Содержание
- 2. Steroids: the worst drugs for adverse effects
- 4. Corticosteroids History Synthesis Pharmacological Actions Pharmacokinetics Preparations Therapeutic principles Dosage schedule & Steroid withdrawal Uses: Therapeutic
- 5. History 1855 – Addison's disease 1856 – Adrenal glands essential for life 1930 – Cortex >
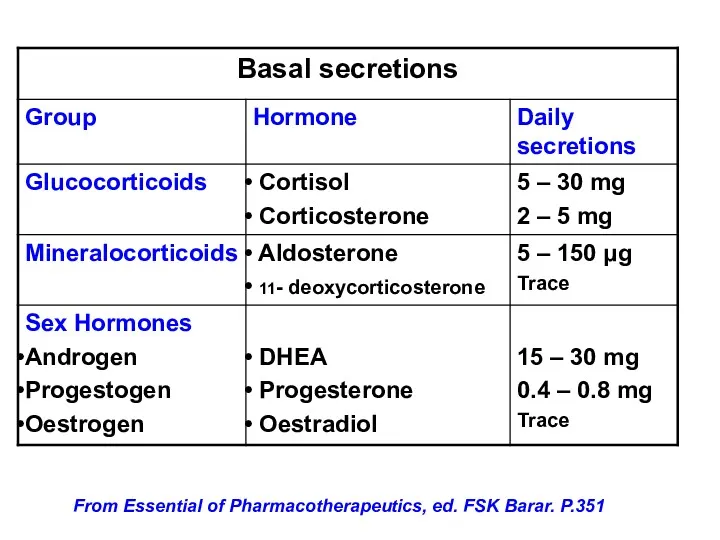
- 8. From Essential of Pharmacotherapeutics, ed. FSK Barar. P.351
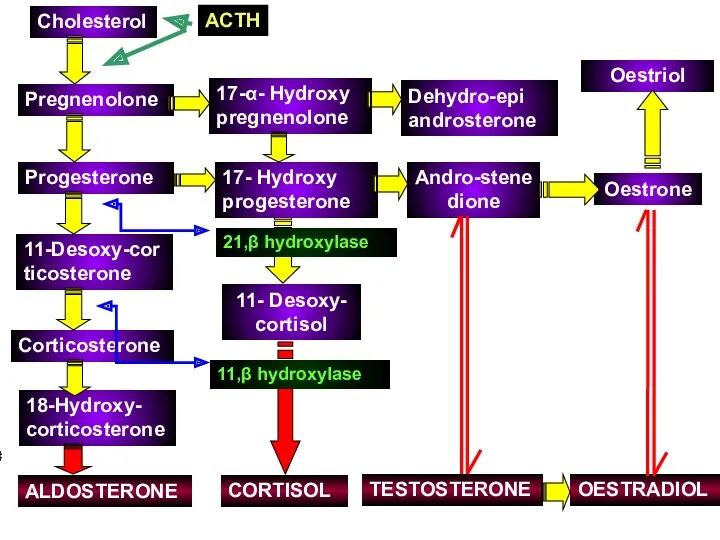
- 9. Cholesterol Pregnenolone Progesterone Corticosterone 11-Desoxy-corticosterone 18-Hydroxy- corticosterone ALDOSTERONE 17-α- Hydroxy pregnenolone 11- Desoxy- cortisol 17- Hydroxy
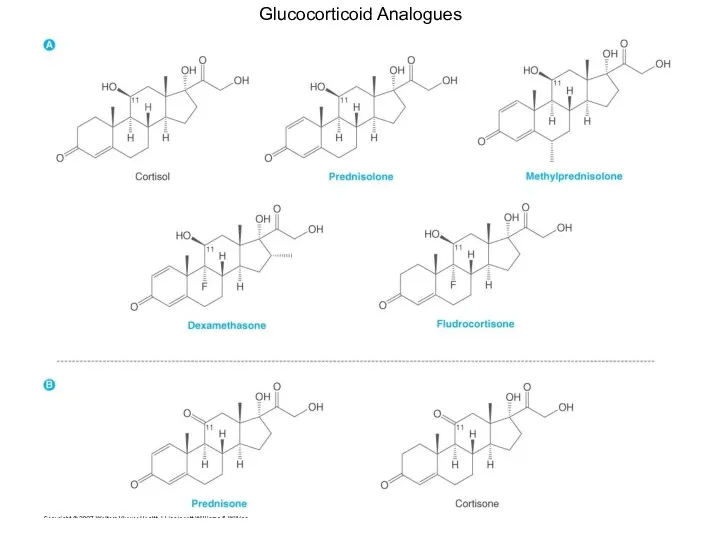
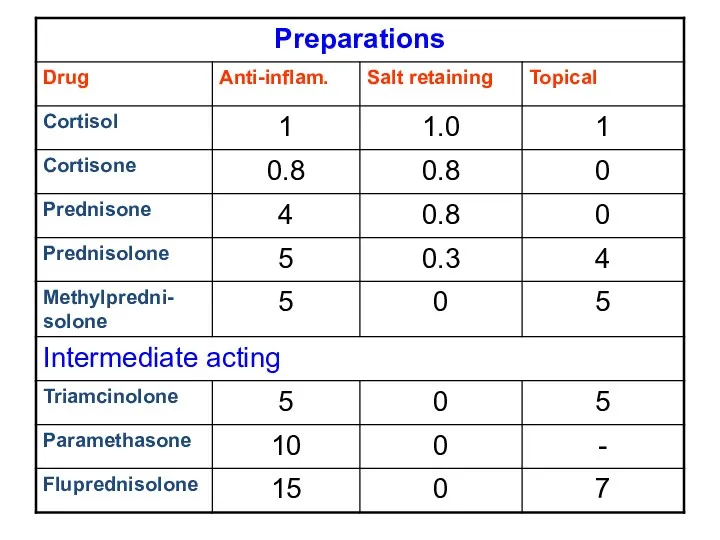
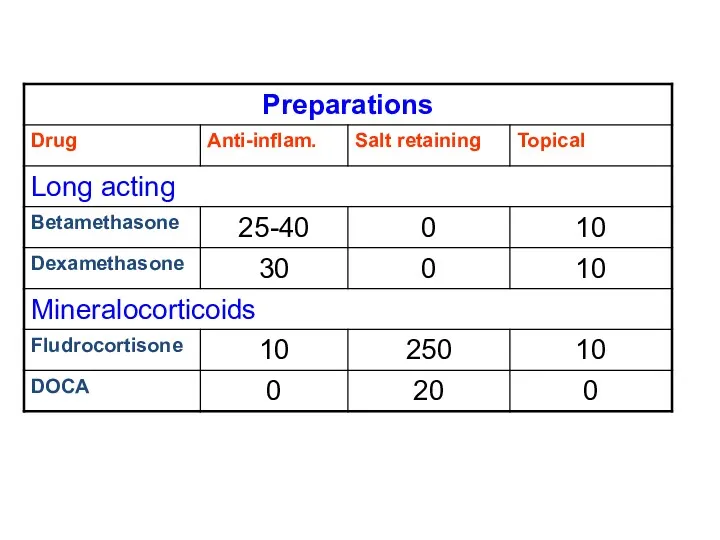
- 10. Glucocorticoid Analogues
- 11. Pharmacological Actions Direct (Intended) Actions Anti-inflammatory Anti-allergy Anti-immunity Permissive Actions Lipolytic effects Effect on bp Effect
