Содержание
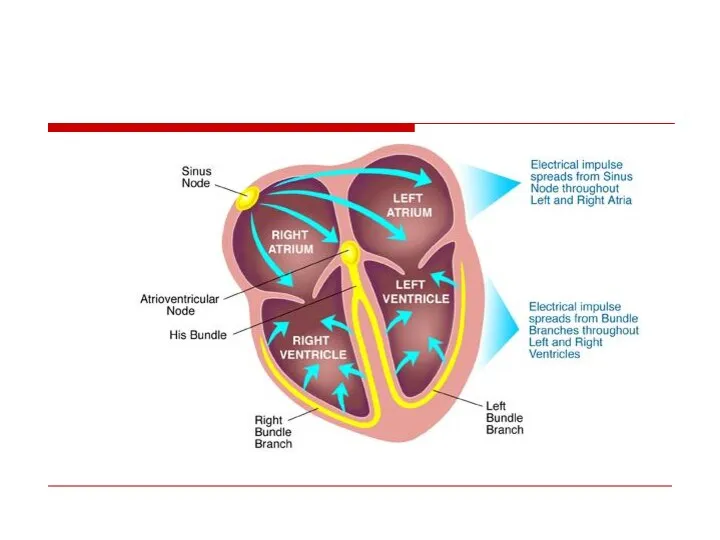
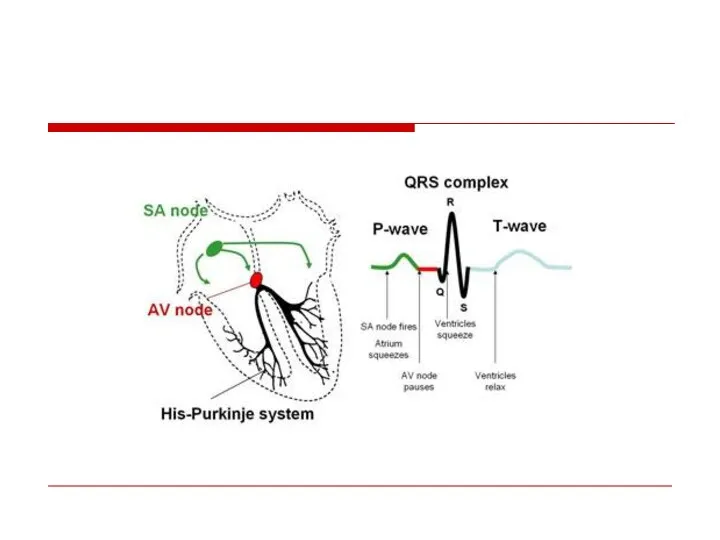
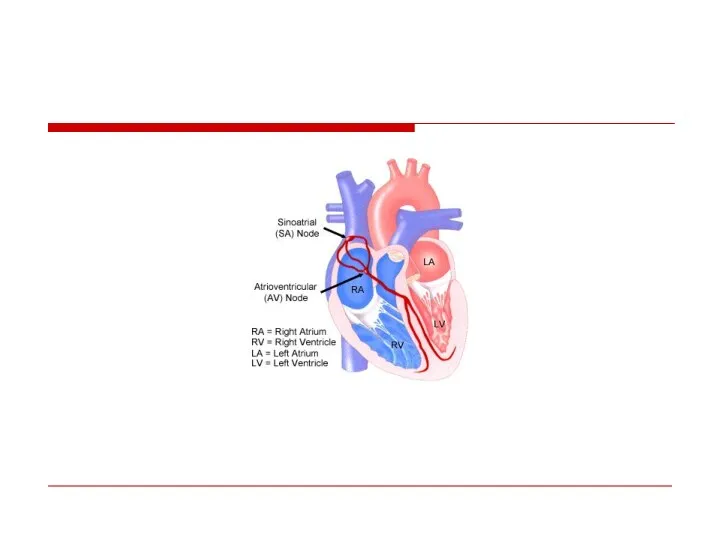
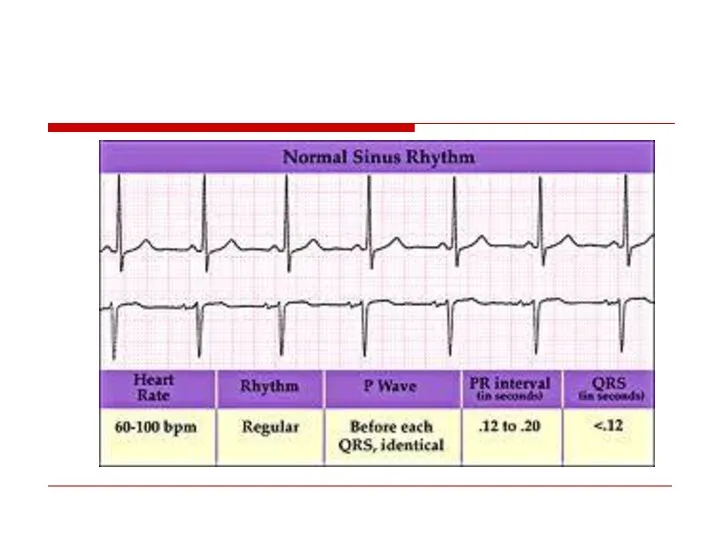
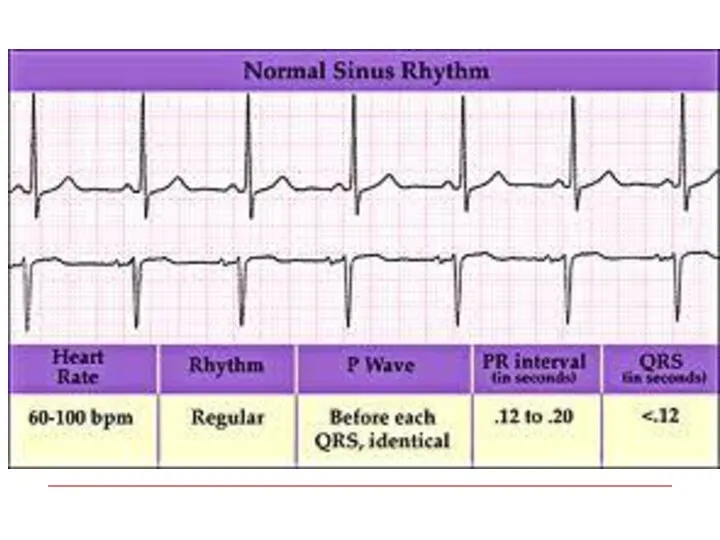
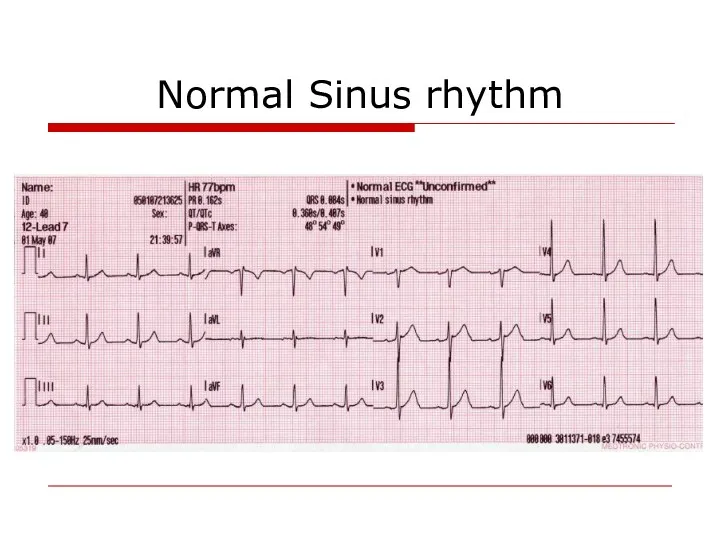
- 9. Normal Sinus rhythm
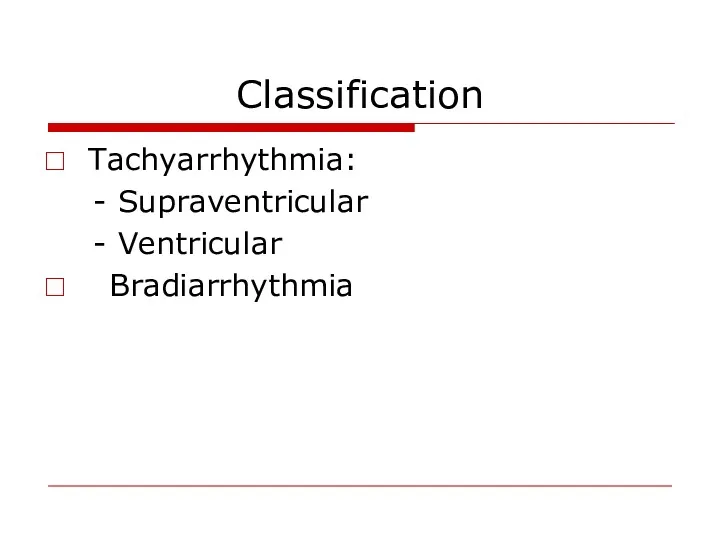
- 10. Classification Tachyarrhythmia: - Supraventricular - Ventricular Bradiarrhythmia
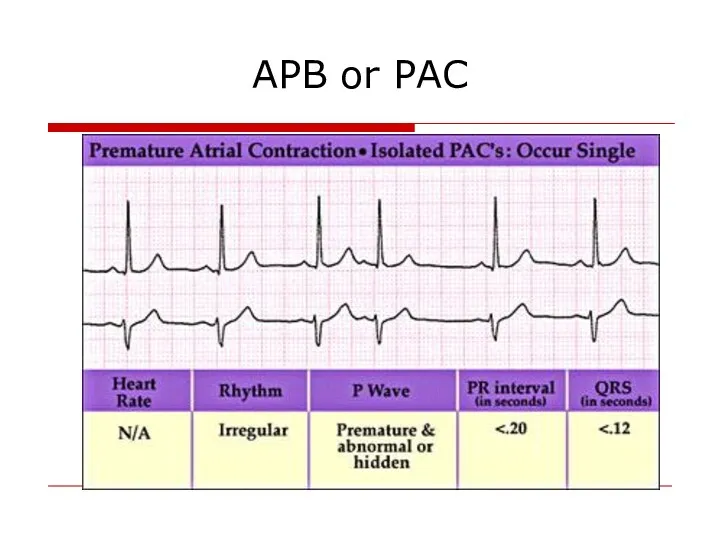
- 11. APB or PAC
- 12. Atrial Fibrillation The most common arrhythmia in clinical practice Frequency increases with age
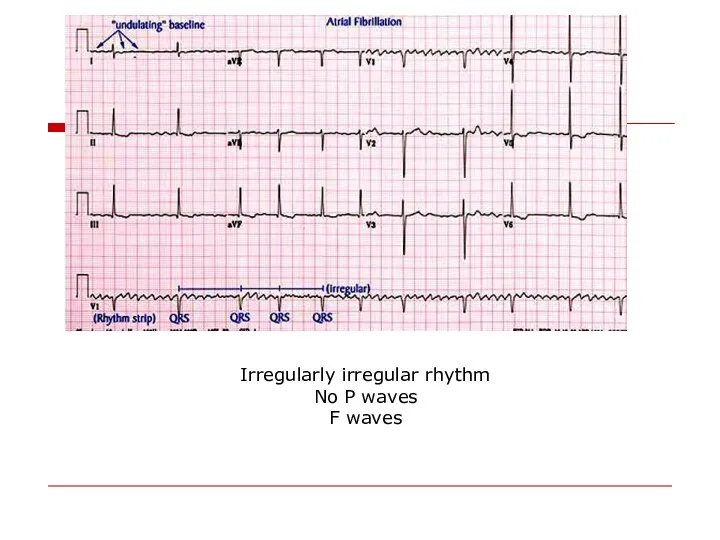
- 13. Irregularly irregular rhythm No P waves F waves
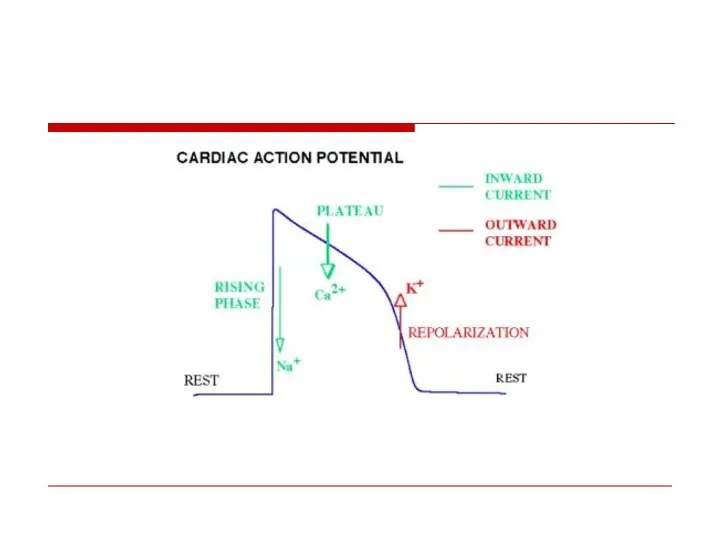
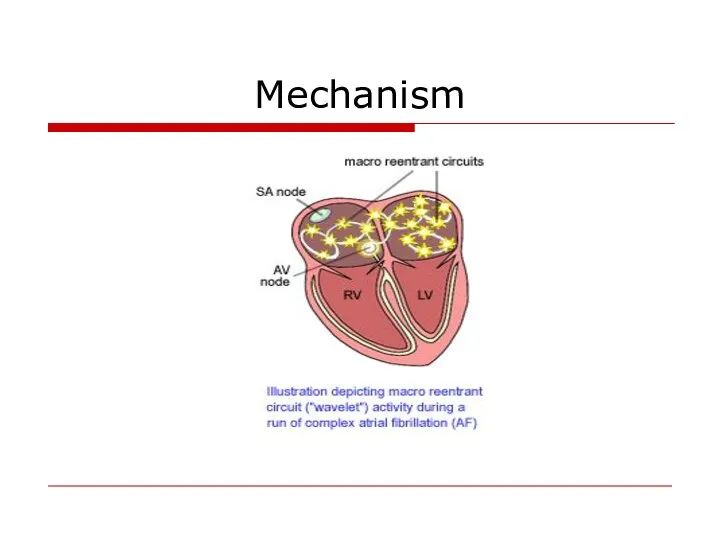
- 14. Mechanism
- 15. Most common causes Valvular heart disease: (MS,MR) LV hypertrophy (HTN, other cause) Cardiomyopathy Thyrotoxicosis Alcohol (“holiday
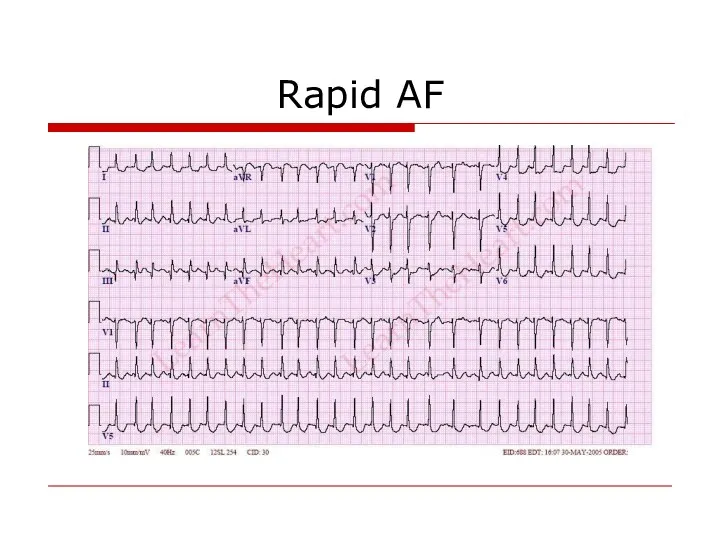
- 16. Rapid AF
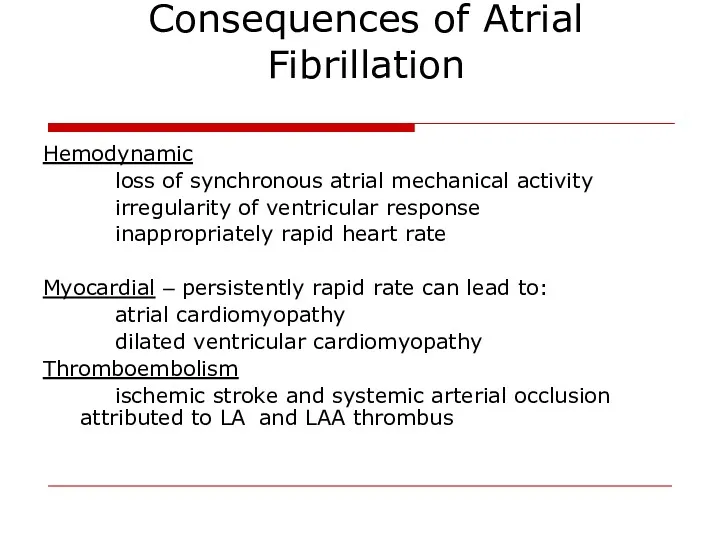
- 17. Consequences of Atrial Fibrillation Hemodynamic loss of synchronous atrial mechanical activity irregularity of ventricular response inappropriately
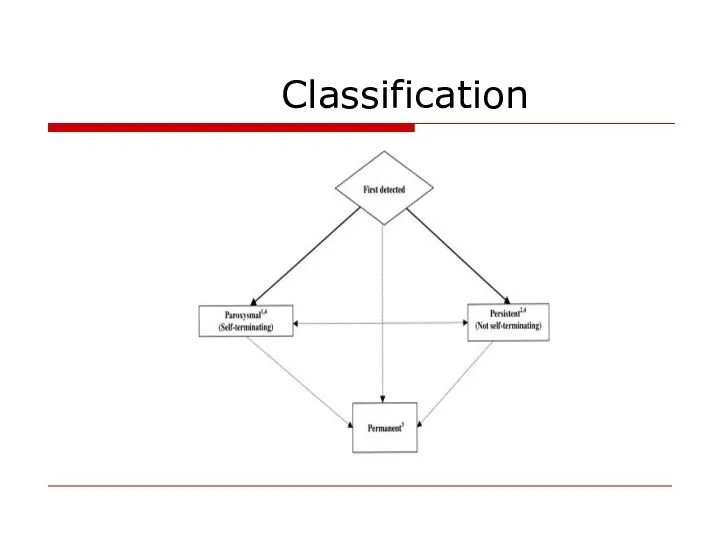
- 18. Classification
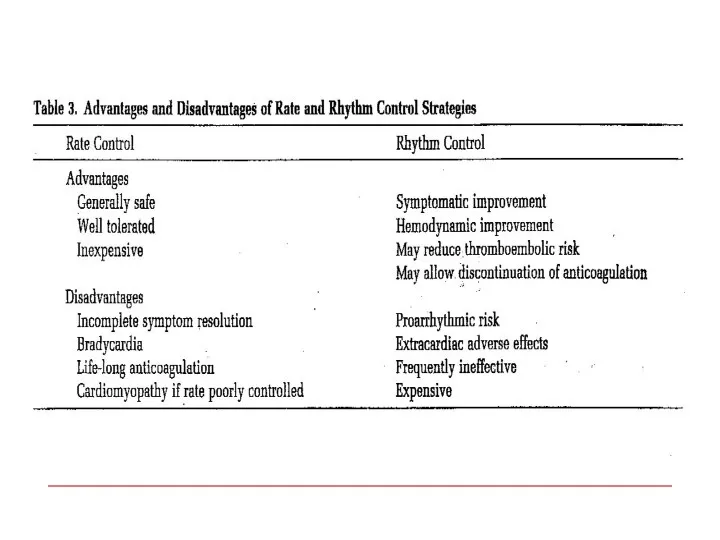
- 19. Treatment options 1. Rhythm control – restoration and maintenance of sinus rhythm 2. Rate control Prevention
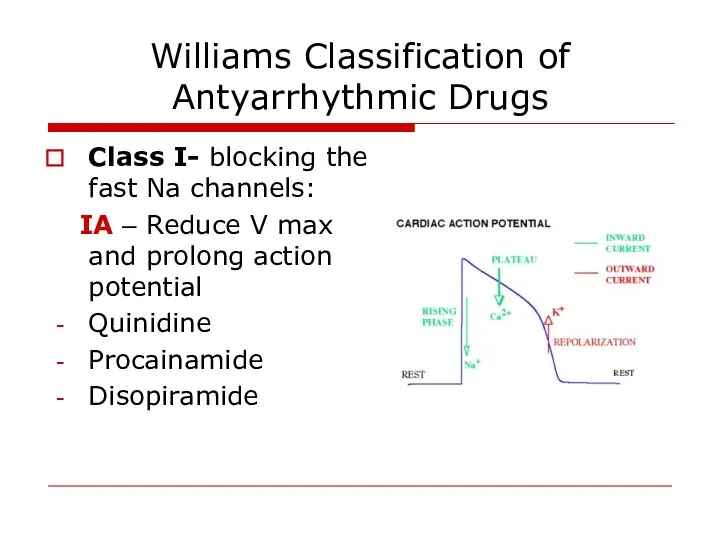
- 20. Williams Classification of Antyarrhythmic Drugs Class I- blocking the fast Na channels: IA – Reduce V
