Содержание
- 3. All these proteins are found out in plasma during replication of viruses!!! The gene C- encodes
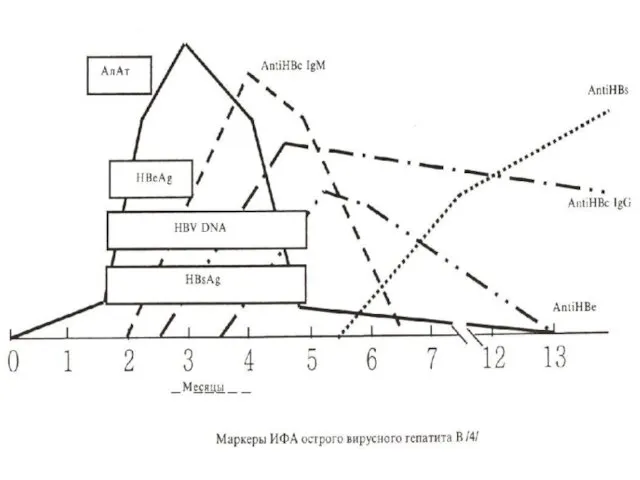
- 5. Against all antigenes the antibodies are worked out major markers of this hepatitis. Cytopathic of effect
- 6. EPIDEMIOLODY: 33 % of the population of a planet transfer VHB and 350 - 400 millions
- 7. Frequency of revealing of markers VHB: - Among medical workers - 33.3 % - Among the
- 8. 2. Artificial of modes of transmission: - all medical manipulations with damage skins and mucous -
- 11. PATHOGENY 1. Implantation of a virus after a sorption on surface of a hepatocyte through protein
- 12. 3. The assembling of viruses is completed by a secretion in a blood soluble nucleocapsid HBeAg,
- 13. 6. The immune system of the host destroys: - hepatocytes, containing VHcAg, - damages cells with
- 15. 9. Except for immune cytolisis hepatocytes damage: - antibody - dependence immune cytolisis of hepato- cytes,
- 16. FREQUENCY of SIGNS of INITIAL PERIOD - Lowering appetite 95,6 (in %) - Weakness 94,5 -
- 18. With appearance of an icterus - intoxication intensify: - a nausea, vomiting, anorexia - icteric colouring
- 19. FULMINANT the FORM Results to acute hepatic unsufficiency and lasts from 2 about 8 weeks, being
- 20. Appearance encephalopathy with an oppression of consciousness, degree expressivenesses which is estimated in marks on Glasgow
- 21. 3. Verbal is oriented Fast answers - 5 The answers the confused speech - 4 The
- 22. 3. Verbal is oriented Fast answers - 5 The answers the confused speech - 4 The
- 23. CLINICAL CRITERIA VHB: - average age of the patients or children till 1 year - positive
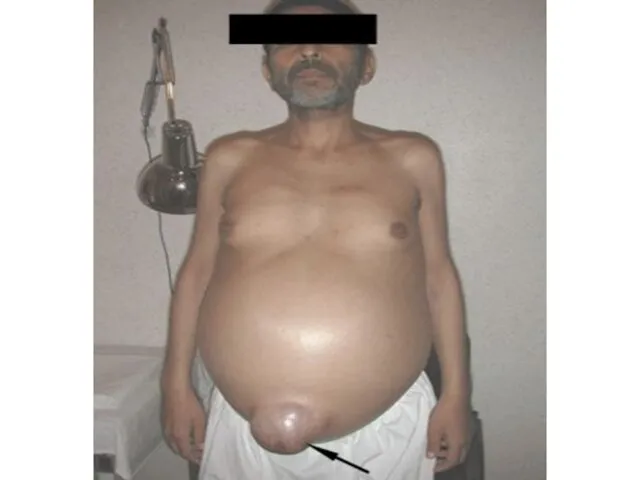
- 26. A 16-year-old Caucasian male born of a hepatitis B carrier mother was incidentlly discovered to have
- 27. A serologic profile to screen for hepatitis B virus infection HBsAg antiABs antiHBc antiHBc HBeAg antiHBe
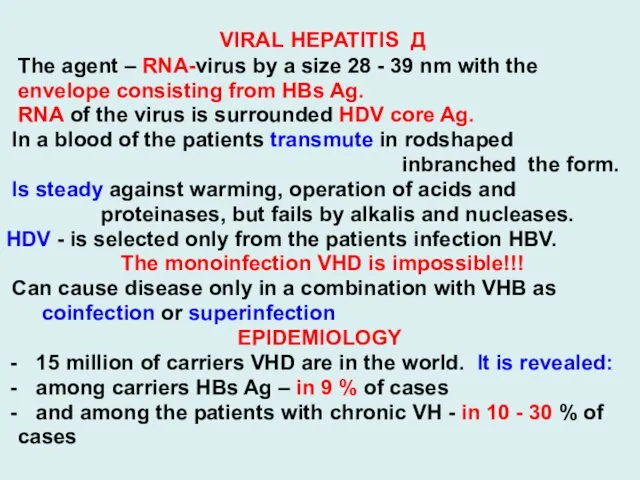
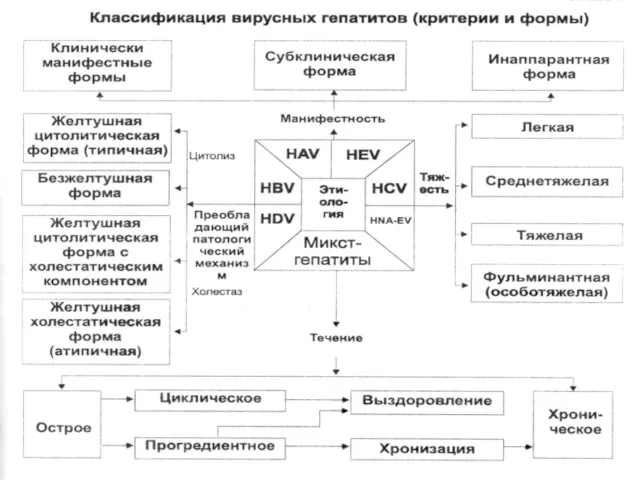
- 28. VIRAL HEPATITIS Д The agent – RNA-virus by a size 28 - 39 nm with the
- 31. CLINIC. Incubation interval 80 days (40 - 200 days) Coinfection - simultaneous infection HBV and HDV.
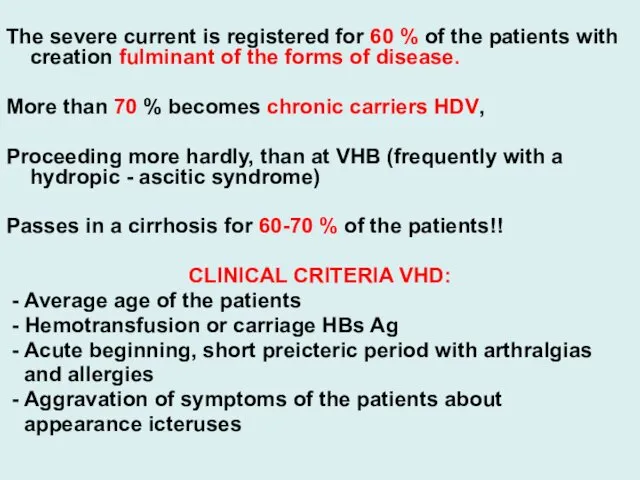
- 32. The severe current is registered for 60 % of the patients with creation fulminant of the
- 35. - pain in the right upper quadrant in initial period - hepatospleenomegalia - high and long-lived
- 40. On a surface are posed glycoproteins Е. 6 genotypes of a virus are known. Is sensitive
- 41. CLINICAL CRITERIA VHC: - average age of the patients - In an anamnesis hemotrasfusions or contact
- 43. A 69 - year-old female presents with fatigue, arthragias, peripheral paraesthesis, leg edema, and purpura. On
- 44. 1. A 48 – year-old male developed an attack of angina for which he underwent a
- 45. TREATMENT The mild forms - bed rest, diet N5, hepatoprotections, vitamin therapy, PO desintoxication, antioxidants Moderate
- 46. Hemosorption, enterosorbents , streptomycin 2- 4 gr PO, drugs of a levulose etc. At encephalopathy –
- 47. For unloading a small circle of a circulation - lasixum, euphyllinum, sulfocamphocainum, cardiac glycosides At an
- 49. 1. A 48 – year-old male developed an attack of angina for which he underwent a
- 50. 2
- 55. Скачать презентацию
Слайд 2
Слайд 3
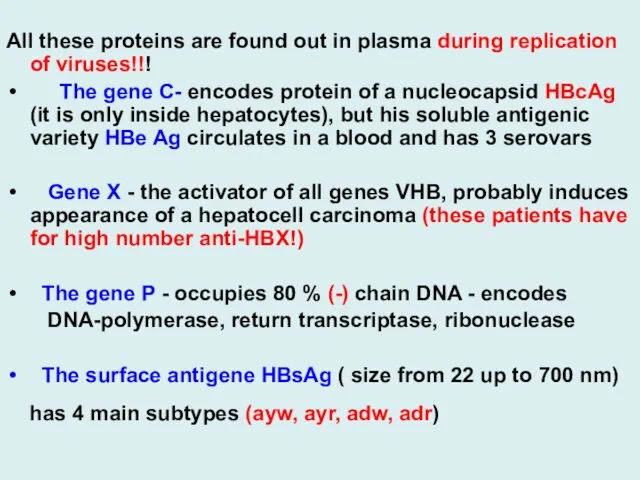
All these proteins are found out in plasma during replication of
viruses!!!
