Содержание
- 2. Renal cell carcinoma ETIOLOGY: CIGARETTE SMOKING OBESITY ANALGESIC ABUSE (phenacetin) INDUSTRIAL SOLVENT, TRICHLOROETHYLENE EXPOSURE TO CADMIUM
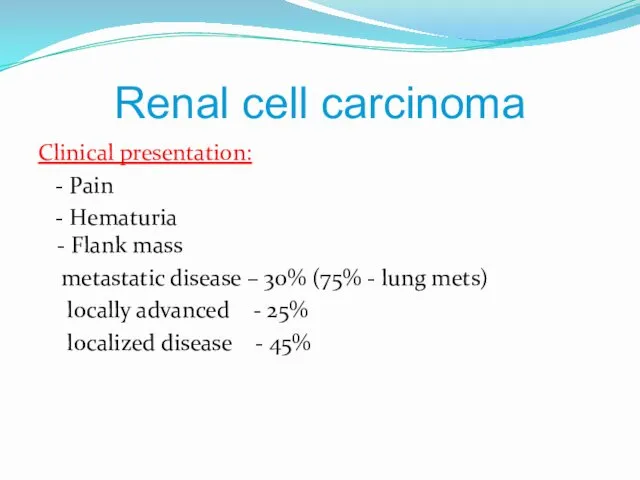
- 3. Renal cell carcinoma Clinical presentation: - Pain - Hematuria - Flank mass metastatic disease – 30%
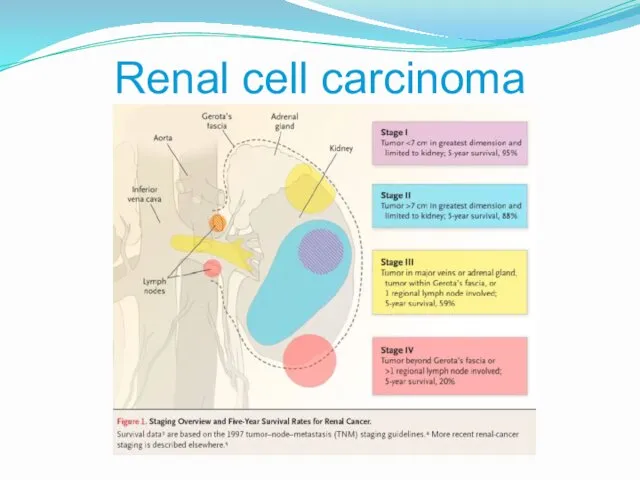
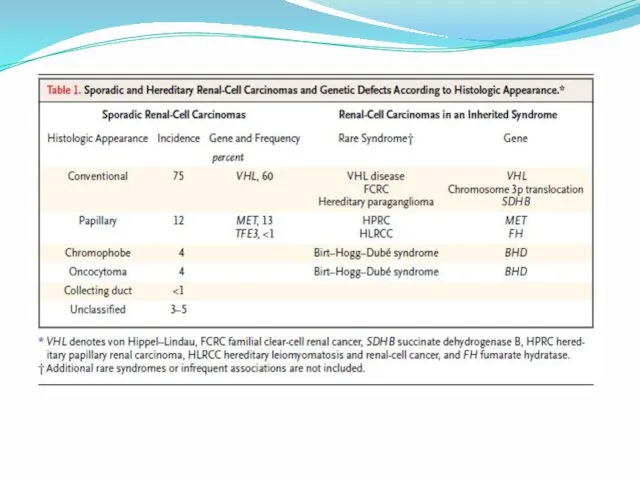
- 4. Renal cell carcinoma
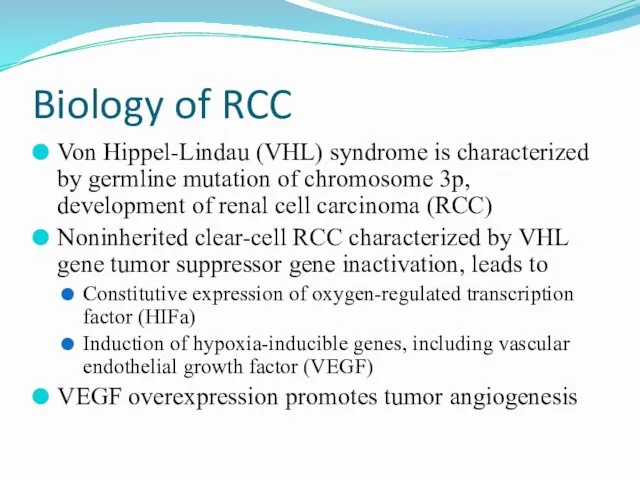
- 6. Biology of RCC Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome is characterized by germline mutation of chromosome 3p, development
