Содержание
- 2. Objectives The Basics Interpretation Clinical Pearls Practice Recognition
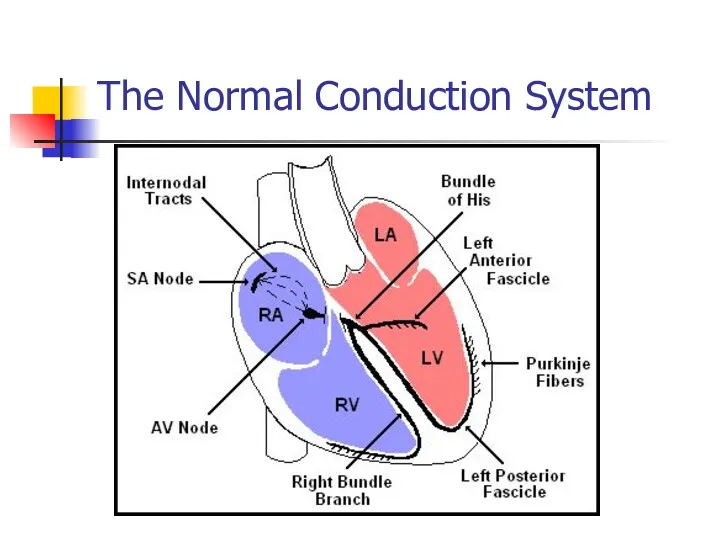
- 3. The Normal Conduction System
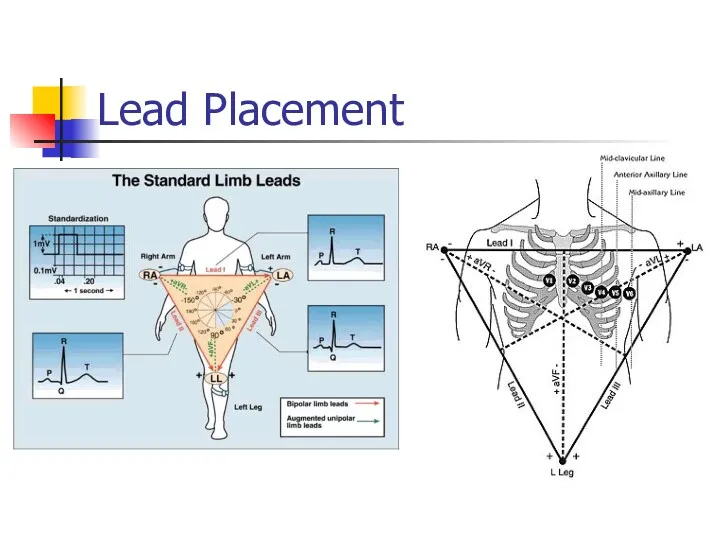
- 4. Lead Placement aVF
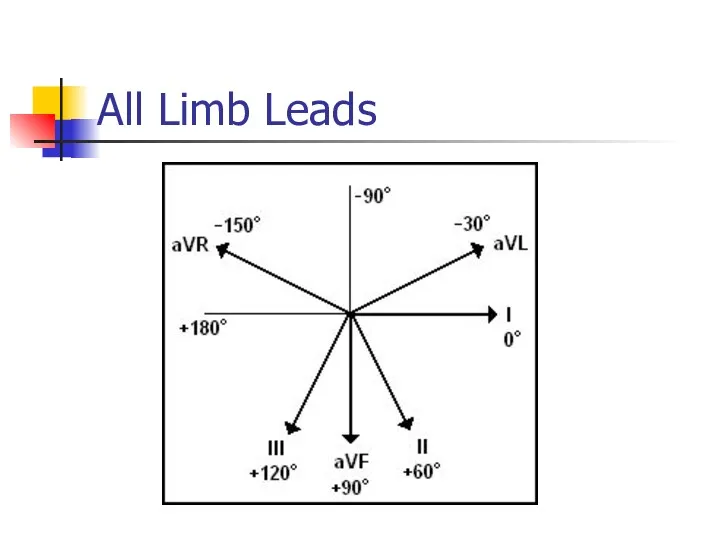
- 5. All Limb Leads
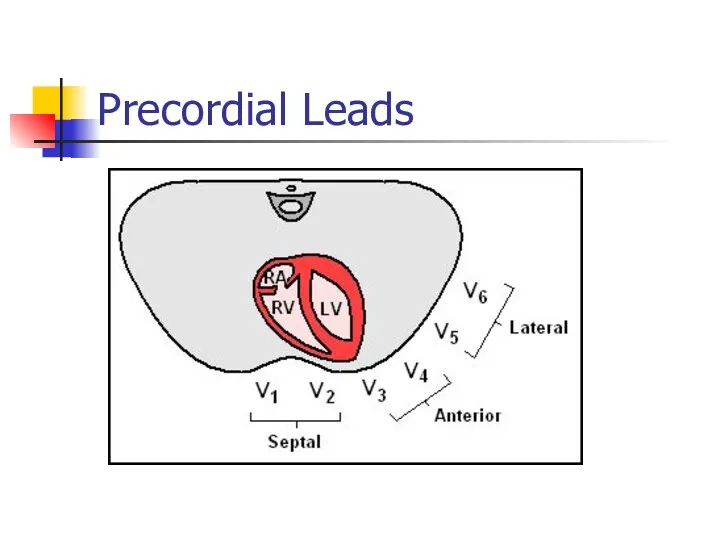
- 6. Precordial Leads
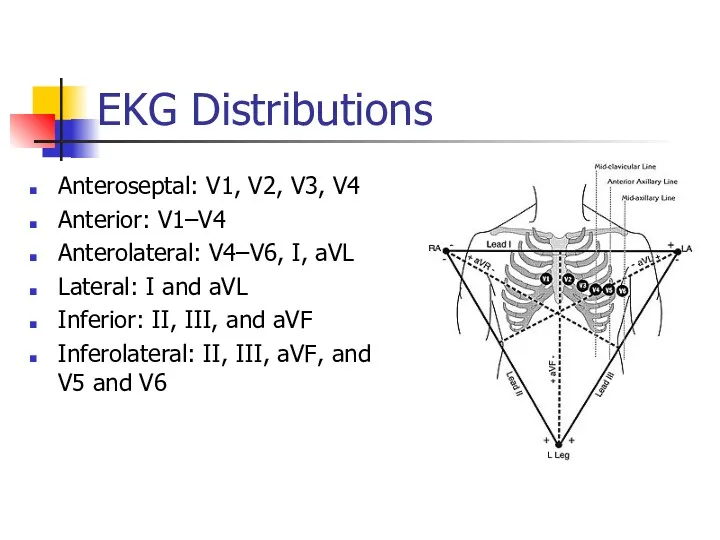
- 7. EKG Distributions Anteroseptal: V1, V2, V3, V4 Anterior: V1–V4 Anterolateral: V4–V6, I, aVL Lateral: I and
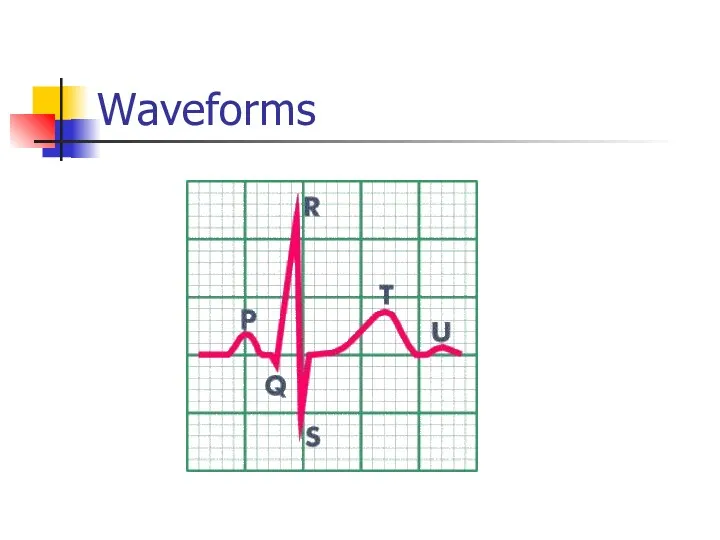
- 8. Waveforms
- 9. Interpretation Develop a systematic approach to reading EKGs and use it every time The system we
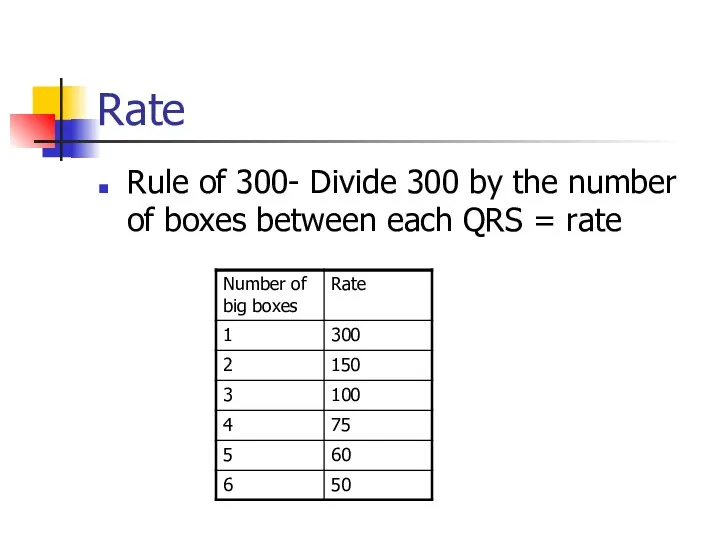
- 10. Rate Rule of 300- Divide 300 by the number of boxes between each QRS = rate
- 11. Rate HR of 60-100 per minute is normal HR > 100 = tachycardia HR
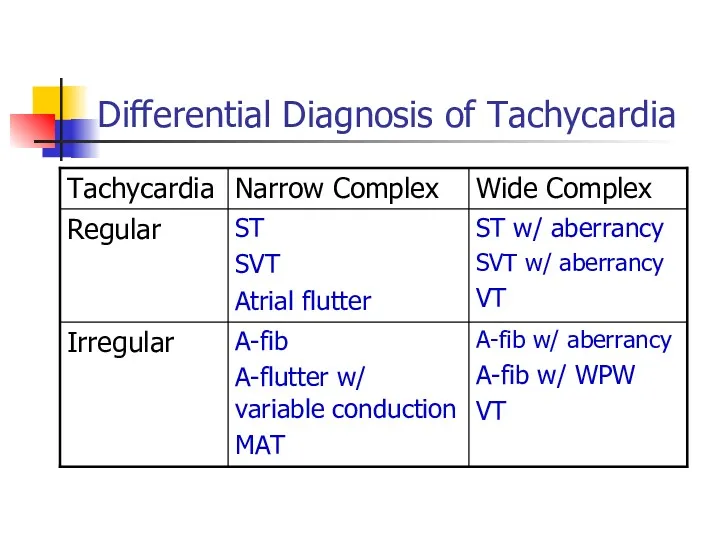
- 12. Differential Diagnosis of Tachycardia
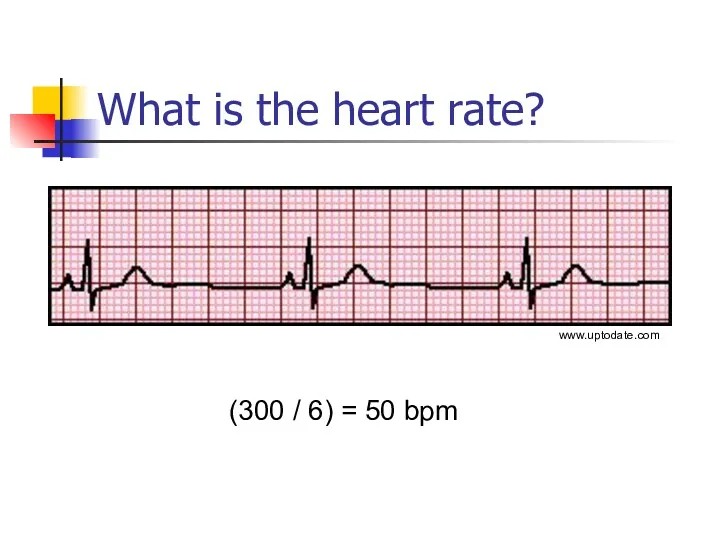
- 13. What is the heart rate? (300 / 6) = 50 bpm www.uptodate.com
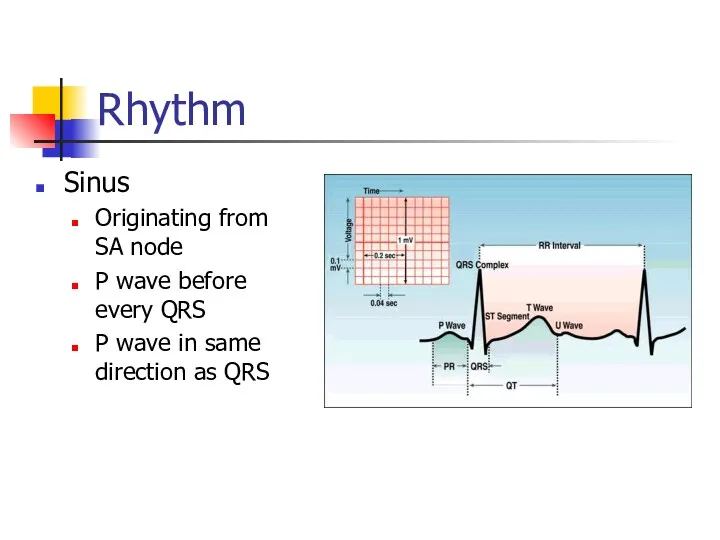
- 14. Rhythm Sinus Originating from SA node P wave before every QRS P wave in same direction