The gene C- encodes protein of a nucleocapsid HBcAg (it is only inside hepatocytes), but his soluble antigenic variety HBe Ag circulates in a blood and has 3 serovars
Gene Х - the activator of all genes VHB, probably induces appearance of a hepatocell carcinoma (these patients have for high number anti-HBX!)
The gene Р - occupies 80 % (-) chain DNA - encodes
DNA-polymerase, return transcriptase, ribonuclease
The surface antigene НBsAg ( size from 22 up to 700 nm)
has 4 main subtypes (ayw, ayr, adw, adr)
The gene C- encodes protein of a nucleocapsid HBcAg (it is only inside hepatocytes), but his soluble antigenic variety HBe Ag circulates in a blood and has 3 serovars
Gene Х - the activator of all genes VHB, probably induces appearance of a hepatocell carcinoma (these patients have for high number anti-HBX!)
The gene Р - occupies 80 % (-) chain DNA - encodes
DNA-polymerase, return transcriptase, ribonuclease
The surface antigene НBsAg ( size from 22 up to 700 nm)
has 4 main subtypes (ayw, ayr, adw, adr)
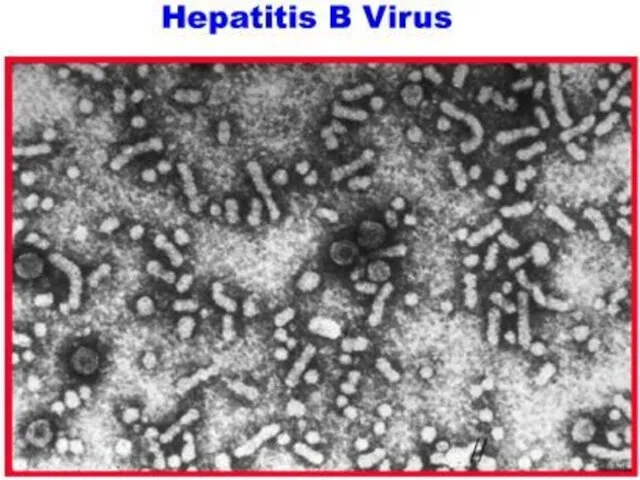
Слайд 4
Слайд 5
Against all antigenes the antibodies are worked out
major markers
major markers
of this hepatitis.
Cytopathic of effect virus - DOES NOT RENDER!!!
Is very steady in the environment, being inactivated:
- At room temperature - in 6 months
- At 60 dg. C- in 10 hours
- At 98 dg. C- in 20 minutes
- At 160 dg. C (dry fever) - in 1 hour
- In an autoclave (120 dg. С) - in 30 minutes
- In the dried up plasma - in 25 YEARS!!!
- In a refrigerator - in 6 months
- At рН 2.4 - in 2 hours
- In usual concentrations of disinfectant solutions - through 2 - 7 days!!!
Cytopathic of effect virus - DOES NOT RENDER!!!
Is very steady in the environment, being inactivated:
- At room temperature - in 6 months
- At 60 dg. C- in 10 hours
- At 98 dg. C- in 20 minutes
- At 160 dg. C (dry fever) - in 1 hour
- In an autoclave (120 dg. С) - in 30 minutes
- In the dried up plasma - in 25 YEARS!!!
- In a refrigerator - in 6 months
- At рН 2.4 - in 2 hours
- In usual concentrations of disinfectant solutions - through 2 - 7 days!!!
Слайд 6
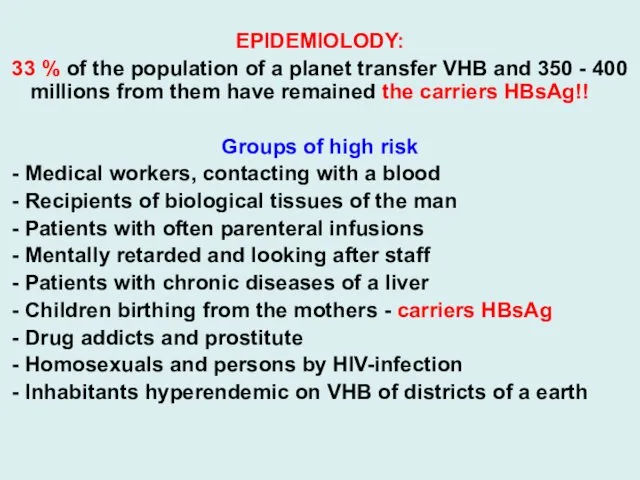
EPIDEMIOLODY:
33 % of the population of a planet transfer VHB
33 % of the population of a planet transfer VHB
and 350 - 400 millions from them have remained the carriers HBsAg!!
Groups of high risk
- Мedical workers, contacting with a blood
- Recipients of biological tissues of the man
- Patients with often parenteral infusions
- Mentally retarded and looking after staff
- Patients with chronic diseases of a liver
- Children birthing from the mothers - carriers HBsAg
- Drug addicts and prostitute
- Homosexuals and persons by HIV-infection
- Inhabitants hyperendemic on VHB of districts of a earth
Groups of high risk
- Мedical workers, contacting with a blood
- Recipients of biological tissues of the man
- Patients with often parenteral infusions
- Mentally retarded and looking after staff
- Patients with chronic diseases of a liver
- Children birthing from the mothers - carriers HBsAg
- Drug addicts and prostitute
- Homosexuals and persons by HIV-infection
- Inhabitants hyperendemic on VHB of districts of a earth
Слайд 7
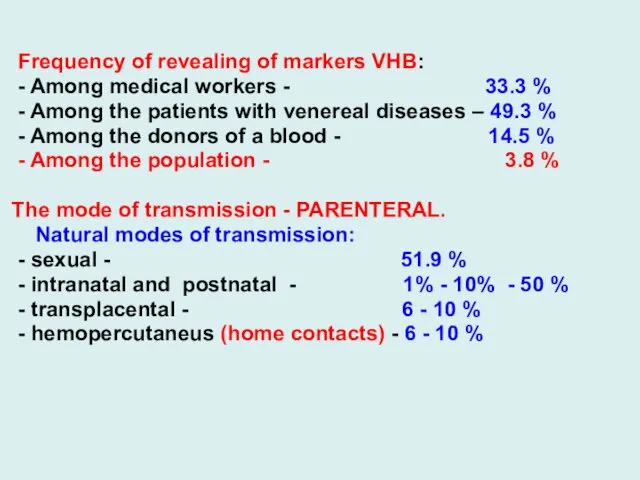
Frequency of revealing of markers VHB:
- Among medical workers
Frequency of revealing of markers VHB:
- Among medical workers
- 33.3 %
- Among the patients with venereal diseases – 49.3 %
- Among the donors of a blood - 14.5 %
- Among the population - 3.8 %
The mode of transmission - PARENTERAL.
Natural modes of transmission:
- sexual - 51.9 %
- intranatal and postnatal - 1% - 10% - 50 %
- transplacental - 6 - 10 %
- hemopercutaneus (home contacts) - 6 - 10 %
- Among the patients with venereal diseases – 49.3 %
- Among the donors of a blood - 14.5 %
- Among the population - 3.8 %
The mode of transmission - PARENTERAL.
Natural modes of transmission:
- sexual - 51.9 %
- intranatal and postnatal - 1% - 10% - 50 %
- transplacental - 6 - 10 %
- hemopercutaneus (home contacts) - 6 - 10 %
Слайд 8
2. Artificial of modes of transmission:
- all medical manipulations with
- all medical manipulations with
damage skins and
mucous
- IV drug addicts , tattoo, cosmetic procedures
Infection a dose of a blood - 0,00004 - 0,000001 ml.
