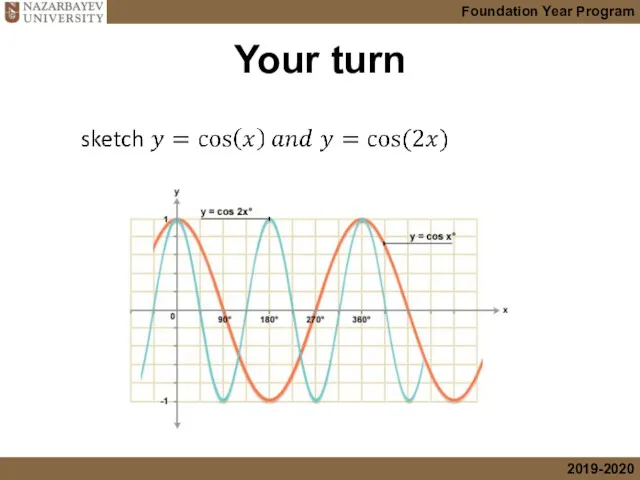
- 13. Your turn
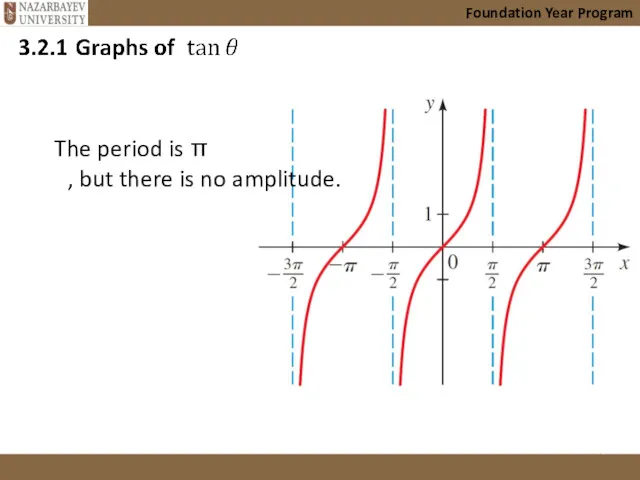
- 14. Foundation Year Program The period is π , but there is no amplitude.
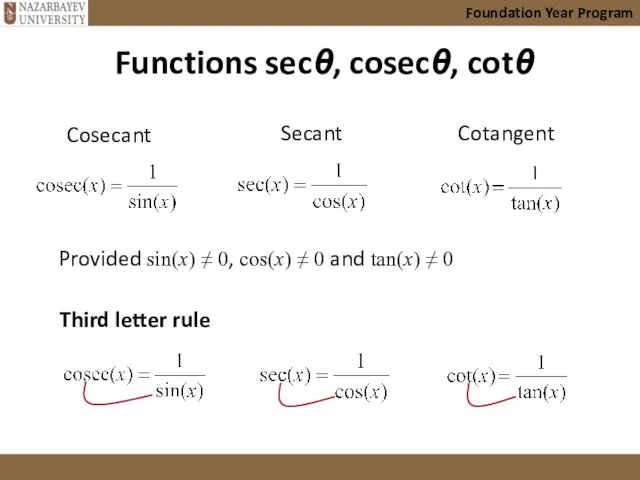
- 15. Functions secθ, cosecθ, cotθ Foundation Year Program Cosecant Secant Cotangent Provided sin(x) ≠ 0, cos(x) ≠
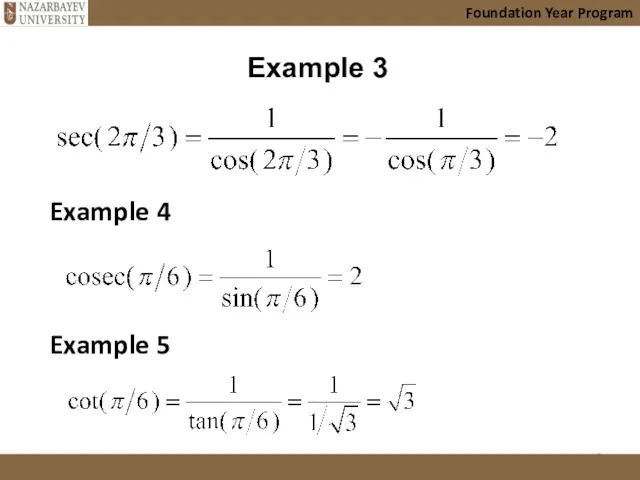
- 16. Foundation Year Program Example 3 Example 4 Example 5
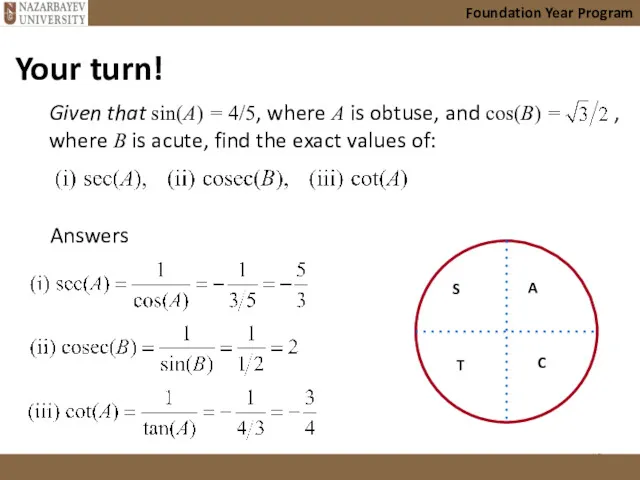
- 17. Foundation Year Program Given that sin(A) = 4/5, where A is obtuse, and cos(B) = ,
- 18. Foundation Year Program Answers Given that sin(A) = 4/5, where A is obtuse, and cos(B) =
- 19. 3.2.1 Graphs of secθ, cosecθ, cotθ Foundation Year Program The graphs of the reciprocal functions can
