Содержание
- 2. Plan of the lecture 1. Definition of bronchial asthma 2. Factors of development 3. Bronchial asthma
- 3. What do we know about asthma? Bronchial asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways
- 4. Asthma is a problem worldwide with an estimated 300 million affected individuals BA morbidity increased twice
- 5. Predisposing Factors: Genes pre-disposing to allergic reactions Airway hyperresponsiveness– The characteristic functional abnormality of asthma results
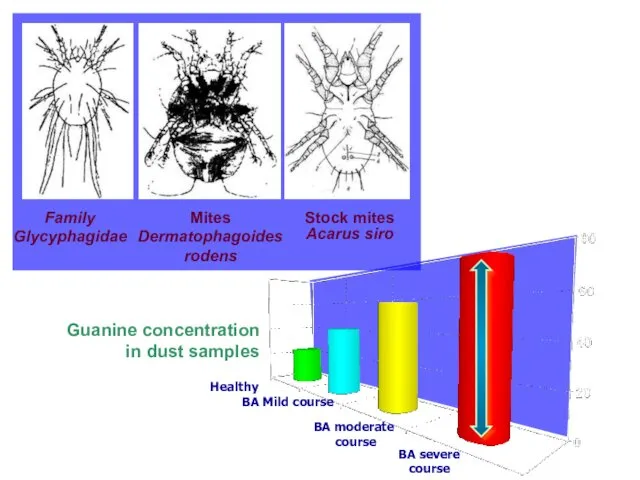
- 6. Sensibilization Factors : Indoor: domestic mites, domestic and library dust, cockroaches allergenes, fish fodder, feather of
- 7. Family Glycyphagidae Mites Dermatophagoides rodens Stock mites Acarus siro Healthy BA Mild course BA moderate course