- 21. IB : Do not reduce V max and shorten action potential duration Lidocaine Phenytoin Mexiletine IC:
- 22. Class II – beta blockers Class III – K channel blockers - Amiodaron - Sotalol -
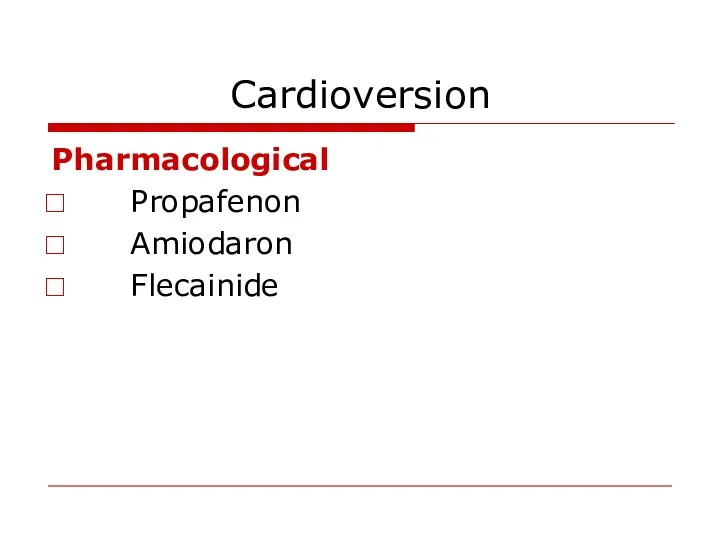
- 23. Cardioversion Pharmacological Propafenon Amiodaron Flecainide
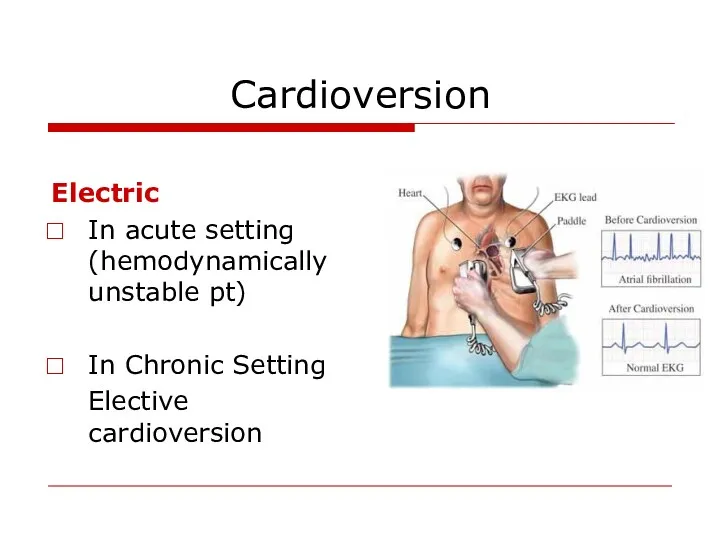
- 24. Cardioversion Electric In acute setting (hemodynamically unstable pt) In Chronic Setting Elective cardioversion
- 25. Predictors of successful cardioverson Short AF duration Young age Normal atrial size No organic heart pathology
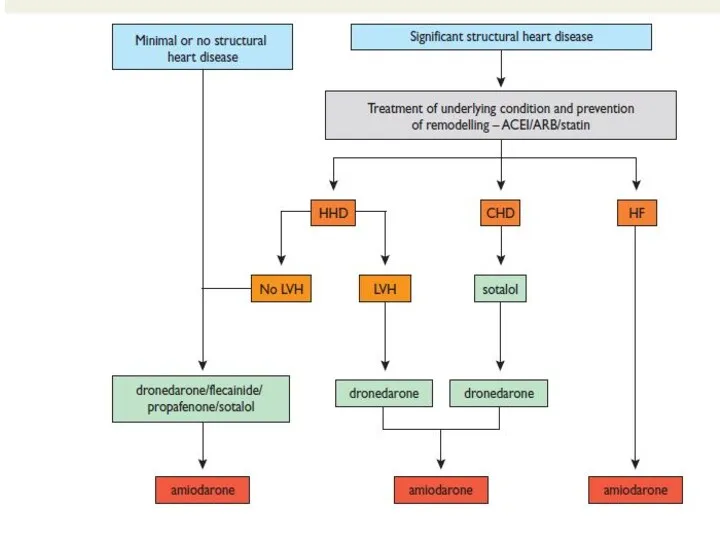
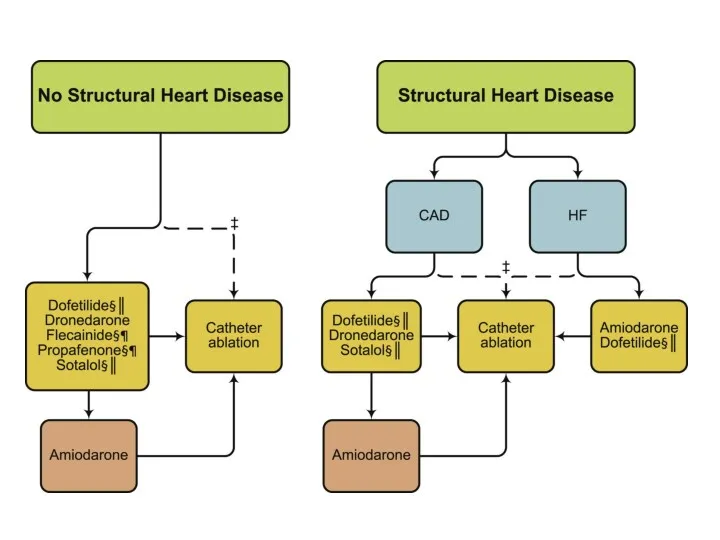
- 26. Maintenance of sinus rhythm Propafenon Amiodaron Dronedaron Sotalol Flecainide
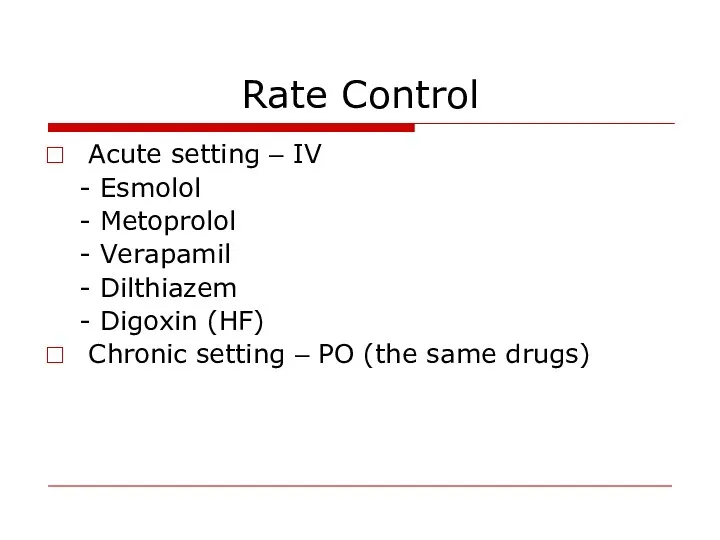
- 29. Rate Control Acute setting – IV - Esmolol - Metoprolol - Verapamil - Dilthiazem - Digoxin
- 31. – Severe symptoms due to AF – Patients with CHF – Younger patients – Patients with
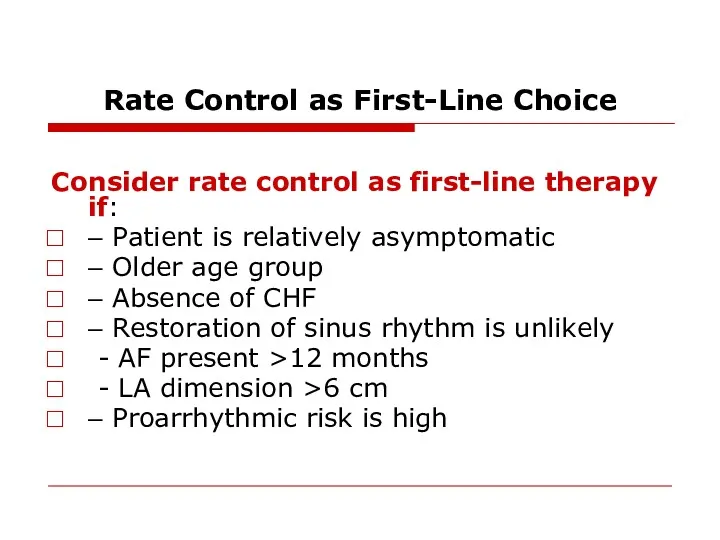
- 32. Rate Control as First-Line Choice Consider rate control as first-line therapy if: – Patient is relatively
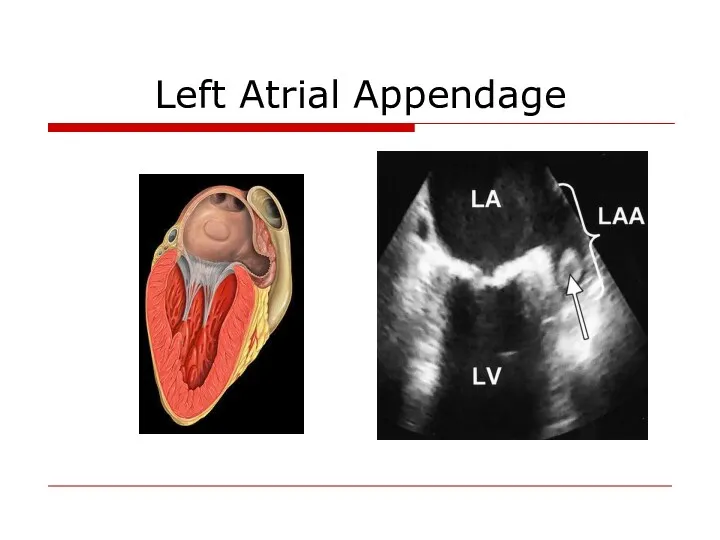
- 33. Left Atrial Appendage
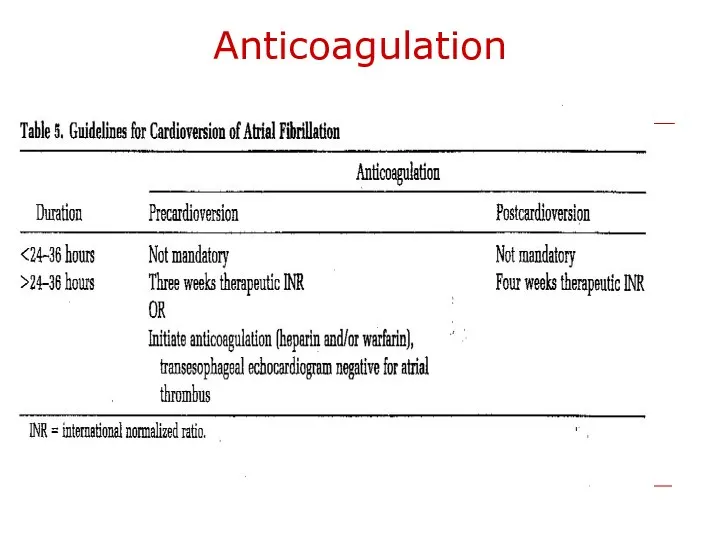
- 34. Anticoagulation
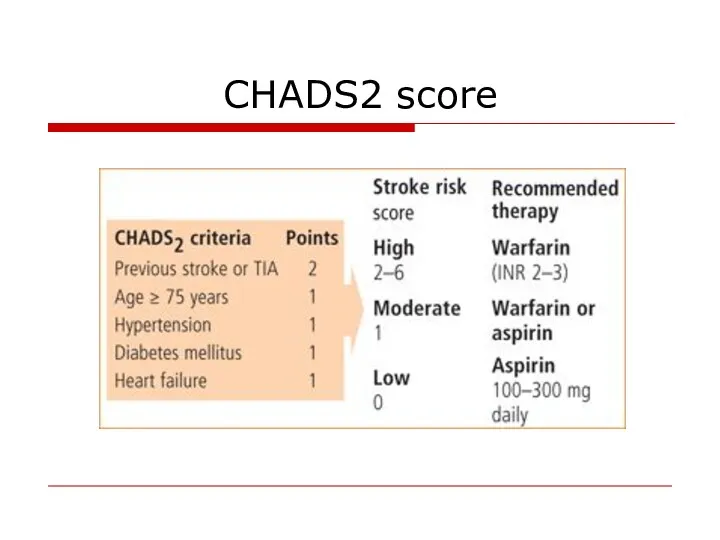
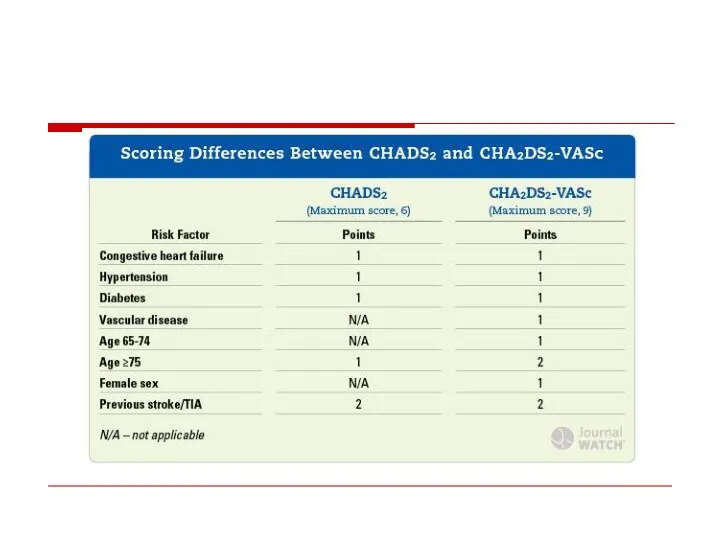
- 35. CHADS2 score
- 37. Novel Oral Anticoagulants Dabigatran (Pradaxa)- direct oral thrombin inhibitor Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)– direct oral factor Xa inhibitor
- 38. Invasive AF treatment
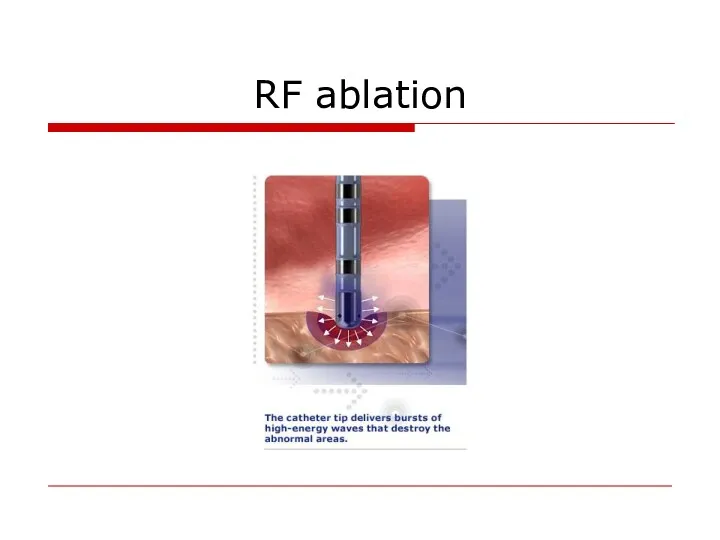