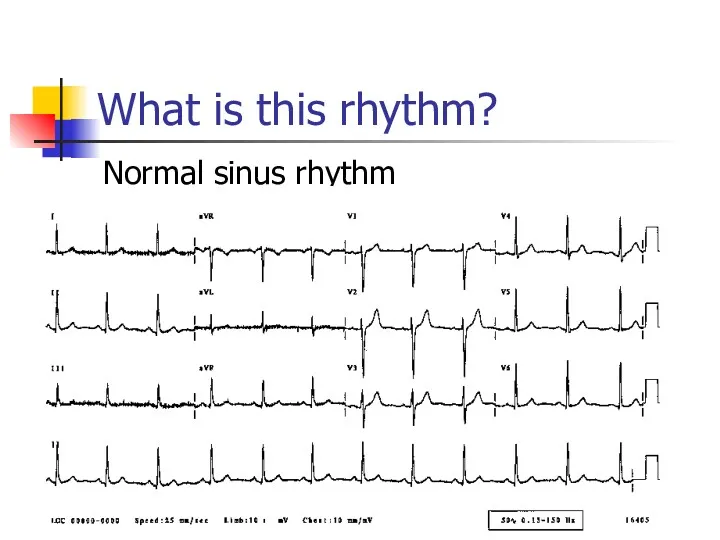
- 15. What is this rhythm? Normal sinus rhythm
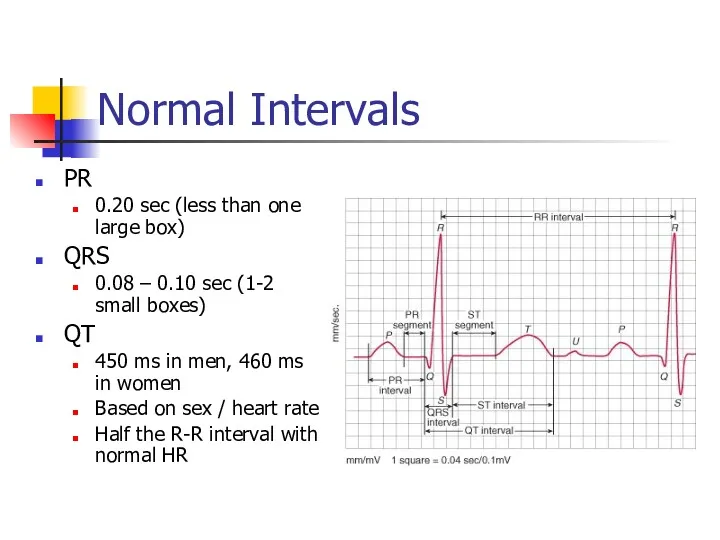
- 16. Normal Intervals PR 0.20 sec (less than one large box) QRS 0.08 – 0.10 sec (1-2
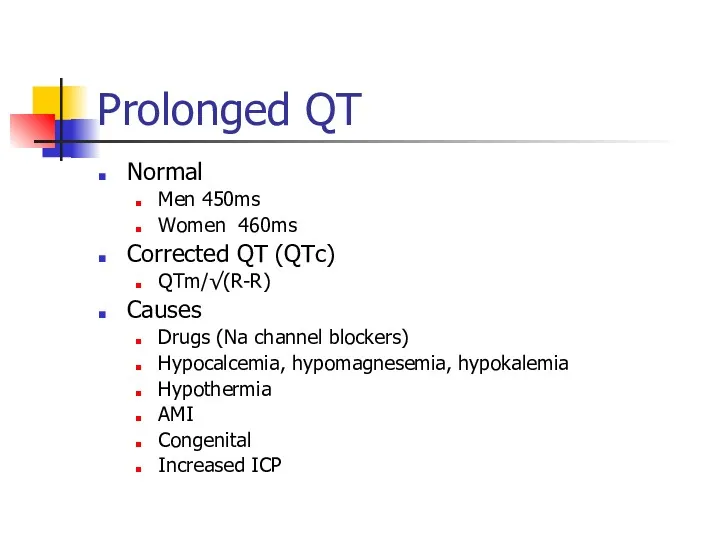
- 17. Prolonged QT Normal Men 450ms Women 460ms Corrected QT (QTc) QTm/√(R-R) Causes Drugs (Na channel blockers)
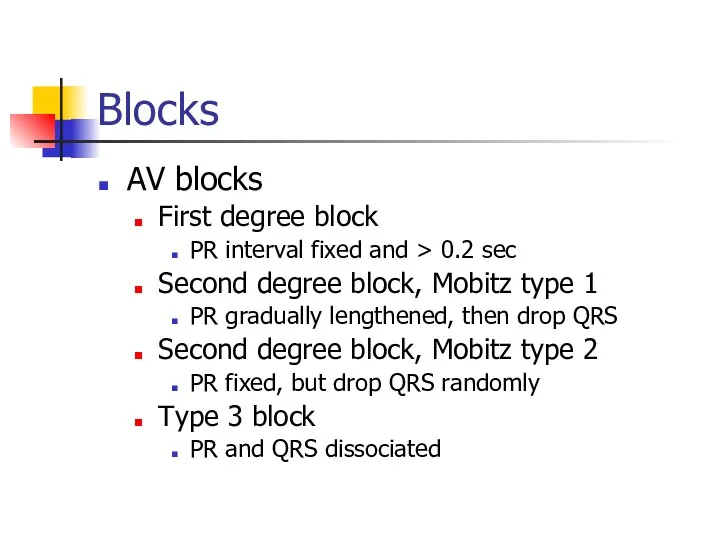
- 18. Blocks AV blocks First degree block PR interval fixed and > 0.2 sec Second degree block,
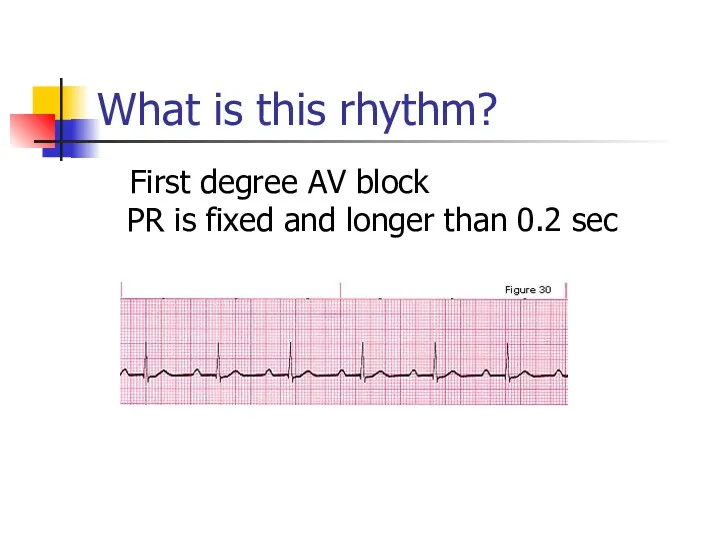
- 19. What is this rhythm? First degree AV block PR is fixed and longer than 0.2 sec
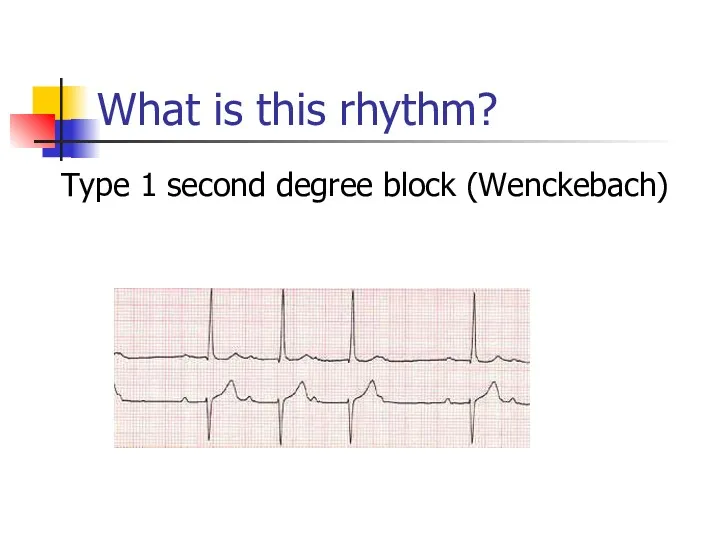
- 20. What is this rhythm? Type 1 second degree block (Wenckebach)
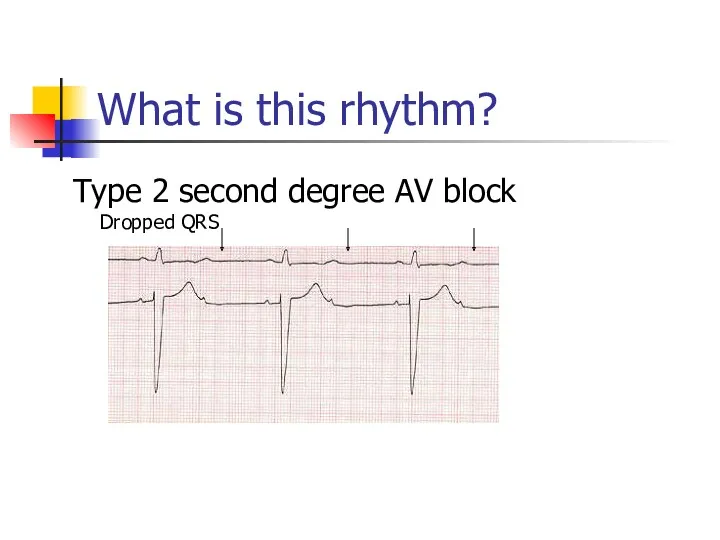
- 21. What is this rhythm? Type 2 second degree AV block Dropped QRS
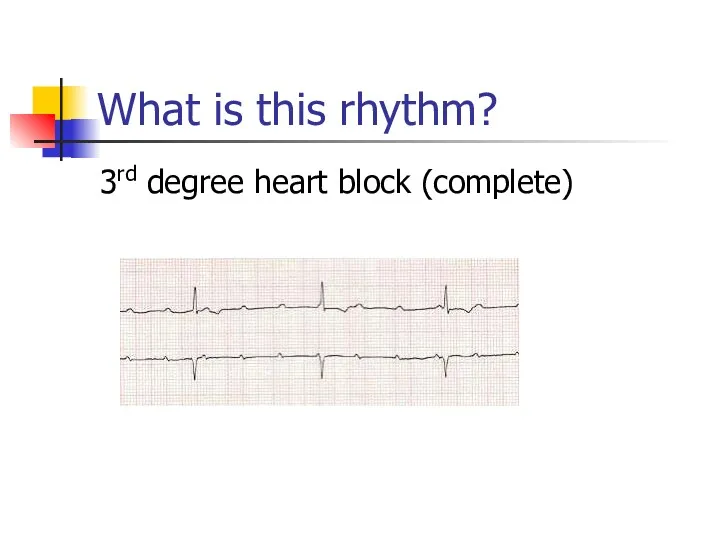
- 22. What is this rhythm? 3rd degree heart block (complete)
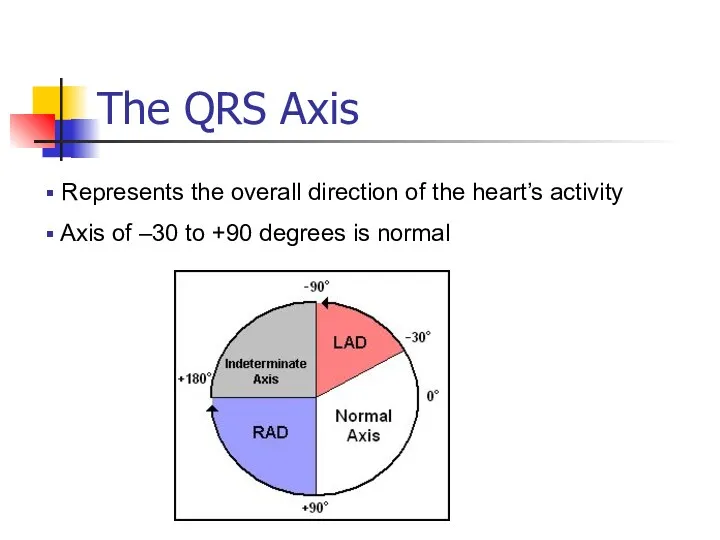
- 23. The QRS Axis Represents the overall direction of the heart’s activity Axis of –30 to +90
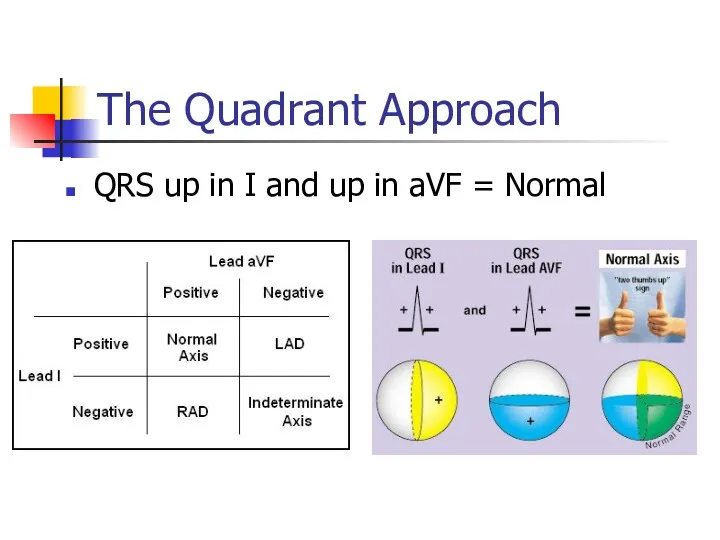