- 7. Motzer. Five variables as risk factors for short survival Low KPS ( High LDH (>1.5 upper
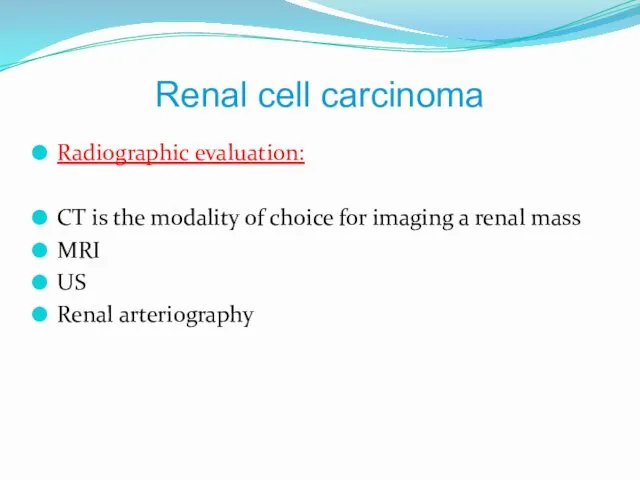
- 8. Renal cell carcinoma Radiographic evaluation: CT is the modality of choice for imaging a renal mass
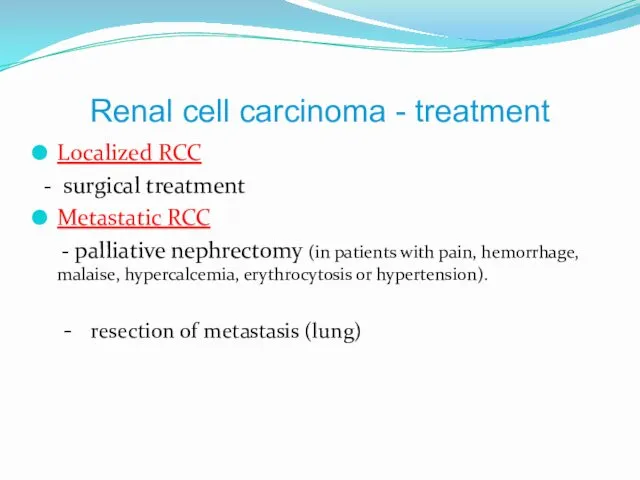
- 9. Renal cell carcinoma - treatment Localized RCC - surgical treatment Metastatic RCC - palliative nephrectomy (in
- 10. Renal cell carcinoma - treatment Chemotherapy - Chemotherapy currently has little to no role in the