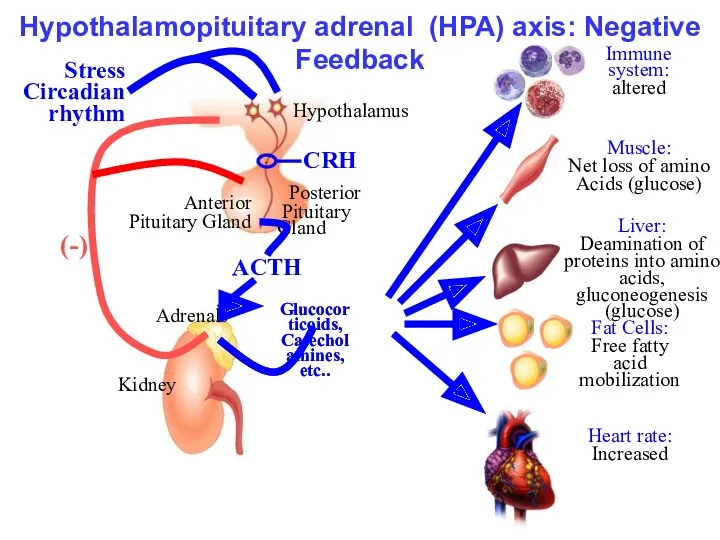
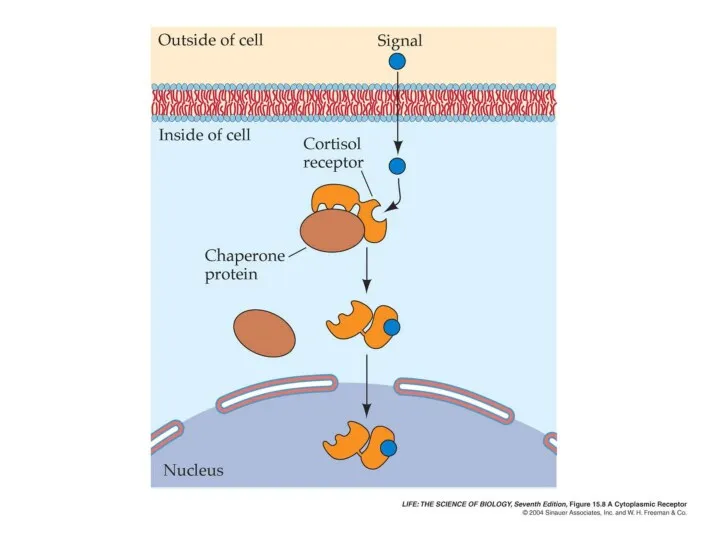
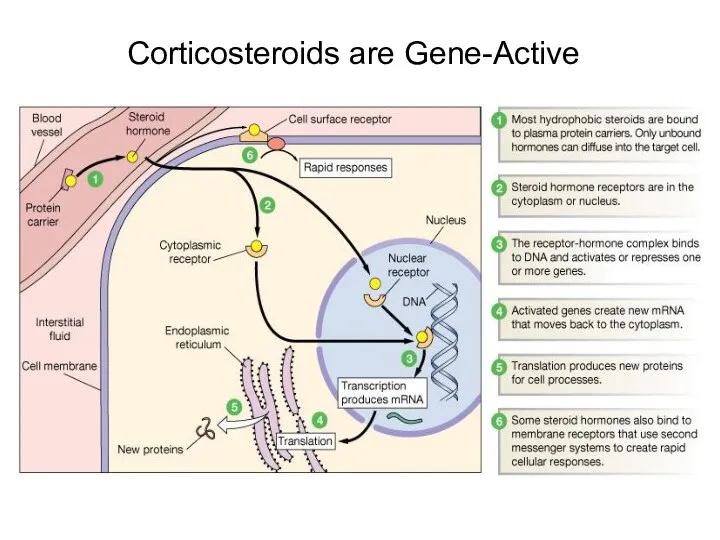
- 12. Pharmacological Actions Negative feedback mechanism. Steroids and drugs designed to mimic them are directly gene-active. Glucocorticoids
- 13. Hypothalamopituitary adrenal (HPA) axis: Negative Feedback
- 16. Corticosteroids are Gene-Active
- 17. Pharmacological Actions For most clinical purposes, synthetic glucocorticoids are used because they have a higher affinity
- 18. Pharmacological Actions Betamethasone and dexamethasone: very potent, w/o salt-retaining properties; thus, very useful for high-dose therapies
- 19. Pharmacological Actions Carbohydrate Protein Lipid Electrolyte and H2O CVS Skeletal Muscle CNS Stomach Blood Anti-inflammatory Immunosuppressant
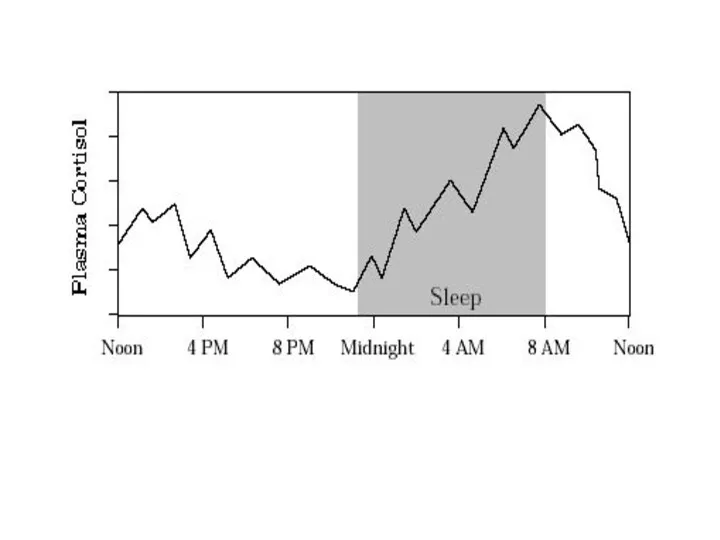
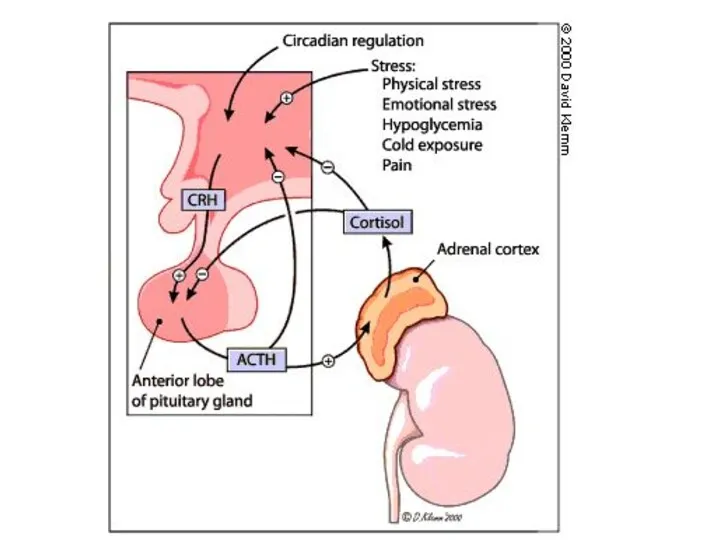
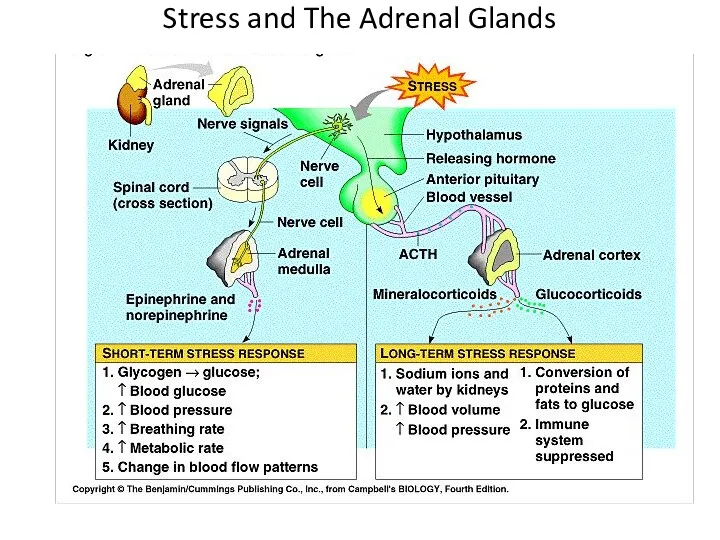
- 20. Stress and The Adrenal Glands