- 24. The Quadrant Approach QRS up in I and up in aVF = Normal
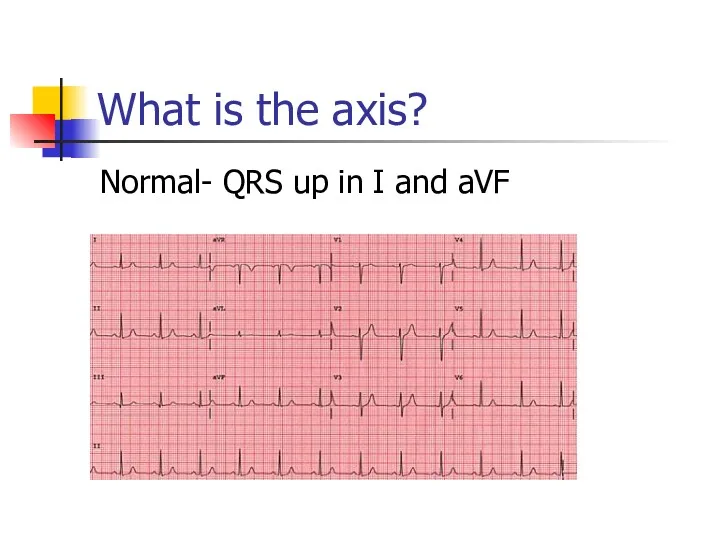
- 25. What is the axis? Normal- QRS up in I and aVF
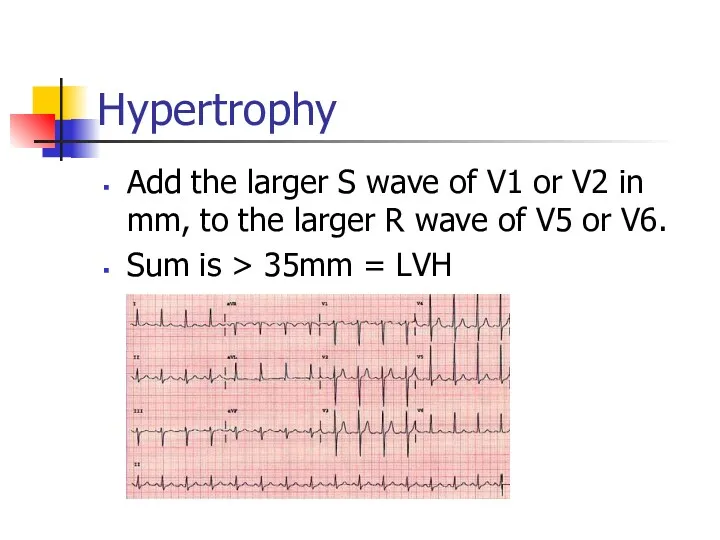
- 26. Hypertrophy Add the larger S wave of V1 or V2 in mm, to the larger R
- 27. Ischemia Usually indicated by ST changes Elevation = Acute infarction Depression = Ischemia Can manifest as
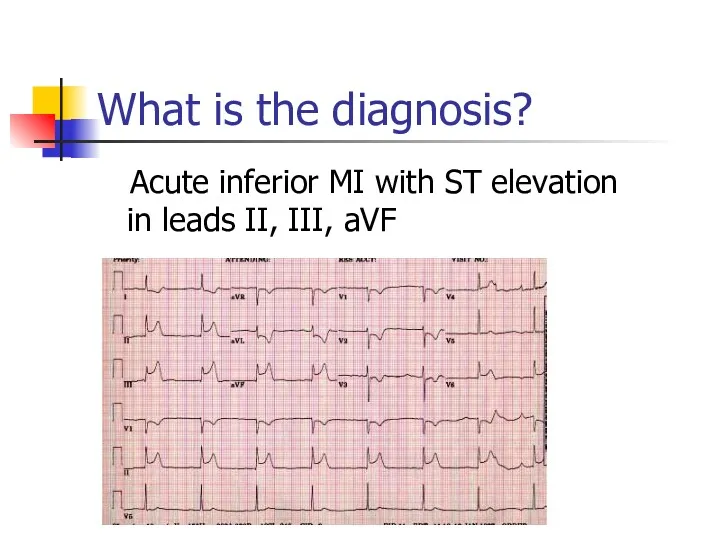
- 28. What is the diagnosis? Acute inferior MI with ST elevation in leads II, III, aVF
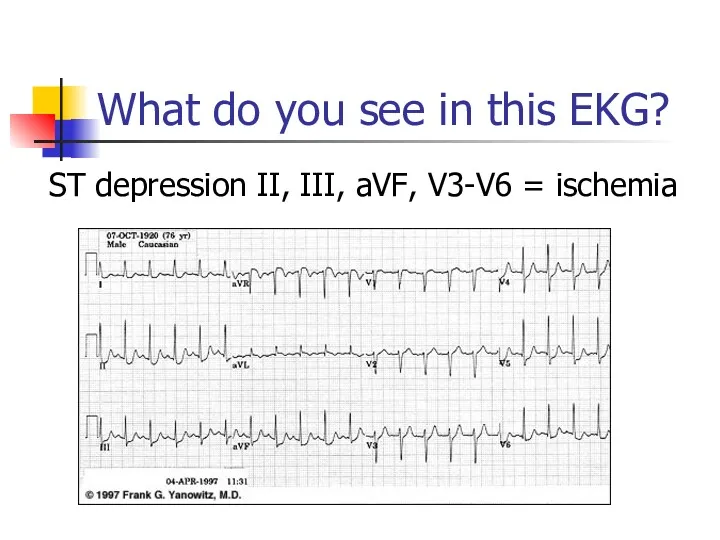
- 29. What do you see in this EKG? ST depression II, III, aVF, V3-V6 = ischemia
- 30. Let’s Practice The sample EKGs were obtained from the following text:
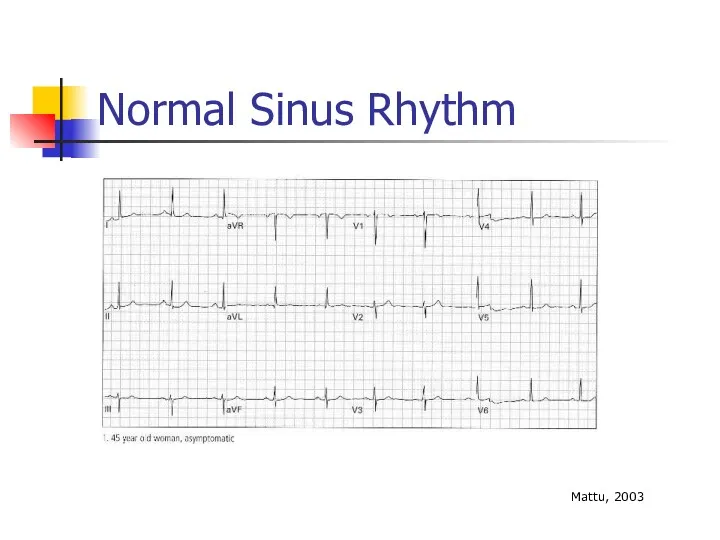
- 31. Normal Sinus Rhythm Mattu, 2003
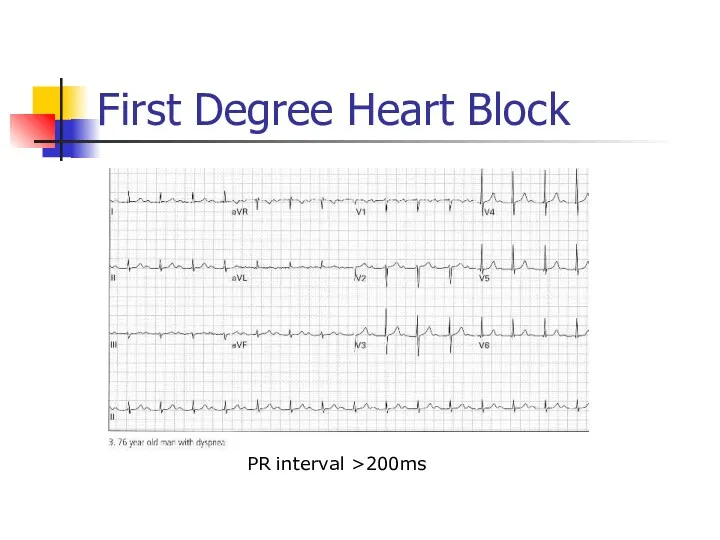
- 32. First Degree Heart Block PR interval >200ms
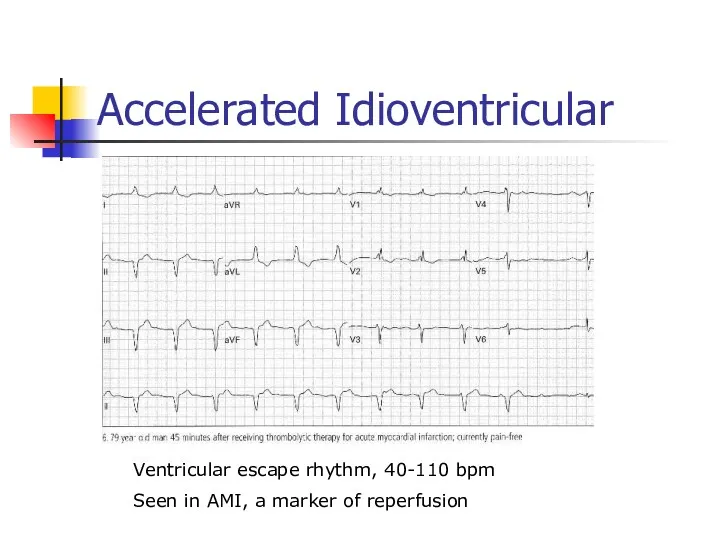
- 33. Accelerated Idioventricular Ventricular escape rhythm, 40-110 bpm Seen in AMI, a marker of reperfusion
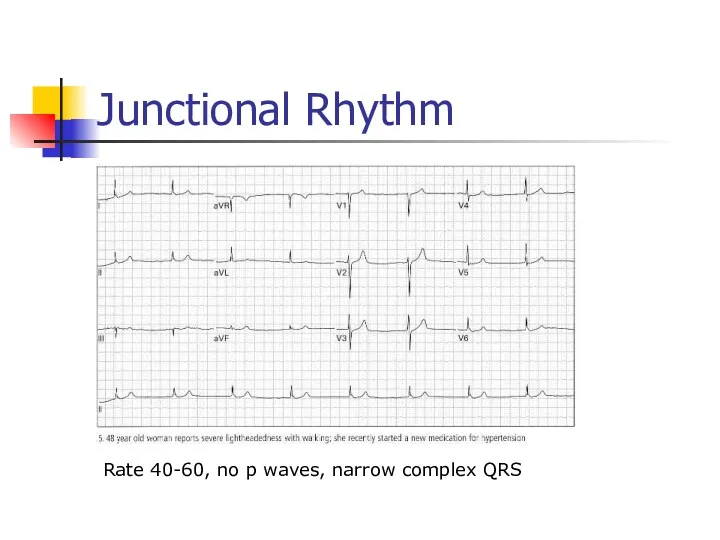
- 34. Junctional Rhythm Rate 40-60, no p waves, narrow complex QRS