- 39. RF ablation
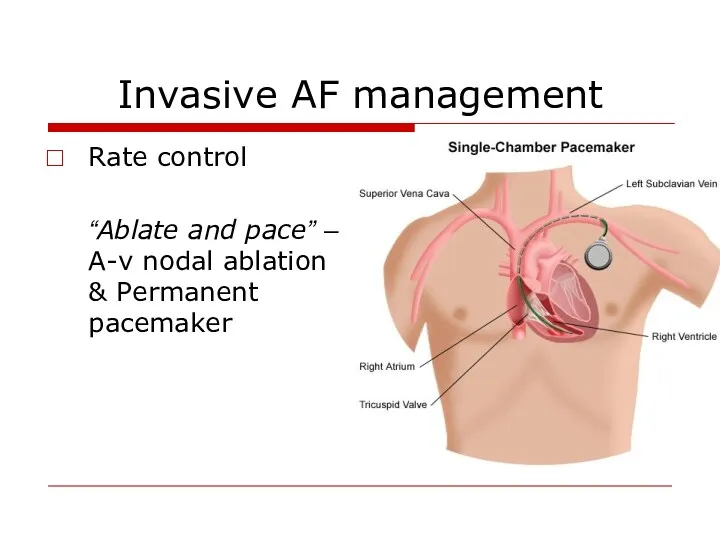
- 40. Invasive AF management Rate control “Ablate and pace” – A-v nodal ablation & Permanent pacemaker
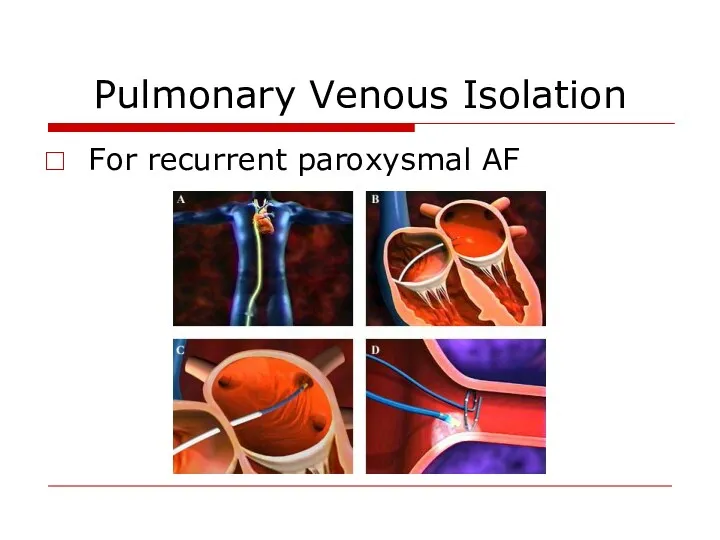
- 41. Pulmonary Venous Isolation For recurrent paroxysmal AF
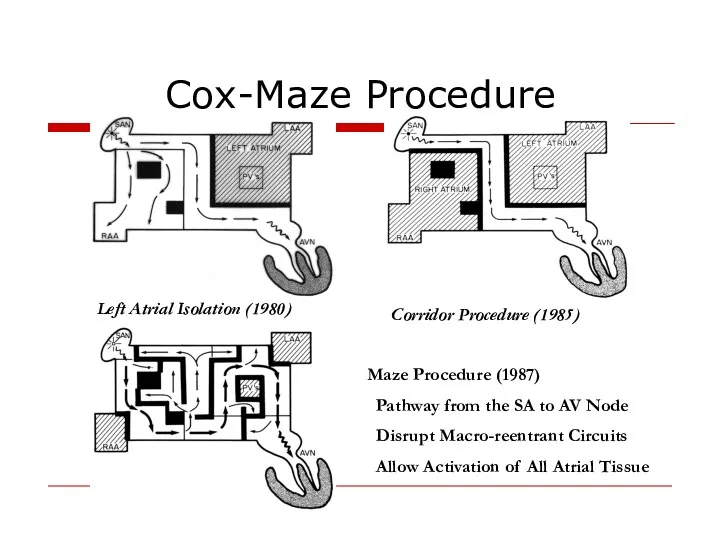
- 42. Cox-Maze Procedure Left Atrial Isolation (1980) Corridor Procedure (1985) Maze Procedure (1987) Pathway from the SA
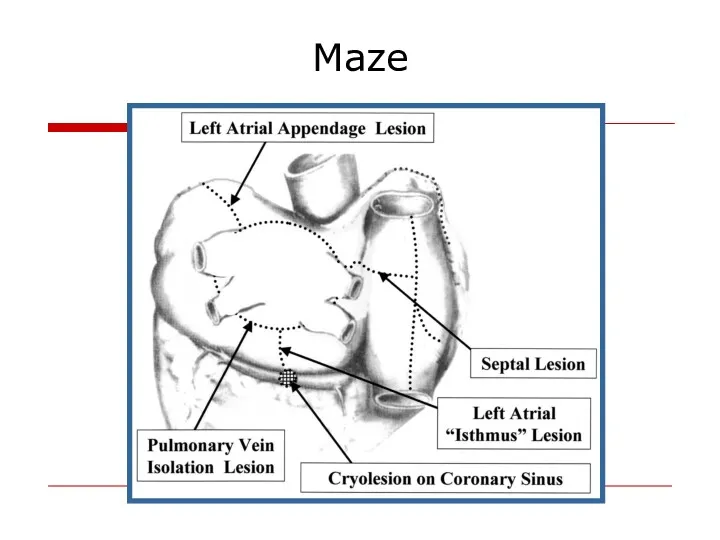
- 43. Maze
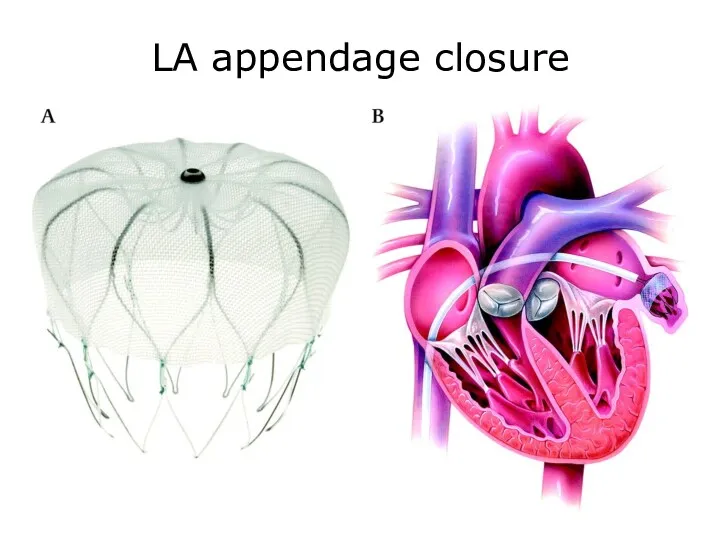
- 44. LA appendage closure
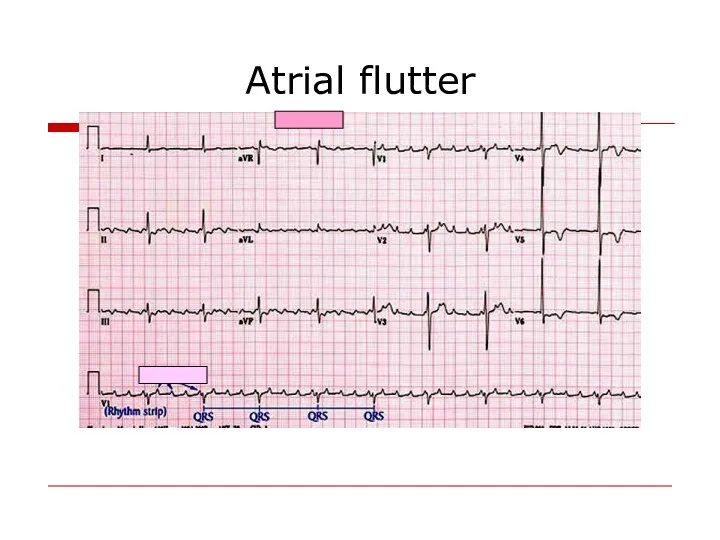
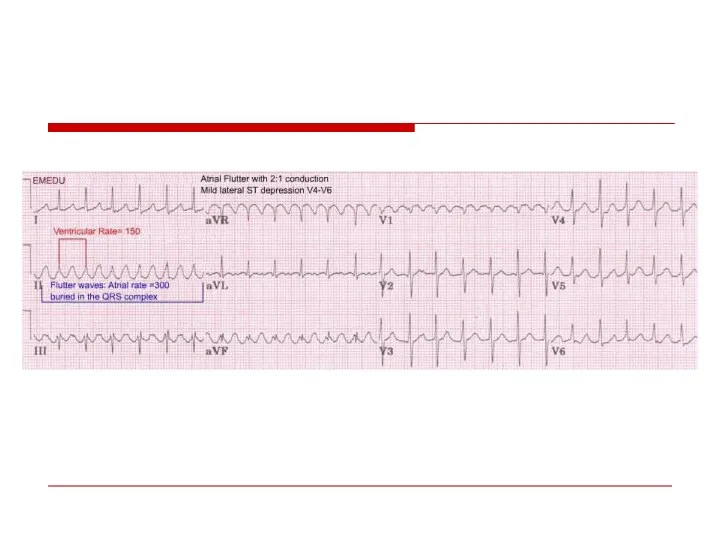
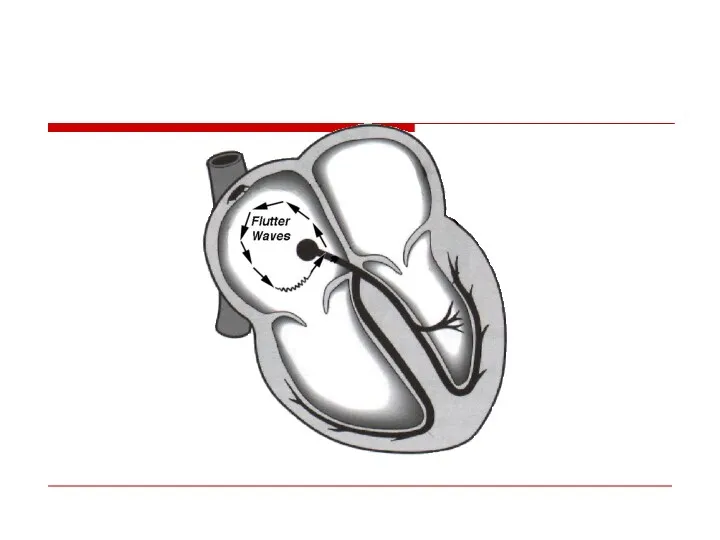
- 45. Atrial flutter
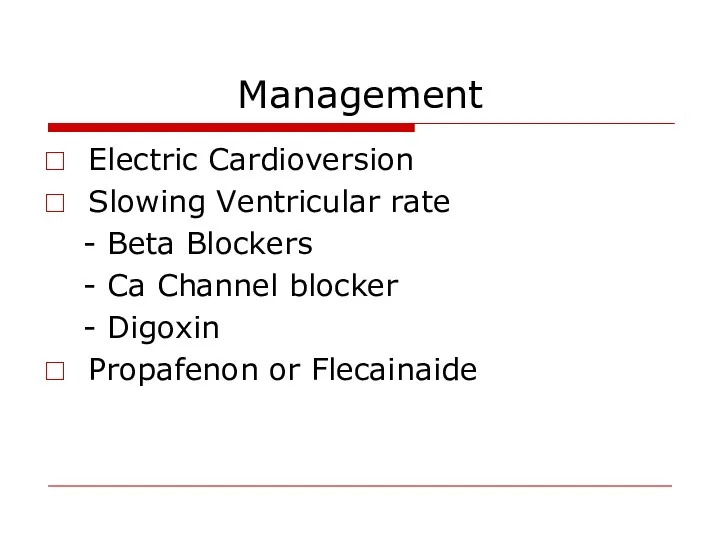
- 48. Management Electric Cardioversion Slowing Ventricular rate - Beta Blockers - Ca Channel blocker - Digoxin Propafenon
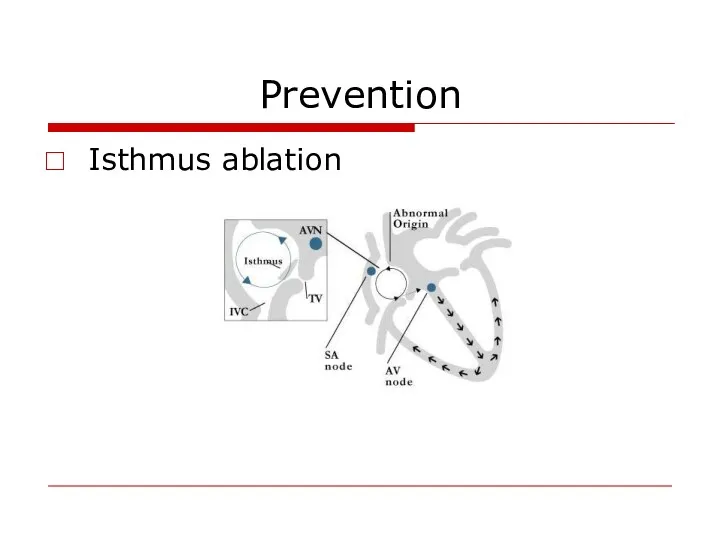
- 49. Prevention Isthmus ablation
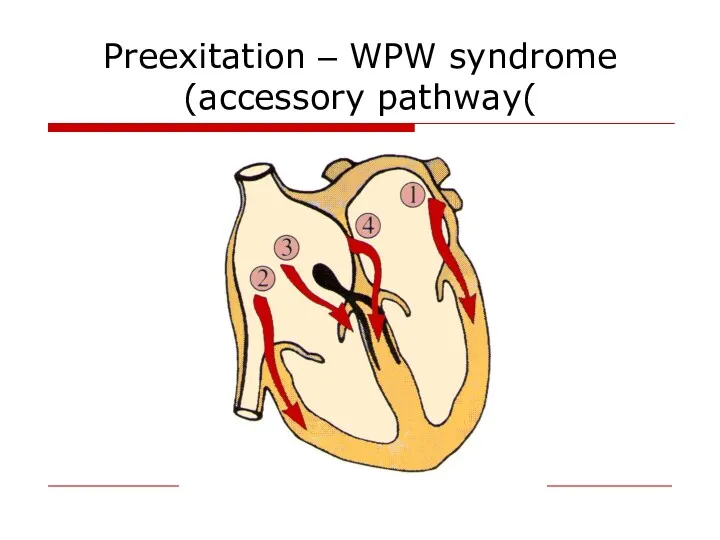
- 50. Preexitation – WPW syndrome (accessory pathway(
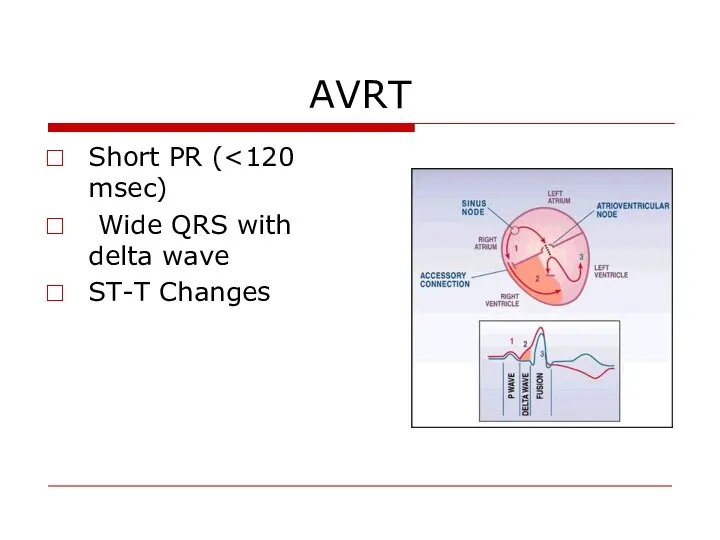
- 51. AVRT Short PR ( Wide QRS with delta wave ST-T Changes
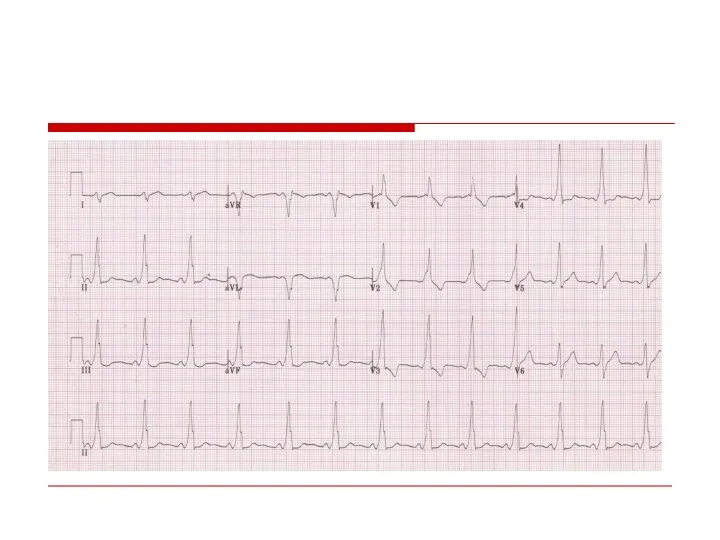
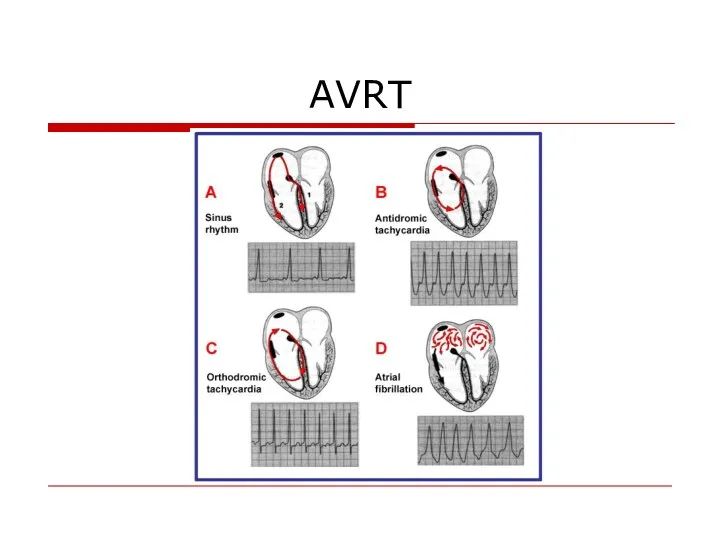
- 53. AVRT
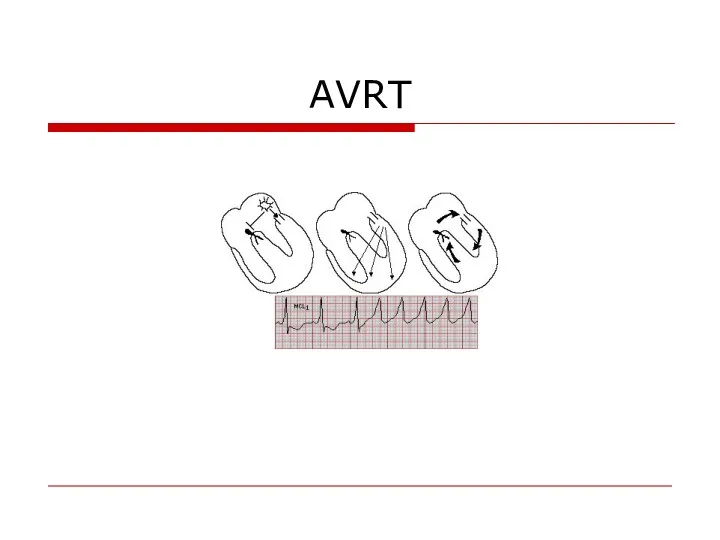
- 54. AVRT
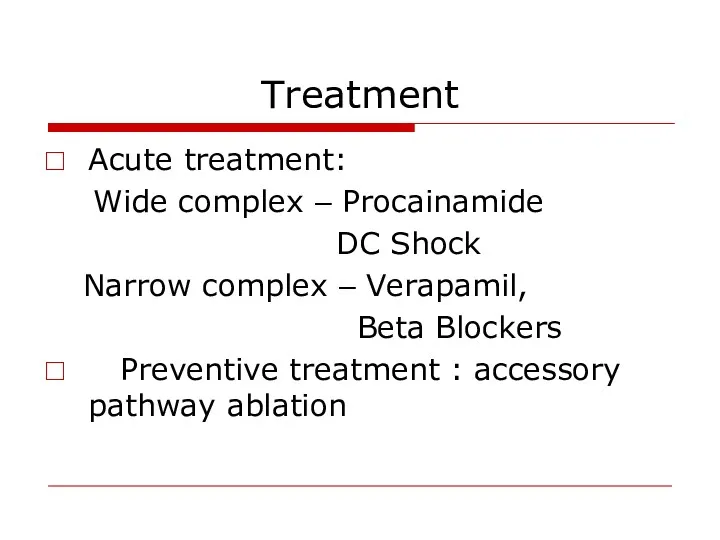
- 55. Treatment Acute treatment: Wide complex – Procainamide DC Shock Narrow complex – Verapamil, Beta Blockers Preventive
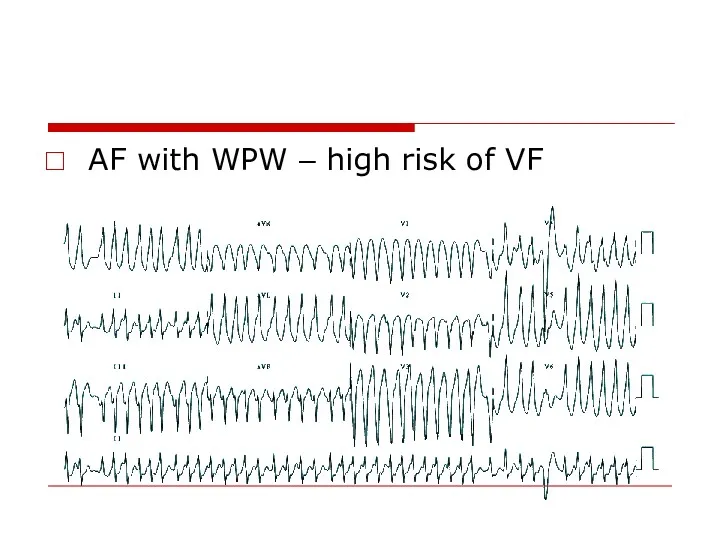
- 56. AF with WPW – high risk of VF