- 8. Resolution factors ( triggers): Pollutants – compounds of serum, nickel, Cobalt etc.-result of industrial plants activity,
- 9. Extrinsic asthma The asthma episode is typically initiated by the type1hypersensitivity reaction induced by exposure to
- 10. Intrinsic asthma The triggering mechanisms are non-immune in this form a number of stimuli that have
- 11. Drug induced asthma Is seen most commonly with 1.NSAID’S (COX-1 inhibitors) 2.Aspirin, Ibuprofen 3.Propranolol (because non
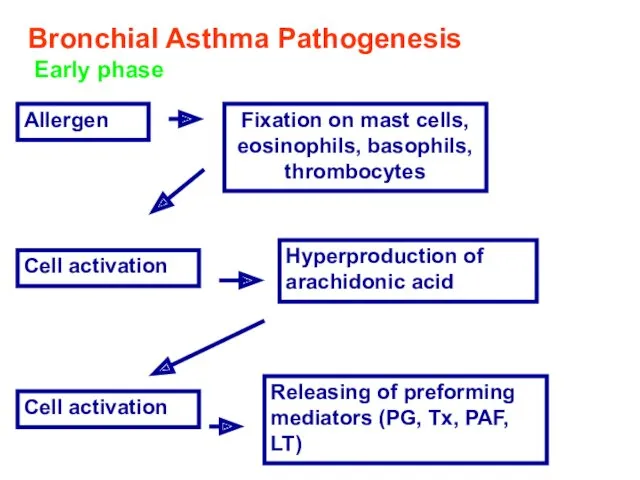
- 12. Bronchial Asthma Pathogenesis Early phase Allergen Fixation on mast cells, eosinophils, basophils, thrombocytes Cell activation Hyperproduction
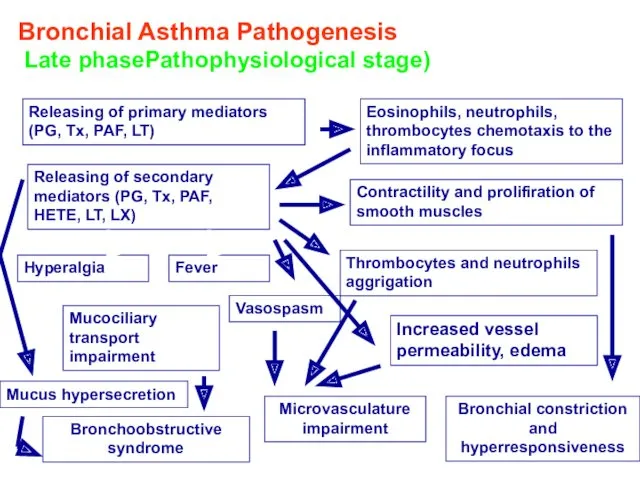
- 13. Bronchial Asthma Pathogenesis Late phasePathophysiological stage) Releasing of primary mediators (PG, Tx, PAF, LT) Eosinophils, neutrophils,