Frequency infection newborn – 0.02 - 40 %
The hazard of a chronic carriage HBsAg after infection:
- at infection newborn - 90 %,
- 1-st year of life - 50 %,
- is higher than 1-st year 20 %
- and for adult - 5 - 10 %
The one injection of a blood with HBsAg - causes diseases
in 90 % of cases.
Hazard after a one prick of infection needle - 34 %
In 50 % of cases the source of an infection is not revealed!
mucous
- IV drug addicts , tattoo, cosmetic procedures
Infection a dose of a blood - 0,00004 - 0,000001 ml.
Frequency infection newborn – 0.02 - 40 %
The hazard of a chronic carriage HBsAg after infection:
- at infection newborn - 90 %,
- 1-st year of life - 50 %,
- is higher than 1-st year 20 %
- and for adult - 5 - 10 %
The one injection of a blood with HBsAg - causes diseases
in 90 % of cases.
Hazard after a one prick of infection needle - 34 %
In 50 % of cases the source of an infection is not revealed!
Слайд 9
Слайд 10
Слайд 11
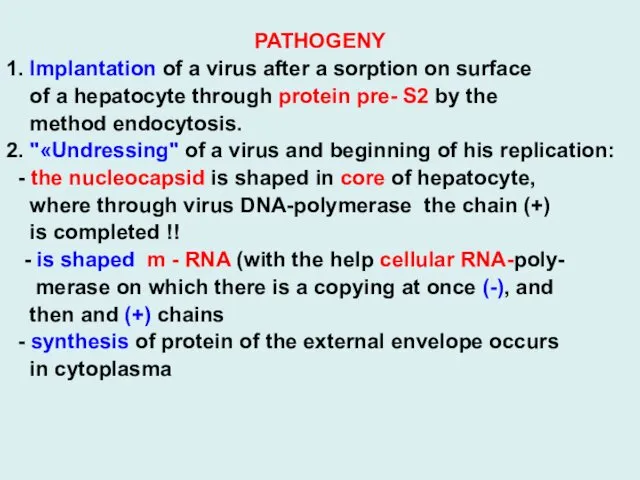
PATHOGENY
1. Implantation of a virus after a sorption on surface
of
1. Implantation of a virus after a sorption on surface
of
a hepatocyte through protein pre- S2 by the
method endocytosis.
2. "«Undressing" of a virus and beginning of his replication:
- the nucleocapsid is shaped in core of hepatocyte,
where through virus DNA-polymerase the chain (+)
is completed !!
- is shaped m - RNA (with the help cellular RNA-poly-
merase on which there is a copying at once (-), and
then and (+) chains
- synthesis of protein of the external envelope occurs
in cytoplasma
method endocytosis.
2. "«Undressing" of a virus and beginning of his replication:
- the nucleocapsid is shaped in core of hepatocyte,
where through virus DNA-polymerase the chain (+)
is completed !!
- is shaped m - RNA (with the help cellular RNA-poly-
merase on which there is a copying at once (-), and
then and (+) chains
- synthesis of protein of the external envelope occurs
in cytoplasma
Слайд 12
3. The assembling of viruses is completed by a secretion
in a blood soluble nucleocapsid HBeAg, which
decrease both cellular (lowering of production Inter-
ferons) and humoral (suppression formation antibody
and induction immunotolerance), which impedes his
going out from hepatocytes
4. Except for liver replication of a virus is possible in cells
of an marrow brain, spleen, monocytes and of lymphatic
tissue.
5. The immune answer at VHB corresponds immuno-
pathological response - clinical form arise at parti-
cular activity Т-cellular immunity. When this immunity
depressed completely - the disease does not develop!!!
decrease both cellular (lowering of production Inter-
ferons) and humoral (suppression formation antibody
and induction immunotolerance), which impedes his
going out from hepatocytes
4. Except for liver replication of a virus is possible in cells
of an marrow brain, spleen, monocytes and of lymphatic
tissue.
5. The immune answer at VHB corresponds immuno-
pathological response - clinical form arise at parti-
cular activity Т-cellular immunity. When this immunity
depressed completely - the disease does not develop!!!
Слайд 13
6. The immune system of the host destroys:
- hepatocytes, containing
- hepatocytes, containing
VHcAg,
- damages cells with protein pre-S2
- but is neutral to cells with HBsAg!!!
7. Humoral immunity formation of an antibody In the
following sequence:
- anti - HBc Ag Ig M, then IgG
- anti -pol and anti -pre S1
- anti -HBe Ag and anti -pre S2
- anti -HBs Ag (occur last)
- anti -HBxAg (are not reveald for all patients)
8. Can occur circulating immune complexes especial at
shape of the chronic forms hepatitis!!!
- damages cells with protein pre-S2
- but is neutral to cells with HBsAg!!!
7. Humoral immunity formation of an antibody In the
following sequence:
- anti - HBc Ag Ig M, then IgG
- anti -pol and anti -pre S1
- anti -HBe Ag and anti -pre S2
- anti -HBs Ag (occur last)
- anti -HBxAg (are not reveald for all patients)
8. Can occur circulating immune complexes especial at
shape of the chronic forms hepatitis!!!
Слайд 14
Слайд 15
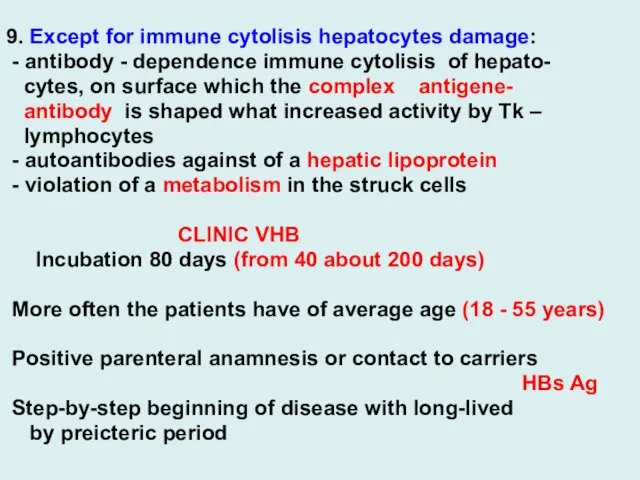
9. Except for immune cytolisis hepatocytes damage:
- antibody - dependence
- antibody - dependence
immune cytolisis of hepato-
cytes, on surface which the complex antigene-
antibody is shaped what increased activity by Tk –
lymphocytes
- autoantibodies against of a hepatic lipoprotein
- violation of a metabolism in the struck cells
CLINIC VHB
Incubation 80 days (from 40 about 200 days)
More often the patients have of average age (18 - 55 years)
Positive parenteral anamnesis or contact to carriers
HBs Ag
Step-by-step beginning of disease with long-lived
by preicteric period
cytes, on surface which the complex antigene-
antibody is shaped what increased activity by Tk –
lymphocytes
- autoantibodies against of a hepatic lipoprotein
- violation of a metabolism in the struck cells
CLINIC VHB
Incubation 80 days (from 40 about 200 days)
More often the patients have of average age (18 - 55 years)
Positive parenteral anamnesis or contact to carriers
HBs Ag
Step-by-step beginning of disease with long-lived
by preicteric period
Слайд 16
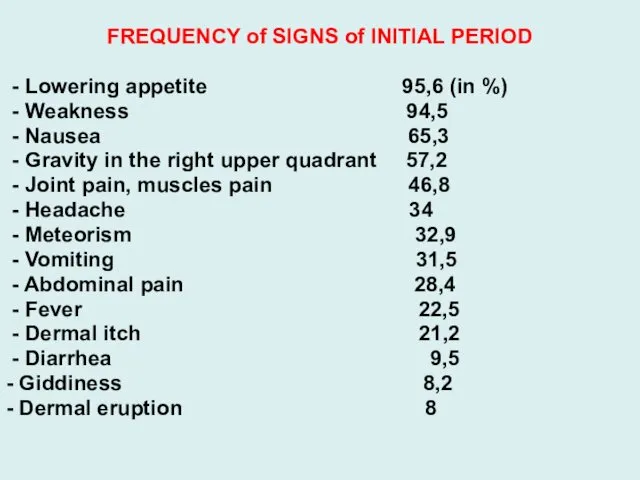
FREQUENCY of SIGNS of INITIAL PERIOD
- Lowering appetite 95,6 (in
- Lowering appetite 95,6 (in
%)
- Weakness 94,5
- Nausea 65,3
- Gravity in the right upper quadrant 57,2
- Joint pain, muscles pain 46,8
- Headache 34
- Meteorism 32,9
- Vomiting 31,5
- Abdominal pain 28,4
- Fever 22,5
- Dermal itch 21,2
- Diarrhea 9,5
- Giddiness 8,2
- Dermal eruption 8
- Weakness 94,5
- Nausea 65,3
- Gravity in the right upper quadrant 57,2
- Joint pain, muscles pain 46,8
- Headache 34
- Meteorism 32,9
- Vomiting 31,5
- Abdominal pain 28,4
- Fever 22,5
- Dermal itch 21,2
- Diarrhea 9,5
- Giddiness 8,2
- Dermal eruption 8
Слайд 17
Слайд 18
With appearance of an icterus - intoxication intensify:
- a nausea,
- a nausea,
vomiting, anorexia
- icteric colouring of a skin and scleras, dark urine,
decolorized feces,
- increase of a liver and lien for all patients.