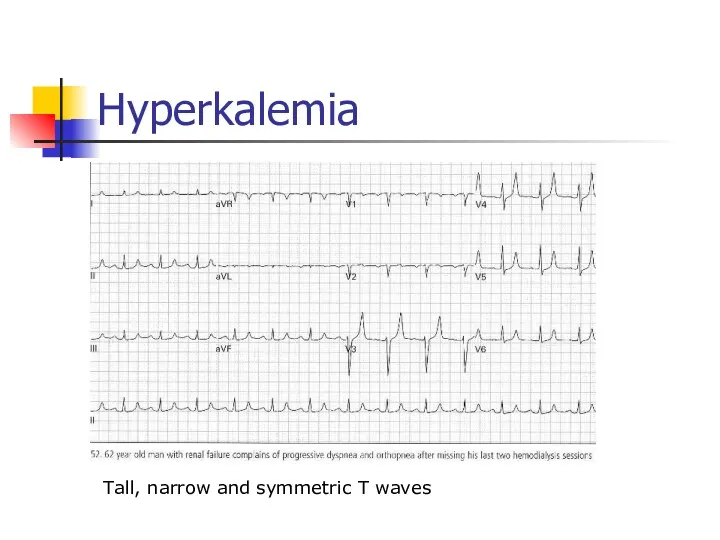
- 35. Hyperkalemia Tall, narrow and symmetric T waves
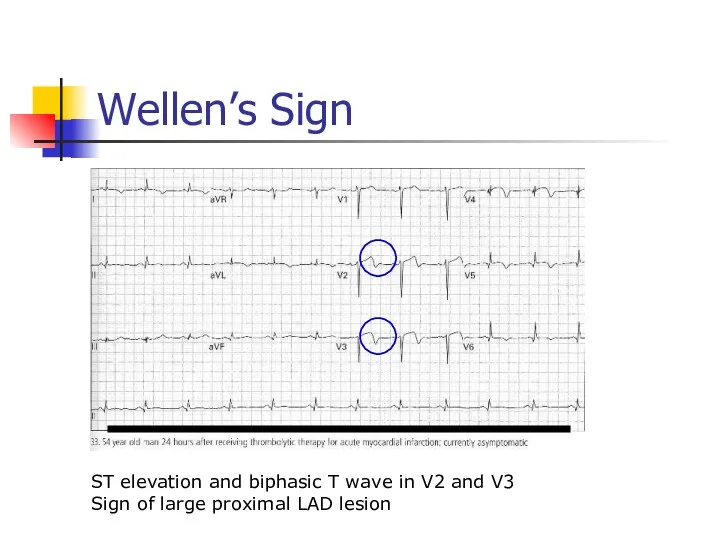
- 36. Wellen’s Sign ST elevation and biphasic T wave in V2 and V3 Sign of large proximal
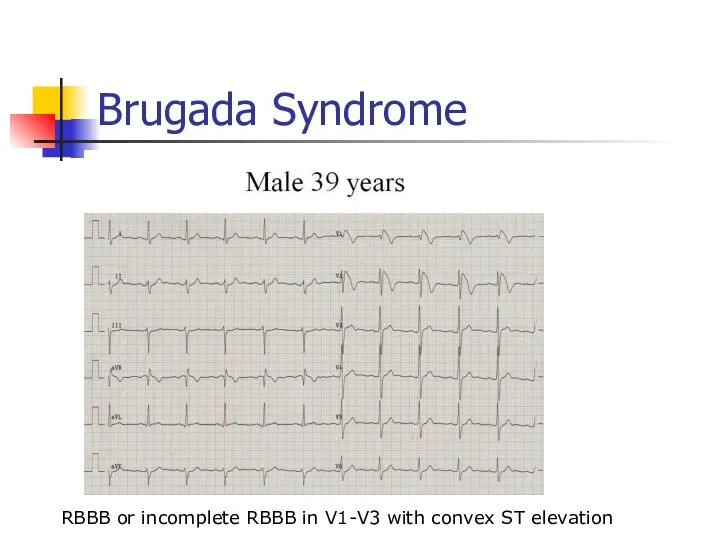
- 37. Brugada Syndrome RBBB or incomplete RBBB in V1-V3 with convex ST elevation
- 38. Brugada Syndrome Autosomal dominant genetic mutation of sodium channels Causes syncope, v-fib, self terminating VT, and
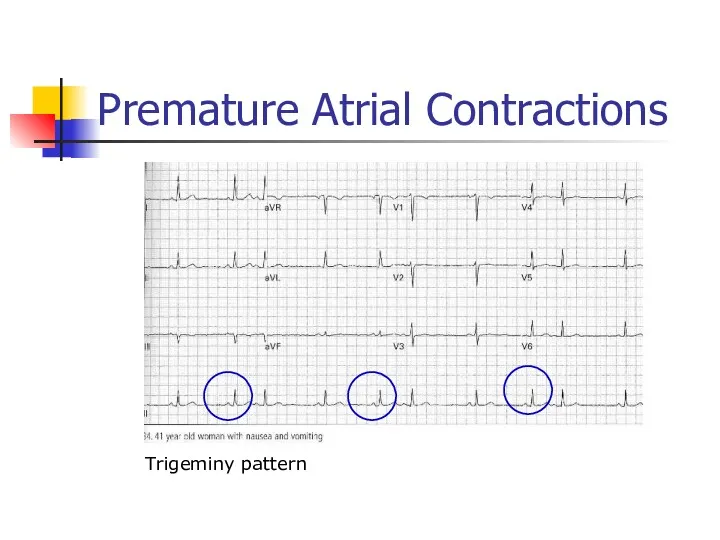
- 39. Premature Atrial Contractions Trigeminy pattern
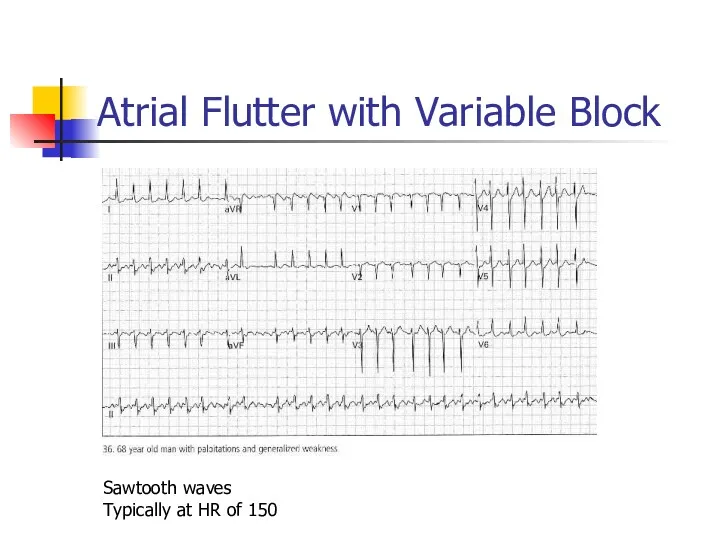
- 40. Atrial Flutter with Variable Block Sawtooth waves Typically at HR of 150
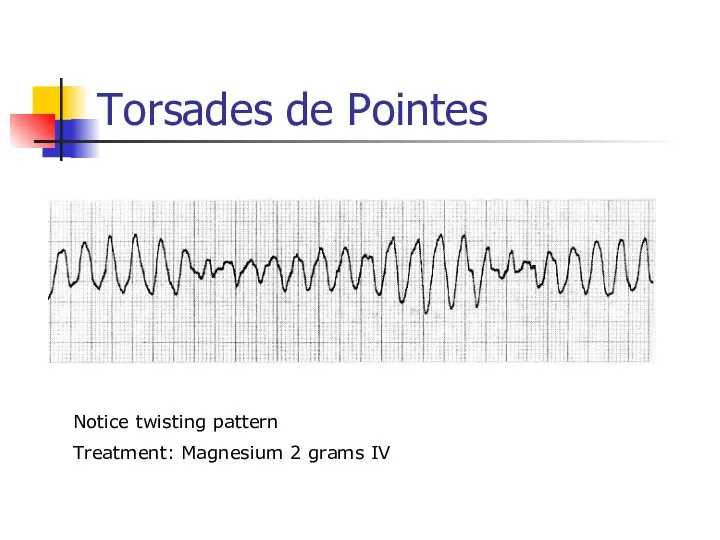
- 41. Torsades de Pointes Notice twisting pattern Treatment: Magnesium 2 grams IV
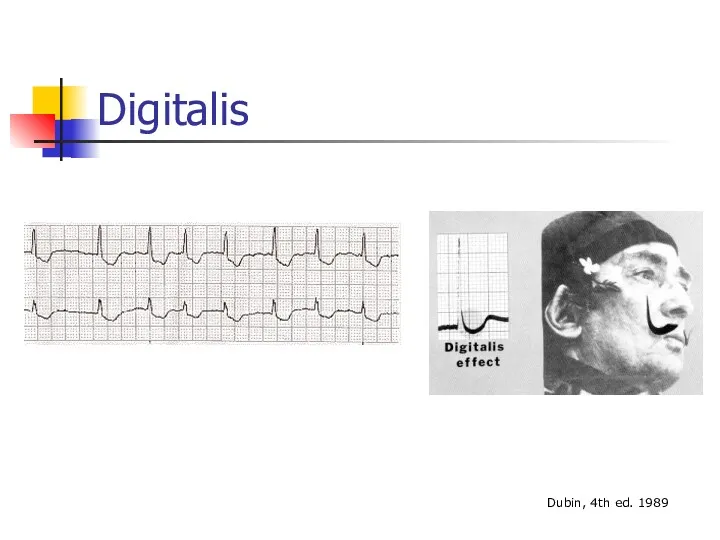
- 42. Digitalis Dubin, 4th ed. 1989
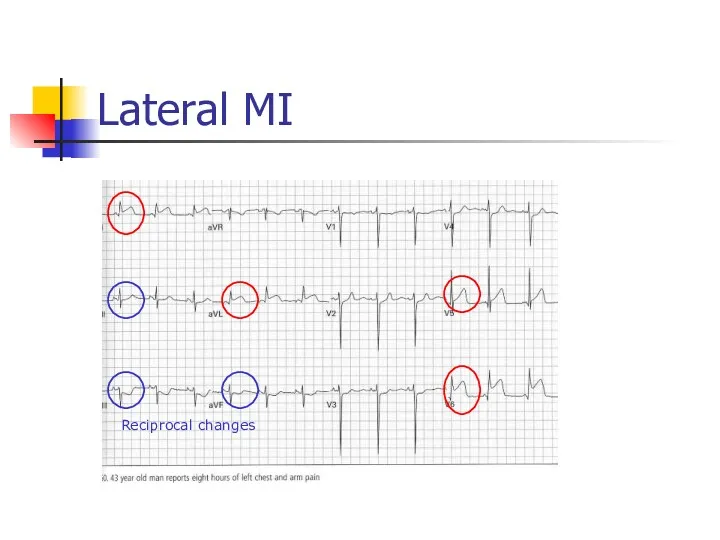
- 43. Lateral MI Reciprocal changes
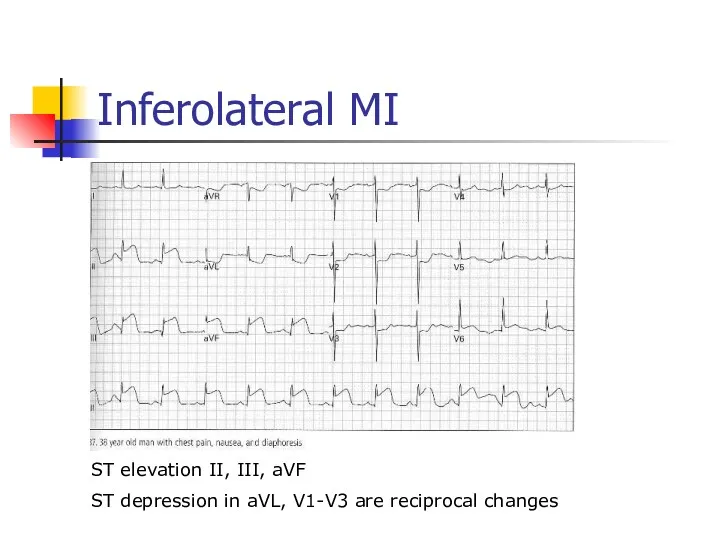
- 44. Inferolateral MI ST elevation II, III, aVF ST depression in aVL, V1-V3 are reciprocal changes
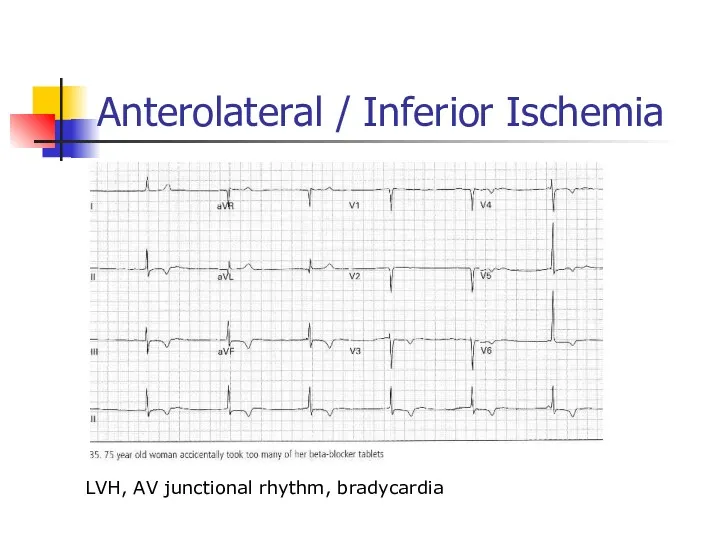