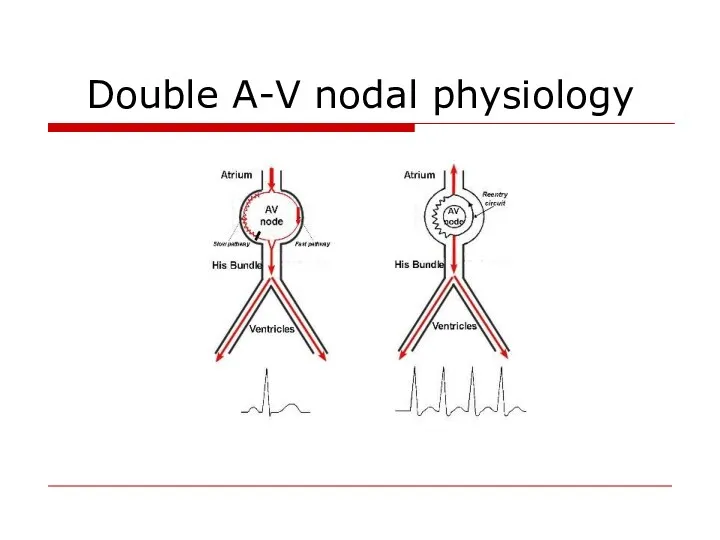
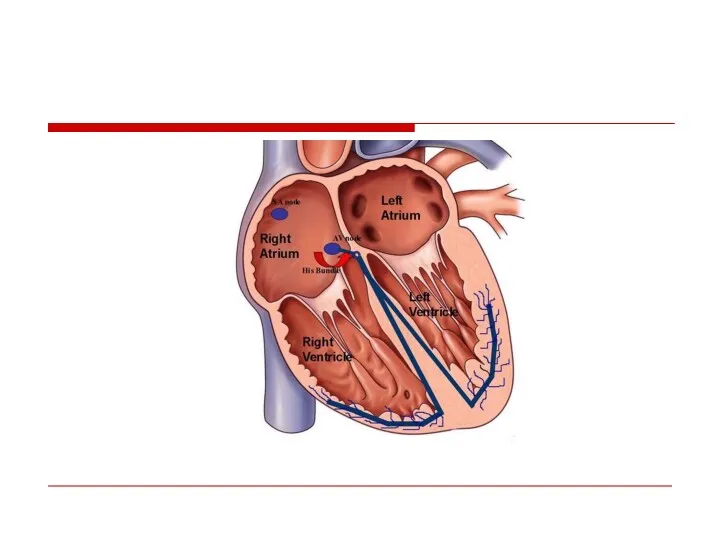
- 57. Double A-V nodal physiology
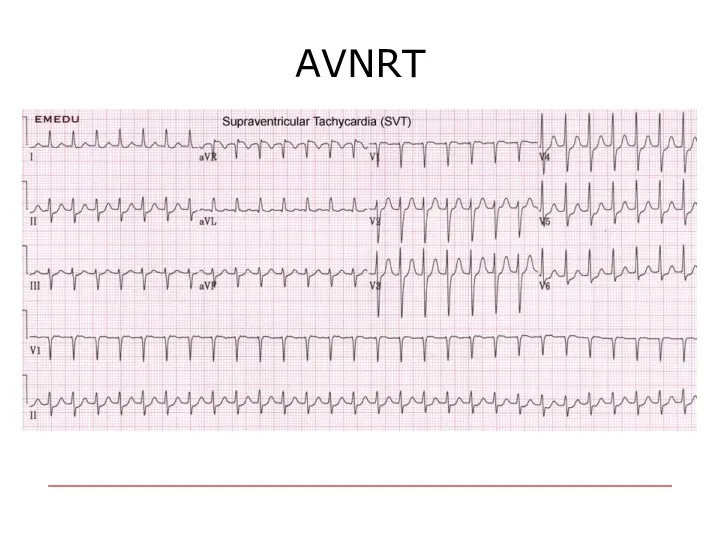
- 59. AVNRT
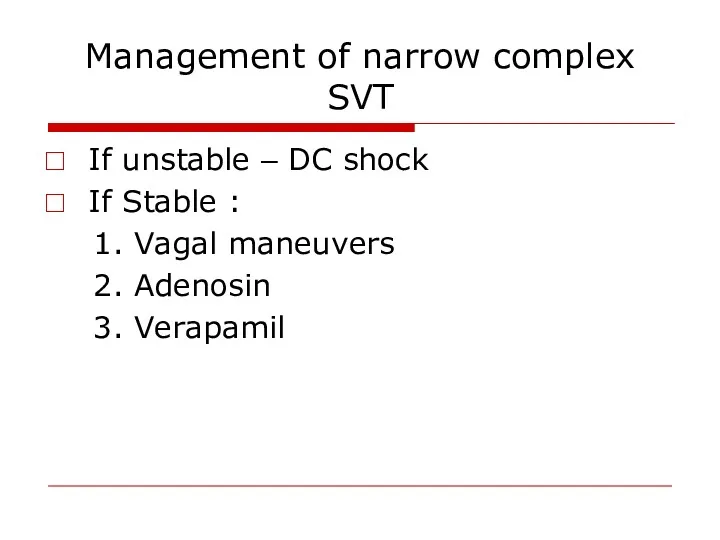
- 60. Management of narrow complex SVT If unstable – DC shock If Stable : 1. Vagal maneuvers
- 61. Preventive treatment Drugs EPS
- 62. Ventricular Arrhythmias
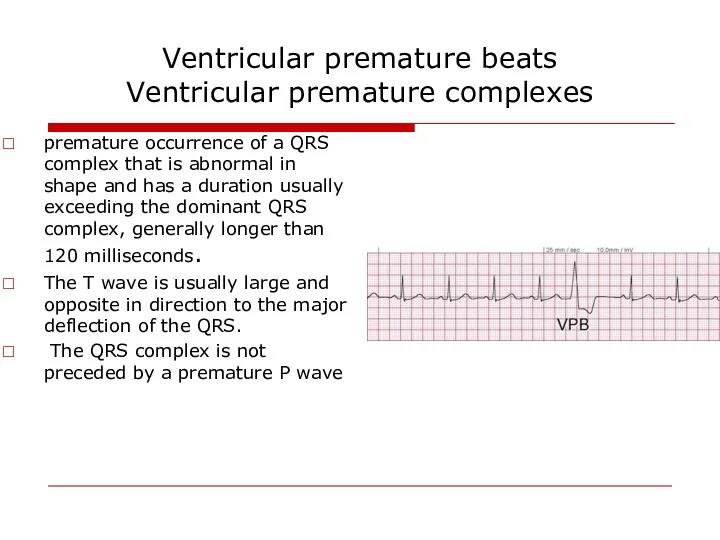
- 63. Ventricular premature beats Ventricular premature complexes premature occurrence of a QRS complex that is abnormal in
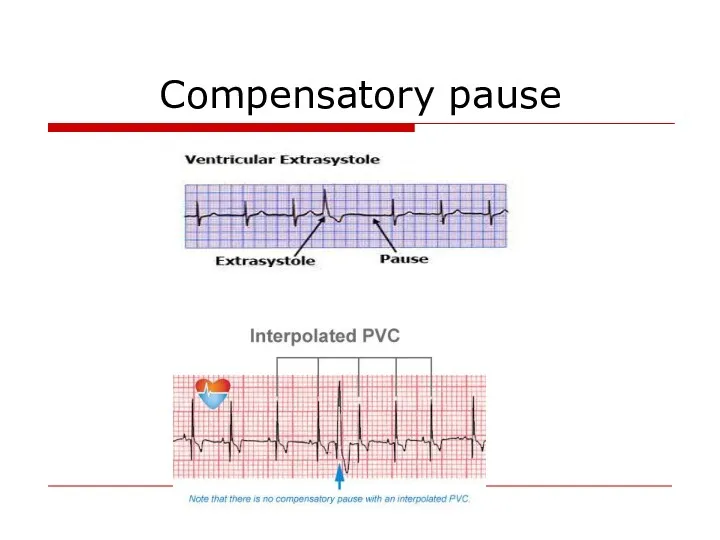
- 64. Compensatory pause
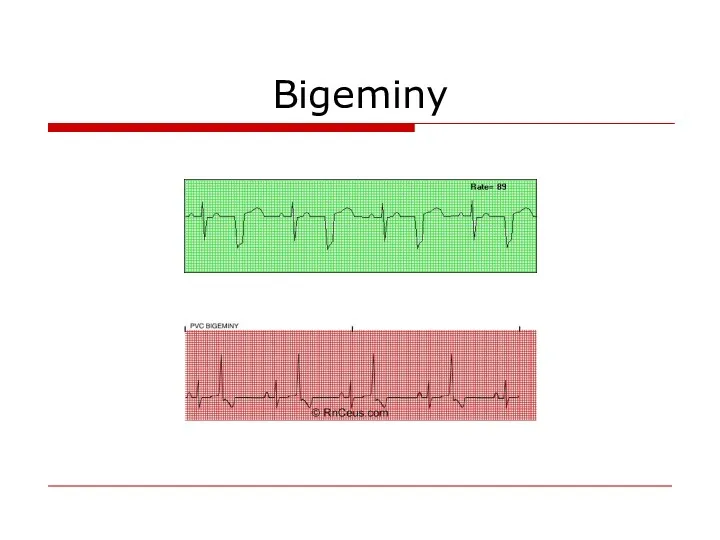
- 65. Bigeminy
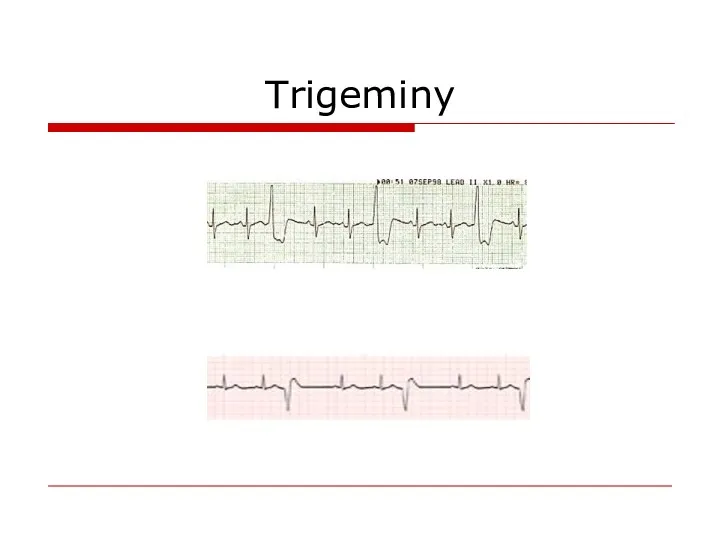
- 66. Trigeminy
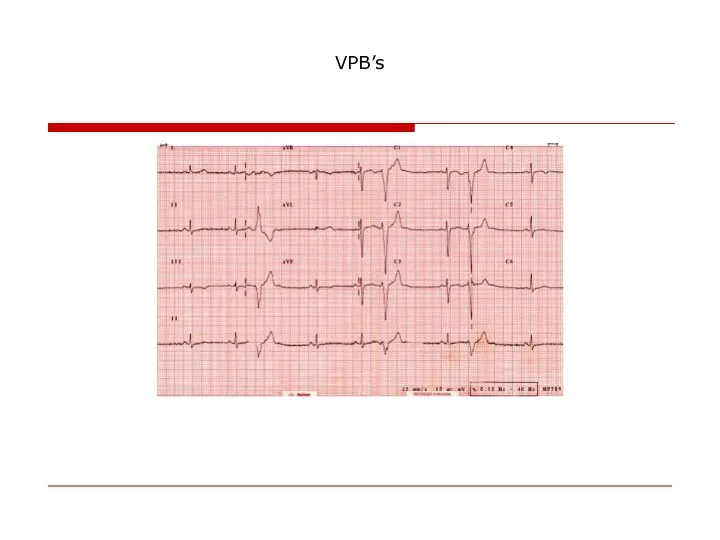
- 67. VPB’s
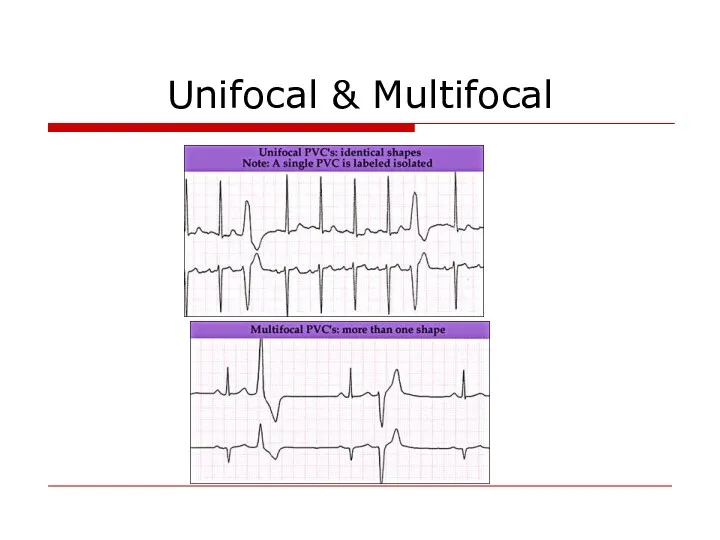
- 68. Unifocal & Multifocal
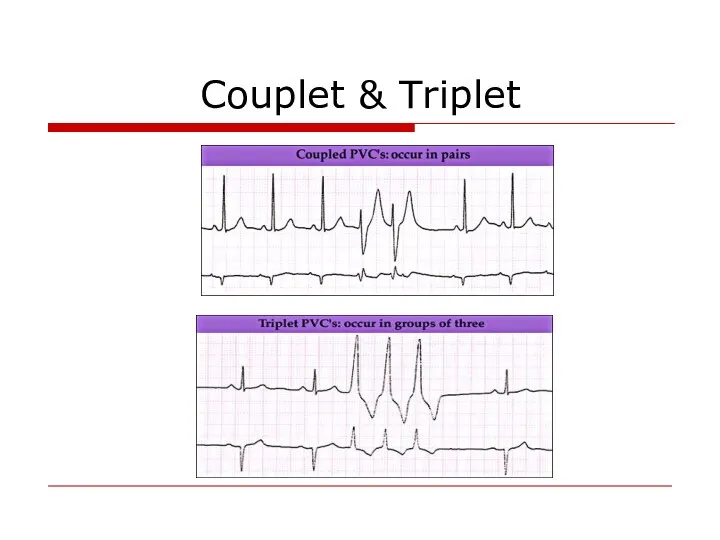
- 69. Couplet & Triplet
- 70. Causes LV false tendons, infection in ischemic or inflamed myocardium, hypoxia, Anesthesiaor surgery. Medications electrolyte imbalance,
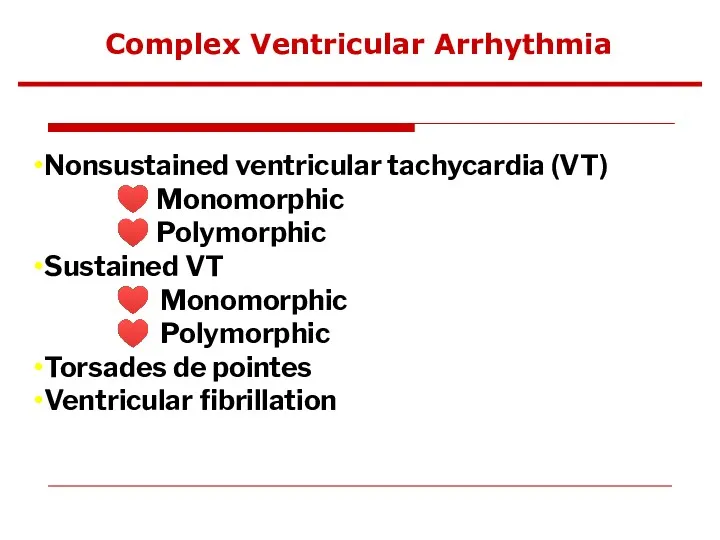
- 71. Complex Ventricular Arrhythmia Nonsustained ventricular tachycardia (VT) ♥ Monomorphic ♥ Polymorphic Sustained VT ♥ Monomorphic ♥
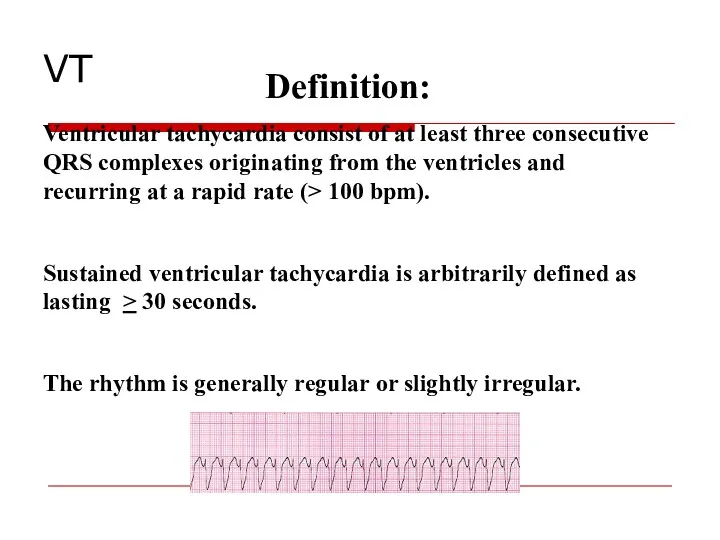
- 72. Definition: Ventricular tachycardia consist of at least three consecutive QRS complexes originating from the ventricles and
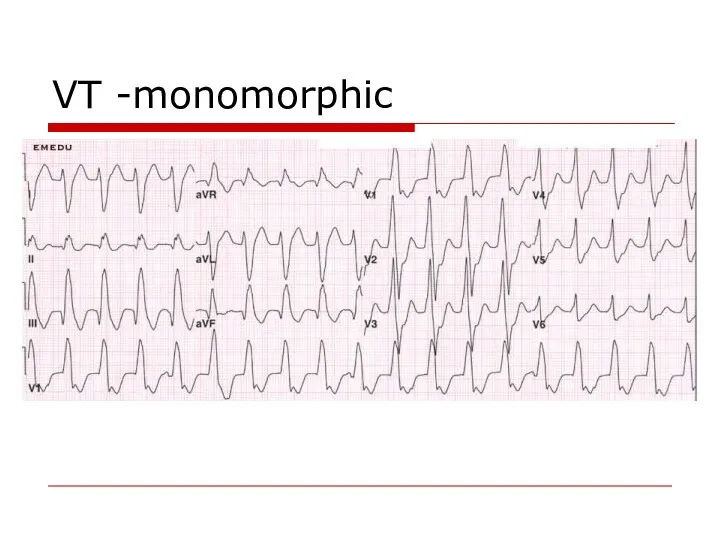
- 73. VT -monomorphic
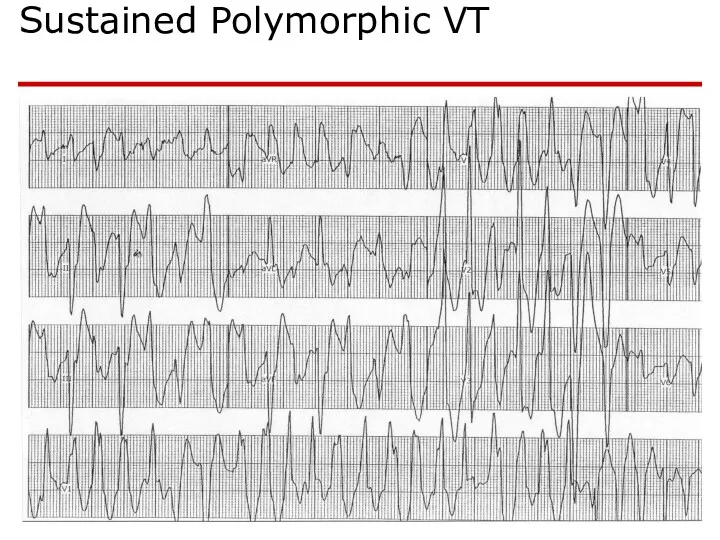
- 74. Sustained Polymorphic VT
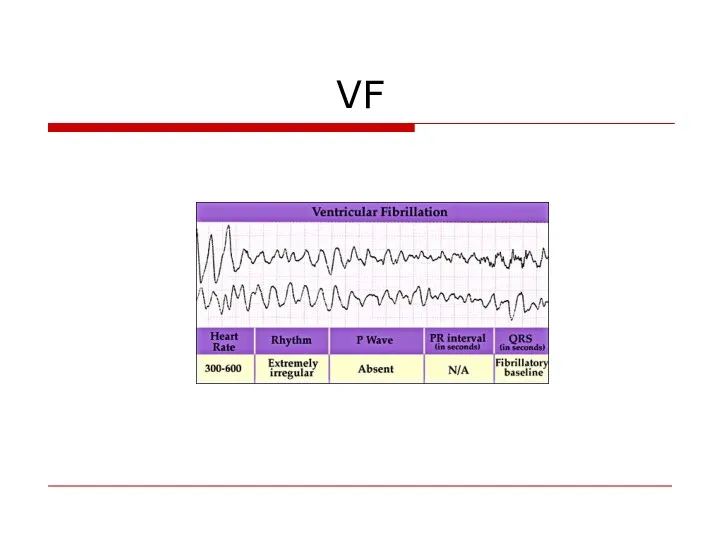