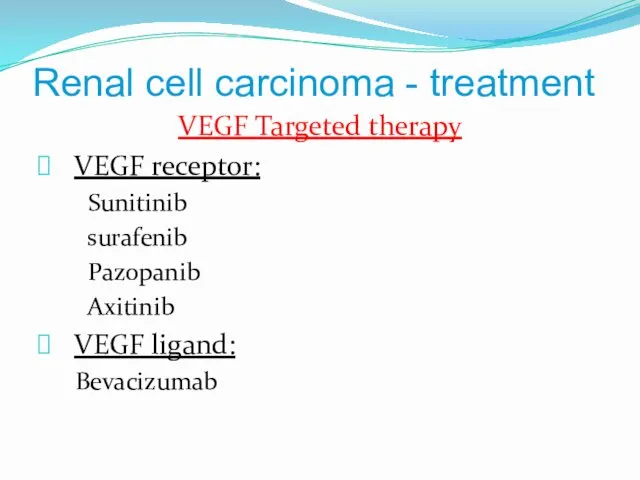
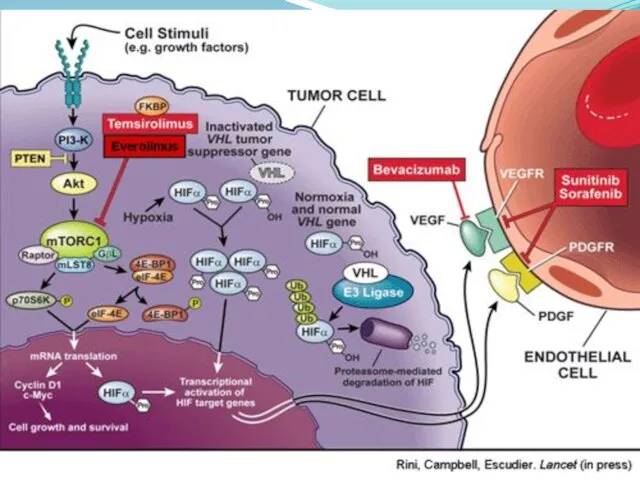
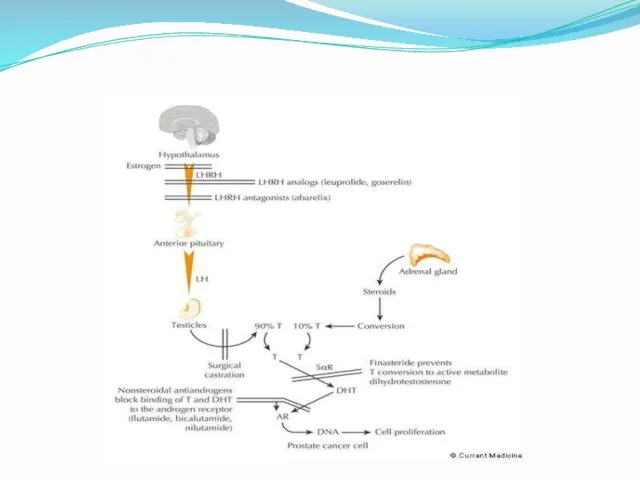
- 11. Renal cell carcinoma - treatment VEGF Targeted therapy VEGF receptor: Sunitinib surafenib Pazopanib Axitinib VEGF ligand:
- 12. immunotherapy Opdivo (Nivolumab) - anti PD1
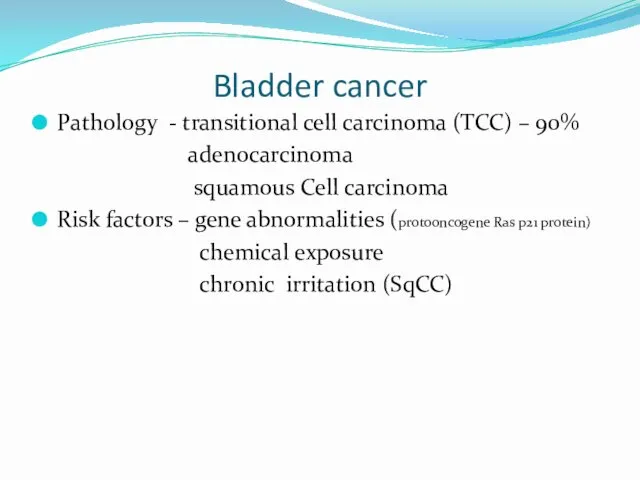
- 14. Bladder cancer Pathology - transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) – 90% adenocarcinoma squamous Cell carcinoma Risk factors
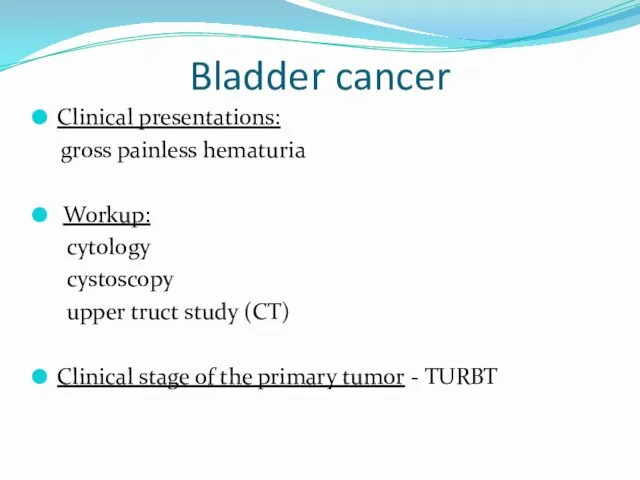