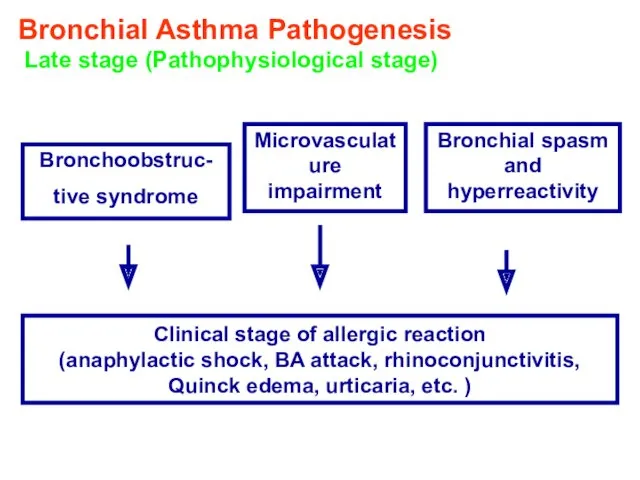
- 14. Bronchial Asthma Pathogenesis Late stage (Pathophysiological stage) Bronchoobstruc- tive syndrome Microvasculature impairment Bronchial spasm and hyperreactivity
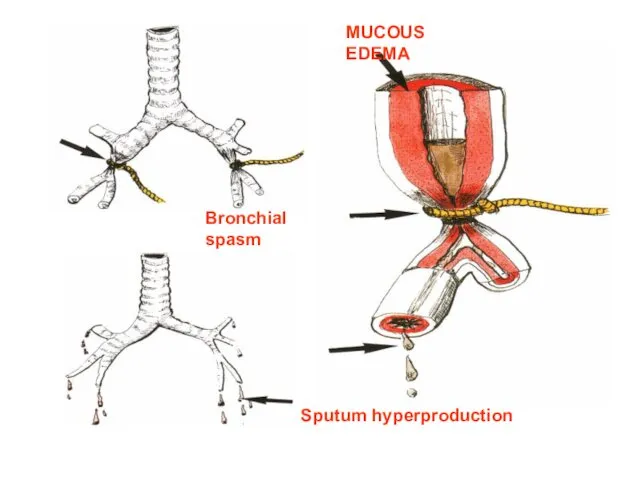
- 15. MUCOUS EDEMA Sputum hyperproduction Bronchial spasm
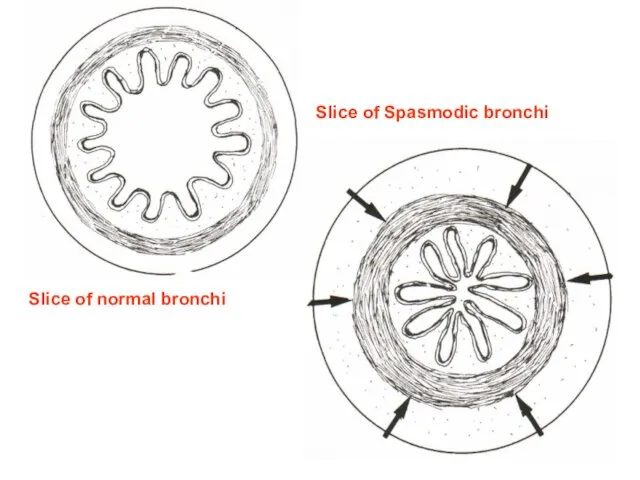
- 16. Slice of normal bronchi Slice of Spasmodic bronchi
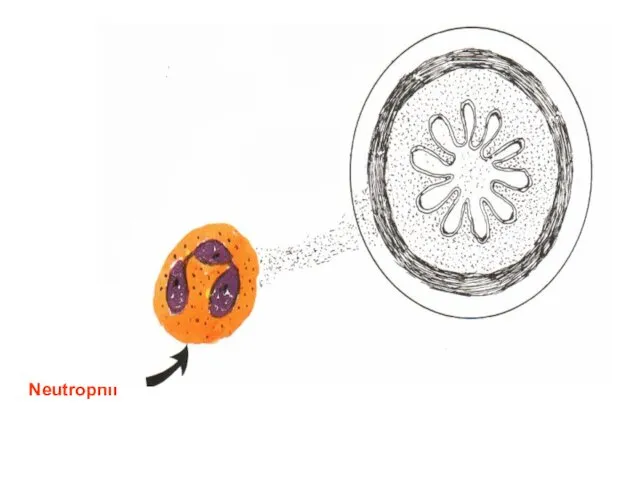
- 17. Neutrophil
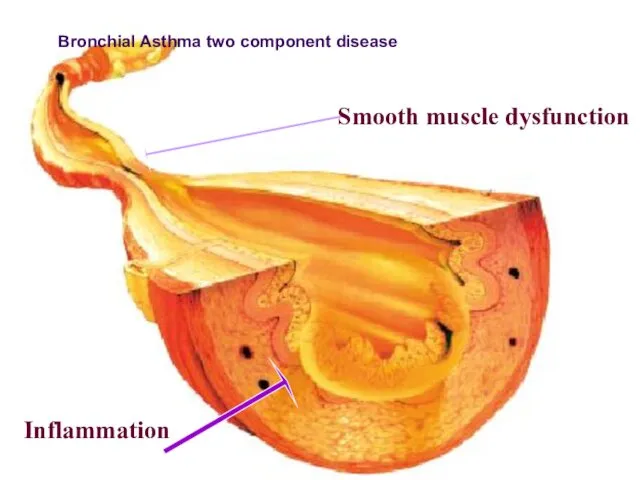
- 18. Smooth muscle dysfunction Inflammation ПАТОГЕНЕЗ БРОНХИАЛЬНОЙ АСТМЫ Bronchial Asthma two component disease
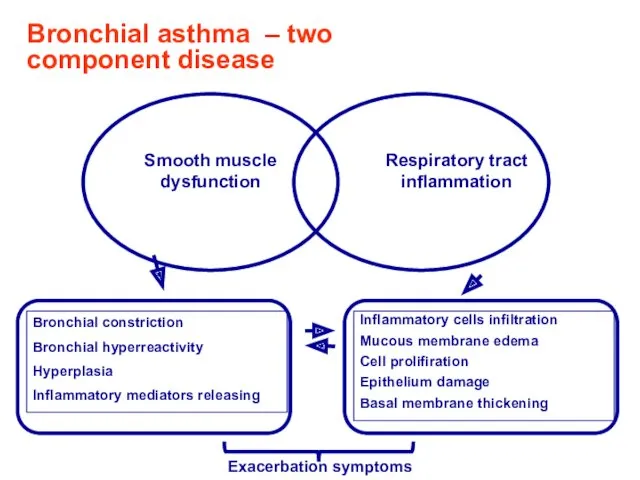
- 19. Bronchial asthma – two component disease Exacerbation symptoms
- 20. Clinics of asthma exacerbation cough typical attacks of chest tightness, exhalative dyspnea, wheezing, dry cough, viscous
