Содержание
- 3. Filth flies, belonging to suborder Brachycera (Family; Muscidae, Calliphoridae and Sarcophagidae), are a major cause of
- 4. Muscidae, Stable Flies, and Fanniidae, Lesser HousefliesMuscidae or stable flies and Fanniidae, lesser houseflies, are genera
- 5. The Calliphoridae (commonly known as blow flies, blow-flies, carrion flies, bluebottles, greenbottles, or cluster flies)are a
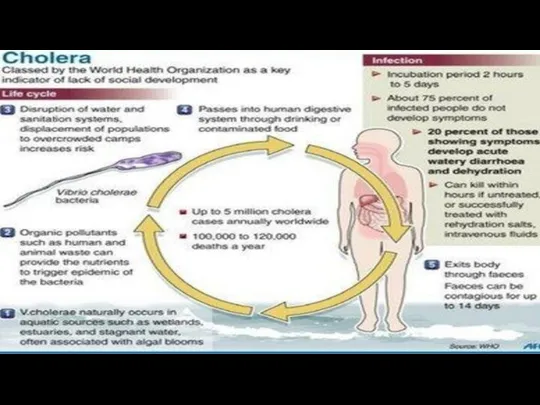
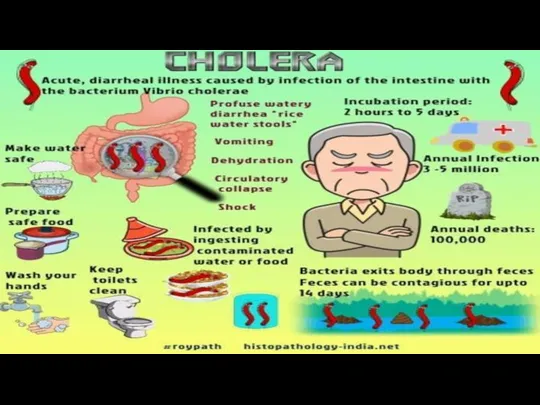
- 10. Diseases caused by flies Typhoid fever Polio Cholera Bacillary dysentery Tricoma virus Leprosy Tuberculosis Enteric infections
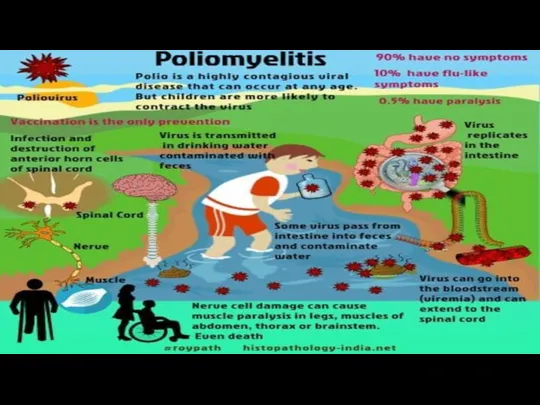
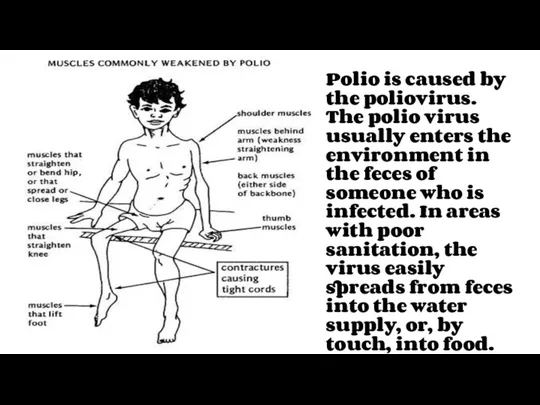
- 14. Polio is caused by the poliovirus. The polio virus usually enters the environment in the feces
- 15. Typhoid is caused by the bacteria S. typhi and spread through food, drinks, and drinking water
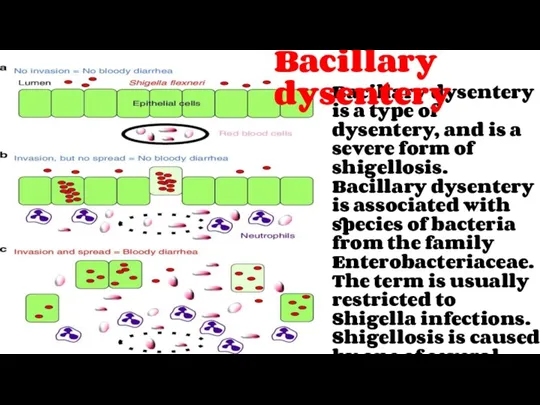
- 16. Bacillary dysentery is a type of dysentery, and is a severe form of shigellosis. Bacillary dysentery
- 17. Enteric Diseases and Food-Borne Diseases. Enteric diseases are caused by micro-organisms such as viruses, bacteria and
- 18. Cockroaches, along with other insects, are suspected of being carriers of the bacillus Mycobacterium leprae which
- 19. References https://www.science.gov/topicpages/c/calliphoridae+sarcophagidae+muscidae https://www.researchgate.net/publication/265612586_Flies_as_Predators_and_Parasitoids_of_Terrestrial_Gastropods_with_Emphasis_on_Phoridae_Calliphoridae_Sarcophagidae_Muscidae_and_Fanniidae_Diptera_Brachycera_Cyclorrhapha