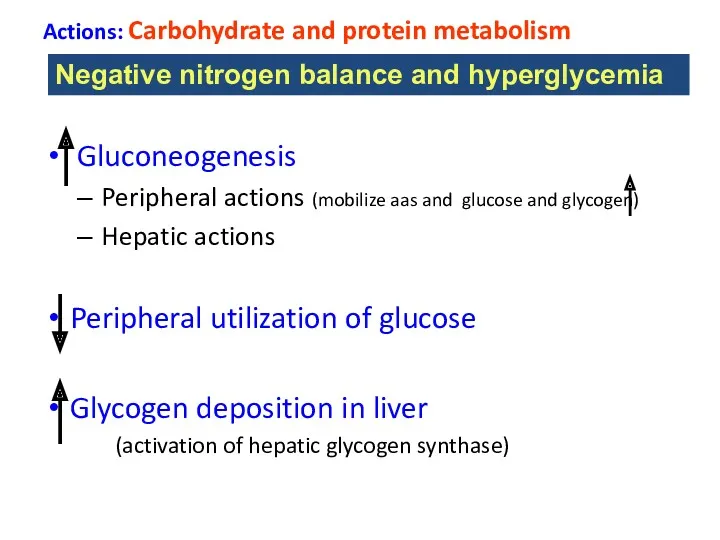
- 21. Actions: Carbohydrate and protein metabolism Gluconeogenesis Peripheral actions (mobilize aas and glucose and glycogen) Hepatic actions
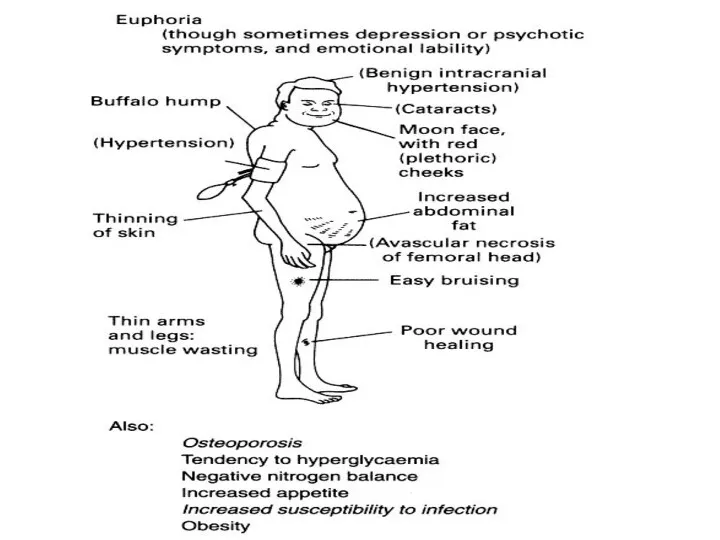
- 22. Redistribution of Fat Buffalo hump Moon face Promote adipokinetic agents activity (glucagon, growth hormone, adrenaline, thyroxine)
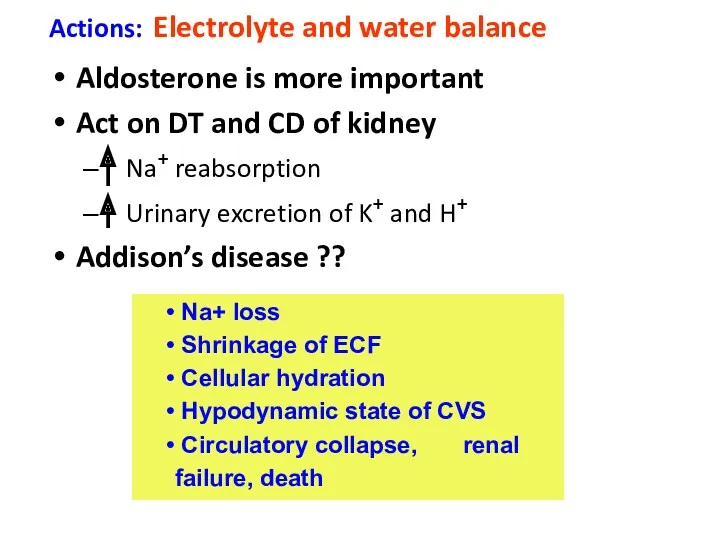
- 23. Actions: Electrolyte and water balance Aldosterone is more important Act on DT and CD of kidney
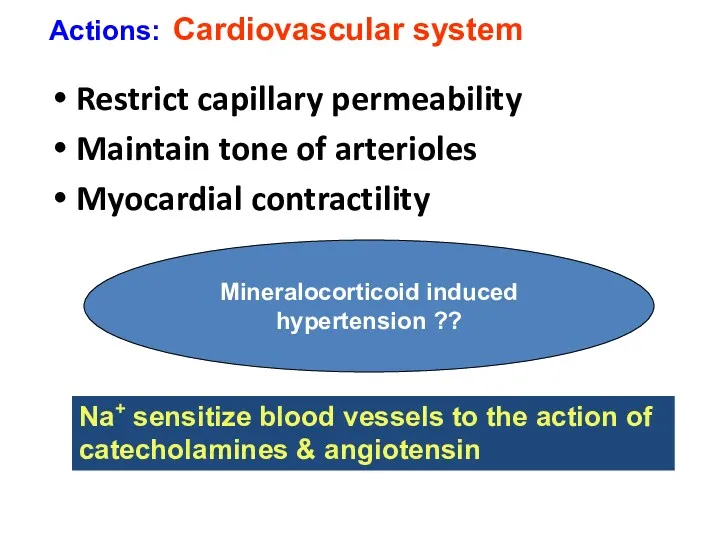
- 24. Restrict capillary permeability Maintain tone of arterioles Myocardial contractility Actions: Cardiovascular system Mineralocorticoid induced hypertension ??
- 25. Addison's disease: weakness and fatigue is due to Prolonged use: Actions: Skeletal Muscles Needed for maintaining
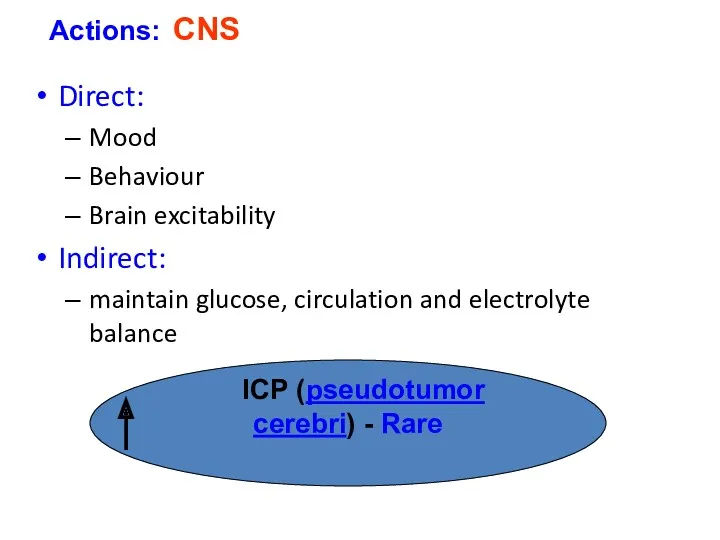
- 26. Direct: Mood Behaviour Brain excitability Indirect: maintain glucose, circulation and electrolyte balance Actions: CNS ICP (pseudotumor
