Содержание
- 2. DIURETICS I. Saluretics - have the Sulfonamide Group - SO2NH2 1. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors: Diacarbe (Acetazolamide)
- 3. II. K+- sparing Diuretics: Amiloride – Tab. 2.5 and 5 mg Triamteren – Caps 50 mg
- 4. Accordingt to the ability to enhance Na+ excretion: 1.STRONG DIURETICS: LOOP DIURETICS - Furosemide, Ethacrynic acid
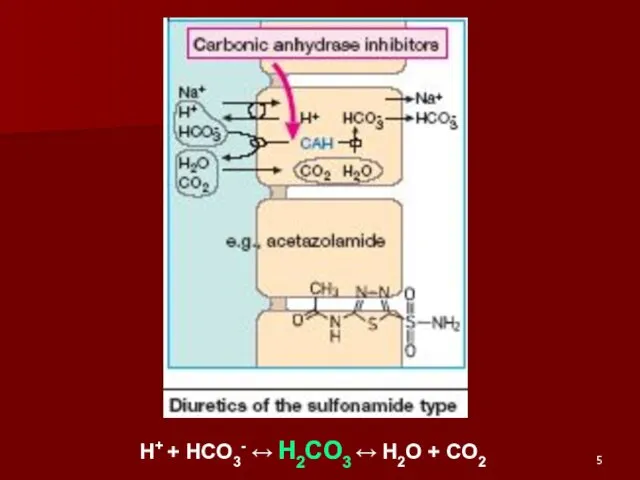
- 5. H+ + HCO3- ↔ H2CO3 ↔ H2O + CO2
- 6. CLINICAL USES OF DIACARB: GLAUCOMA - at Open-Angle Glaucoma EPILEPSY - both Generalized and Partial -
- 7. 2. LOOP DIURETICS Furosemide (Lasix ) – Tab. 40 mg Amp. 1%-2 ml Ethacrinic acid –
- 8. Mechanism of action of Loop Diuretics: They produce Na+ / K+ /2Cl- cotransport inhibition of the
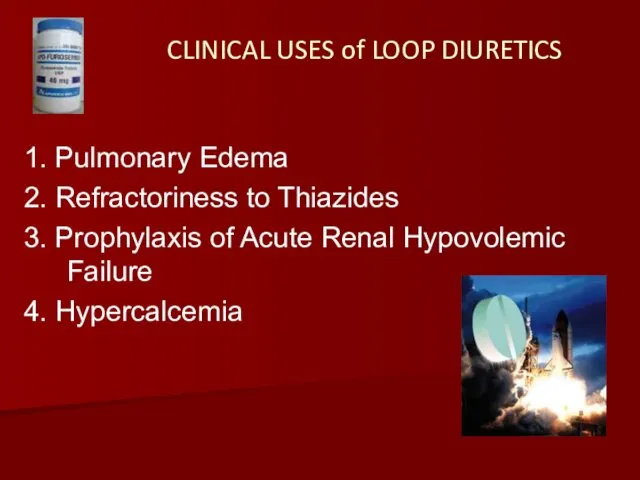
- 9. CLINICAL USES of LOOP DIURETICS 1. Pulmonary Edema 2. Refractoriness to Thiazides 3. Prophylaxis of Acute
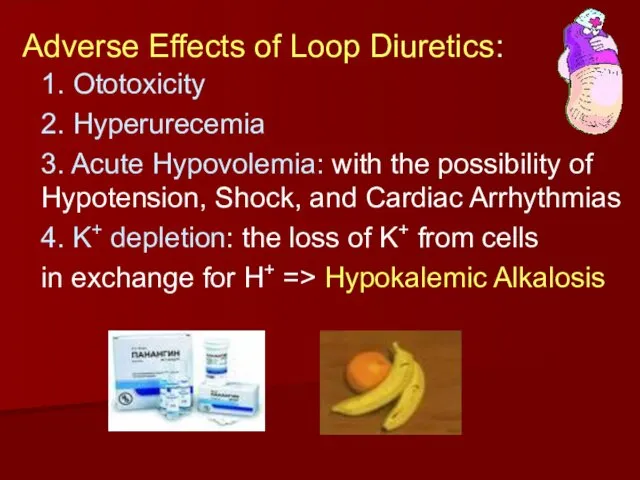
- 10. Adverse Effects of Loop Diuretics: 1. Ototoxicity 2. Hyperurecemia 3. Acute Hypovolemia: with the possibility of
- 11. THIAZIDE DIURETICS: Hydrochlorthiazide – tab. 25 and 100 mg Cyclomethiazide – tab. 0.5 g Oxodoline –
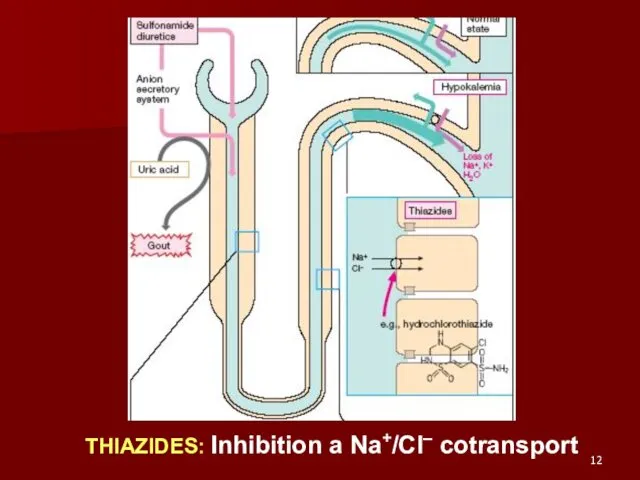
- 12. THIAZIDES: Inhibition a Na+/Cl– cotransport
- 13. CLINICAL USES OF THIAZIDES: 1. Hypertension 2. CHF. Thiazides can be the diuretic of choice in
- 14. ADVERSE EFFECTS of THIAZIDES : 1. Hypokalemia 2. Hyperglycemia and Glycosuria. 3. Hyperuricemia - ? Plasma
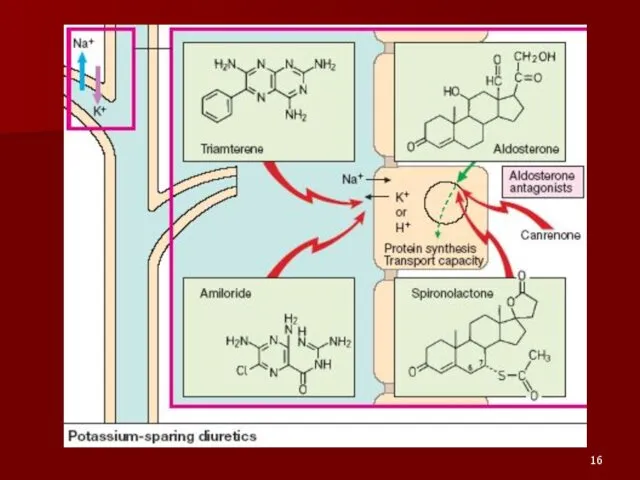
- 15. ALDOSTERONE promotes the reabsorption of Na+ (Cl– and H2O follow) in exchange for K+. Hormonal effect
- 17. Clinical uses of Spironolactone: Gynecomastia Hyperkalemia Lethargy Mental Confusion Edemas Secondary Hyperaldosteronism – Liver Cirrhosis with
- 18. Triamterene and Amiloride: Block Na+ transport channels => => ?Na+- K+ exchange Have K+- sparing diuretic
- 19. III. OSMOTIC DIURETICS: Mannitol Vial 15% - 200, 400 ml Urea – Vial 30, 45, 60
- 20. GOUT - a metabolic disease in which plasma URATE concentration is raised because of overproduction or