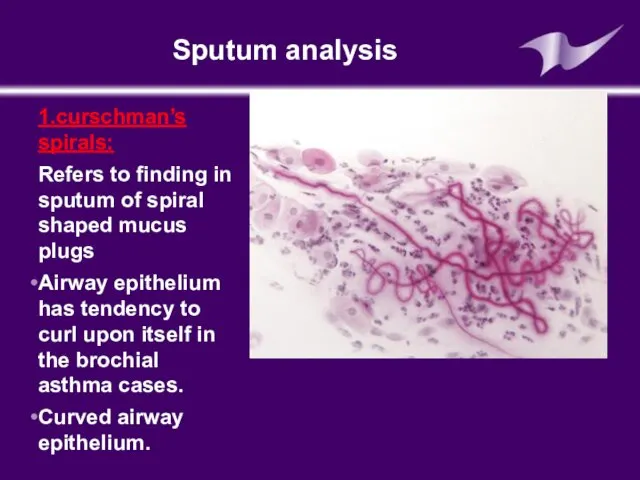
- 21. Sputum analysis 1.curschman’s spirals: Refers to finding in sputum of spiral shaped mucus plugs Airway epithelium
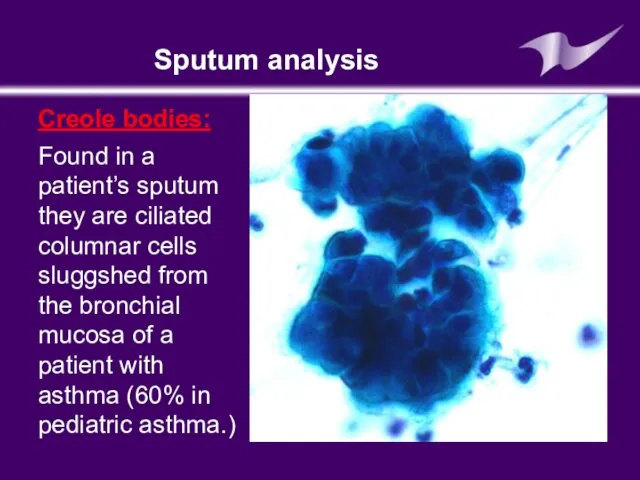
- 22. Sputum analysis Creole bodies: Found in a patient’s sputum they are ciliated columnar cells sluggshed from
- 23. Blood analysis Neutrophiles (band cells increased) Eosinophils also increased Serum IgE increased (Extrinsic asthma)
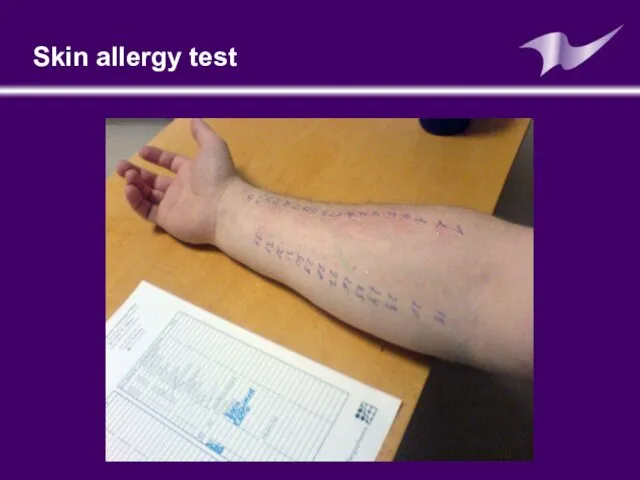
- 24. Skin allergy test: (prick test) Is a method for medical diagnosis of allergies that attempts to
- 25. Skin allergy test
- 26. It is very important that the subject should stay in the observation of physician for at
- 27. Peakflow meter Used to measure a persons maximum speed of expiration.