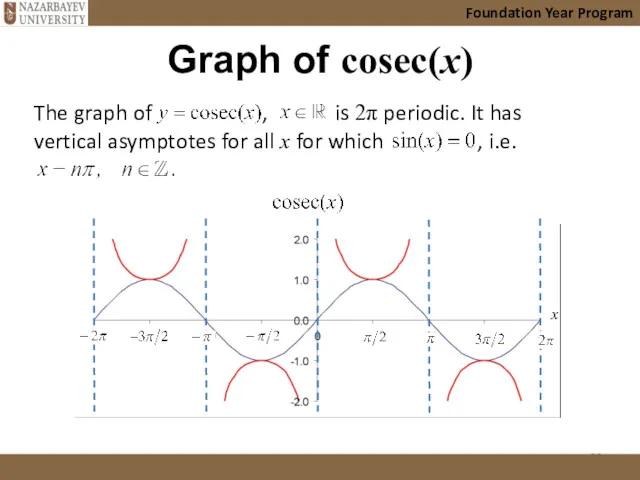
- 20. Graph of cosec(x) Foundation Year Program The graph of , is 2π periodic. It has vertical
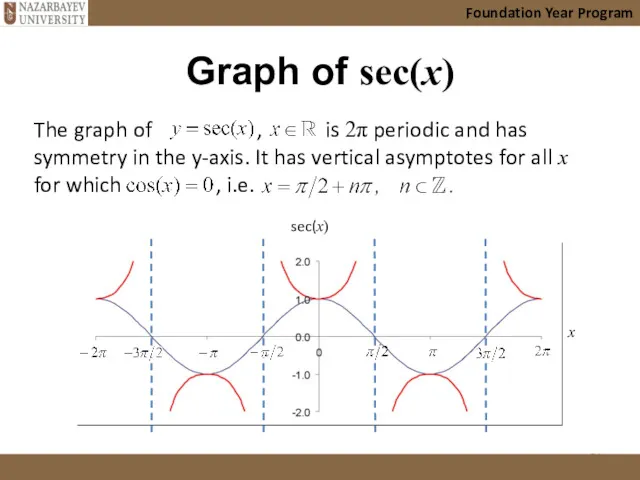
- 21. Graph of sec(x) Foundation Year Program The graph of , is 2π periodic and has symmetry
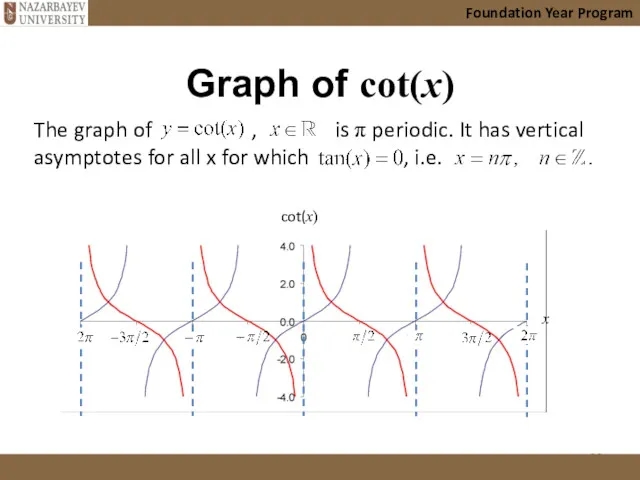
- 22. Graph of cot(x) Foundation Year Program The graph of , is π periodic. It has vertical
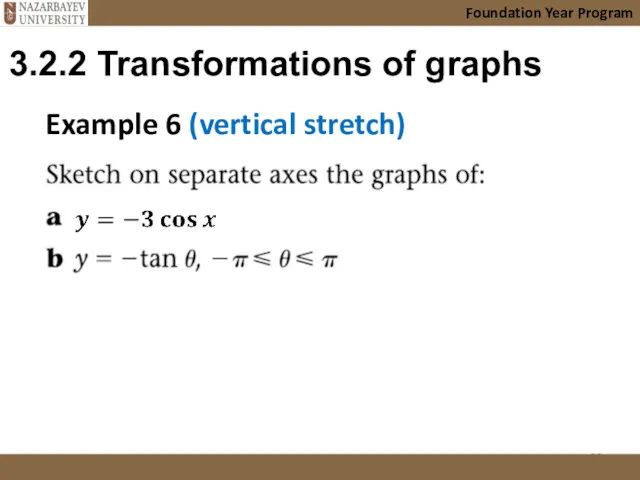
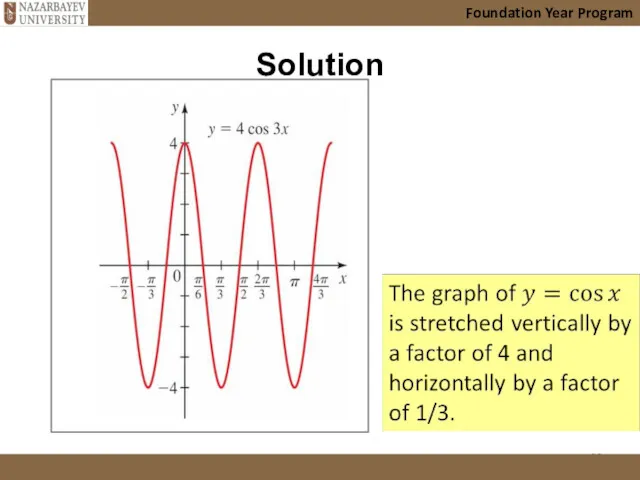
- 23. 3.2.2 Transformations of graphs Foundation Year Program Example 6 (vertical stretch)
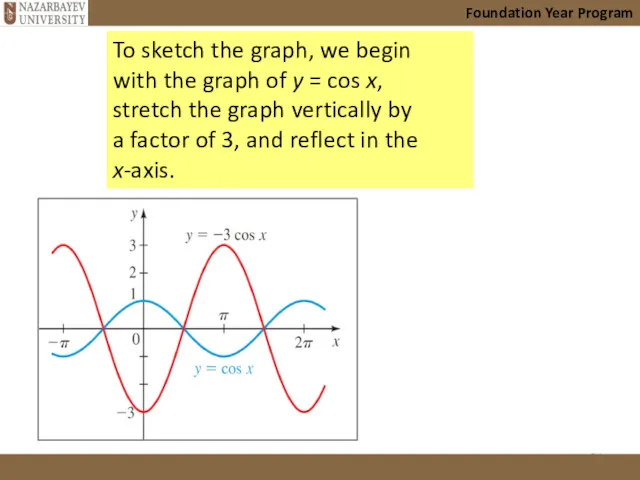
- 24. Foundation Year Program To sketch the graph, we begin with the graph of y = cos
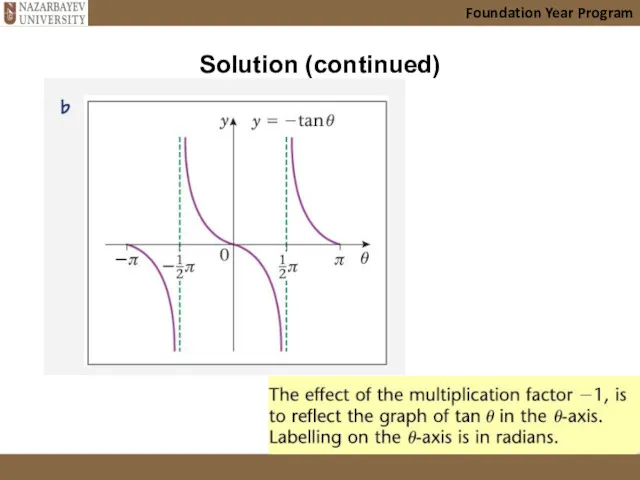