- 27. Pseudotumor cerebri (Intracranial hypertension) Glucocorticoids Mineralocorticoids Amiodarone Vitamin A Oral contraceptives Tetracyclines From Harrison. 15th edition,
- 28. Aggravate peptic ulcer. May be due to: Acid and pepsin secretion immune response to H.Pylori Actions:
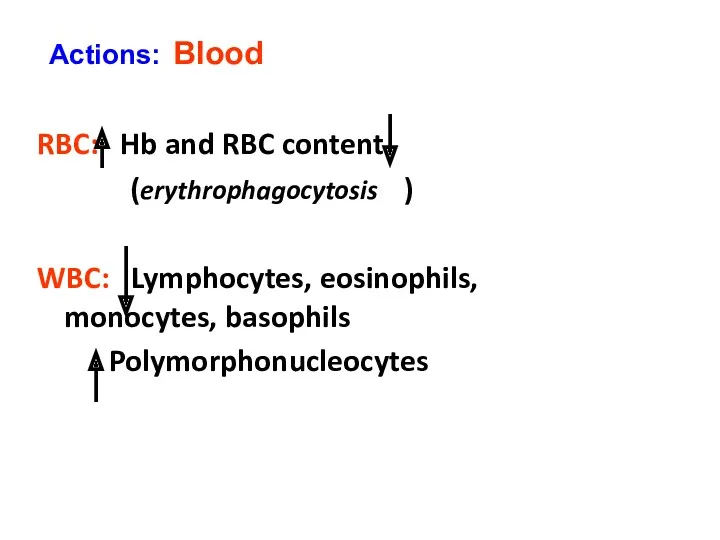
- 29. RBC: Hb and RBC content (erythrophagocytosis ) WBC: Lymphocytes, eosinophils, monocytes, basophils Polymorphonucleocytes Actions: Blood
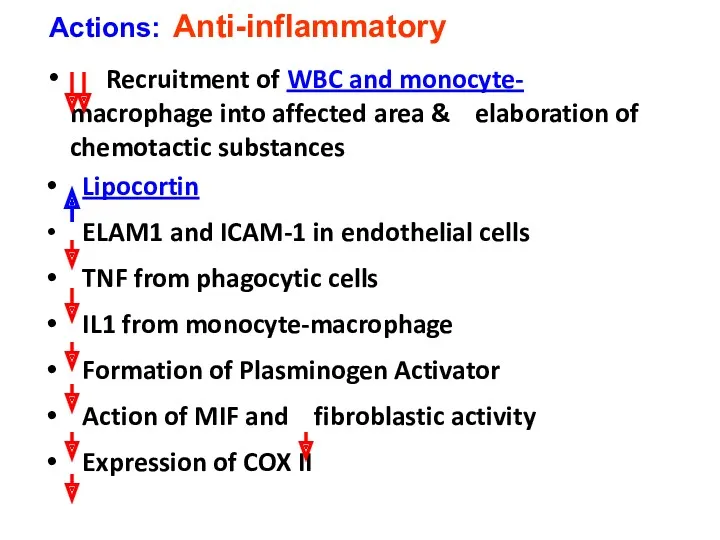
- 30. Recruitment of WBC and monocyte- macrophage into affected area & elaboration of chemotactic substances Lipocortin ELAM1
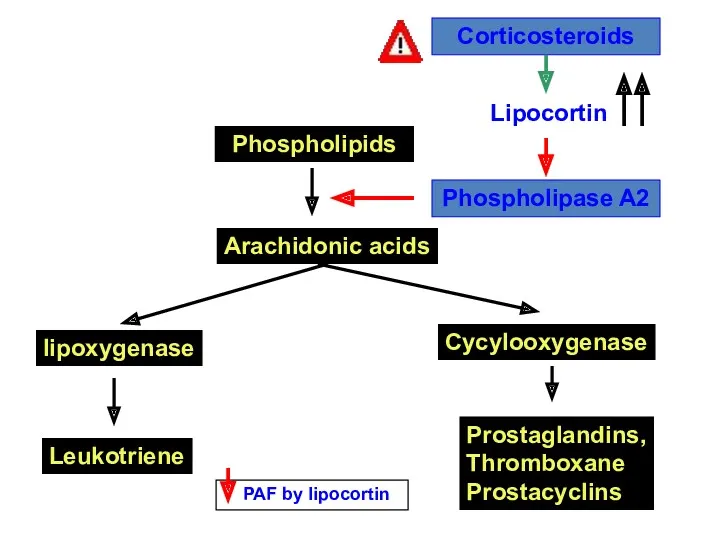
- 31. Phospholipids Arachidonic acids lipoxygenase Cycylooxygenase Leukotriene Prostaglandins, Thromboxane Prostacyclins Phospholipase A2 Lipocortin Corticosteroids PAF by lipocortin
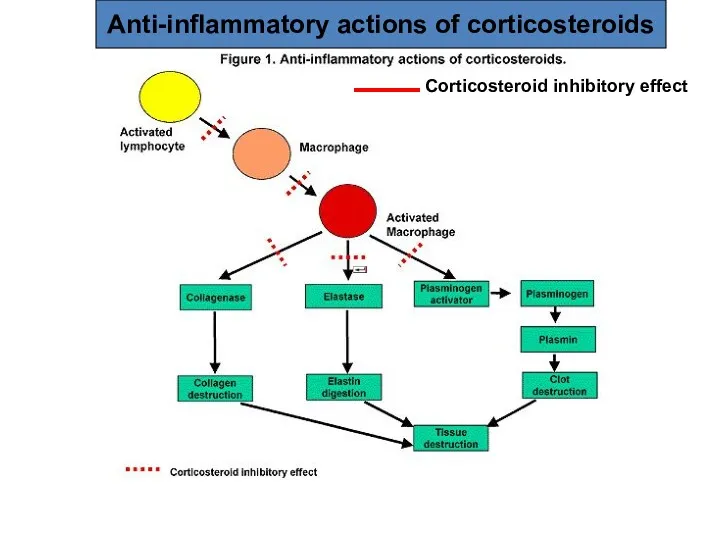