- 45. Anterolateral / Inferior Ischemia LVH, AV junctional rhythm, bradycardia
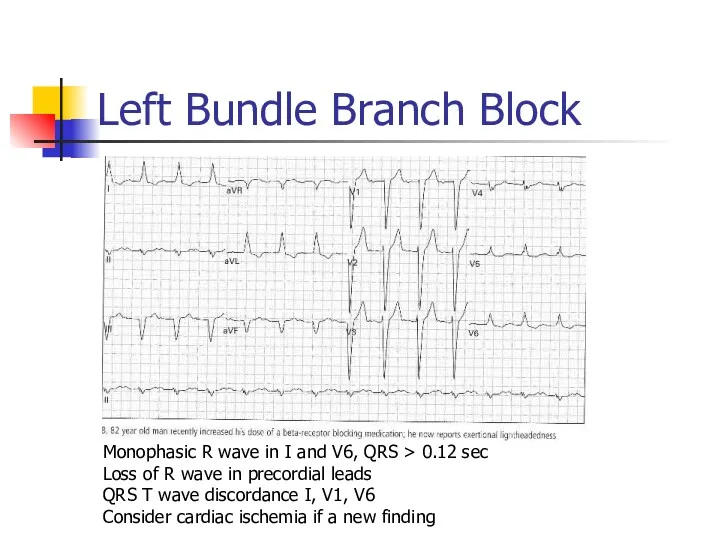
- 46. Left Bundle Branch Block Monophasic R wave in I and V6, QRS > 0.12 sec Loss
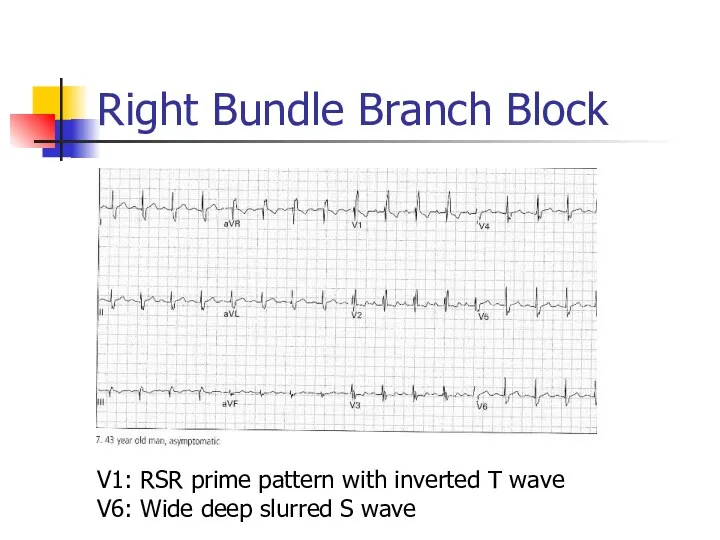
- 47. Right Bundle Branch Block V1: RSR prime pattern with inverted T wave V6: Wide deep slurred
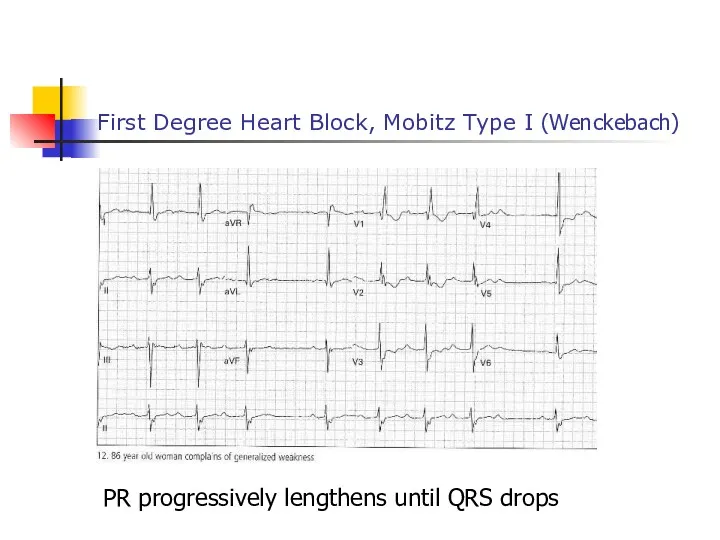
- 48. First Degree Heart Block, Mobitz Type I (Wenckebach) PR progressively lengthens until QRS drops
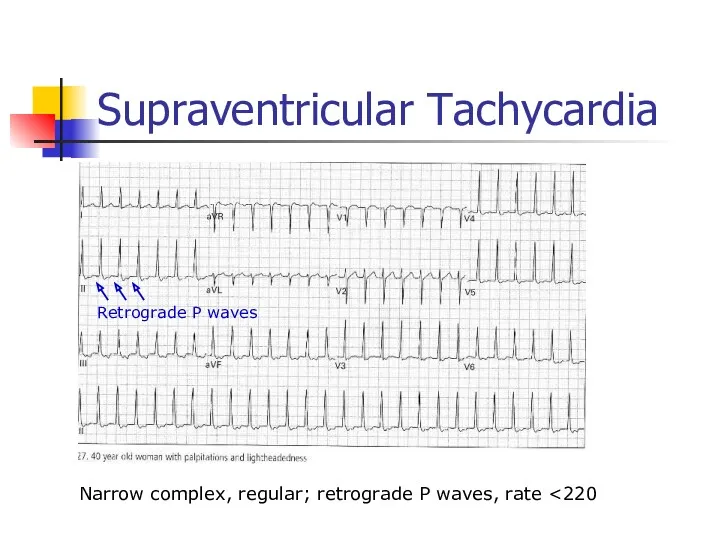
- 49. Supraventricular Tachycardia Narrow complex, regular; retrograde P waves, rate Retrograde P waves
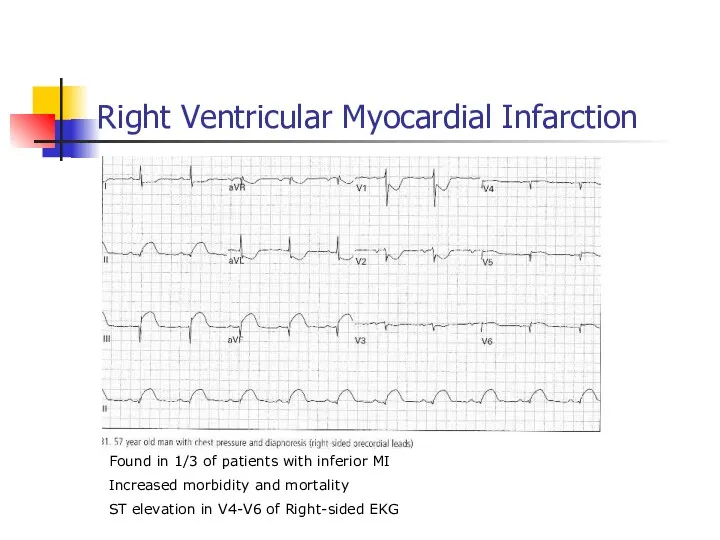
- 50. Right Ventricular Myocardial Infarction Found in 1/3 of patients with inferior MI Increased morbidity and mortality
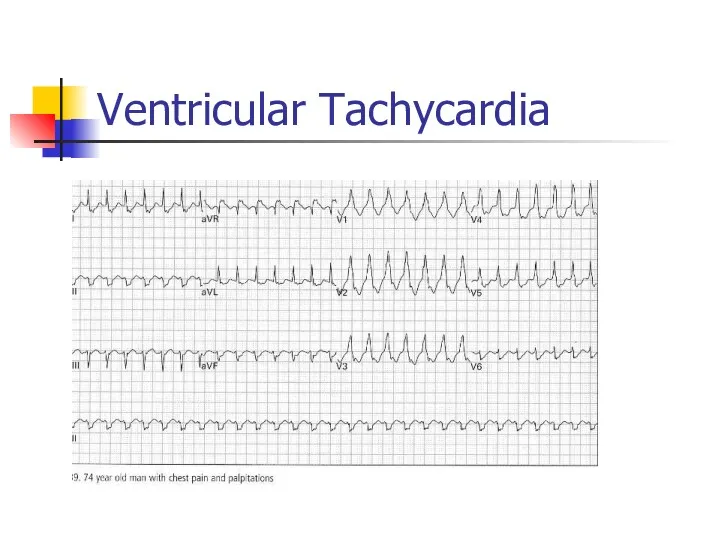
- 51. Ventricular Tachycardia
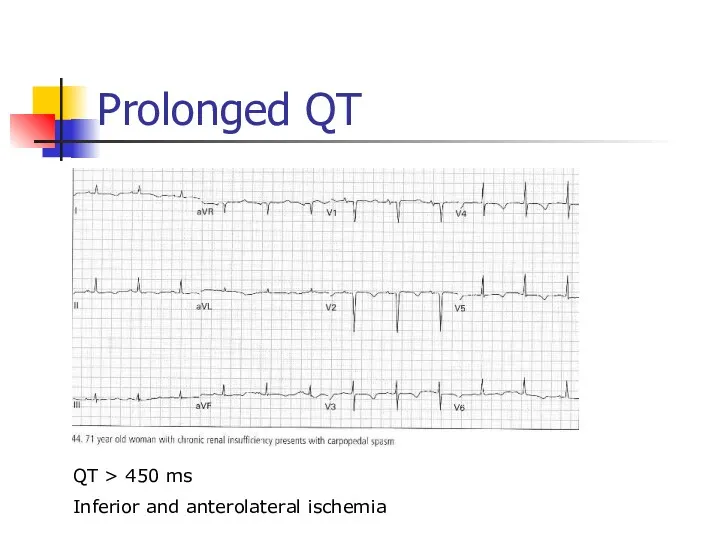
- 52. Prolonged QT QT > 450 ms Inferior and anterolateral ischemia
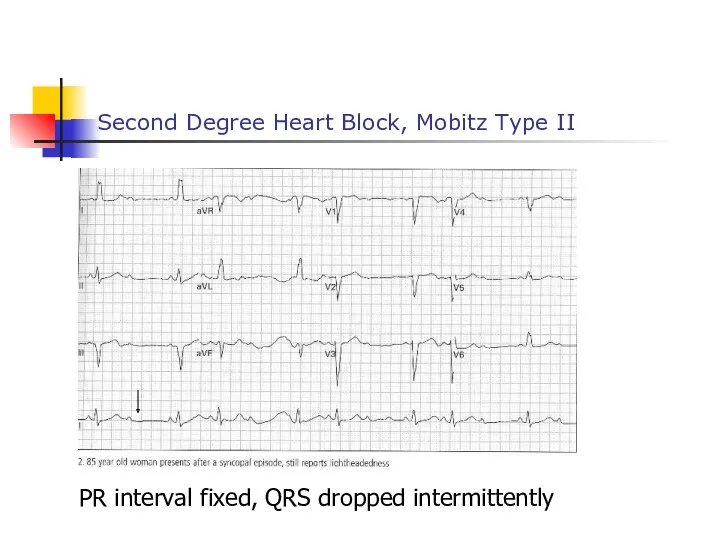
- 53. Second Degree Heart Block, Mobitz Type II PR interval fixed, QRS dropped intermittently
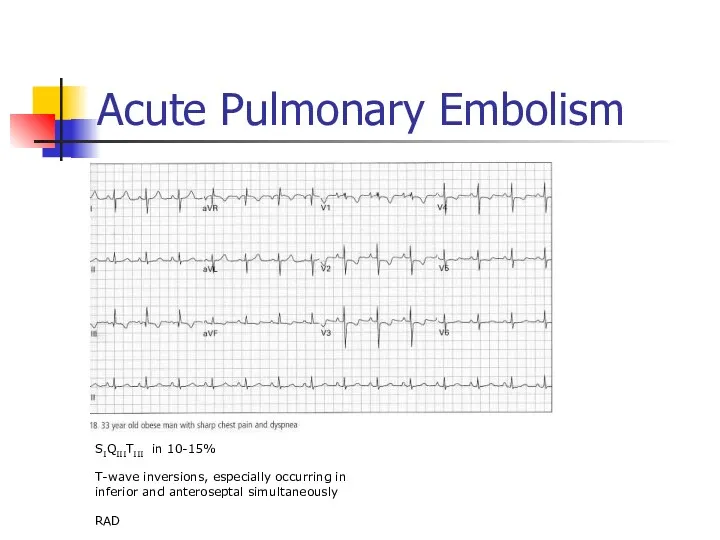