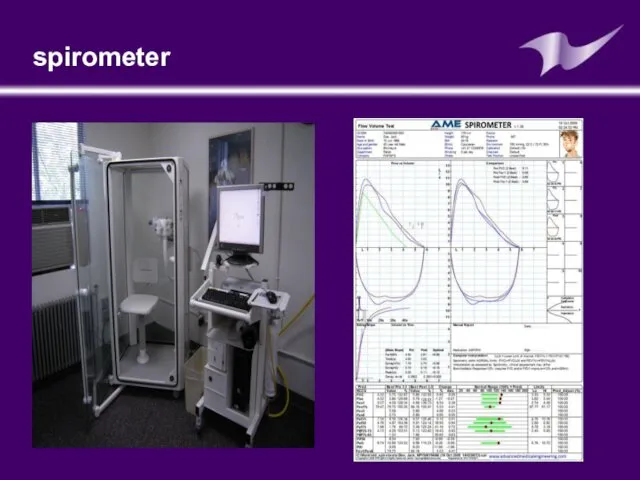
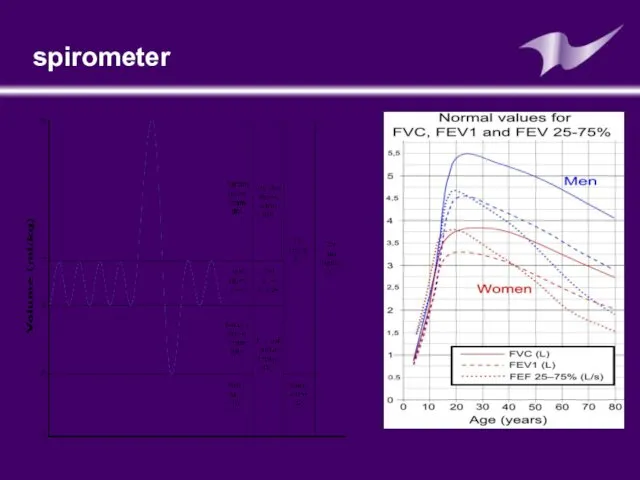
- 28. Pulmonary function test are carried out mostly by using spirometer The air in the lungs is
- 29. spirometer
- 30. spirometer
- 31. Late diagnostics of bronchial asthma Complicate bronchial asthma course prognosis Worsen life quality in bronchial asthma
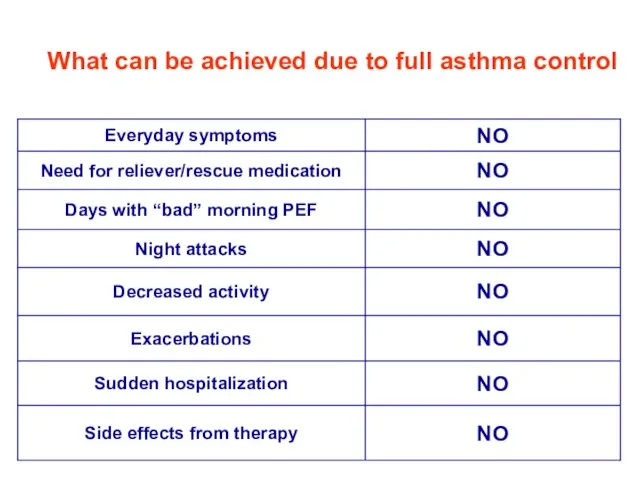
- 32. What can be achieved due to full asthma control
- 33. Classification of Asthma severity Протокол по лечению и диагностке астмы у детей GINA 2003
- 34. The goal of asthma treatment is to achieve and maintain clinical control Treatment of asthma is
- 35. Step approach of BA treatment means increasing of medication according to severity of asthma. Physician can
- 36. BA treatment in acute period: Termination of the contact with allergen Oxygen therapy Inhaled В2-adrenomymetics (salbutamol
- 37. Medications for basic BA therapy Cromoglycium acid derivates Glucocorticosteroids (systemic, inhaled) Long acting inhaled b2-agonists Leukotriene
- 38. Antiinflammatory medications- derivates of cromoglycium acid Inhibit mast cells degranulation process Retard IgE- linked secretion of
- 39. Derivates of cromoglycium acid Mast cells membranes stabilizers: cromoglycium acid (intal,chromohexal,chromogenum) Nedocromyl sodium (tailed,tailed-mint)
- 40. Inhaled corticosteroids Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) has the most manifested anti-inflammatory activity Reduce BA symptoms Decrease quantity
- 41. Systemic corticosteroids (hydrocortisone,dexamethasone, methylprednisolone, prednisolone, polcortolone) Inhaled corticosteroids Beclomethasone (becodisk, becotide, aldecine ) Fluticasone propionate (seretide,
- 42. Leukotriene modifiers Acolad (Zaferlucast) Singular (Montelucast)
- 43. Long acting b-2-agonistsагонисты: Salmeterol (Serevent,Serevent rotadisk) Clenbutirole (Spiropent) Formoterol (Formoteroloxis, Foradil)
- 44. Reliever Medications Broncholytic medications (bronchospasmolytics) Short acting b –adrenomymetics Salbutamol ( ventolin- nebulas,ventolin, bolmax, salomol, salben,
- 45. Reliever Medication Methylxantines (euphylline, theophylline) M-cholynoblockers - Ipratropium bromide (Atrovent)
- 46. Combined medications: Phenoterol + Ipratropium bromide = berodual Salbutamol + Ipratropium bromide = combivent Cromoglycate sodium
- 47. Medications for Nebulizer therapy Nebulizer – is inhalation device for spraying aerosol into very small disperse
- 48. The main goal of nebulizer therapy Delivering of medication therapeutic dosage in aerosol form Gaining of
- 49. Indications for nebulizer therapy It is used for intensive care in obstructive lung diseases, changed secretory
- 50. Advantages of nebulizer treatment It isn’t necessary coordinate respiratory with aerosole puffs Possibility to use high
- 51. Medications for nebulizer therapy Ventolin ( in nebulas 2,5 ml/2,5 mg nondeluted form) Berodual (solution for