VHB more often proceeds in the moderate form, but can
be both mild, and severe forms of disease .
Fulminant the form up to 2 %
Duration of icteric period from 1 about 12 weeks.
Cholestatic of the form of illness from 5 up to 15 %
Lingering current from 5 up to 10 %
The period of a reconvalescence can be delayed on
some months
- icteric colouring of a skin and scleras, dark urine,
decolorized feces,
- increase of a liver and lien for all patients.
VHB more often proceeds in the moderate form, but can
be both mild, and severe forms of disease .
Fulminant the form up to 2 %
Duration of icteric period from 1 about 12 weeks.
Cholestatic of the form of illness from 5 up to 15 %
Lingering current from 5 up to 10 %
The period of a reconvalescence can be delayed on
some months
Слайд 19
FULMINANT the FORM
Results to acute hepatic unsufficiency
FULMINANT the FORM
Results to acute hepatic unsufficiency
and lasts from 2 about 8 weeks, being ended in 80 - 90 % of cases by death of the patients. For it are characteristic:
- obstinate nausea and vomiting, anorexia
- progressing hemorrhagic syndrome
- fast decrease of sizes and density of a liver
- a "hepatic" smell of a skin and exhaled air
- a neutrophilic leukocytosis
- accelerated ESR
- decrease АLТ and АSТ, prothrombin Index
- Increase of a fraction of an indirect bilirubin
- increase of prothrombin time more 12 cek.
- obstinate nausea and vomiting, anorexia
- progressing hemorrhagic syndrome
- fast decrease of sizes and density of a liver
- a "hepatic" smell of a skin and exhaled air
- a neutrophilic leukocytosis
- accelerated ESR
- decrease АLТ and АSТ, prothrombin Index
- Increase of a fraction of an indirect bilirubin
- increase of prothrombin time more 12 cek.
Слайд 20
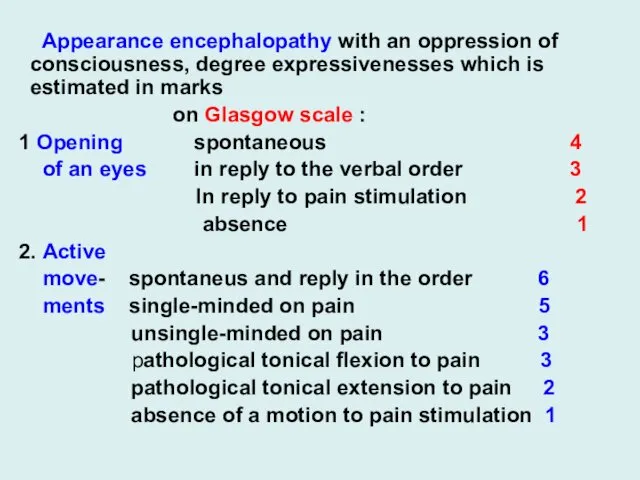
Appearance encephalopathy with an oppression of consciousness, degree expressivenesses which is
estimated in marks
on Glasgow scale :
1 Opening spontaneous 4
of an eyes in reply to the verbal order 3
In reply to pain stimulation 2
absence 1
2. Active
move- spontaneus and reply in the order 6
ments single-minded on pain 5
unsingle-minded on pain 3
pathological tonical flexion to pain 3
pathological tonical extension to pain 2
absence of a motion to pain stimulation 1
on Glasgow scale :
1 Opening spontaneous 4
of an eyes in reply to the verbal order 3
In reply to pain stimulation 2
absence 1
2. Active
move- spontaneus and reply in the order 6
ments single-minded on pain 5
unsingle-minded on pain 3
pathological tonical flexion to pain 3
pathological tonical extension to pain 2
absence of a motion to pain stimulation 1
Слайд 21
3. Verbal is oriented
Fast answers - 5
The answers
3. Verbal is oriented
Fast answers - 5
The answers
the confused speech - 4
The inadequate answers - 3
Inarticulate sound - 2
Absence of speech - 1
15 marks - norm,
13 - 14 marks - somnolencea
9 - 12 marks - sopor,
4-8 marks - coma,
4 marks and less - out-of-limit coma.
The inadequate answers - 3
Inarticulate sound - 2
Absence of speech - 1
15 marks - norm,
13 - 14 marks - somnolencea
9 - 12 marks - sopor,
4-8 marks - coma,
4 marks and less - out-of-limit coma.
Слайд 22
3. Verbal is oriented
Fast answers - 5
The
3. Verbal is oriented
Fast answers - 5
The
answers the confused speech - 4
The inadequate answers - 3
Inarticulate sound - 2
Absence of speech - 1
15 - marks - norm,
13 - 14 marks - somnolencea
9-12 marks - sopor,
4-8 marks - coma,
4 marks and less - out-of-limit coma.
The inadequate answers - 3
Inarticulate sound - 2
Absence of speech - 1
15 - marks - norm,
13 - 14 marks - somnolencea
9-12 marks - sopor,
4-8 marks - coma,
4 marks and less - out-of-limit coma.
Слайд 23
CLINICAL CRITERIA VHB:
- average age of the patients or children
- average age of the patients or children
till 1 year
- positive parenteral anamnesis,
- contact to the carrier HBs Ag or group of hazard
- step-by-step beginning of disease
- long-lived initial period with arthralgias and by allergies
- aggravation of symptoms after appearance of an icterus
- long-lived current with transition in chronic the forms
in 5 - 10 % of cases
- fulminant current up to 2 % of cases
- revealing in a blood of markers VHB (ELISA)
- revealing in a blood of DNA VHB (PCR)
- positive parenteral anamnesis,
- contact to the carrier HBs Ag or group of hazard
- step-by-step beginning of disease
- long-lived initial period with arthralgias and by allergies
- aggravation of symptoms after appearance of an icterus
- long-lived current with transition in chronic the forms
in 5 - 10 % of cases
- fulminant current up to 2 % of cases
- revealing in a blood of markers VHB (ELISA)
- revealing in a blood of DNA VHB (PCR)
Слайд 24
Слайд 25
Слайд 26
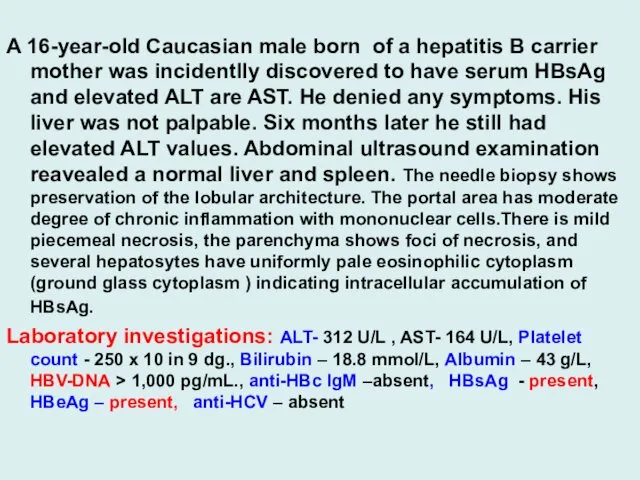
A 16-year-old Caucasian male born of a hepatitis B carrier mother
was incidentlly discovered to have serum HBsAg and elevated ALT are AST. He denied any symptoms. His liver was not palpable. Six months later he still had elevated ALT values. Abdominal ultrasound examination reavealed a normal liver and spleen. The needle biopsy shows preservation of the lobular architecture. The portal area has moderate degree of chronic inflammation with mononuclear cells.There is mild piecemeal necrosis, the parenchyma shows foci of necrosis, and several hepatosytes have uniformly pale eosinophilic cytoplasm (ground glass cytoplasm ) indicating intracellular accumulation of HBsAg.