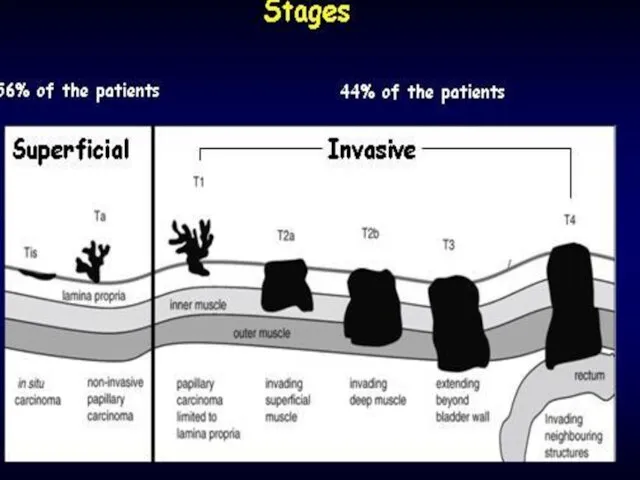
- 15. Bladder cancer Clinical presentations: gross painless hematuria Workup: cytology cystoscopy upper truct study (CT) Clinical stage
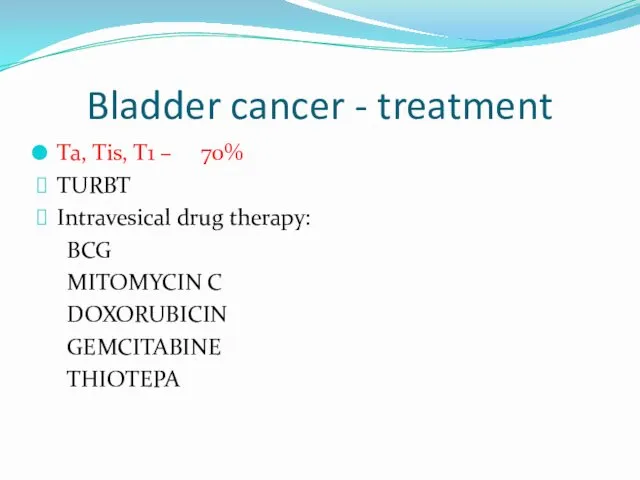
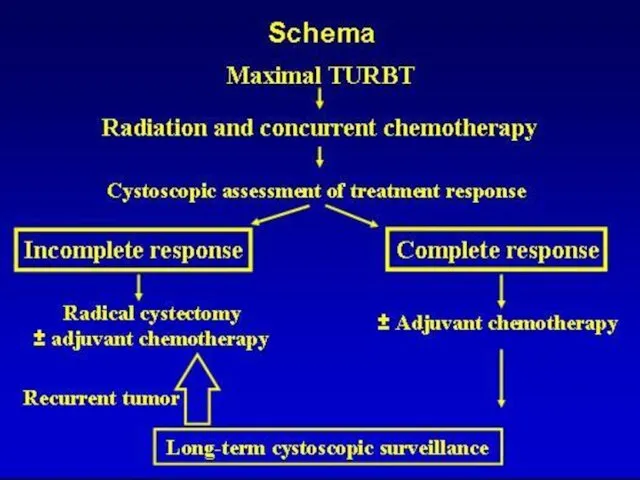
- 17. Bladder cancer - treatment Ta, Tis, T1 – 70% TURBT Intravesical drug therapy: BCG MITOMYCIN C
- 18. Bladder cancer - treatment Muscularis propria-invasive disease Radical cystectomy Complications of Cystectomy (ileal Conduit): Metabolic acidosis