- 25. Solution (continued) Foundation Year Program
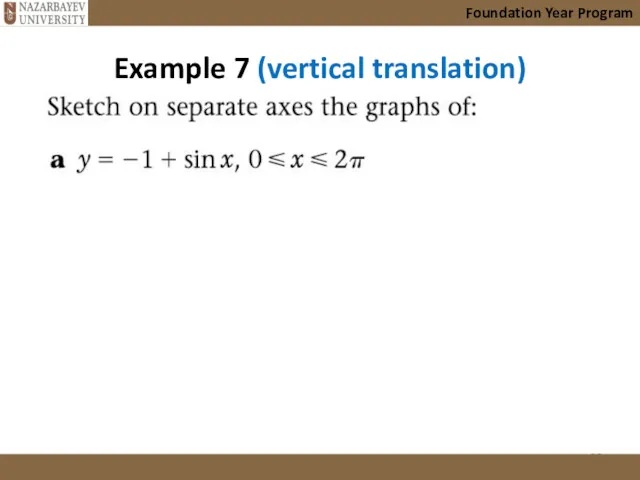
- 26. Example 7 (vertical translation) Foundation Year Program
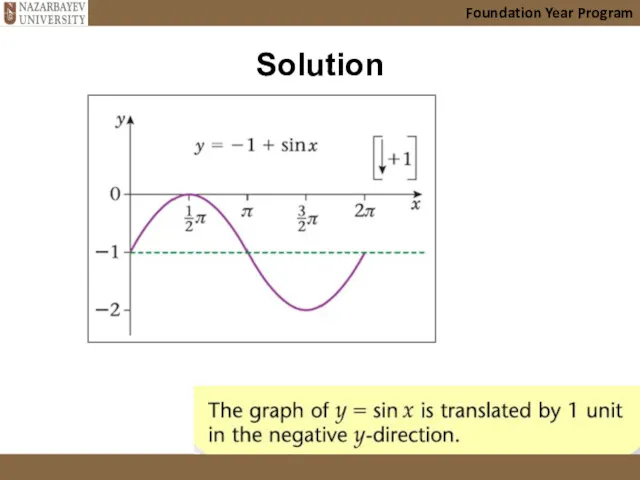
- 27. Solution Foundation Year Program
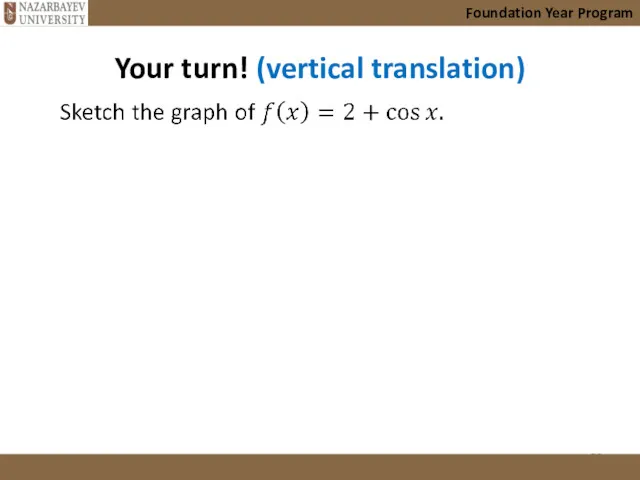
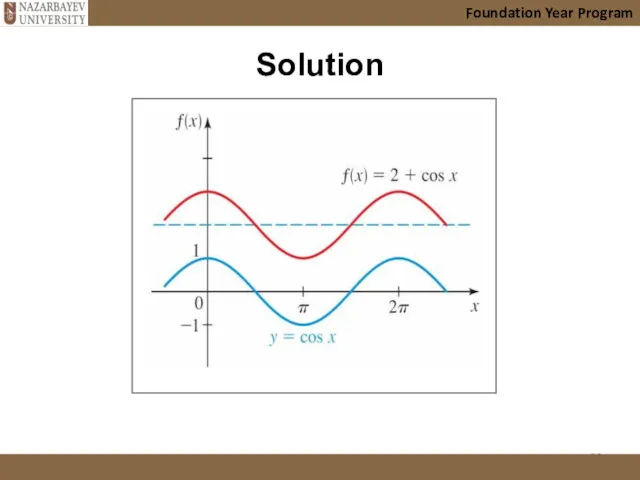
- 28. Your turn! (vertical translation) Foundation Year Program
- 29. Solution Foundation Year Program
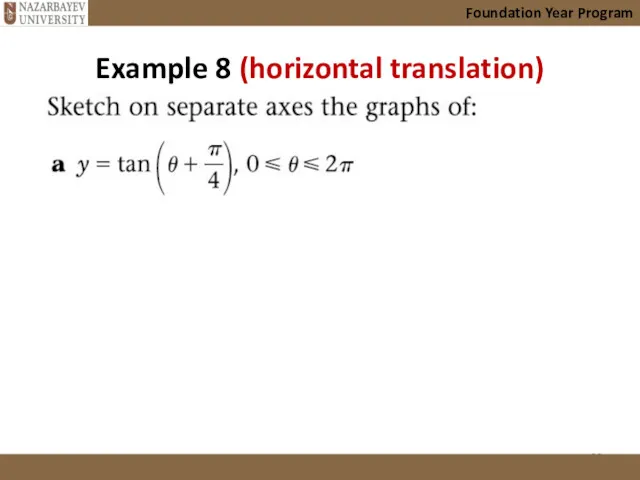
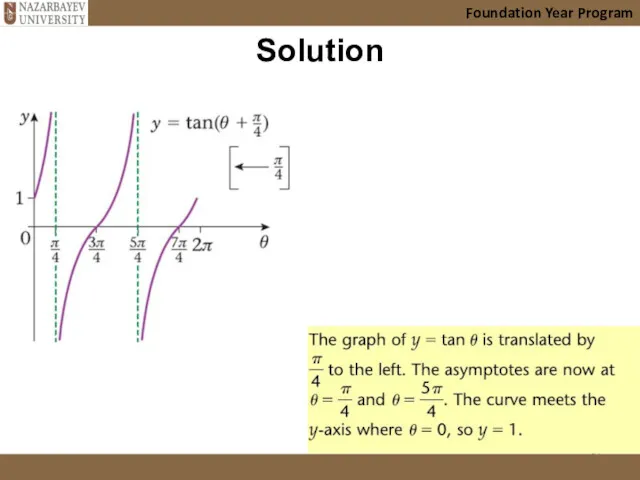
- 30. Example 8 (horizontal translation) Foundation Year Program
- 31. Solution Foundation Year Program
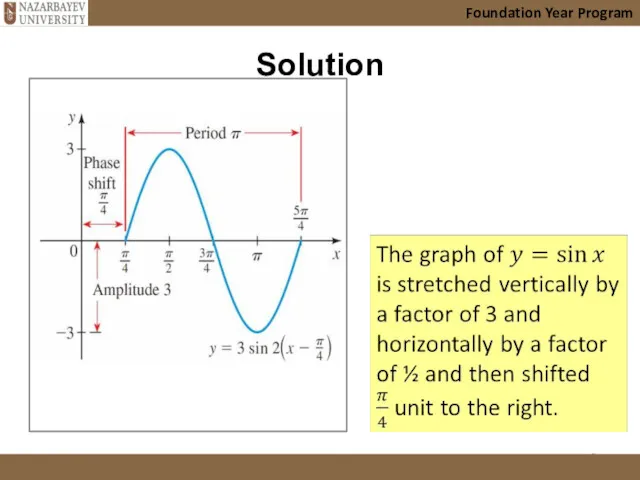
- 32. Example 9 (vertical and horizontal stretches) Foundation Year Program
- 33. Solution Foundation Year Program