Laboratory investigations: ALT- 312 U/L , AST- 164 U/L, Platelet count - 250 x 10 in 9 dg., Bilirubin – 18.8 mmol/L, Albumin – 43 g/L, HBV-DNA > 1,000 pg/mL., anti-HBc IgM –absent, HBsAg - present, HBeAg – present, anti-HCV – absent
Laboratory investigations: ALT- 312 U/L , AST- 164 U/L, Platelet count - 250 x 10 in 9 dg., Bilirubin – 18.8 mmol/L, Albumin – 43 g/L, HBV-DNA > 1,000 pg/mL., anti-HBc IgM –absent, HBsAg - present, HBeAg – present, anti-HCV – absent
Слайд 27
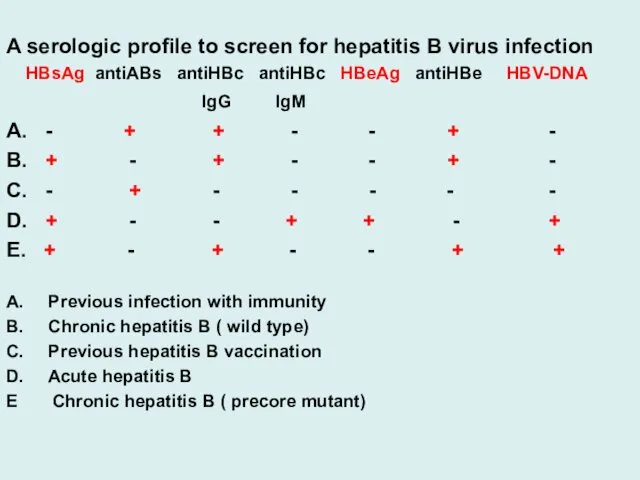
A serologic profile to screen for hepatitis B virus infection
A serologic profile to screen for hepatitis B virus infection
HBsAg antiABs antiHBc antiHBc HBeAg antiHBe HBV-DNA
IgG IgM
A. - + + - - + -
B. + - + - - + -
C. - + - - - - -
D. + - - + + - +
E. + - + - - + +
A. Previous infection with immunity
B. Chronic hepatitis B ( wild type)
C. Previous hepatitis B vaccination
D. Acute hepatitis B
E Chronic hepatitis B ( precore mutant)
IgG IgM
A. - + + - - + -
B. + - + - - + -
C. - + - - - - -
D. + - - + + - +
E. + - + - - + +
A. Previous infection with immunity
B. Chronic hepatitis B ( wild type)
C. Previous hepatitis B vaccination
D. Acute hepatitis B
E Chronic hepatitis B ( precore mutant)
Слайд 28
VIRAL HEPATITIS Д
The agent – RNA-virus by a size 28
The agent – RNA-virus by a size 28
- 39 nm with the
envelope consisting from HBs Ag.
RNA of the virus is surrounded HDV core Ag.
In a blood of the patients transmute in rodshaped
inbranched the form.
Is steady against warming, operation of acids and
proteinases, but fails by alkalis and nucleases.
HDV - is selected only from the patients infection HBV.
The monoinfection VHD is impossible!!!
Can cause disease only in a combination with VHB as
coinfection or superinfection
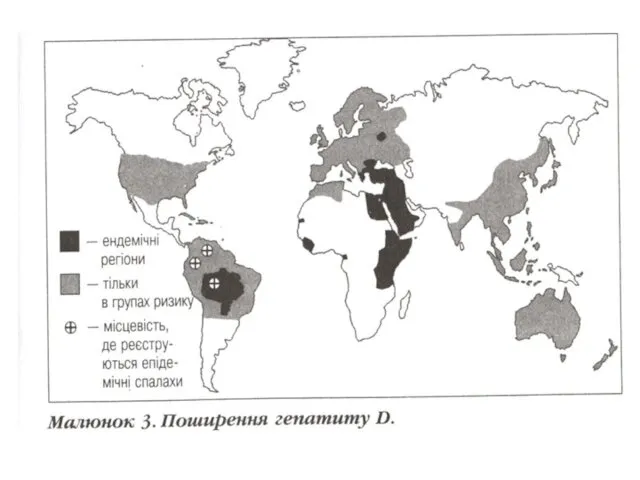
EPIDEMIOLOGY
15 million of carriers VHD are in the world. It is revealed:
among carriers HBs Ag – in 9 % of cases
and among the patients with chronic VH - in 10 - 30 % of
cases
envelope consisting from HBs Ag.
RNA of the virus is surrounded HDV core Ag.
In a blood of the patients transmute in rodshaped
inbranched the form.
Is steady against warming, operation of acids and
proteinases, but fails by alkalis and nucleases.
HDV - is selected only from the patients infection HBV.
The monoinfection VHD is impossible!!!
Can cause disease only in a combination with VHB as
coinfection or superinfection
EPIDEMIOLOGY
15 million of carriers VHD are in the world. It is revealed:
among carriers HBs Ag – in 9 % of cases
and among the patients with chronic VH - in 10 - 30 % of
cases
Слайд 29
Слайд 30
Слайд 31
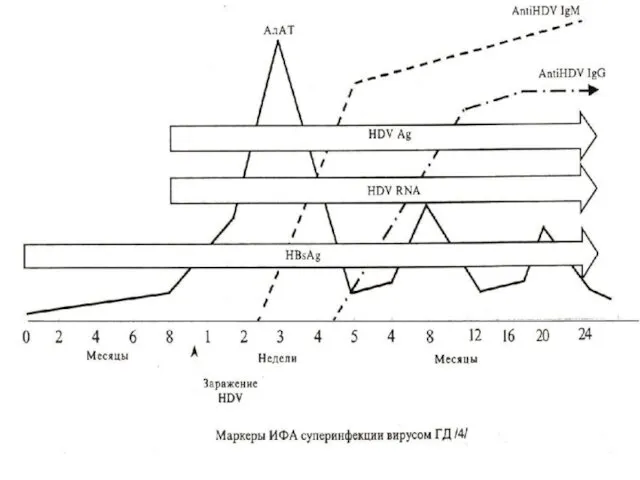
CLINIC. Incubation interval 80 days (40 - 200 days)
Coinfection -
Coinfection -
simultaneous infection HBV and HDV.
Clinical manifestations of VHD differs from a VHB little, but more often:
- high temperature from 3 to 5 days and long-lived 37,2 –
37,8 dg.С the one registers .
- more often complain of a pain in the right upper quadrant
- characteristicly two-undular current with peaking on 15 –
32 days of illness.
It more often revials among the recipients of a blood and drug addicts.
Transform to a chronic hepatitis in 5 % of cases
The superinfection develops for carriers HBsAg
After repeated hemotrasfusion and infection result - aggravate a hepatitis with intensive reproduction of a virus in hepatocytes.
Clinical manifestations of VHD differs from a VHB little, but more often:
- high temperature from 3 to 5 days and long-lived 37,2 –
37,8 dg.С the one registers .
- more often complain of a pain in the right upper quadrant
- characteristicly two-undular current with peaking on 15 –
32 days of illness.
It more often revials among the recipients of a blood and drug addicts.
Transform to a chronic hepatitis in 5 % of cases
The superinfection develops for carriers HBsAg
After repeated hemotrasfusion and infection result - aggravate a hepatitis with intensive reproduction of a virus in hepatocytes.
Слайд 32
The severe current is registered for 60 % of the patients
with creation fulminant of the forms of disease.
More than 70 % becomes chronic carriers HDV,
Proceeding more hardly, than at VHB (frequently with a hydropic - ascitic syndrome)
Passes in a cirrhosis for 60-70 % of the patients!!
CLINICAL CRITERIA VHD:
- Average age of the patients
- Hemotransfusion or carriage HBs Ag
- Acute beginning, short preicteric period with arthralgias
and allergies
- Aggravation of symptoms of the patients about
appearance icteruses
More than 70 % becomes chronic carriers HDV,
Proceeding more hardly, than at VHB (frequently with a hydropic - ascitic syndrome)
Passes in a cirrhosis for 60-70 % of the patients!!