- 75. VF
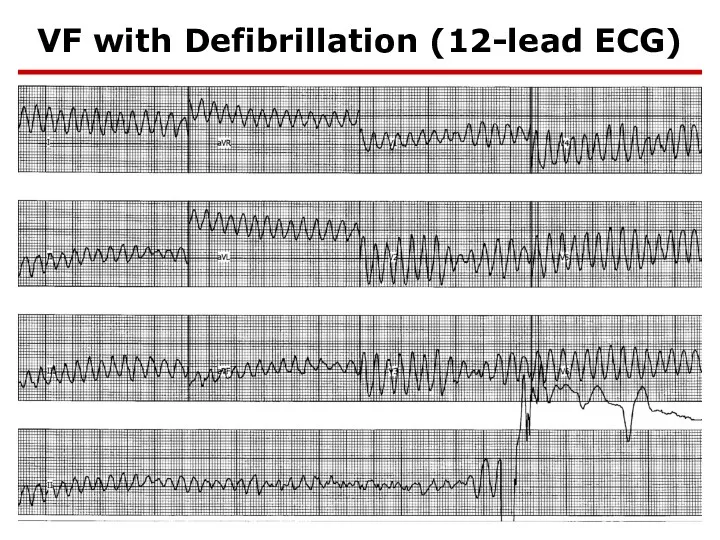
- 76. VF with Defibrillation (12-lead ECG)
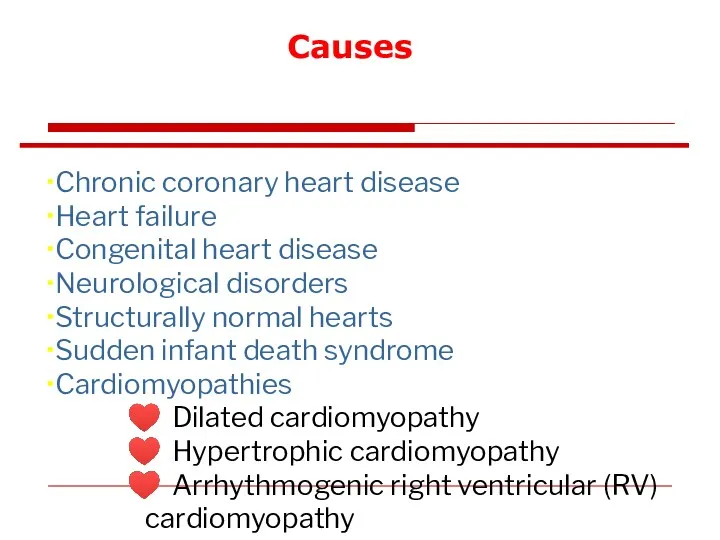
- 77. Causes Chronic coronary heart disease Heart failure Congenital heart disease Neurological disorders Structurally normal hearts Sudden
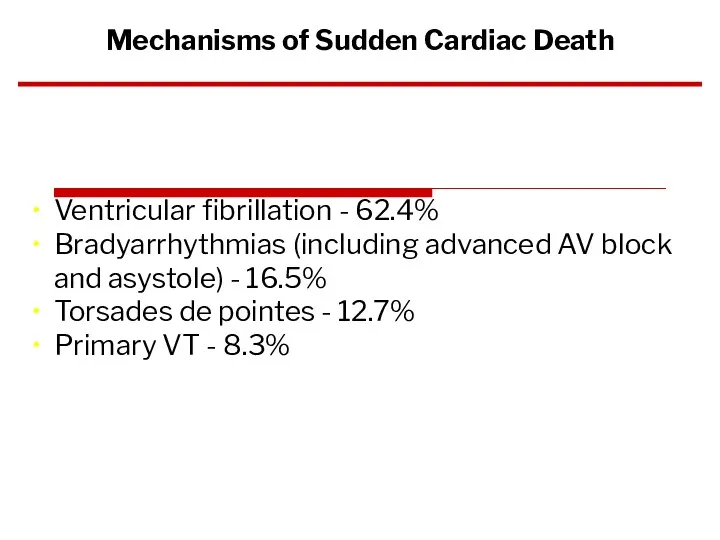
- 78. Ventricular fibrillation - 62.4% Bradyarrhythmias (including advanced AV block and asystole) - 16.5% Torsades de pointes
- 79. VA management Acute Chronic (secondary prevention)
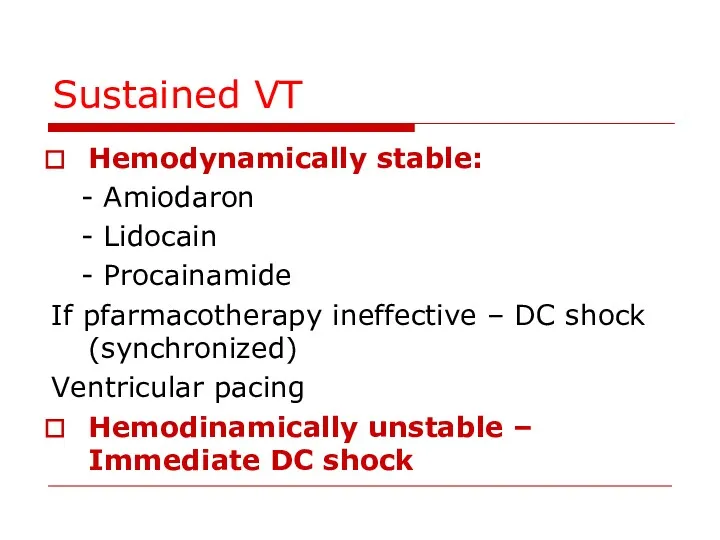
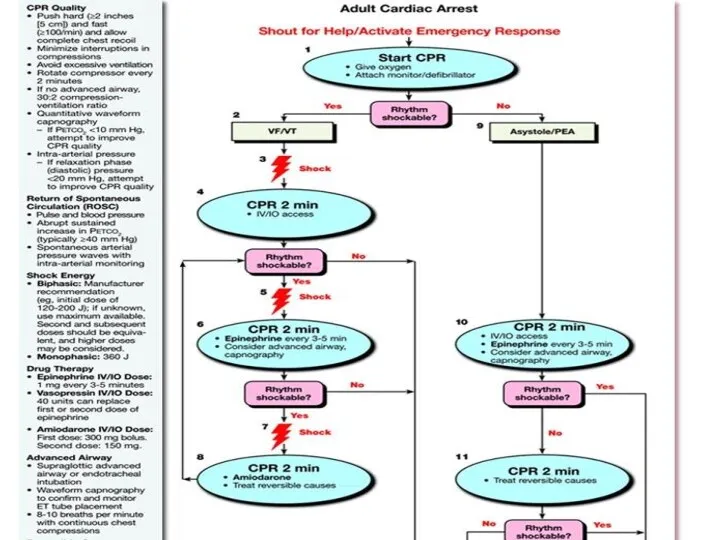
- 80. Sustained VT Hemodynamically stable: - Amiodaron - Lidocain - Procainamide If pfarmacotherapy ineffective – DC shock
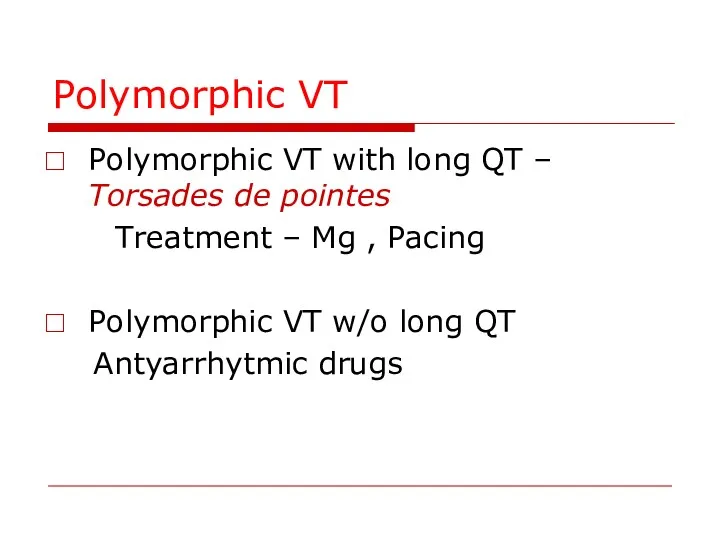
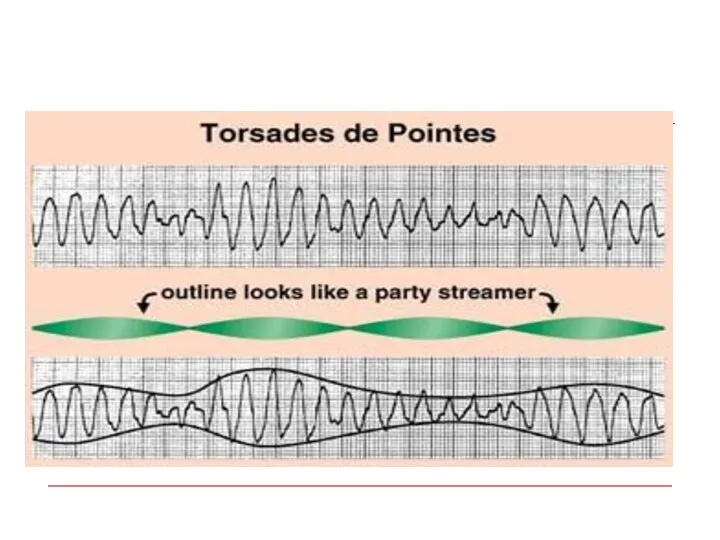
- 81. Polymorphic VT Polymorphic VT with long QT – Torsades de pointes Treatment – Mg , Pacing
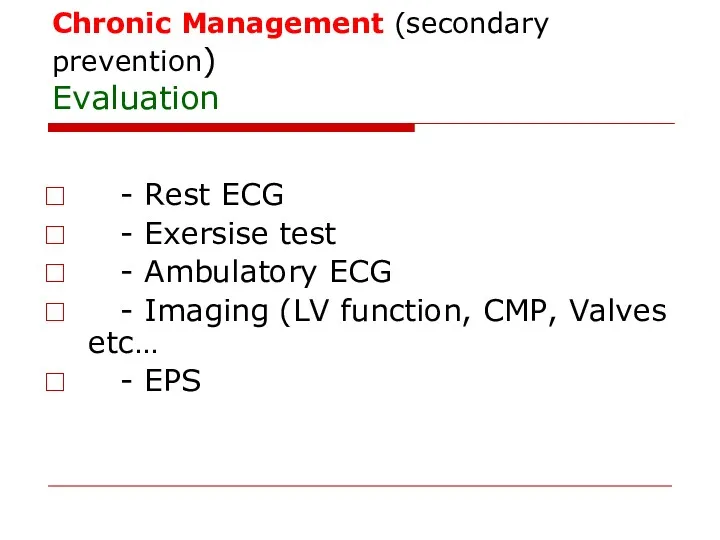
- 83. Chronic Management (secondary prevention) Evaluation - Rest ECG - Exersise test - Ambulatory ECG - Imaging
- 84. Treatment of the underlying disease Revascularisation Valve surgery CHD repair
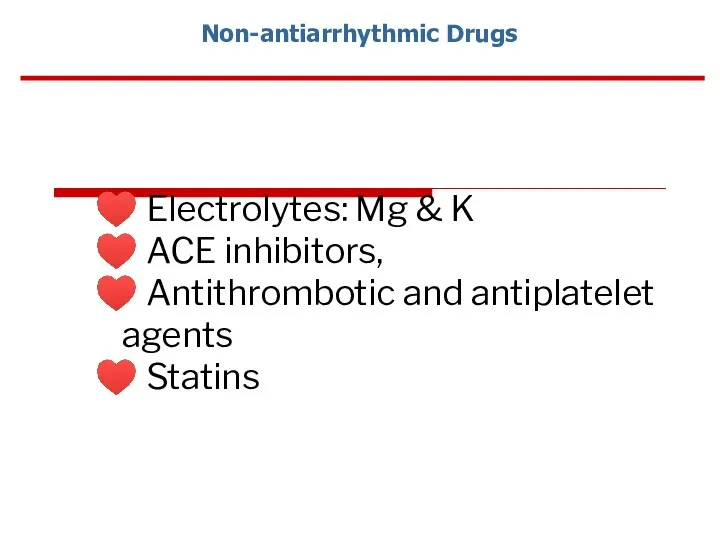
- 85. ♥ Electrolytes: Mg & K ♥ ACE inhibitors, ♥ Antithrombotic and antiplatelet agents ♥ Statins Non-antiarrhythmic
- 86. Antiarrhytmic drugs Antiarrhythmic drugs (except for BB) should not be used as primary preventive therapy of
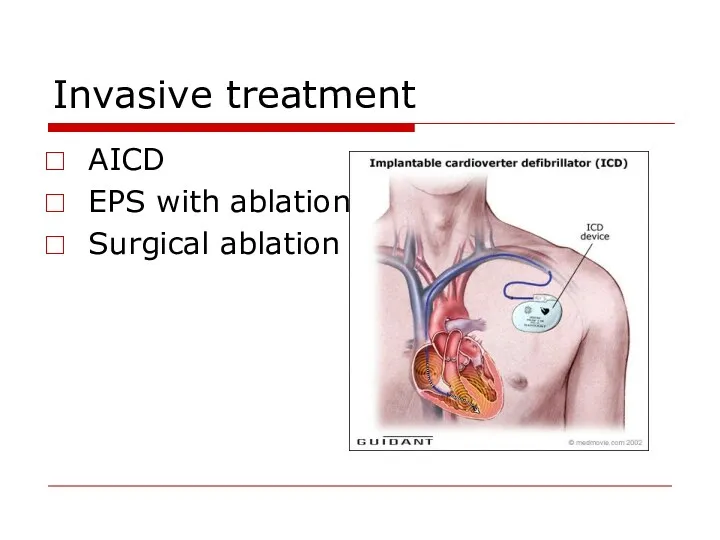
- 87. Invasive treatment AICD EPS with ablation Surgical ablation
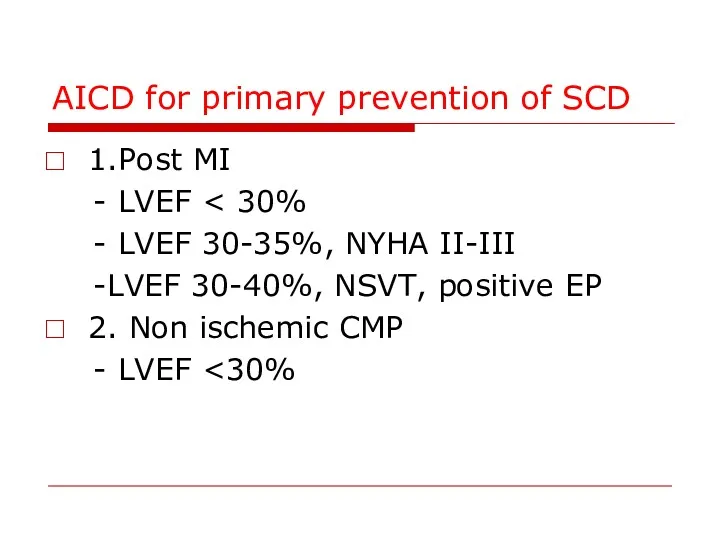