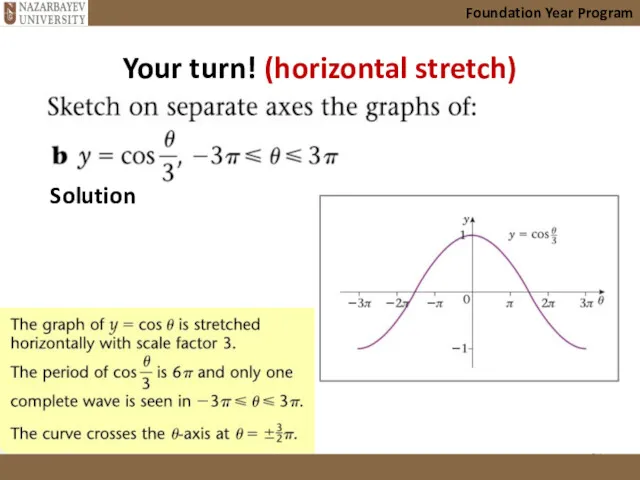
- 34. Your turn! (horizontal stretch) Foundation Year Program Solution
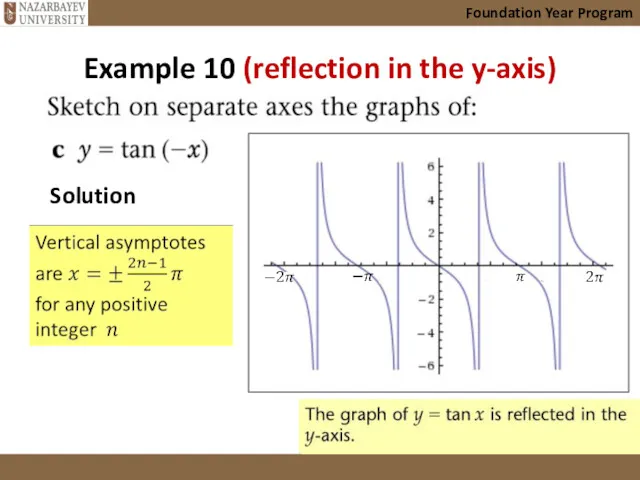
- 35. Example 10 (reflection in the y-axis) Foundation Year Program Solution
- 36. Your turn! Foundation Year Program
- 37. Solution Foundation Year Program
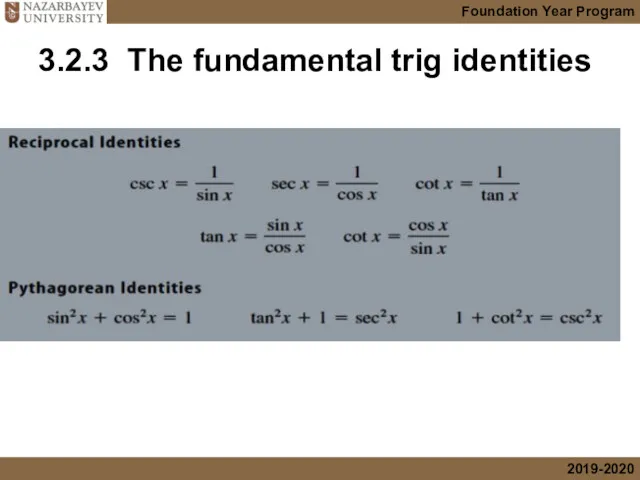
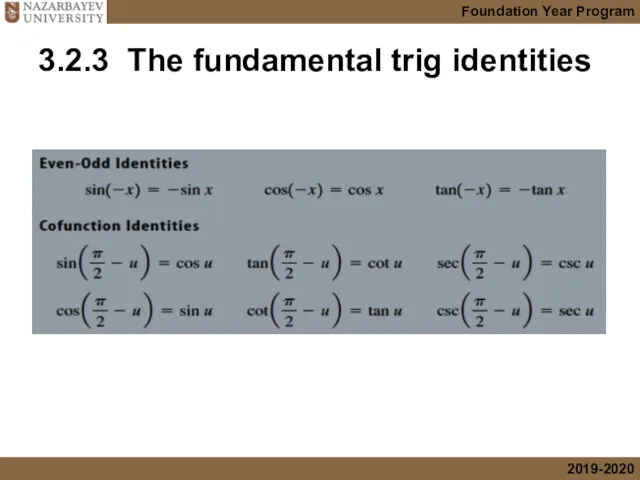
- 38. 3.2.3 The fundamental trig identities
- 39. 3.2.3 The fundamental trig identities
- 40. Simplifying trig expressions Example 11
- 41. Simplifying by combining fractions Example 12
- 42. Proving identities Example 13: Prove the following identity
- 43. Learning outcomes 3.2.1 Sketch the graphs of sin, cos, tan, and their reciprocals, and identifying their
- 45. Скачать презентацию