CLINICAL CRITERIA VHD:
- Average age of the patients
- Hemotransfusion or carriage HBs Ag
- Acute beginning, short preicteric period with arthralgias
and allergies
- Aggravation of symptoms of the patients about
appearance icteruses
Слайд 33
Слайд 34
Слайд 35
- pain in the right upper quadrant in initial period
- pain in the right upper quadrant in initial period
- hepatospleenomegalia
- high and long-lived hyperbilirubinemia
- appearance of a hydropic - ascitic syndrome at
superinfections
- clinico-enzymatic peakings at coinfection
- severe current for 60 % of the patients and often
outcomes In a chronic hepatitis for 70 % at a
superinfection
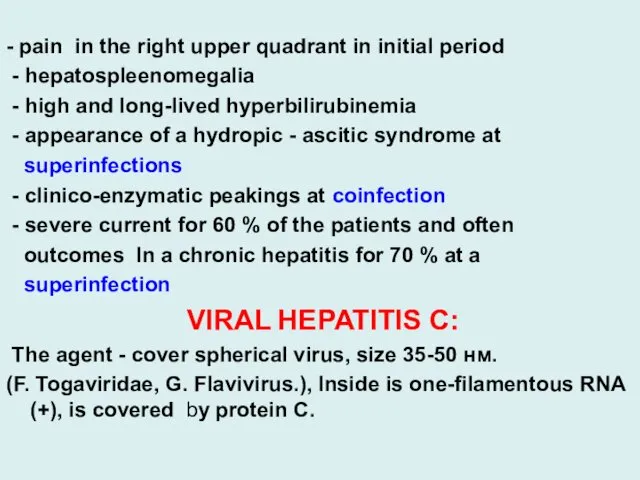
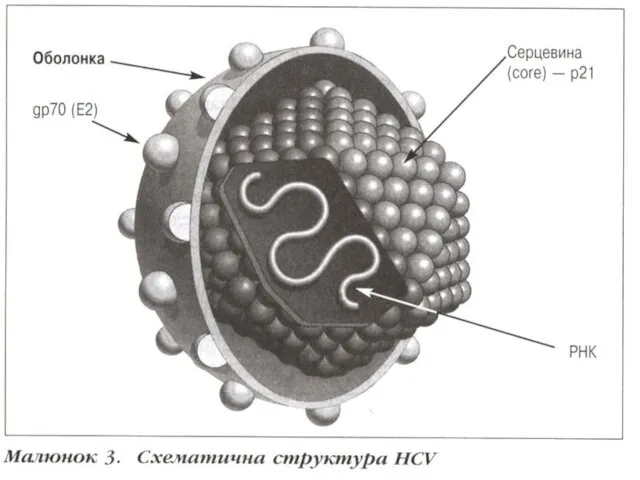
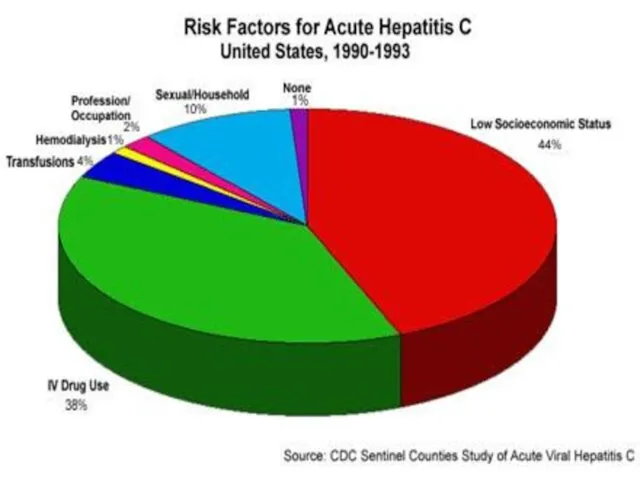
VIRAL HEPATITIS С:
The agent - cover spherical virus, size 35-50 нм.
(F. Togaviridae, G. Flavivirus.), Inside is one-filamentous RNA (+), is covered by protein C.
- high and long-lived hyperbilirubinemia
- appearance of a hydropic - ascitic syndrome at
superinfections
- clinico-enzymatic peakings at coinfection
- severe current for 60 % of the patients and often
outcomes In a chronic hepatitis for 70 % at a
superinfection
VIRAL HEPATITIS С:
The agent - cover spherical virus, size 35-50 нм.
(F. Togaviridae, G. Flavivirus.), Inside is one-filamentous RNA (+), is covered by protein C.
Слайд 36
Слайд 37
Слайд 38
Слайд 39
Слайд 40
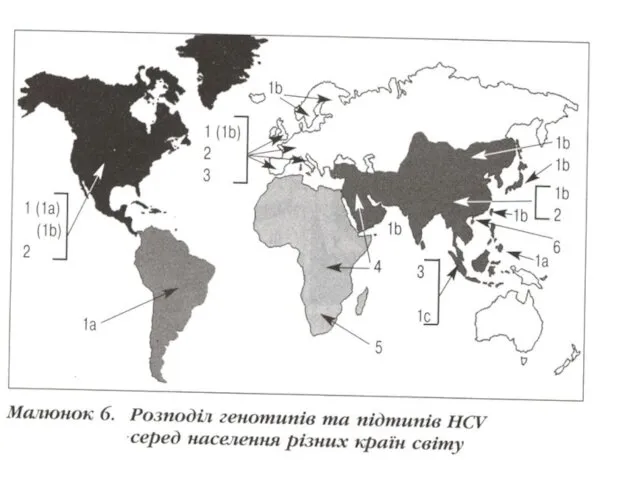
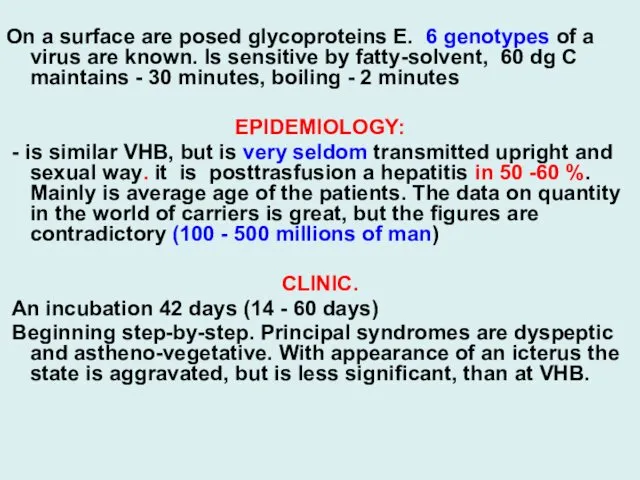
On a surface are posed glycoproteins Е. 6 genotypes of a
virus are known. Is sensitive by fatty-solvent, 60 dg С maintains - 30 minutes, boiling - 2 minutes
EPIDEMIOLOGY:
- is similar VHB, but is very seldom transmitted upright and sexual way. it is posttrasfusion a hepatitis in 50 -60 %. Mainly is average age of the patients. The data on quantity in the world of carriers is great, but the figures are contradictory (100 - 500 millions of man)
CLINIC.
An incubation 42 days (14 - 60 days)
Beginning step-by-step. Principal syndromes are dyspeptic and astheno-vegetative. With appearance of an icterus the state is aggravated, but is less significant, than at VHB.
EPIDEMIOLOGY:
- is similar VHB, but is very seldom transmitted upright and sexual way. it is posttrasfusion a hepatitis in 50 -60 %. Mainly is average age of the patients. The data on quantity in the world of carriers is great, but the figures are contradictory (100 - 500 millions of man)
CLINIC.
An incubation 42 days (14 - 60 days)
Beginning step-by-step. Principal syndromes are dyspeptic and astheno-vegetative. With appearance of an icterus the state is aggravated, but is less significant, than at VHB.