- 88. AICD for primary prevention of SCD 1.Post MI - LVEF - LVEF 30-35%, NYHA II-III -LVEF
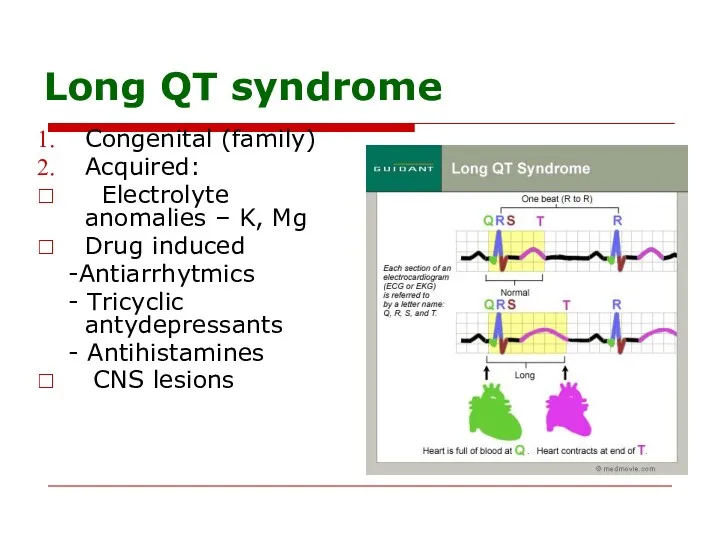
- 89. Long QT syndrome Congenital (family) Acquired: Electrolyte anomalies – K, Mg Drug induced -Antiarrhytmics - Tricyclic
- 91. Long QT syndrome treatment Acute 1.Remove the precipitating factor 2. Mg IV 3. Pacing 4. Isoproterenol
- 92. Long QT syndrome treatment Chronic – for congenital long QT 1.Beta blockers 2. AICD
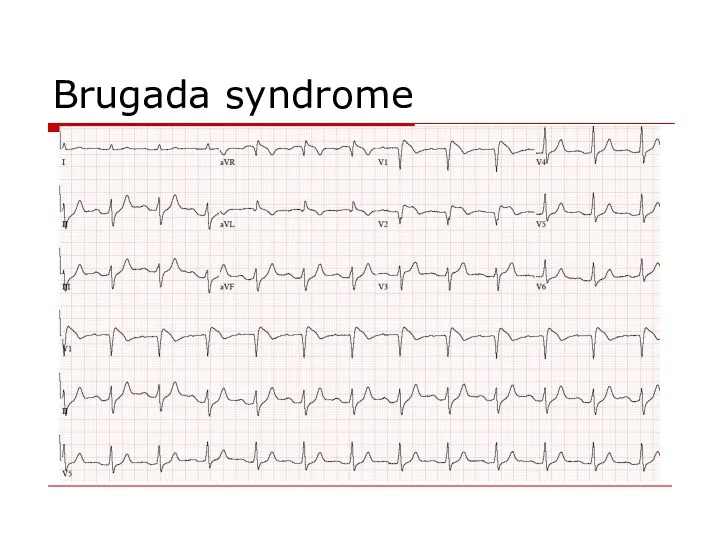
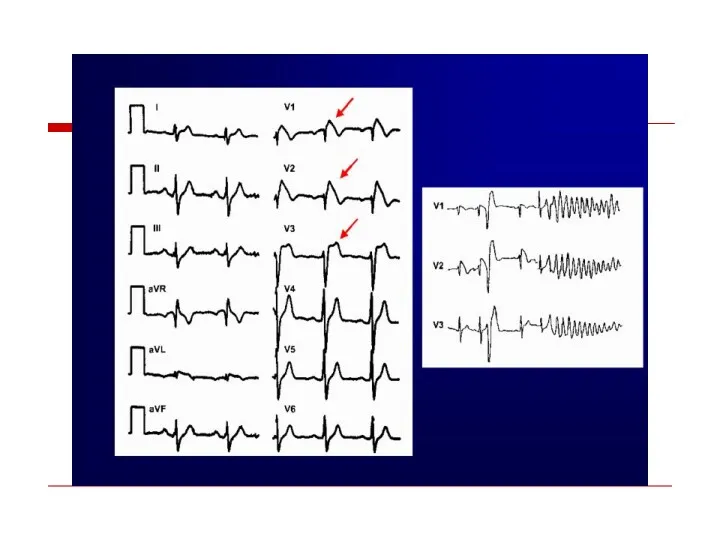
- 94. Brugada syndrome
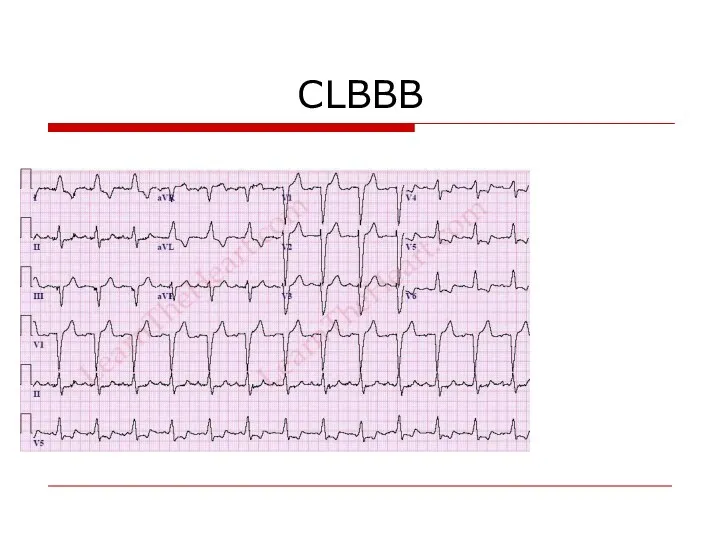
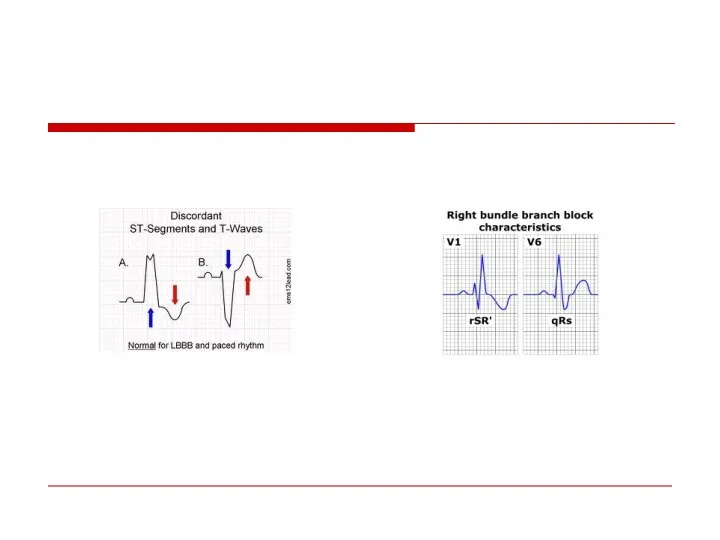
- 97. CLBBB
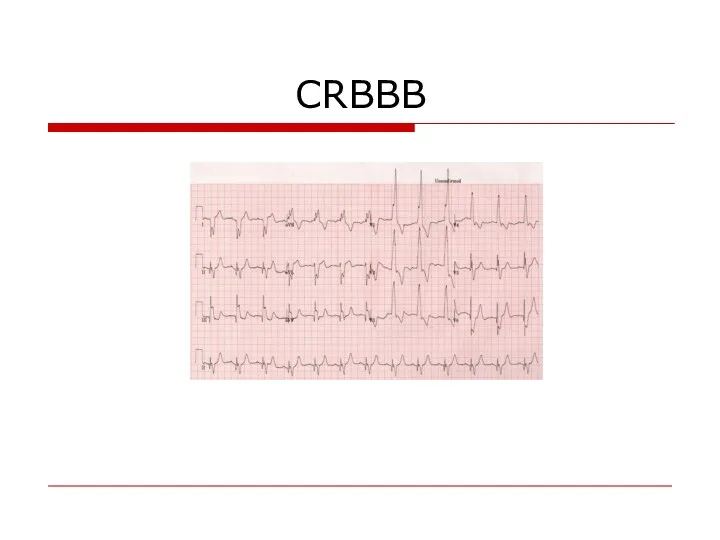
- 98. CRBBB
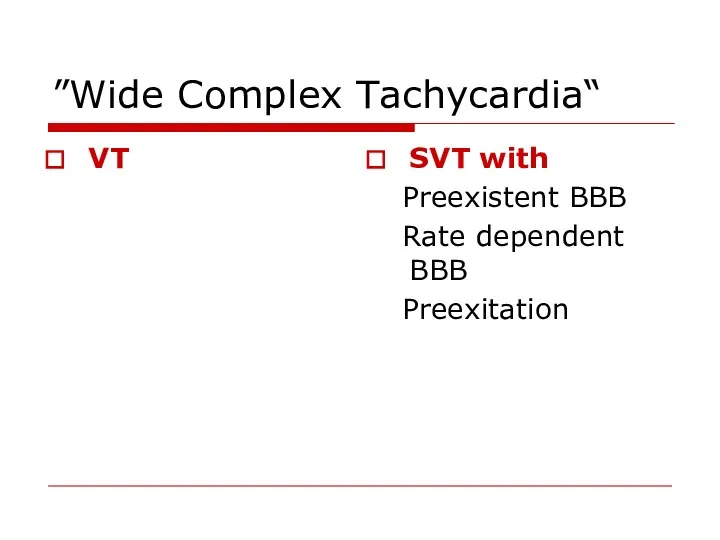
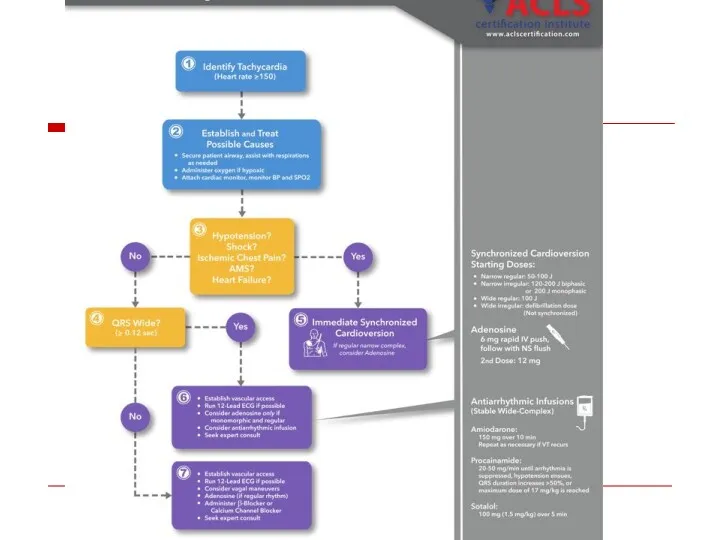
- 100. “Wide Complex Tachycardia” VT SVT with Preexistent BBB Rate dependent BBB Preexitation
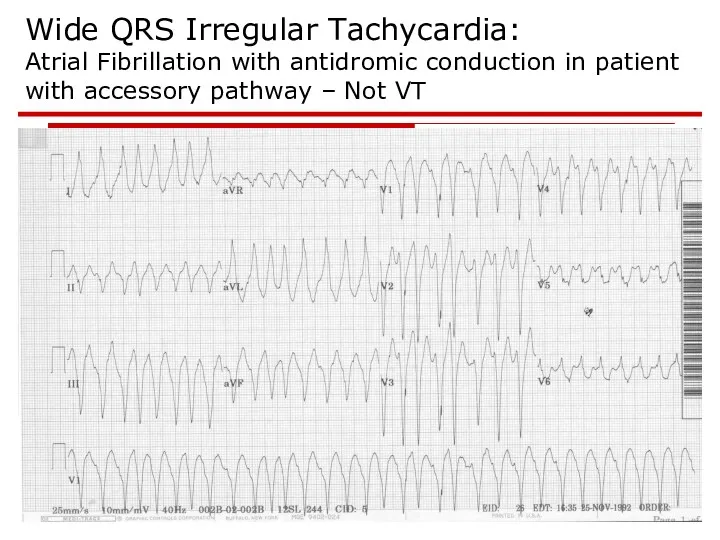
- 102. Wide QRS Irregular Tachycardia: Atrial Fibrillation with antidromic conduction in patient with accessory pathway – Not
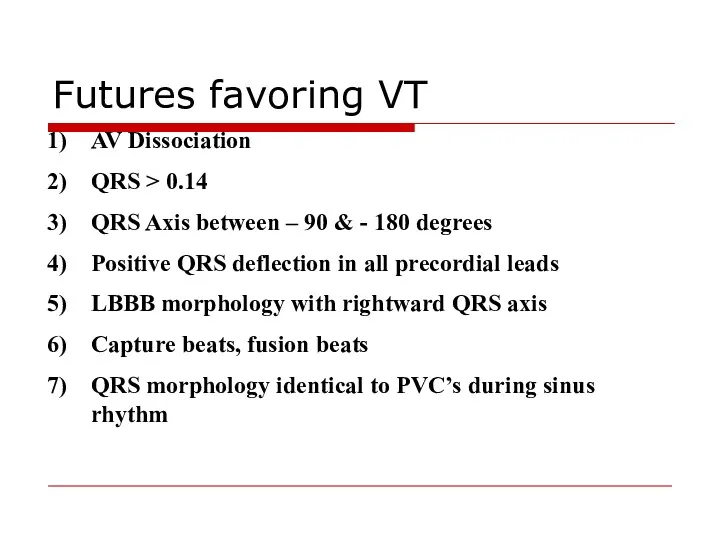
- 103. AV Dissociation QRS > 0.14 QRS Axis between – 90 & - 180 degrees Positive QRS
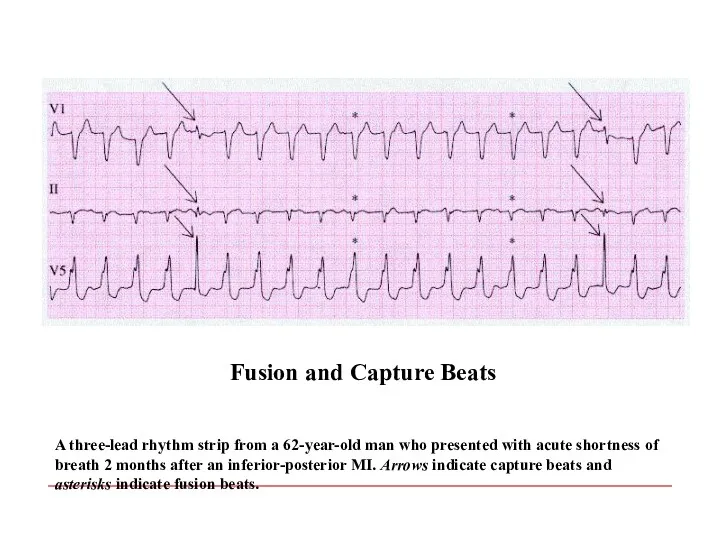
- 104. A three-lead rhythm strip from a 62-year-old man who presented with acute shortness of breath 2
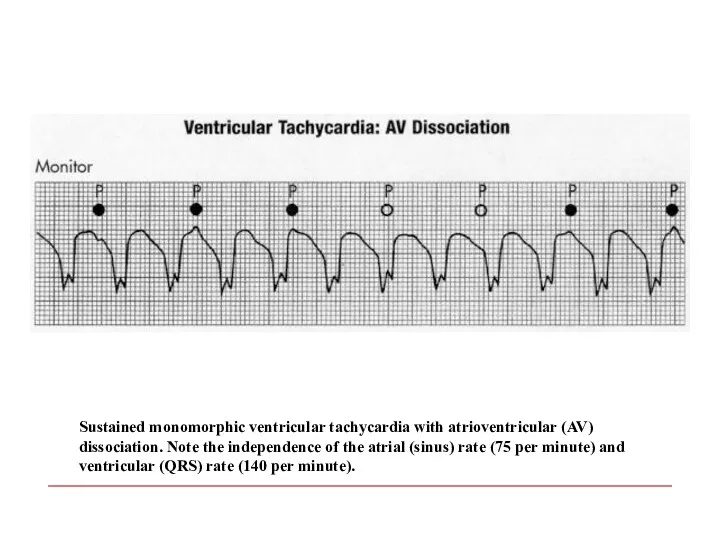
- 105. Sustained monomorphic ventricular tachycardia with atrioventricular (AV) dissociation. Note the independence of the atrial (sinus) rate
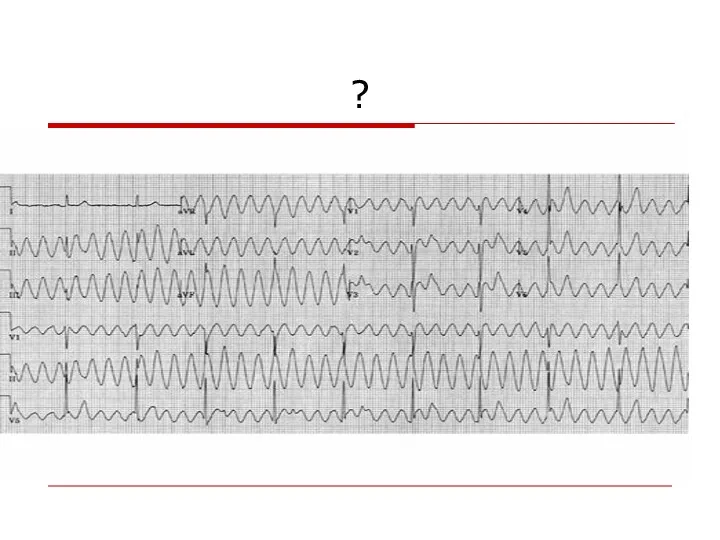
- 106. ?