- 32. Anti-inflammatory actions of corticosteroids Corticosteroid inhibitory effect
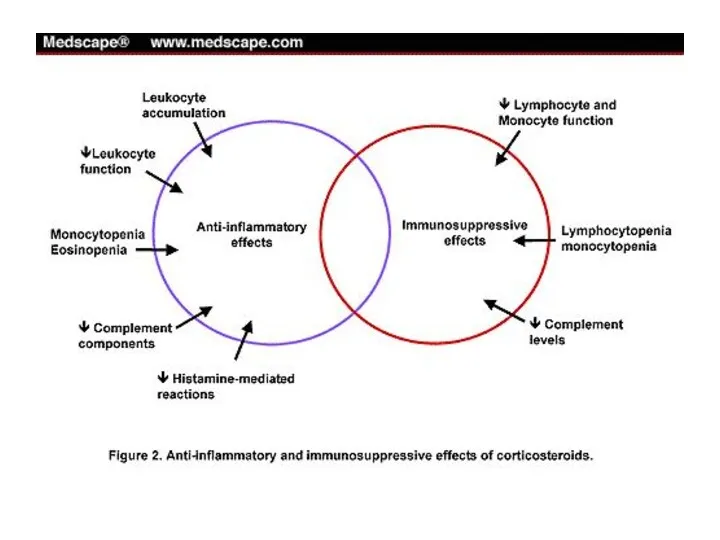
- 33. Immunosuppressive and anti-allergic actions Suppresses all types of hypersensitivity and allergic phenomenon At High dose: Interfere
- 35. Inhibit cell division or synthesis of DNA Delay the process of healing Retard the growth of
- 36. Intestinal absorption Renal excretion Excessive loss of calcium from spongy bones (e.g., vertebrae, ribs, etc) Actions:
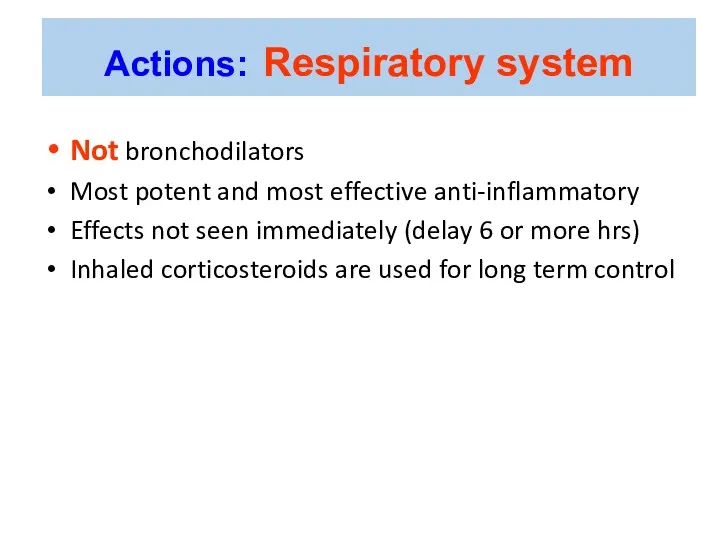
- 37. Not bronchodilators Most potent and most effective anti-inflammatory Effects not seen immediately (delay 6 or more
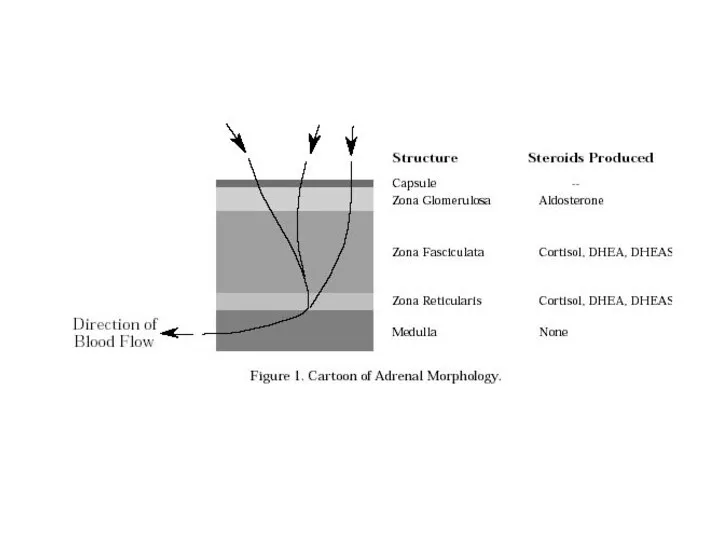
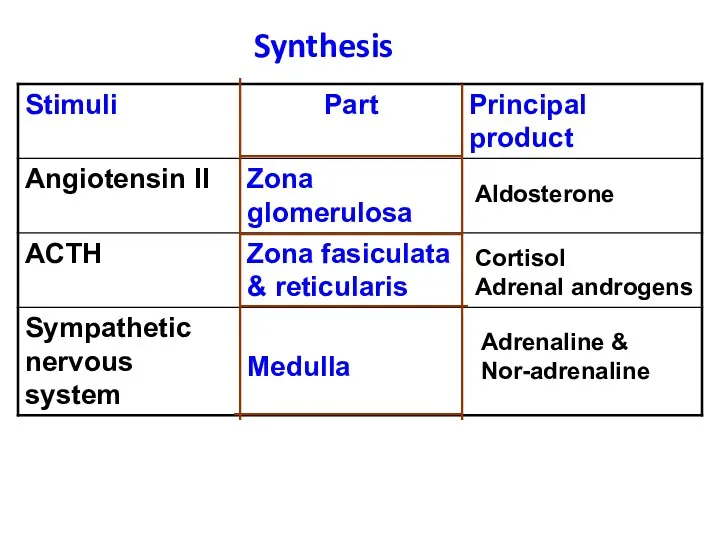
- 40. Synthesis Aldosterone Cortisol Adrenal androgens Adrenaline & Nor-adrenaline
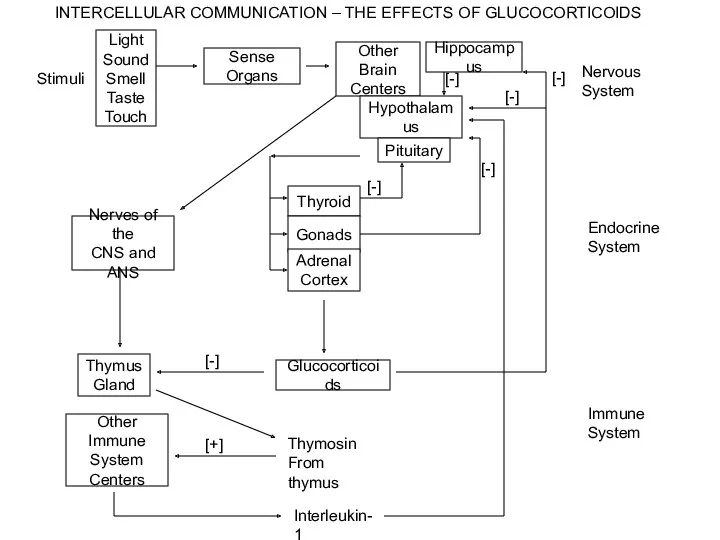
- 41. Stimuli Sense Organs Other Brain Centers Hippocampus Hypothalamus Pituitary Thyroid Gonads Adrenal Cortex Nerves of the