Слайд 41
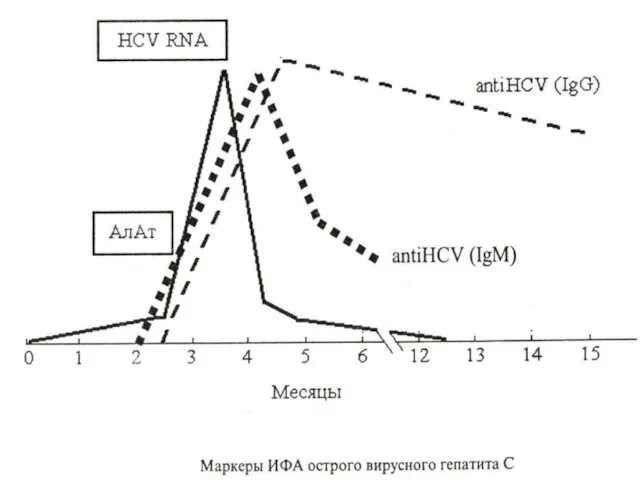
CLINICAL CRITERIA VHC:
- average age of the patients
- In
- average age of the patients
- In
an anamnesis hemotrasfusions or contact to the ill
patient
- step-by-step beginning
- aggravation of symptoms with appearance of an icterus
- moderate increase of a bilirubin and liver
- transition in 50 - 80 % of cases in the chronic form with
the subsequent flaccid current ( “affectionate”
the murderer)
- antibodies occurs late, in 5 years of an antibody
do not influence to replication of a virus
- It are found out of antibodies- ELISA and RNA- PCR
patient
- step-by-step beginning
- aggravation of symptoms with appearance of an icterus
- moderate increase of a bilirubin and liver
- transition in 50 - 80 % of cases in the chronic form with
the subsequent flaccid current ( “affectionate”
the murderer)
- antibodies occurs late, in 5 years of an antibody
do not influence to replication of a virus
- It are found out of antibodies- ELISA and RNA- PCR
Слайд 42
Слайд 43
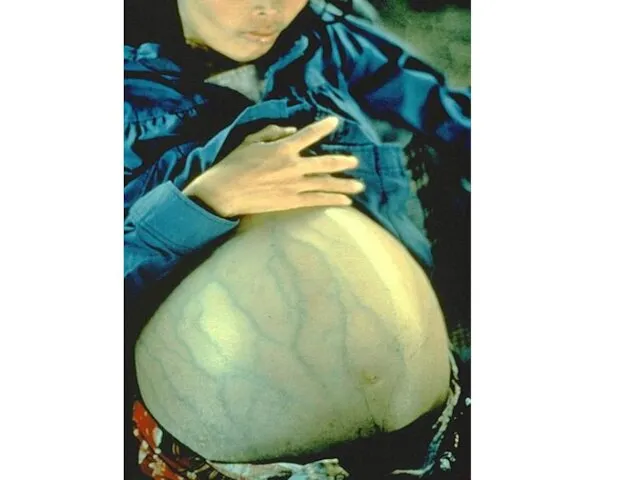
A 69 - year-old female presents with fatigue, arthragias, peripheral
A 69 - year-old female presents with fatigue, arthragias, peripheral
paraesthesis, leg edema, and purpura. On examination, the patient has moderate hypertesion ( 170/110 mmHG ). Purpura involves both extremites and the left hemithorax. The liver and spleen are not palpable.
Abdominal ultrasoud shows ascitic fluid around liver and in the pelvis. Chest X-rays show bilateral basal pleural effusions. A liver biopsy shows minimal inflammatory changes.
Laboratory investigations: Hemoglobin – 76 g/L, Both ALT and AST- normal, Cryoglobulins present 4.1 g/L:IgG+A+M, Total protein 51 g/L, Albumin 26 g/L, Creatinin 194.5 mm/L, BUN- blood urea nitrogen 11.1 mmol/L, HBsAg absent, Anti-HCV present, Albuminuria 17g/L, Rheumatoid factor positive , Urine showed micro/macro hematuria.
Abdominal ultrasoud shows ascitic fluid around liver and in the pelvis. Chest X-rays show bilateral basal pleural effusions. A liver biopsy shows minimal inflammatory changes.
Laboratory investigations: Hemoglobin – 76 g/L, Both ALT and AST- normal, Cryoglobulins present 4.1 g/L:IgG+A+M, Total protein 51 g/L, Albumin 26 g/L, Creatinin 194.5 mm/L, BUN- blood urea nitrogen 11.1 mmol/L, HBsAg absent, Anti-HCV present, Albuminuria 17g/L, Rheumatoid factor positive , Urine showed micro/macro hematuria.
Слайд 44
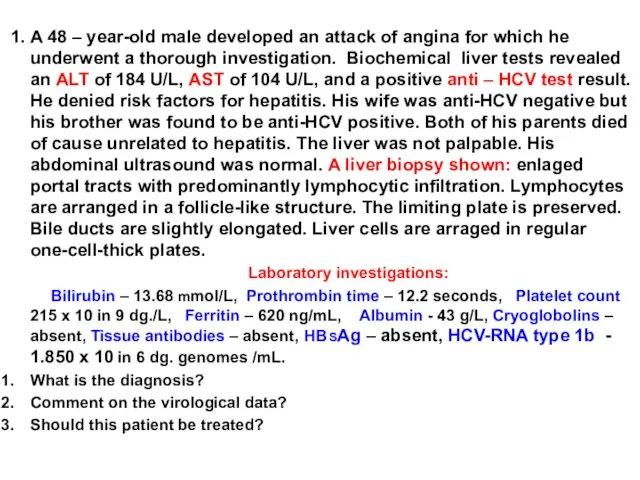
1. A 48 – year-old male developed an attack of
1. A 48 – year-old male developed an attack of
angina for which he underwent a thorough investigation. Biochemical liver tests revealed an ALT of 184 U/L, AST of 104 U/L, and a positive anti – HCV test result. He denied risk factors for hepatitis. His wife was anti-HCV negative but his brother was found to be anti-HCV positive. Both of his parents died of cause unrelated to hepatitis. The liver was not palpable. His abdominal ultrasound was normal.
A liver biopsy shown: enlaged portal tracts with predominantly lymphocytic infiltration. Lymphocytes are arranged in a follicle-like structure. The limiting plate is preserved. Bile ducts are slightly elongated. Liver cells are arraged in regular one-cell-thick plates.
Laboratory investigations:
Bilirubin – 13.68 mmol/L, Prothrombin time – 12.2 seconds, Platelet count 215 x 10 in 9 dg./L, Ferritin – 620 ng/mL, Albumin - 43 g/L, Cryoglobolins – absent, Tissue antibodies – absent, HB SAg – absent, HCV-RNA type 1b - 1.850 x 10 in 6 dg. genomes /mL.
A liver biopsy shown: enlaged portal tracts with predominantly lymphocytic infiltration. Lymphocytes are arranged in a follicle-like structure. The limiting plate is preserved. Bile ducts are slightly elongated. Liver cells are arraged in regular one-cell-thick plates.
Laboratory investigations:
Bilirubin – 13.68 mmol/L, Prothrombin time – 12.2 seconds, Platelet count 215 x 10 in 9 dg./L, Ferritin – 620 ng/mL, Albumin - 43 g/L, Cryoglobolins – absent, Tissue antibodies – absent, HB SAg – absent, HCV-RNA type 1b - 1.850 x 10 in 6 dg. genomes /mL.
Слайд 45
TREATMENT
The mild forms - bed rest, diet N5, hepatoprotections, vitamin therapy,
The mild forms - bed rest, diet N5, hepatoprotections, vitamin therapy,
PO desintoxication, antioxidants
Moderate forms: therapy as mild form + follow-up amplifies desintoxication, the glucocorticoids (at VHB are more often)
The severe forms:
- antiviral drugs (interferons, vidarabin, lamivudin,( is rare)
- immunodepretion drugs at VHB (antilymphocytic
Immunoglobulin, glucocorticoids etc.)
- antiferment drugs and antifibrinolytic drugs
-Intensifying desintoxication (exception of a diet of a
protein)
Moderate forms: therapy as mild form + follow-up amplifies desintoxication, the glucocorticoids (at VHB are more often)
The severe forms:
- antiviral drugs (interferons, vidarabin, lamivudin,( is rare)
- immunodepretion drugs at VHB (antilymphocytic
Immunoglobulin, glucocorticoids etc.)
- antiferment drugs and antifibrinolytic drugs
-Intensifying desintoxication (exception of a diet of a
protein)
Слайд 46
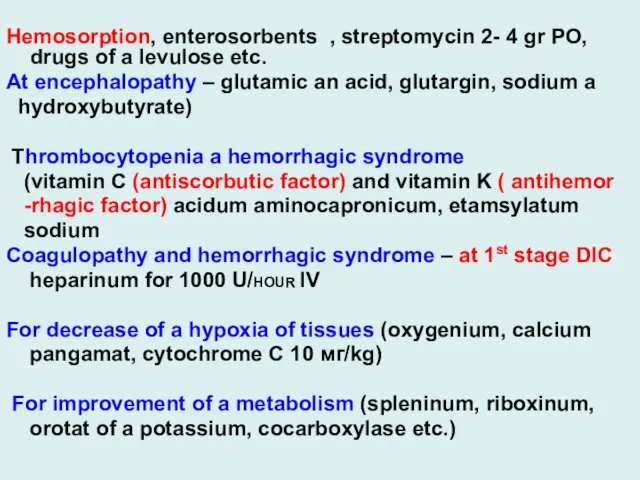
Hemosorption, enterosorbents , streptomycin 2- 4 gr PO, drugs of
Hemosorption, enterosorbents , streptomycin 2- 4 gr PO, drugs of
a levulose etc.