- 20. Bladder cancer - treatment Adjuvant chemotherapy? 4 cycles of Cisplatin plus gemcitabine or MVAC? Metastatic Bladder
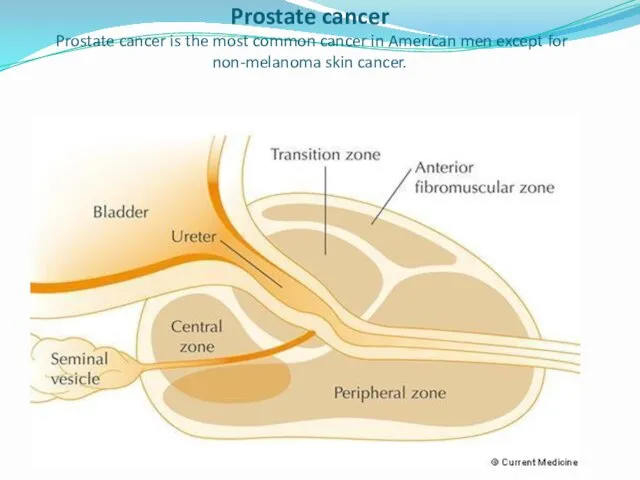
- 21. Prostate cancer Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in American men except for non-melanoma skin
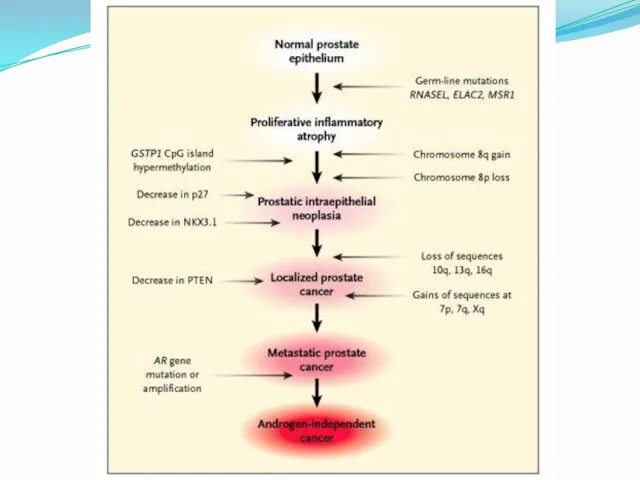
- 22. Risk factors GENETIC FACTORS two-fold elevated in men with an affected first degree relative (brother, father),
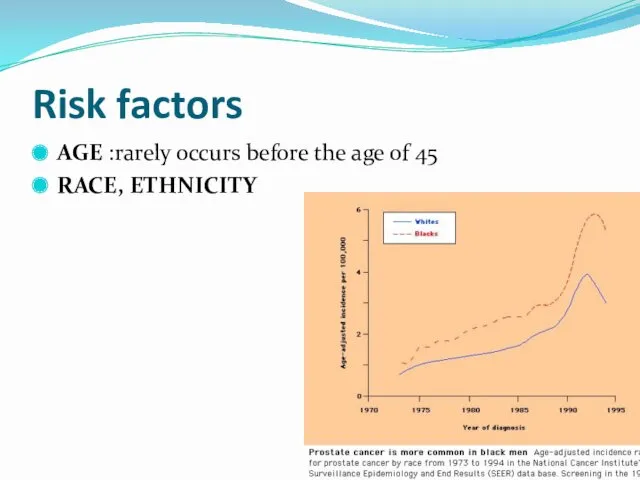
- 23. Risk factors AGE :rarely occurs before the age of 45 RACE, ETHNICITY