 устный счёт для 2 класса
устный счёт для 2 класса Задачі на знаходження невідомого доданка
Задачі на знаходження невідомого доданка Степень с натуральным, целым и рациональным показателем. Свойства степеней
Степень с натуральным, целым и рациональным показателем. Свойства степеней Свойства равнобедренного треугольника
Свойства равнобедренного треугольника Отрицательные числа
Отрицательные числа Способы решения уравнений. Графический способ
Способы решения уравнений. Графический способ Конспект урока по математике по теме: Таблица умножения. Закрепление
Конспект урока по математике по теме: Таблица умножения. Закрепление Математические бои
Математические бои Презентация к урокам математики УМК Школа России, 1 класс, 4 четверть
Презентация к урокам математики УМК Школа России, 1 класс, 4 четверть Авторская мультимедийная игра На что похоже для детей старшего дошкольного возраста.
Авторская мультимедийная игра На что похоже для детей старшего дошкольного возраста. Геометрическое моделирование 2D. Растровая модель
Геометрическое моделирование 2D. Растровая модель Презентация Состав 6 1 класс УМК Гармония
Презентация Состав 6 1 класс УМК Гармония Число и цифра 8
Число и цифра 8 Квадратные уравнения
Квадратные уравнения Математика. 1 класс. Урок 30. Числа 1-5 - Презентация
Математика. 1 класс. Урок 30. Числа 1-5 - Презентация Цифры и числа
Цифры и числа Решение дробных рациональных уравнений
Решение дробных рациональных уравнений Метрология. Измерение
Метрология. Измерение Построение сечений многогранников
Построение сечений многогранников Логарифмы вокруг нас
Логарифмы вокруг нас конкурс ЭМУ-Специалист 2011г.
конкурс ЭМУ-Специалист 2011г. Задачи на перебор вариантов. Ознакомление с решением задач путём составления таблиц.
Задачи на перебор вариантов. Ознакомление с решением задач путём составления таблиц. Среднее арифметическое
Среднее арифметическое Математика. 1 класс. Урок 32. Числа 1-5 - Презентация
Математика. 1 класс. Урок 32. Числа 1-5 - Презентация Пересекающиеся прямые. Вертикальные и смежные углы
Пересекающиеся прямые. Вертикальные и смежные углы Логическое мышление
Логическое мышление Solução Numérica de Equações Diferenciais
Solução Numérica de Equações Diferenciais Таблица умножения на пальцах
Таблица умножения на пальцах