- 54. Acute Pulmonary Embolism SIQIIITIII in 10-15% T-wave inversions, especially occurring in inferior and anteroseptal simultaneously RAD
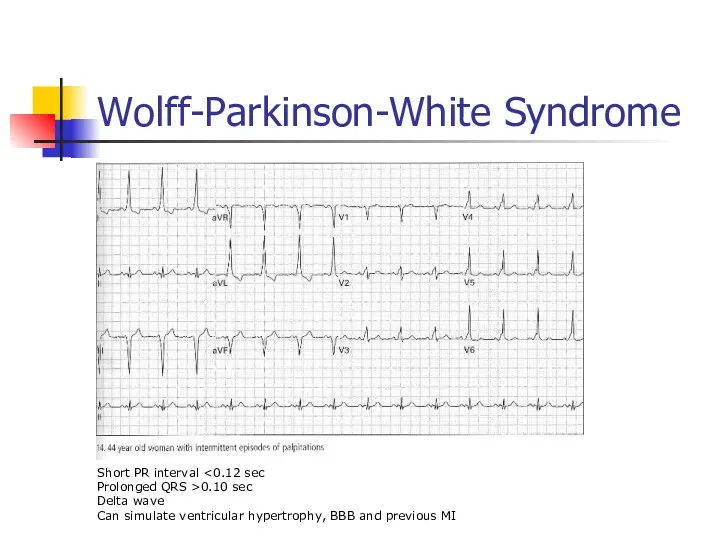
- 55. Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome Short PR interval Prolonged QRS >0.10 sec Delta wave Can simulate ventricular hypertrophy, BBB
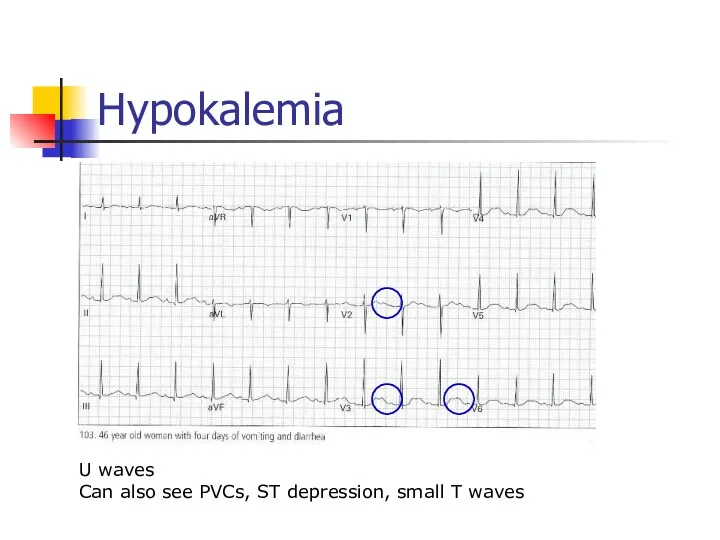
- 56. Hypokalemia U waves Can also see PVCs, ST depression, small T waves
- 59. Скачать презентацию





 Общие правила оказания первой доврачебной помощи. Алгоритм оказания первой помощи. Юридические и моральные аспекты
Общие правила оказания первой доврачебной помощи. Алгоритм оказания первой помощи. Юридические и моральные аспекты Клинические формы вторичного туберкулеза
Клинические формы вторичного туберкулеза Рентгеноконтрастные исследования и препараты
Рентгеноконтрастные исследования и препараты Анатомо-физиологические особенности эндокринной системы у детей
Анатомо-физиологические особенности эндокринной системы у детей Мочекаменная болезнь. Гидронефроз
Мочекаменная болезнь. Гидронефроз Вич и Спид
Вич и Спид Інфузійна терапія