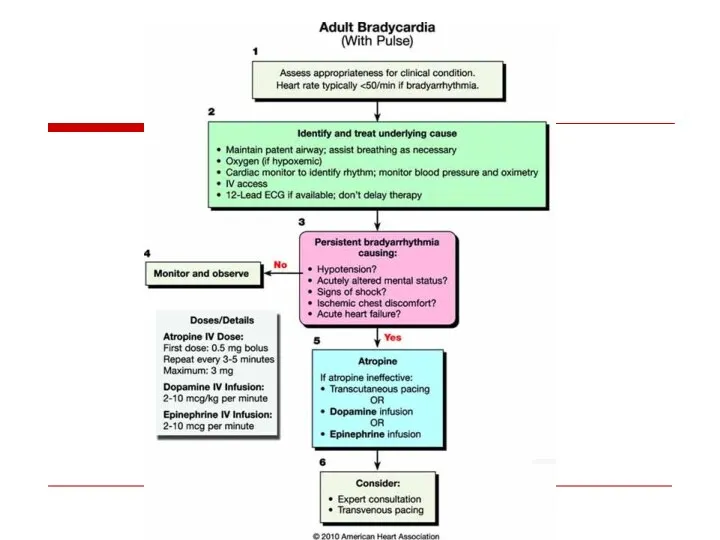
- 108. Atrioventricular Conduction Disturbances and Bradyarrhythmias
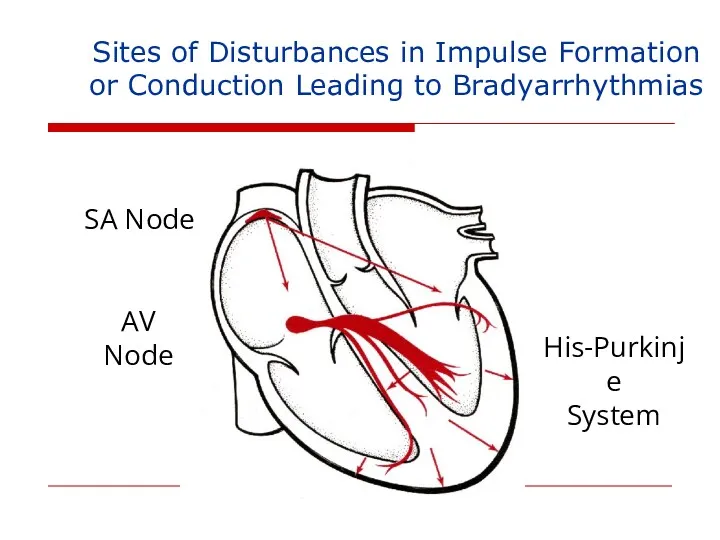
- 109. Sites of Disturbances in Impulse Formation or Conduction Leading to Bradyarrhythmias SA Node AV Node His-Purkinje
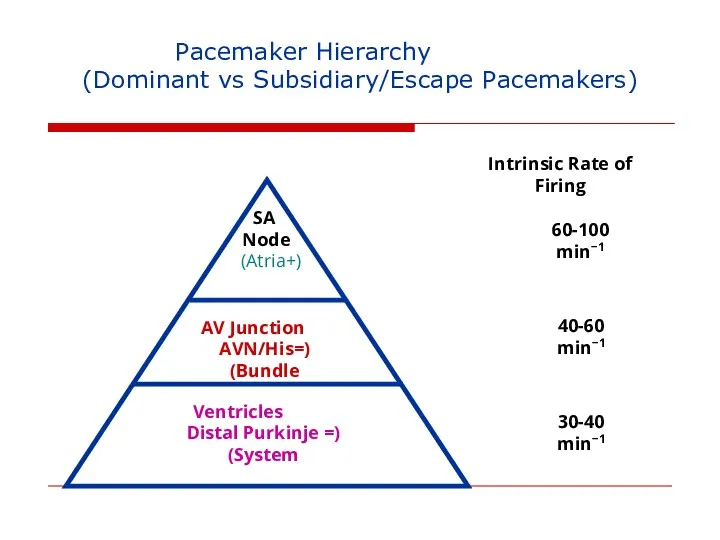
- 110. Pacemaker Hierarchy (Dominant vs Subsidiary/Escape Pacemakers) SA Node (+Atria) AV Junction (=AVN/His Bundle) Ventricles (= Distal
- 111. AV Block
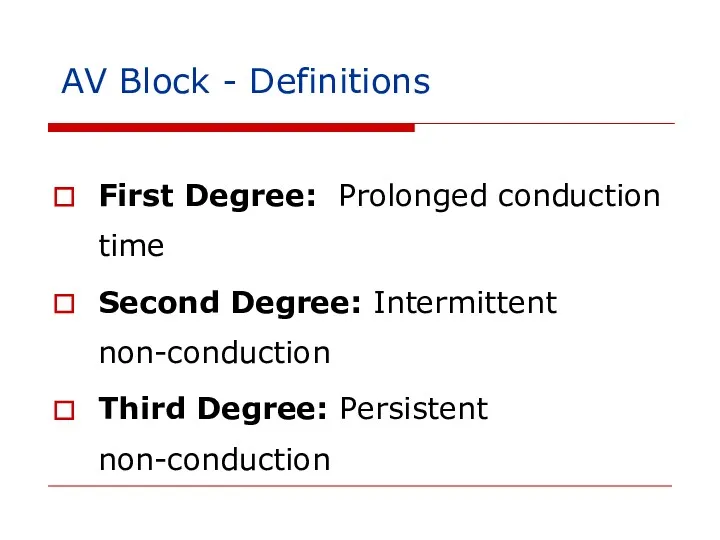
- 112. AV Block - Definitions First Degree: Prolonged conduction time Second Degree: Intermittent non-conduction Third Degree: Persistent
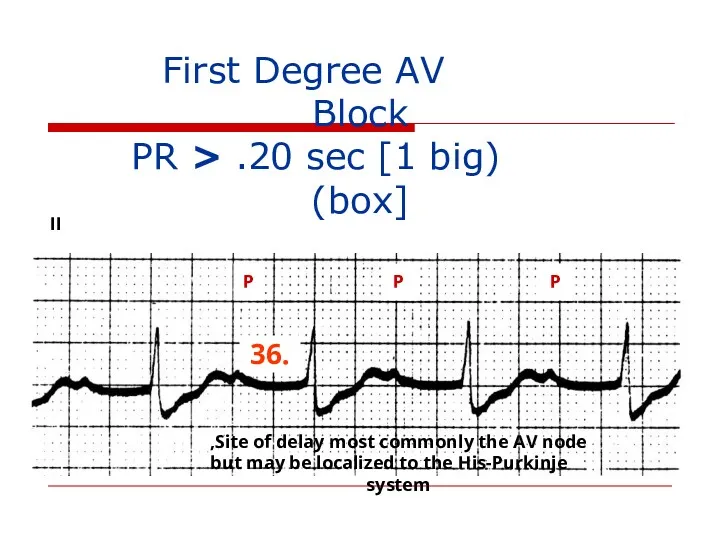
- 113. First Degree AV Block (PR > .20 sec [1 big box]) II P P P .36
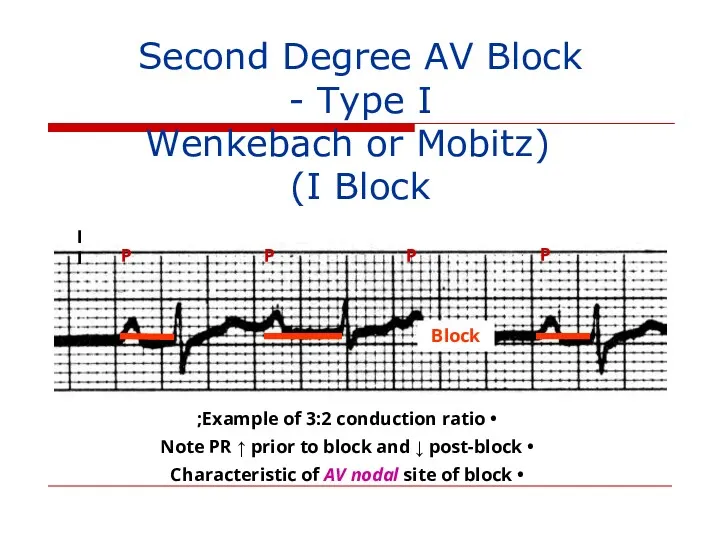
- 115. Second Degree AV Block - Type I (Wenkebach or Mobitz I Block) P P P P
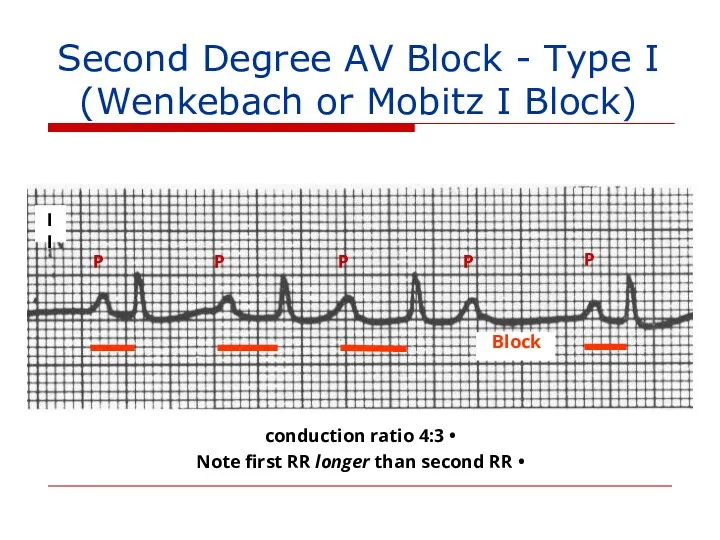
- 116. II Block P P P P P 4:3 conduction ratio Note first RR longer than second
- 117. II
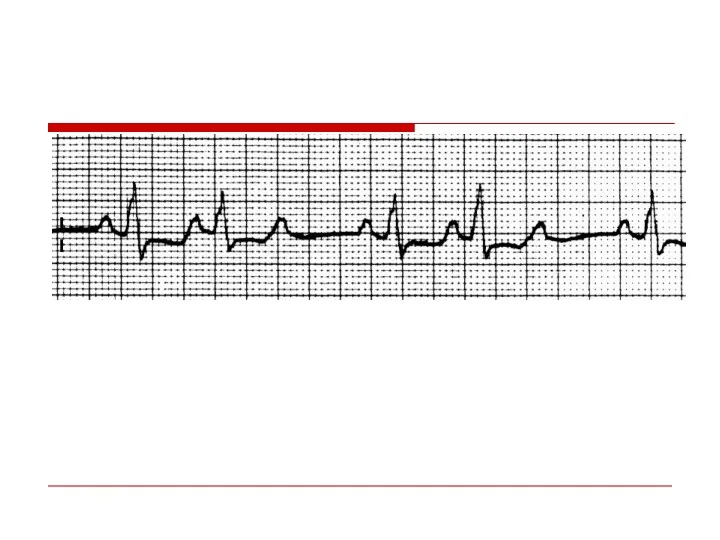
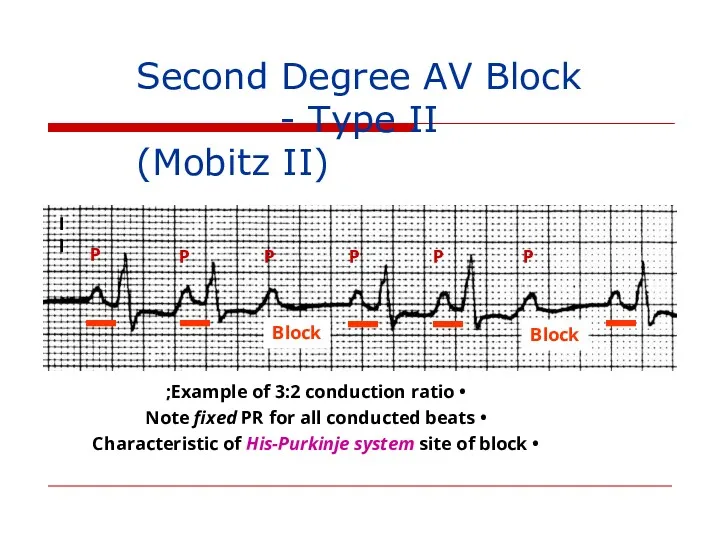
- 118. II P P P P P P Second Degree AV Block - Type II (Mobitz II)
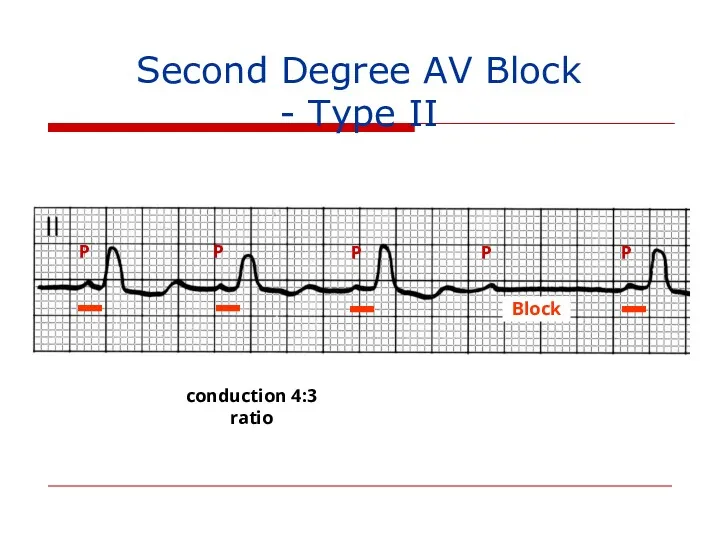
- 119. Second Degree AV Block - Type II P P P P P 4:3 conduction ratio Block
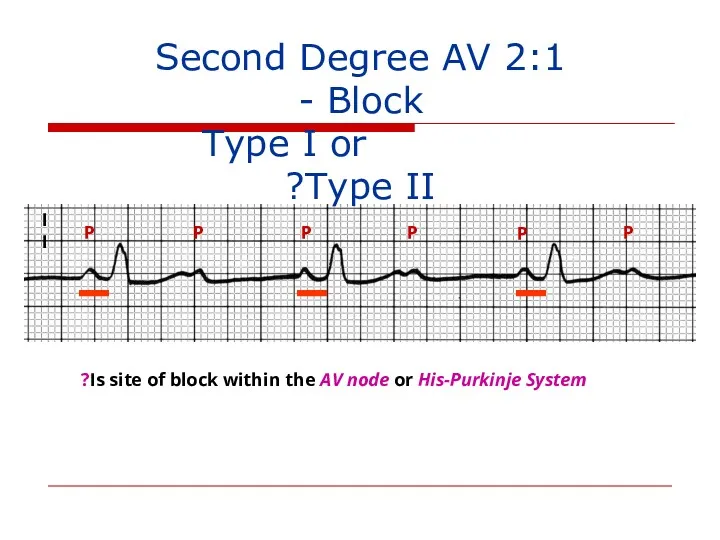
- 120. II P P P P P P 2:1 Second Degree AV Block - Type I or
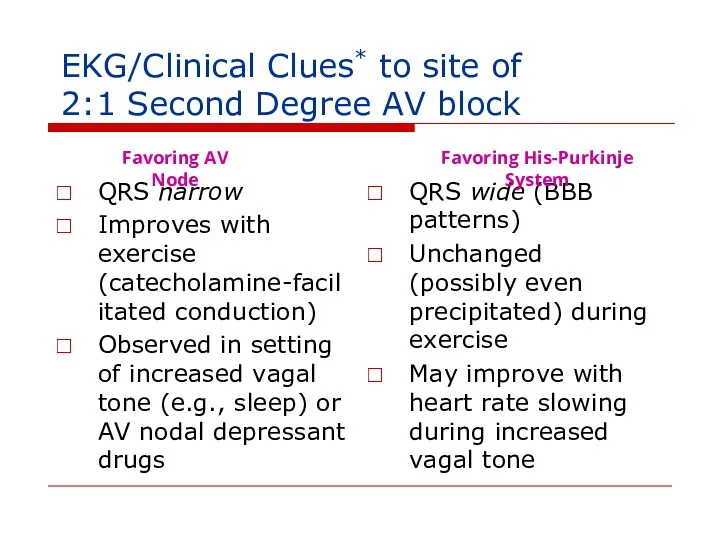
- 121. EKG/Clinical Clues* to site of 2:1 Second Degree AV block QRS narrow Improves with exercise (catecholamine-facilitated
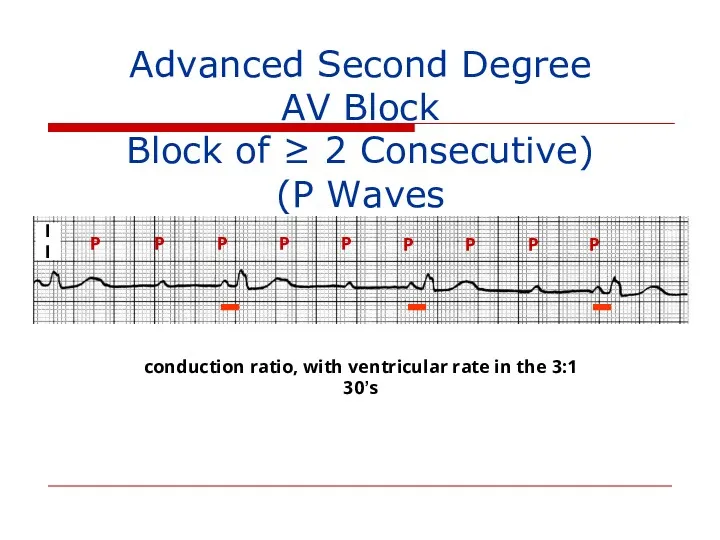
- 122. II P P P P P P P P P 3:1 conduction ratio, with ventricular rate
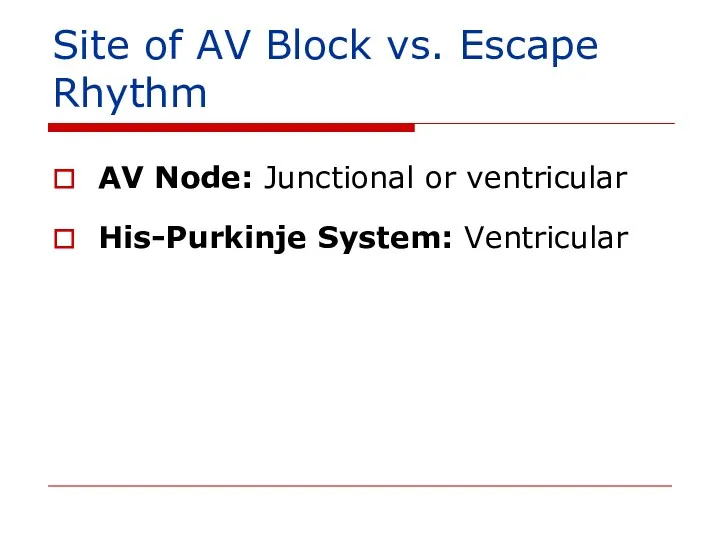
- 123. Site of AV Block vs. Escape Rhythm AV Node: Junctional or ventricular His-Purkinje System: Ventricular
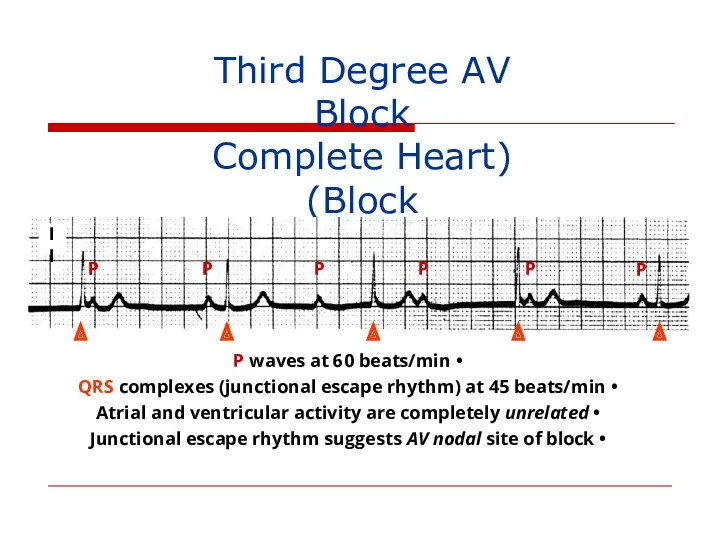
- 125. Third Degree AV Block (Complete Heart Block) P P P P P P P waves at
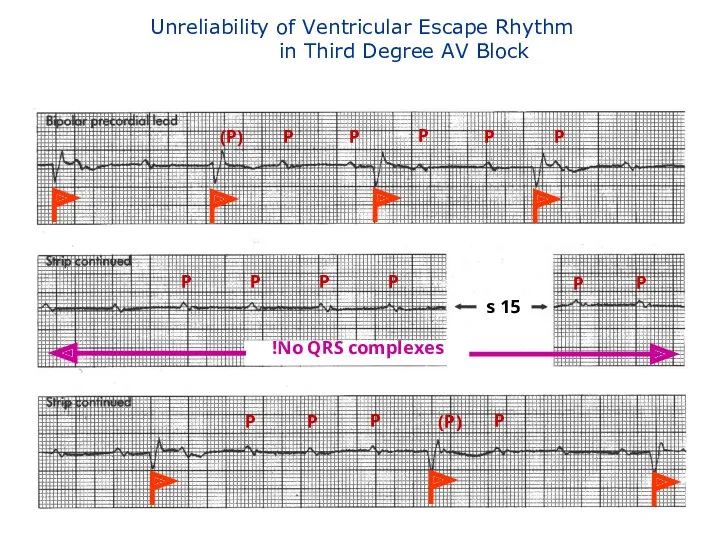
- 126. Unreliability of Ventricular Escape Rhythm in Third Degree AV Block P P (P) P P P
- 129. Causes of NON-Physiologic AV Block Ischemic heart disease, cardiomyopathy and degenerative changes Drugs that depress AV
- 130. Sinus Bradyarrhythmias
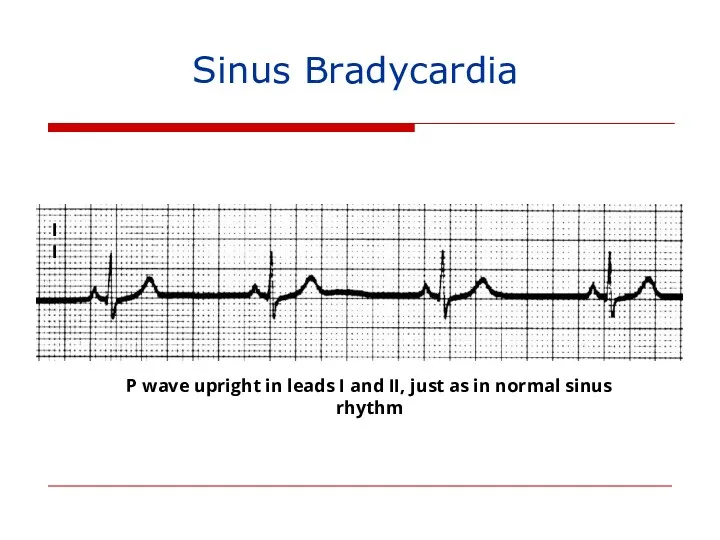
- 131. Sinus Bradycardia II P wave upright in leads I and II, just as in normal sinus
- 132. Causes of Sinus Bradycardia Increased vagal tone Drugs: beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, amiodarone, digoxin (indirect
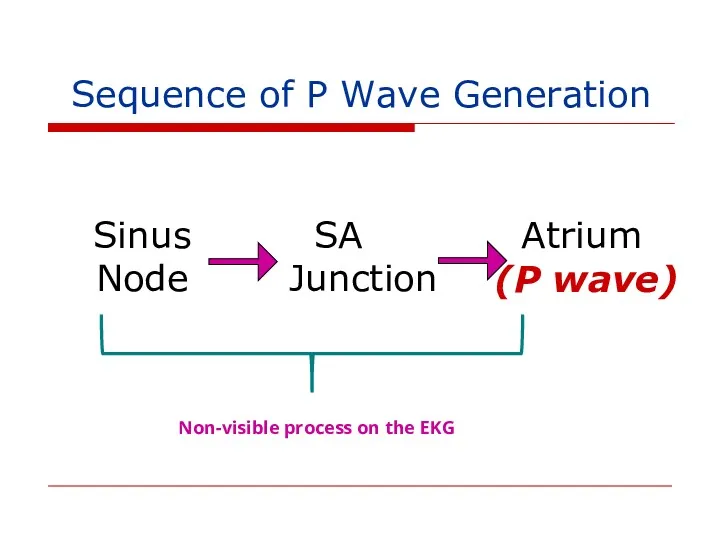
- 133. Sequence of P Wave Generation Sinus Node SA Junction Atrium (P wave) Non-visible process on the
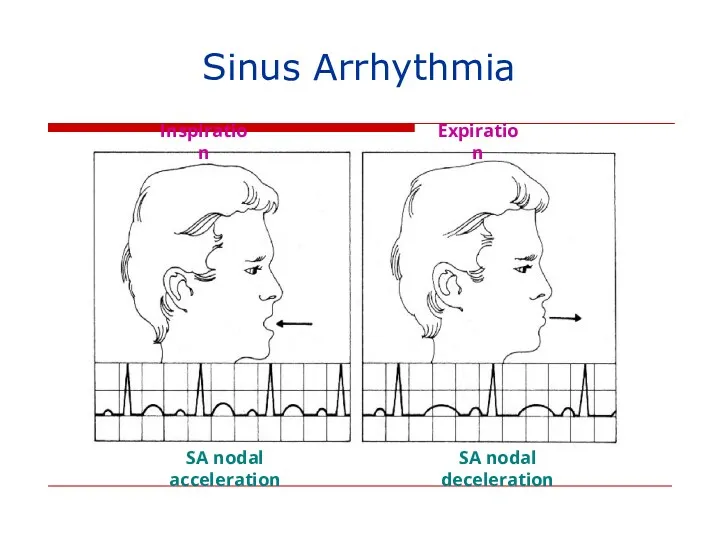
- 134. Inspiration Expiration SA nodal acceleration SA nodal deceleration Sinus Arrhythmia
- 135. Sinoatrial (SA) Exit Block - Definitions First Degree: Prolonged SA conduction time (non-detectable on EKG; no
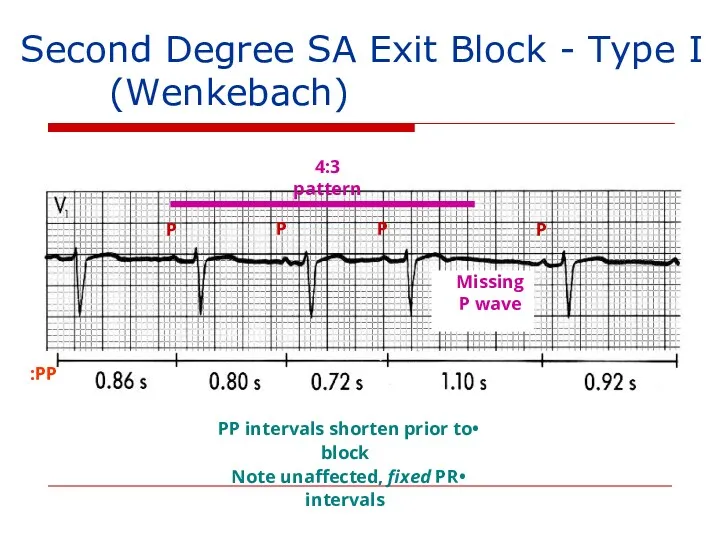
- 136. Second Degree SA Exit Block - Type I (Wenkebach) P P P P 4:3 pattern Missing
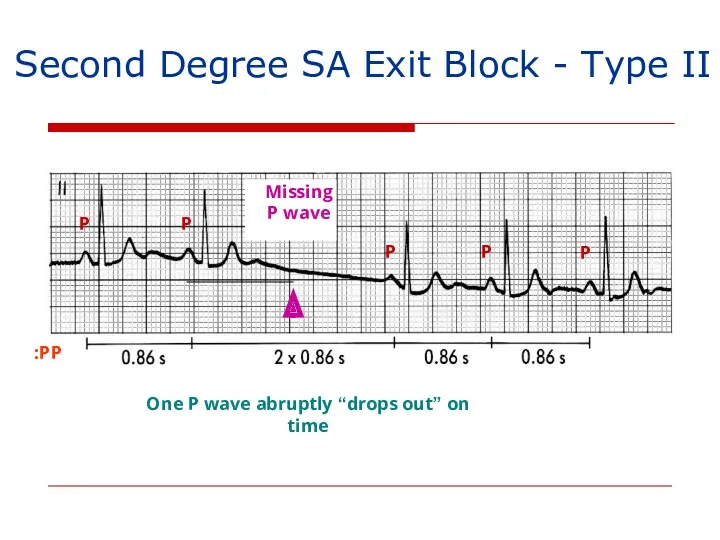
- 137. Second Degree SA Exit Block - Type II PP: P P P P P One P
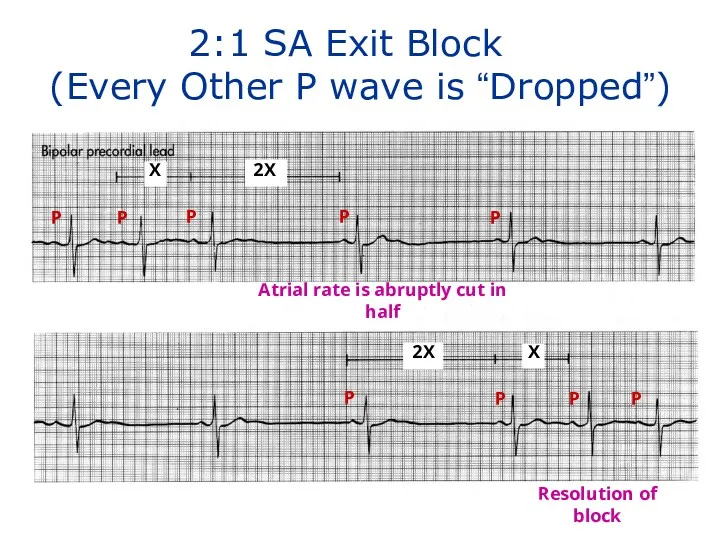
- 138. X 2X 2X X P P P P P P P P 2:1 SA Exit Block
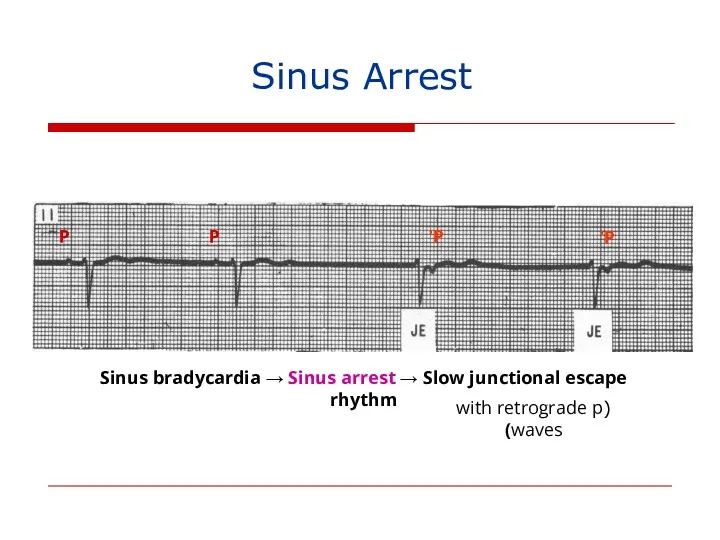
- 139. P P P’ P’ Sinus bradycardia → Sinus arrest → Slow junctional escape rhythm (with retrograde
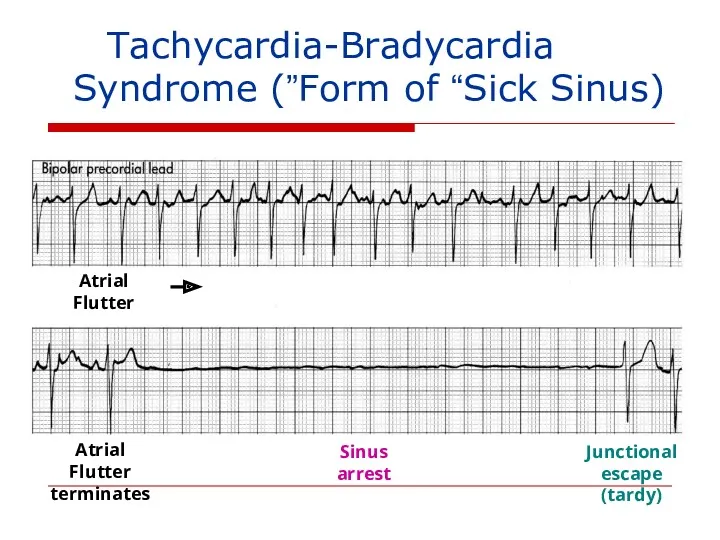
- 140. Tachycardia-Bradycardia (Form of “Sick Sinus”) Syndrome Atrial Flutter Sinus arrest Junctional escape (tardy) Atrial Flutter terminates