- 21. ANTIGOUTY AGENTS 1. Inhibitors of Uric Acid synthesis: Allopurinol – Tab. 0.1 g 2. Inducers of
- 22. 3. Inhibiting leukocyte migration into the joint: Colchycine: Tab. 2 mg, 0.5% Ointment a Colchicum autumnale
- 23. URODAN– granules 100.0 g - 1 teasp. in ½ glass of water 3-4 times a day
- 24. UROLESAN - vial 15 ml: 8-10 drops on a bit of sugar Contains: Fir Oil Peppermint
- 25. Agents Affecting the Uterus Function
- 26. AGENTS AFFECTING MAINLY THE UTERUS CONTRACTILITY 1. Enhancing mainly the Contractive Activity: Oxytocin - amp. 5
- 27. OXITOCINE (amp. 5 units/ml) - ? Na+ permeability of uterine myofibrils, indirectly Stimulating the Contraction of
- 28. Clinical uses of OXITOCINE: ∙ to induce or augment Labour when the Uterine muscle is not
- 29. DINORPOSTONE (PG E2) amp. 0.1%-1 ml, vaginal supp. 20 mg Stimulates myometrial contractions in the gravid
- 30. RU-486 - is an antiprogestin (Antigestagen) – it has been combined with an oral oxytocic PG
- 31. 2. TOCOLYTICS ⮚ β2-AMs: Fenoterol, Terbutaline, Ritodrine ⮚ MgSO4 and Mg2+ agents ⮚ Ca2+ Channels Blockers
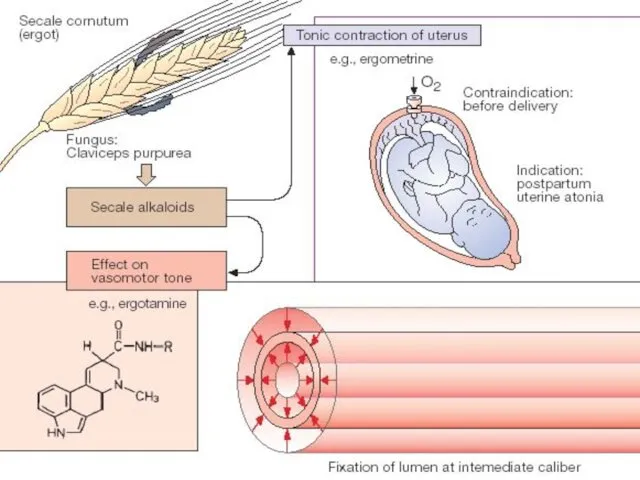
- 32. B. Agents Enhancing mainly Tonus of Myometrium 1. Plant Origin - Alkaloids and Preparation of Ergot
- 34. ERGOT ALKALOIDS Ergotamine maleate Ergotamine hydrotartrate Ergotal - act on several types of receptors. Effects include
- 35. Adverse Effects of ERGOT ALKALOIDS: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea Dementia with florid hallucinations Prolonged Vasospasm => Gangrene
- 36. C. Agents Reducing Tonus of the Uterine Neck ● M-cholinoblockers: Atropine sulfate ● Myotropic spasmolytics: Papaverine
- 38. Скачать презентацию





























 Вегетативные дисфункции у детей
Вегетативные дисфункции у детей Питание детей с муковисцидозом
Питание детей с муковисцидозом Травма головы
Травма головы Дене шынықтыру мен спорт
Дене шынықтыру мен спорт Іріңді-септикалық инфекциялар кезінде алдын алу және эпидемияға қарсы шаралар.Күйік бөлімшелеріндегі инфекциялық бақылау
Іріңді-септикалық инфекциялар кезінде алдын алу және эпидемияға қарсы шаралар.Күйік бөлімшелеріндегі инфекциялық бақылау Определение и оценка физического развития