Інфузійна терапія Градация доказательств и уровни рекомендаций
Градация доказательств и уровни рекомендаций Особенности сестринского ухода за инфекционными больными. Сестринский процесс. Сестринский диагноз
Особенности сестринского ухода за инфекционными больными. Сестринский процесс. Сестринский диагноз Анализ затрат на лекарственные средства с помощью ABC/VEV методологии
Анализ затрат на лекарственные средства с помощью ABC/VEV методологии Моногибридті будандастыру. Гибридологиялық зерттеу әдісі
Моногибридті будандастыру. Гибридологиялық зерттеу әдісі Опухоли. Онкология
Опухоли. Онкология Анонимные Наркоманы г. Йошкар-Ола
Анонимные Наркоманы г. Йошкар-Ола Энтеробиоз: определение
Энтеробиоз: определение Ожирение. Степени ожирения
Ожирение. Степени ожирения Генетика человека. Генные болезни
Генетика человека. Генные болезни Острые воспалительные заболевания матки и придатков как причина развития клиники острого живота в гинекологии
Острые воспалительные заболевания матки и придатков как причина развития клиники острого живота в гинекологии Лекарственная токсикология
Лекарственная токсикология Орталық және шеткі жүйке жүйесінің клиникалық физиологиясы бен биохимиясы
Орталық және шеткі жүйке жүйесінің клиникалық физиологиясы бен биохимиясы История развития психогенетики в мировой науке
История развития психогенетики в мировой науке Ас қорыту жүйесіне жалпы шолу
Ас қорыту жүйесіне жалпы шолу Микробиологическая диагностика брюшного тифа, паратифов и других сальмонеллезных инфекций. Пищевые отравления и их диагностика
Микробиологическая диагностика брюшного тифа, паратифов и других сальмонеллезных инфекций. Пищевые отравления и их диагностика Лабораторная диагностика заболеваний, вызываемых извитыми формами бактерий. Спирохетозы (сифилис, лептоспироз, возвратные тифы)
Лабораторная диагностика заболеваний, вызываемых извитыми формами бактерий. Спирохетозы (сифилис, лептоспироз, возвратные тифы) Жарақаттар
Жарақаттар Диагностическая информативность онкомаркеров в гинекологии
Диагностическая информативность онкомаркеров в гинекологии Специфическая (антидотная) фармакотерапия острых отравлений
Специфическая (антидотная) фармакотерапия острых отравлений Эректильная дисфункция (ЭД)
Эректильная дисфункция (ЭД) Лекарственные препараты по химии
Лекарственные препараты по химии