- 21. Скачать презентацию













 Констатация смерти и правила обращения с трупом
Констатация смерти и правила обращения с трупом Одонтогенные воспалительные заболевания челюстно лицевой области
Одонтогенные воспалительные заболевания челюстно лицевой области Scarlet fever
Scarlet fever Кровотечение
Кровотечение Визуальная диагностика дерматитов (контактно-аллергический, атопический, токсикодермический)
Визуальная диагностика дерматитов (контактно-аллергический, атопический, токсикодермический) Тістем және оның түрлері
Тістем және оның түрлері Аритмии и блокады сердца
Аритмии и блокады сердца Радиобиологиялық әсерлер
Радиобиологиялық әсерлер Вакцинациялау дегеніміз не және ол не үшін қажет?
Вакцинациялау дегеніміз не және ол не үшін қажет?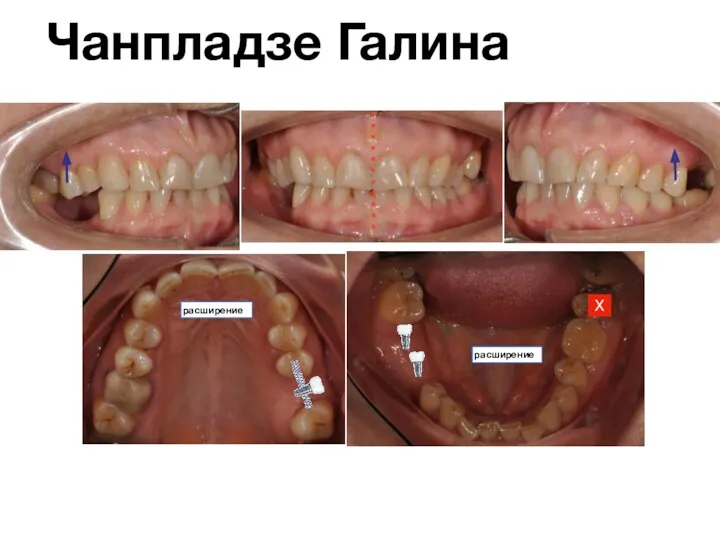 Чанпладзе Галина
Чанпладзе Галина Основные проблемы социальной медицины и организации здравоохранения
Основные проблемы социальной медицины и организации здравоохранения Повреждения клетки
Повреждения клетки Қазақстан Республикасындағы стоматологиялық көмекті ұйымдастыру. Шет елдердегі стоматологиялық көмектің ұйымдастырылуы
Қазақстан Республикасындағы стоматологиялық көмекті ұйымдастыру. Шет елдердегі стоматологиялық көмектің ұйымдастырылуы Клиника алды, арнайы фармакологиялық белсенділік, токсикология, канцерогендік, мутагендік, аллергендік