At encephalopathy – glutamic an acid, glutargin, sodium a
hydroxybutyrate)
Thrombocytopenia a hemorrhagic syndrome
(vitamin C (antiscorbutic factor) and vitamin K ( antihemor
-rhagic factor) acidum aminocapronicum, etamsylatum
sodium
Coagulopathy and hemorrhagic syndrome – at 1st stage DIC
heparinum for 1000 U/HOUR IV
For decrease of a hypoxia of tissues (oxygenium, calcium
pangamat, cytochrome C 10 мг/kg)
For improvement of a metabolism (spleninum, riboxinum,
orotat of a potassium, cocarboxylase etc.)
At encephalopathy – glutamic an acid, glutargin, sodium a
hydroxybutyrate)
Thrombocytopenia a hemorrhagic syndrome
(vitamin C (antiscorbutic factor) and vitamin K ( antihemor
-rhagic factor) acidum aminocapronicum, etamsylatum
sodium
Coagulopathy and hemorrhagic syndrome – at 1st stage DIC
heparinum for 1000 U/HOUR IV
For decrease of a hypoxia of tissues (oxygenium, calcium
pangamat, cytochrome C 10 мг/kg)
For improvement of a metabolism (spleninum, riboxinum,
orotat of a potassium, cocarboxylase etc.)
Слайд 47
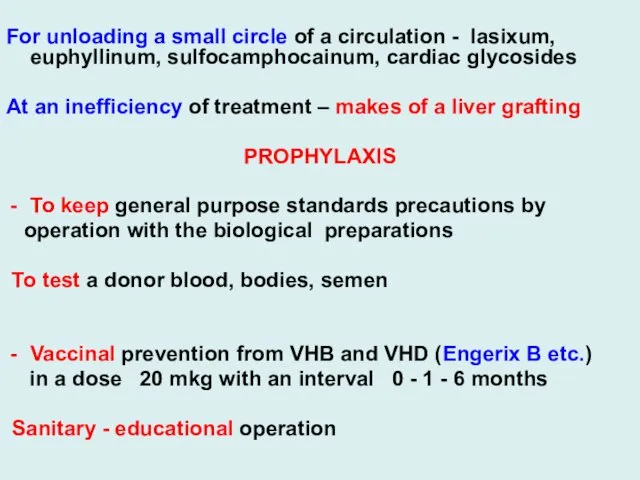
For unloading a small circle of a circulation - lasixum, euphyllinum,
sulfocamphocainum, cardiac glycosides
At an inefficiency of treatment – makes of a liver grafting
PROPHYLAXIS
To keep general purpose standards precautions by
operation with the biological preparations
To test a donor blood, bodies, semen
Vaccinal prevention from VHB and VHD (Engerix B etc.)
in a dose 20 mkg with an interval 0 - 1 - 6 months
Sanitary - educational operation
At an inefficiency of treatment – makes of a liver grafting
PROPHYLAXIS
To keep general purpose standards precautions by
operation with the biological preparations
To test a donor blood, bodies, semen
Vaccinal prevention from VHB and VHD (Engerix B etc.)
in a dose 20 mkg with an interval 0 - 1 - 6 months
Sanitary - educational operation
Слайд 48
Слайд 49
1. A 48 – year-old male developed an attack
1. A 48 – year-old male developed an attack
of angina for which he underwent a thorough investigation. Biochemical liver tests revealed an ALT of 184 U/L, AST of 104 U/L, and a positive anti – HCV test result. He denied risk factors for hepatitis. His wife was anti-HCV negative but his brother was found to be anti-HCV positive. Both of his parents died of cause unrelated to hepatitis. The liver was not palpable. His abdominal ultrasound was normal. A liver biopsy shown: enlaged portal tracts with predominantly lymphocytic infiltration. Lymphocytes are arranged in a follicle-like structure. The limiting plate is preserved. Bile ducts are slightly elongated. Liver cells are arraged in regular one-cell-thick plates.
Laboratory investigations:
Bilirubin – 13.68 mmol/L, Prothrombin time – 12.2 seconds, Platelet count 215 x 10 in 9 dg./L, Ferritin – 620 ng/mL, Albumin - 43 g/L, Cryoglobolins – absent, Tissue antibodies – absent, HB SAg – absent, HCV-RNA type 1b - 1.850 x 10 in 6 dg. genomes /mL.
What is the diagnosis?
Comment on the virological data?
Should this patient be treated?
Laboratory investigations:
Bilirubin – 13.68 mmol/L, Prothrombin time – 12.2 seconds, Platelet count 215 x 10 in 9 dg./L, Ferritin – 620 ng/mL, Albumin - 43 g/L, Cryoglobolins – absent, Tissue antibodies – absent, HB SAg – absent, HCV-RNA type 1b - 1.850 x 10 in 6 dg. genomes /mL.
What is the diagnosis?
Comment on the virological data?
Should this patient be treated?
Слайд 50
2
2
Слайд 51
Слайд 52
Слайд 53
- Предыдущая
Несахарный диабетСледующая -
GLP – Тиісті зертханалық тәжірибе


















 Электрофизиологические основы ЭКГ. Лекция 17
Электрофизиологические основы ЭКГ. Лекция 17 Амбулаторлы стоматологиялық хирургия қабылдауындағы АИВ-инфекциясы мен гепатиттің профилактикасы
Амбулаторлы стоматологиялық хирургия қабылдауындағы АИВ-инфекциясы мен гепатиттің профилактикасы Көпіршікті дерматоздар: Ұшық тәрізді Дюринг дерматозы
Көпіршікті дерматоздар: Ұшық тәрізді Дюринг дерматозы Оказание первой медицинской помощи
Оказание первой медицинской помощи Аэробтық тыныс алу. Тыныс алу жүйелері
Аэробтық тыныс алу. Тыныс алу жүйелері Профилактика профессиональных заболеваний, мероприятия по сохранению и укреплению здоровья населения
Профилактика профессиональных заболеваний, мероприятия по сохранению и укреплению здоровья населения Использование здоровьесберегающих технологий в образовательном процессе
Использование здоровьесберегающих технологий в образовательном процессе Кокцидиидозы животных
Кокцидиидозы животных Захворювання серцево-судинної системи та їх профілактика
Захворювання серцево-судинної системи та їх профілактика Будови лімфатичної системи
Будови лімфатичної системи Мышечная система человека. (Тема 2.2)
Мышечная система человека. (Тема 2.2) Учетно-отчетная документация и оценка показателей. МКБ 10
Учетно-отчетная документация и оценка показателей. МКБ 10 Сестринскя деятельность в профилактическом и реабилитационном процессах у пациентов с острым нарушением мозгового кровообращения
Сестринскя деятельность в профилактическом и реабилитационном процессах у пациентов с острым нарушением мозгового кровообращения Выбор торка при использовании брекетов Damon Q
Выбор торка при использовании брекетов Damon Q Предстерил.обраб. Контроль кач. ПО
Предстерил.обраб. Контроль кач. ПО Амбулатория жағдайында іш қуысының ауырсынуы кезіндегі рационалды дифференциалды диагностика алгоритмі
Амбулатория жағдайында іш қуысының ауырсынуы кезіндегі рационалды дифференциалды диагностика алгоритмі Вторичный туберкулёз. Макропрепараты
Вторичный туберкулёз. Макропрепараты Рентгенодиагностика переломов проксимальных отделов бедренной кости
Рентгенодиагностика переломов проксимальных отделов бедренной кости Аллергический ринит
Аллергический ринит СРС: терминальное состояние : стади, клиника, диагностика, критерии оценки тяжести состояния больного
СРС: терминальное состояние : стади, клиника, диагностика, критерии оценки тяжести состояния больного Диспансеризация населения
Диспансеризация населения Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome Шок
Шок Организация и проведение профилактических прививок
Организация и проведение профилактических прививок Functions of autonomic nervous system
Functions of autonomic nervous system Первая помощь при отравлении бытовыми химикатами
Первая помощь при отравлении бытовыми химикатами Сколиоз, мүсіннің бұзылыстары
Сколиоз, мүсіннің бұзылыстары Иммунопатологиялық процесстер
Иммунопатологиялық процесстер