- 52. Allergen specific immunotherapy Nowadays this method is the most effective treatment because of opportunity to influence
- 53. To decrease efficacy of BA therapy Educational programs ( for affected children and their parents in
- 54. Key statements of BA treatment The most efficient BA treatment is causative allergen elimination Asthma can
- 56. Скачать презентацию





































 Дискинезии желчевыводящих путей у детей
Дискинезии желчевыводящих путей у детей Врожденные аномалии роговицы
Врожденные аномалии роговицы Рак шейки матки
Рак шейки матки Эхинококкоз
Эхинококкоз Электроэнцефалография: применение в практике
Электроэнцефалография: применение в практике Противоаллергические ЛС, иммунотропные ЛС, биостимуляторы
Противоаллергические ЛС, иммунотропные ЛС, биостимуляторы Влияние алкоголя на ребенка в период беременности
Влияние алкоголя на ребенка в период беременности Патологиялық анатомия
Патологиялық анатомия Медицинское страхование
Медицинское страхование Атрезия пищевода и пилоростеноз
Атрезия пищевода и пилоростеноз Роль кожи в терморегуляции. Гигиена кожи
Роль кожи в терморегуляции. Гигиена кожи Несостоятельность тазового дна
Несостоятельность тазового дна Синдром раздражённого кишечника
Синдром раздражённого кишечника Возбудители пищевых интоксикаций
Возбудители пищевых интоксикаций Медико-демографические показатели населения Горноуральского городского округа
Медико-демографические показатели населения Горноуральского городского округа Телекоммуникационные системы в медицине. (Лекция 7)
Телекоммуникационные системы в медицине. (Лекция 7) Кардиогенный шок и его причины
Кардиогенный шок и его причины Митральный стеноз
Митральный стеноз Санитарно-гигиенические обработка больных
Санитарно-гигиенические обработка больных Рецепт: структура, правила выписывания и отпуска лекарственных средств
Рецепт: структура, правила выписывания и отпуска лекарственных средств ДВС-синдром (диссеминированное внутрисосудистое свёртывание) у беременных. Геморагический шок. Эмболия околоплодными водами
ДВС-синдром (диссеминированное внутрисосудистое свёртывание) у беременных. Геморагический шок. Эмболия околоплодными водами Инструментальные методы исследования в работе врача общей практики (семейного врача). Электрокардиография. Нормальная ЭКГ
Инструментальные методы исследования в работе врача общей практики (семейного врача). Электрокардиография. Нормальная ЭКГ Болезни и травмы органов дыхания
Болезни и травмы органов дыхания Правила предупреждения заражения глистами
Правила предупреждения заражения глистами Тромбофилия в кардиологической практике
Тромбофилия в кардиологической практике Сахарный диабет у детей
Сахарный диабет у детей Око. Будова ока
Око. Будова ока Грипп и другие острые респираторные вирусные инфекции
Грипп и другие острые респираторные вирусные инфекции