Клиника алды, арнайы фармакологиялық белсенділік, токсикология, канцерогендік, мутагендік, аллергендік Инфильтративный туберкулез
Инфильтративный туберкулез Врожденные пороки развития: диагностика и тактика
Врожденные пороки развития: диагностика и тактика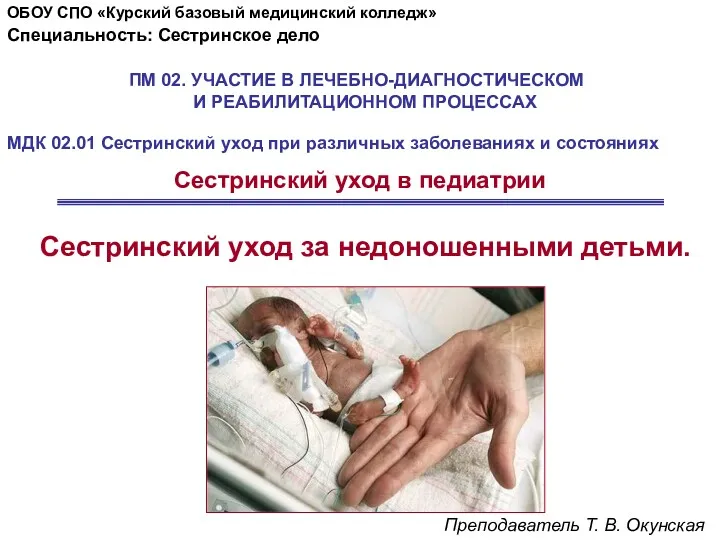 Сестринский уход за недоношенными детьми
Сестринский уход за недоношенными детьми Роль гормонов в регуляции роста, развития и гомеостаза
Роль гормонов в регуляции роста, развития и гомеостаза Лекарственные средства, влияющие на функцию органов дыхания
Лекарственные средства, влияющие на функцию органов дыхания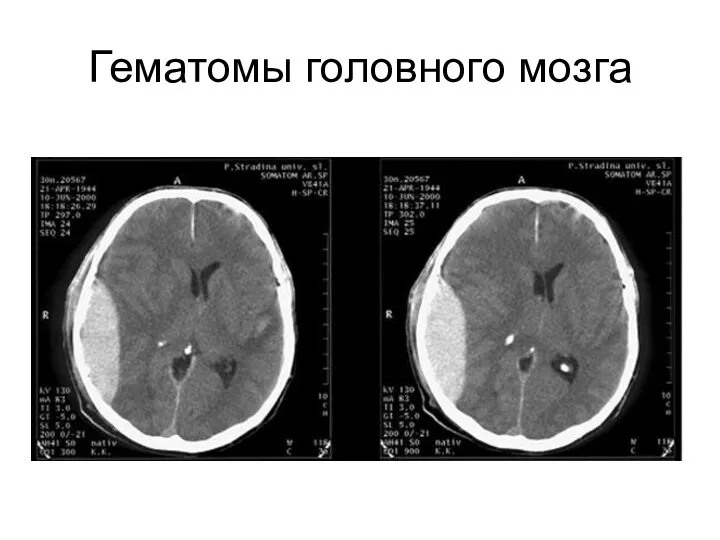 Гематомы головного мозга
Гематомы головного мозга Иммунопрофилактика инфекционных болезней
Иммунопрофилактика инфекционных болезней Амбулатория жағдайында жөтел кезіндегі рационалды дифференциалды диагностика алгоритмі
Амбулатория жағдайында жөтел кезіндегі рационалды дифференциалды диагностика алгоритмі Первая помощь при укусах насекомых и домашних животных
Первая помощь при укусах насекомых и домашних животных Антропометриялық көрсеткіштерді анықтау
Антропометриялық көрсеткіштерді анықтау Презентация по ЭКГ для ветеринарных врачей
Презентация по ЭКГ для ветеринарных врачей Инсулинотерапия. Классификация
Инсулинотерапия. Классификация Пупочная грыжа
Пупочная грыжа Тірі ағзаға электр және магнит өрістерінің әсері. ЯМР және ЭПР құбылыстарды медициналық зерттеулерде қолдану
Тірі ағзаға электр және магнит өрістерінің әсері. ЯМР және ЭПР құбылыстарды медициналық зерттеулерде қолдану