Содержание
- 2. Introduction • • • • • • First described in 1771. 50% of patients present 70%
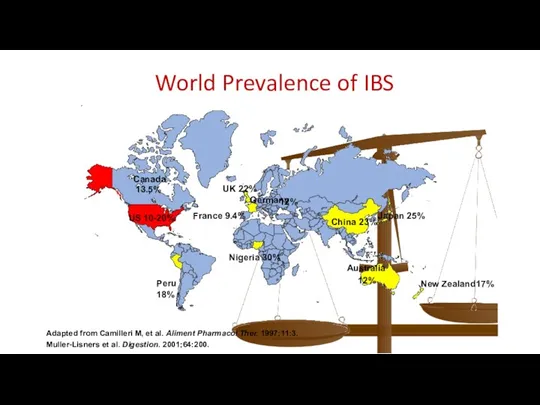
- 3. World Prevalence of IBS Adapted from Camilleri M, et al. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1997;11:3. Muller-Lisners et
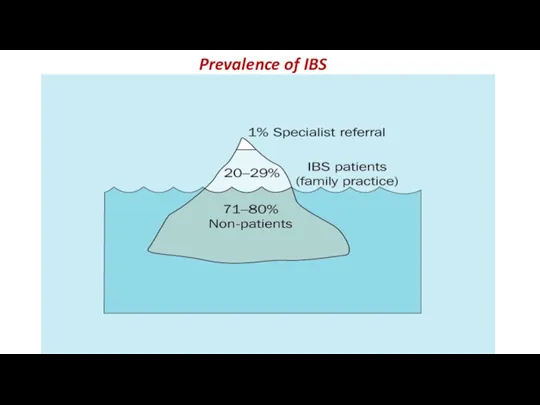
- 4. Prevalence of IBS
- 5. Types of IBS :IBS can be subdivided into Constipation-predominant :the person tends to alternate constipation with
- 6. The Positive Diagnosis of IBS: A Symptom-Based Approach Adapted from Paterson et al. Can Med Assoc
- 7. Identify Red Flags νHistory ν Unintentional weight loss ν Onset in older patient (>50 years) ν
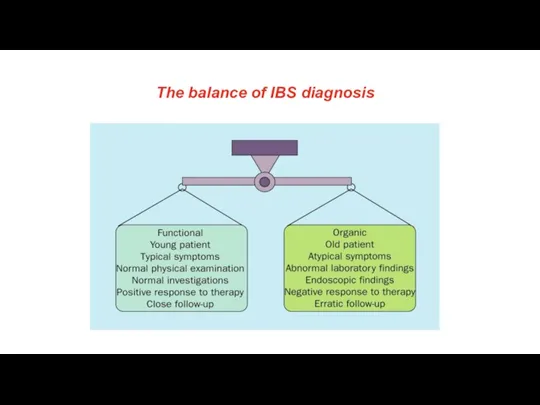
- 8. The balance of IBS diagnosis
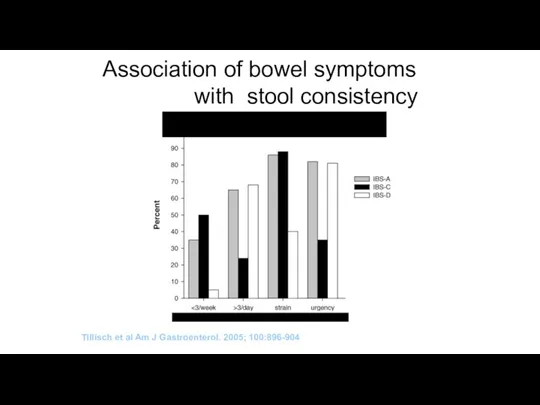
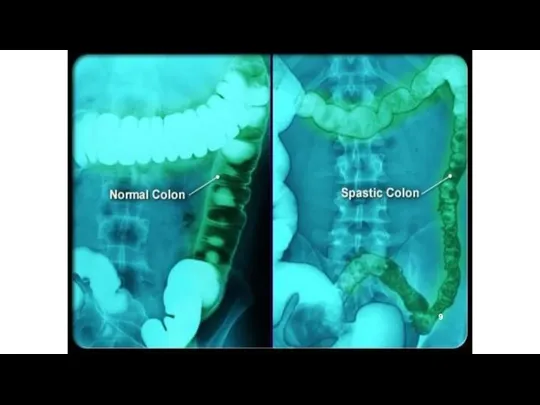
- 9. Association of bowel symptoms with stool consistency Tillisch et al Am J Gastroenterol. 2005; 100:896-904
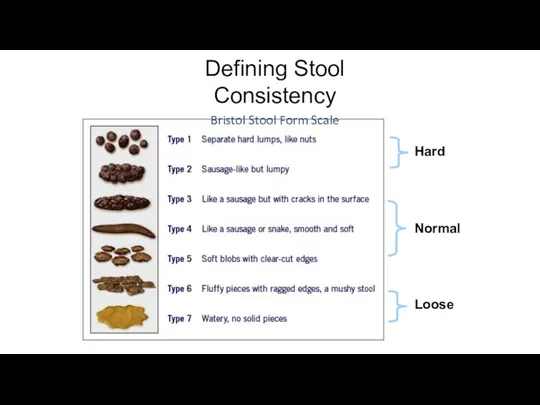
- 10. Defining Stool Consistency Bristol Stool Form Scale Hard Normal Loose
- 11. Changes to IBS classification Rome III Summary No change to basic criteria Length of time needed
- 12. Manning Kruis Rome Rome I Rome II Rome III 1978 1984 1989 1990 1999 2006 IBS
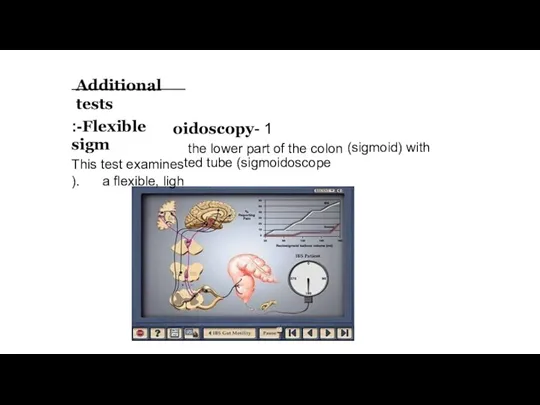
- 13. oidoscopy- 1 the lower part of the colon (sigmoid) with ted tube (sigmoidoscope 18 Additional tests
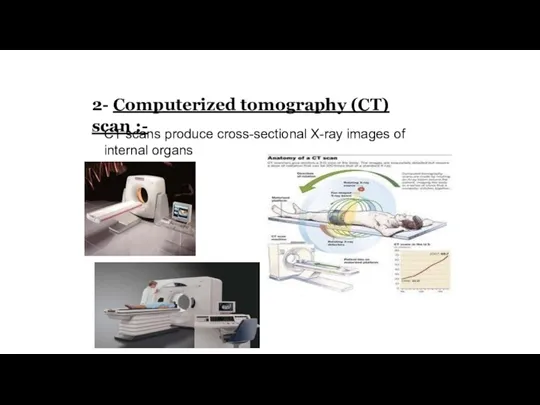
- 14. 2- Computerized tomography (CT) scan :- CT scans produce cross-sectional X-ray images of ′ internal organs
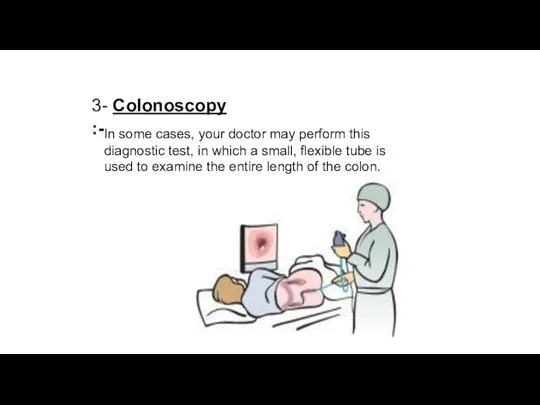
- 15. 3- Colonoscopy :- In some cases, your doctor may perform this diagnostic test, in which a
- 16. 4- Lactose intolerance tests :- Lactase is an enzyme you need to digest the sugar -
- 17. 9
- 18. TREATMENT PATIENT EDUCATION DIETARY INTERVENTION PHARMACOTHERAPY PSYCHOTHERAPY/COGNITIVE AND BAHAVIOR THERAPY HYPNOTHERAPY
- 20. Скачать презентацию








 Первая помощь при кровотечениях
Первая помощь при кровотечениях Зрительный нерв. Заболевания зрительного нерва
Зрительный нерв. Заболевания зрительного нерва Государственное регулирование ценообразования на лекарственные препараты