Определение и оценка физического развития Возрастные особенности опорно-двигательной системы
Возрастные особенности опорно-двигательной системы Тканевая совместимость и переливание крови
Тканевая совместимость и переливание крови Антитела, строение и функции
Антитела, строение и функции Дыхание в необычных условиях
Дыхание в необычных условиях Дегенерация сетчатки глаза
Дегенерация сетчатки глаза Заболевания щитовидной железы
Заболевания щитовидной железы Злокачественные опухоли и их профилактика
Злокачественные опухоли и их профилактика Печеночная кома. Интенсивная терапия
Печеночная кома. Интенсивная терапия Роль формулярной системы в повышении эффективности использования лекарственных средств
Роль формулярной системы в повышении эффективности использования лекарственных средств Новые подходы в организации и проведении предварительных и периодических медицинских осмотров
Новые подходы в организации и проведении предварительных и периодических медицинских осмотров Антигипертензивные препараты при беременности. Влияние на мать и плод
Антигипертензивные препараты при беременности. Влияние на мать и плод Технология сестринских манипуляций. Сестринский процесс в организации питания больных
Технология сестринских манипуляций. Сестринский процесс в организации питания больных Аномалии развития почек
Аномалии развития почек Неврология, психиатрия және наркология. Шизофрения
Неврология, психиатрия және наркология. Шизофрения Электрофорез белков сыворотки крови
Электрофорез белков сыворотки крови Локализованные формы рака молочной железы. Тактика лечения. Прогноз
Локализованные формы рака молочной железы. Тактика лечения. Прогноз Молекулярні хвороби та методи їх діагностики. (Лекція 8)
Молекулярні хвороби та методи їх діагностики. (Лекція 8) Травматические вывихи
Травматические вывихи Цитостатикалық ем
Цитостатикалық ем Рожа - инфекционная болезнь
Рожа - инфекционная болезнь Холера. Клиническая картина
Холера. Клиническая картина Механизмы трофического действия физических упражнений
Механизмы трофического действия физических упражнений