Слайд 2

Слайд 3

INTRODUCTION
Population genetics is the study of change in the frequencies of
allele and genotype within a population.
Population geneticists study the genetic structure of populations, and how they change geographically and over time.
Слайд 4

Gene – a discrete unit of hereditary information consisting of a
specific sequence of DNA
Alleles – alternative forms f a gene
Genotype – the genetic makeup of an organism
Phenotype – the physical traits of an organism
Слайд 5

HARDY WEINBERG PRINCIPAL
Under certain condition, allelic frequencies remain constant from generation
to generation.
If any one condition is not made, genetic equilibrium will be disturbed and the population may evolve.
Слайд 6

Why allele frequencies change
Five evolutionary forces can significantly alter the allele
frequencies of a population
Mutation
Migration
Genetic drift
Non-random mating
Selection
Слайд 7

mutation
Errors n DNA replication result in mutation.
Mutation can also be caused
by mutagens.
It is the ultimate source of new variation n a population.
Слайд 8

migration
Movement of individuals from one place to another.
There are 2 toes
of migration :
Immigration : movement into a population
Emigration : movement out of a population
Слайд 9

Genetic drift
Founder effect
Small group of individuals establishes a population in a
new location.
Bottleneck effect
A sudden decrease in population size due to natural forces
Слайд 10

Non-random mating
Mating that occurs more or less frequently than expected
Inbreeding
Mating
with relatives
Increases homozygosity
Outbreeding
Mating with non-relatives
Increases heterozygosity
Слайд 11

selection
Natural selection
- Environment selects for adapted characteristics
Artificial selection
- Breeder selects for
desired characters
Слайд 12

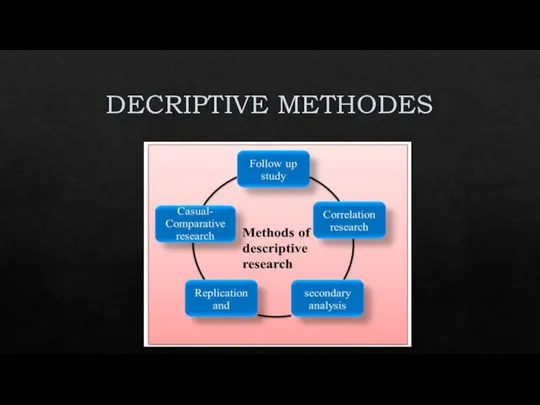
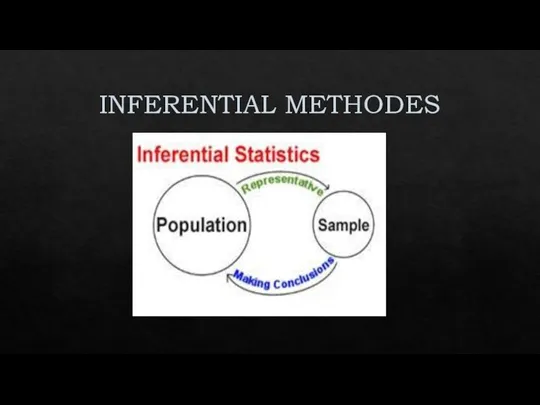
TYPES OF POPULATION STATISTICAL METHODS
Слайд 13
Слайд 14













 Клинико-лабораторная характеристика заболеваний желудочно-кишечного тракта. Лабораторные методы исследования функции ЖКТ
Клинико-лабораторная характеристика заболеваний желудочно-кишечного тракта. Лабораторные методы исследования функции ЖКТ Клостридии - возбудители раневых инфекций
Клостридии - возбудители раневых инфекций Диагностика и лечение анемий
Диагностика и лечение анемий ҰлпАның қабынбалы аурулары
ҰлпАның қабынбалы аурулары Правовые основы профессиональной деятельности медицинских работников
Правовые основы профессиональной деятельности медицинских работников Деонтология в хирургии
Деонтология в хирургии Технология определения хим.свойств мочи
Технология определения хим.свойств мочи Переломы плечевой кости
Переломы плечевой кости Аптечка. Природные лекарственные средства
Аптечка. Природные лекарственные средства Желудочно-кишечные кровотечения
Желудочно-кишечные кровотечения Средства для лечения заболеваний слизистой оболочки рта
Средства для лечения заболеваний слизистой оболочки рта Трансэтмоидальная декомпрессия орбиты при эндокринной офтальмопатии
Трансэтмоидальная декомпрессия орбиты при эндокринной офтальмопатии Хронический пульпит
Хронический пульпит Клеточные факторы врождённого иммунитета. Фагоцитоз и его стадии
Клеточные факторы врождённого иммунитета. Фагоцитоз и его стадии Өкпенің ошақты туберкулезі
Өкпенің ошақты туберкулезі Организация процесса адаптации фармацевтического персонала к условиям работы в аптеке
Организация процесса адаптации фармацевтического персонала к условиям работы в аптеке Нейроинфекции. Виды нейроинфекций
Нейроинфекции. Виды нейроинфекций ЖРДС. Этиология мен патогенез, клиникасы, диагностикасы, емі
ЖРДС. Этиология мен патогенез, клиникасы, диагностикасы, емі Бағаналы жасушалар
Бағаналы жасушалар V-HeFT I and V-HeFT II Trials― The Path to A-HeFT
V-HeFT I and V-HeFT II Trials― The Path to A-HeFT Бюджетное учреждение здравоохранения Вологодской области Великоустюгская центральная районная больница
Бюджетное учреждение здравоохранения Вологодской области Великоустюгская центральная районная больница Роль структур ЦНС в регуляции физиологических функций
Роль структур ЦНС в регуляции физиологических функций Лейомиома
Лейомиома Медициналық аспаптарды стерилизациялау
Медициналық аспаптарды стерилизациялау Клеточные факторы неспецифической защиты
Клеточные факторы неспецифической защиты Заболевание периферических вен и артерий
Заболевание периферических вен и артерий Патология дыхательной системы
Патология дыхательной системы Компьютеризация рабочего места медсестры
Компьютеризация рабочего места медсестры