Государственное регулирование ценообразования на лекарственные препараты Аралас және жасанды тамақтандыру. Жіктелуі мен сипаты.емдік және профилактикалық қоспаларды қолдануға көрсеткіштер
Аралас және жасанды тамақтандыру. Жіктелуі мен сипаты.емдік және профилактикалық қоспаларды қолдануға көрсеткіштер Лекарственные травы
Лекарственные травы Виды кровотечений, их признаки
Виды кровотечений, их признаки Пародонт ауруларының жүйесі
Пародонт ауруларының жүйесі Неотложные состояния в терапии
Неотложные состояния в терапии Основные принципы диагностики анемий
Основные принципы диагностики анемий Возрастная анатомия, физиология и гигиена
Возрастная анатомия, физиология и гигиена Патология почек. Белки мочи
Патология почек. Белки мочи Современные представления о гемокоагуляции
Современные представления о гемокоагуляции Жүйелі склеродермия
Жүйелі склеродермия Близорукость и ее профилактика
Близорукость и ее профилактика Заболевания СОПР. Воспалительные заболевания челюстно-лицевой области
Заболевания СОПР. Воспалительные заболевания челюстно-лицевой области Лечение онкологических больных
Лечение онкологических больных Хронические тонзиллиты
Хронические тонзиллиты Противотуберкулезные лекарственные средства
Противотуберкулезные лекарственные средства Современные методы анестезиологического обеспечения
Современные методы анестезиологического обеспечения Оказание первой помощи при отсутствии сознания, остановке дыхания и кровообращения
Оказание первой помощи при отсутствии сознания, остановке дыхания и кровообращения Клинический случай ХНН
Клинический случай ХНН Мысқыл (паротит)
Мысқыл (паротит) Гнойно-септические заболевание у детей и новорожденных
Гнойно-септические заболевание у детей и новорожденных Экстракттар казакша
Экстракттар казакша Физиология питания. 5 класс
Физиология питания. 5 класс Заболевание молочной железы
Заболевание молочной железы Интерпретация ЭКГ с инфарктом миокарда
Интерпретация ЭКГ с инфарктом миокарда Сестринский процесс при заболеваниях органов дыхания
Сестринский процесс при заболеваниях органов дыхания