- 43. Скачать презентацию















 Программа реабилитации пожилых лиц с сосудистой деменцией
Программа реабилитации пожилых лиц с сосудистой деменцией Предсказание магнитных свойств наночастиц для биомедицинских применений. Машинное обучение
Предсказание магнитных свойств наночастиц для биомедицинских применений. Машинное обучение Значение сна в жизни человека
Значение сна в жизни человека Облачные технологии управления. Модуль скорая помощь
Облачные технологии управления. Модуль скорая помощь Патология водно-солевого обмена
Патология водно-солевого обмена Анатомия зубных рядов
Анатомия зубных рядов Универсальный алгоритм оказания первой помощи. Сердечно легочная реанимация
Универсальный алгоритм оказания первой помощи. Сердечно легочная реанимация Secrets of longevity
Secrets of longevity Основные понятия о хирургическом узле, шве
Основные понятия о хирургическом узле, шве ЛФК при заболеваниях пищеварения
ЛФК при заболеваниях пищеварения Свободные радикалы и болезни человека
Свободные радикалы и болезни человека Мерездің үшінші кезеңі
Мерездің үшінші кезеңі Актуальные вопросы в сфере обязательного медицинского страхования
Актуальные вопросы в сфере обязательного медицинского страхования Принципы анестезиологии в детской стоматологии
Принципы анестезиологии в детской стоматологии Применение денситометрии и определение состава тела в процессе контроля функционального состояния организма человека
Применение денситометрии и определение состава тела в процессе контроля функционального состояния организма человека Түбір өзектерді аспаптармен өңдеу әдістер
Түбір өзектерді аспаптармен өңдеу әдістер Эпидемиология сахарного диабета (в РФ, субъектах РФ и других странах)
Эпидемиология сахарного диабета (в РФ, субъектах РФ и других странах) Состояние оказания помощи взрослым пациентам с гемофилией в Республике Беларусь
Состояние оказания помощи взрослым пациентам с гемофилией в Республике Беларусь Основы поддержания жизни и автоматическая наружная дефибрилляция. Анестезиология и реаниматология
Основы поддержания жизни и автоматическая наружная дефибрилляция. Анестезиология и реаниматология Менструальный цикл
Менструальный цикл Метод иммунодиагностики и иммунопрофилактики инфекционных болезней
Метод иммунодиагностики и иммунопрофилактики инфекционных болезней Основы клинической физиологии сердца
Основы клинической физиологии сердца Медична служба українських збройних сил. Домедична допомога в умовах бойових дій
Медична служба українських збройних сил. Домедична допомога в умовах бойових дій Тіс жарып шыққаннан кейін дамитын тісжегі емес ақаулар
Тіс жарып шыққаннан кейін дамитын тісжегі емес ақаулар Болезнь Паркинсона
Болезнь Паркинсона Внематочная беременность. Апоплексия яичника. Разрыв кисты
Внематочная беременность. Апоплексия яичника. Разрыв кисты Доказательная медицина
Доказательная медицина Ісіктердің пайда болу механизмі
Ісіктердің пайда болу механизмі