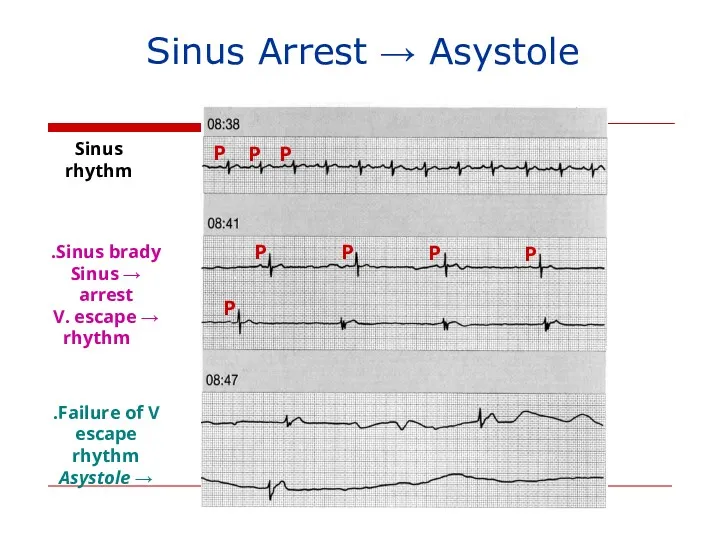
- 141. Sinus Arrest → Asystole Sinus rhythm Sinus brady. → Sinus arrest → V. escape rhythm Failure
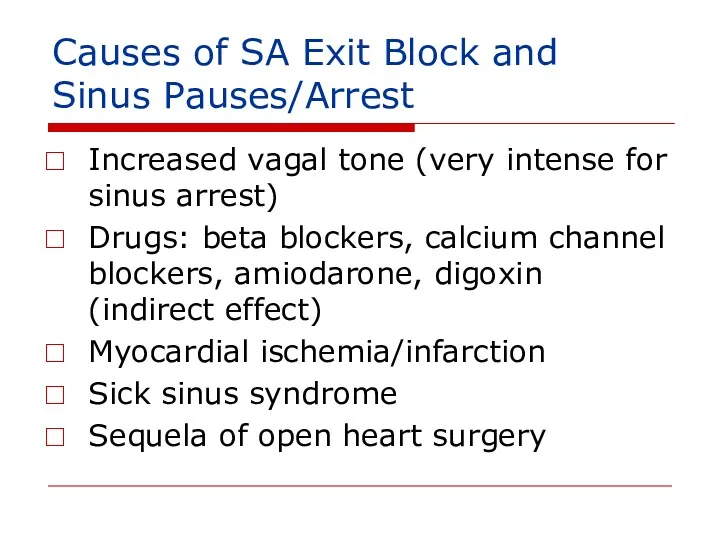
- 142. Causes of SA Exit Block and Sinus Pauses/Arrest Increased vagal tone (very intense for sinus arrest)
- 143. Sick Sinus Syndrome (1) persistent spontaneous sinus bradycardia not caused by drugs and inappropriate for the
- 146. Скачать презентацию

























 В-лимфоциты – основные эффекторы гуморального иммунного ответа. Лекция 5
В-лимфоциты – основные эффекторы гуморального иммунного ответа. Лекция 5 Лицо ассимметрично
Лицо ассимметрично Первичный билиарный цирроз. Диагностика и лечение
Первичный билиарный цирроз. Диагностика и лечение Физиотерапия. Механизмы формирования реакций организма на физические факторы. Принципы лечебного применения физических факторов
Физиотерапия. Механизмы формирования реакций организма на физические факторы. Принципы лечебного применения физических факторов Мейірбикелік күтім
Мейірбикелік күтім Посттранскрипционды гендер экспрессияның регуляциясы
Посттранскрипционды гендер экспрессияның регуляциясы Экстремальные жизненные ситуации. Первая помощь
Экстремальные жизненные ситуации. Первая помощь Особенности сестринского ухода за пациентами и реабилитация при повреждении костей таза
Особенности сестринского ухода за пациентами и реабилитация при повреждении костей таза Геморрагические диатезы
Геморрагические диатезы Гидроцефалия. Диагностика МРТ
Гидроцефалия. Диагностика МРТ Традиционные методы лечения
Традиционные методы лечения Адгезивы. Химическая структура и свойства современных адгезивных систем
Адгезивы. Химическая структура и свойства современных адгезивных систем Правила проведения доклинического исследования лекарственного средства для ветеринарного применения, клинического исследования
Правила проведения доклинического исследования лекарственного средства для ветеринарного применения, клинического исследования Анемиялық синдром (анемиямен көрінетін аурулардың дифференциалы диагностикасы)
Анемиялық синдром (анемиямен көрінетін аурулардың дифференциалы диагностикасы) Пропедевтика внутренних болезней. Цели и задачи. Методы исследования. Исследование сердечно-сосудистой системы
Пропедевтика внутренних болезней. Цели и задачи. Методы исследования. Исследование сердечно-сосудистой системы Правовые и этнические основы оказания первой помощи
Правовые и этнические основы оказания первой помощи Рентгенологические методы исследования
Рентгенологические методы исследования Онкология сегодня
Онкология сегодня Показатели состояния общественного здоровья
Показатели состояния общественного здоровья The subject and tasks of biochemistry. The importance of biochemical research in medicine
The subject and tasks of biochemistry. The importance of biochemical research in medicine Емшекпен емізу
Емшекпен емізу Медицина и робототехника
Медицина и робототехника Рвотные и противорвотные средства
Рвотные и противорвотные средства Акушерская тактика при COVID-19
Акушерская тактика при COVID-19 Остеохондроз и методы его лечения
Остеохондроз и методы его лечения Виды повязок
Виды повязок Картина крови при различных видах анемий
Картина крови при различных видах анемий Аллергические состояния, проявления в полости рта. Клиника, диагностика, лечение
Аллергические состояния, проявления в полости рта. Клиника, диагностика, лечение