- 24. BRCA1/2 mutations The presence of BRCA1/2 mutations may increase the risk of developing prostate cancer at
- 25. Dr.Neiman Victoria
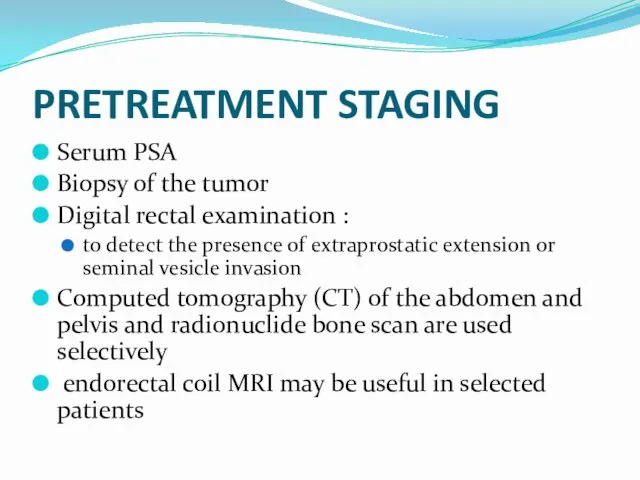
- 26. PRETREATMENT STAGING Serum PSA Biopsy of the tumor Digital rectal examination : to detect the presence
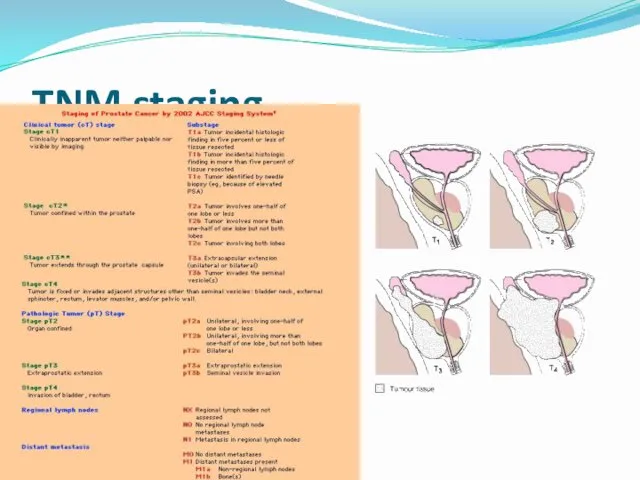
- 27. 27.09.2017 Dr.Neiman Victoria TNM staging
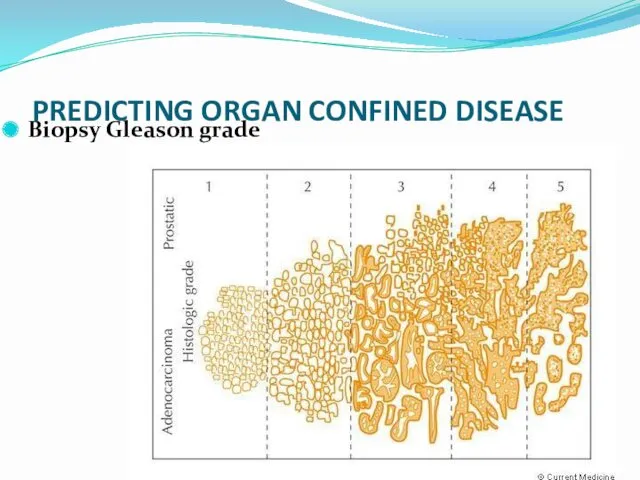
- 28. Dr.Neiman Victoria PREDICTING ORGAN CONFINED DISEASE Biopsy Gleason grade
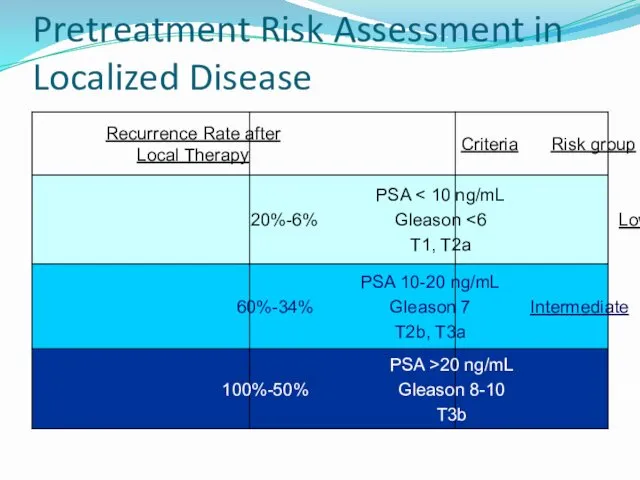
- 29. Pretreatment Risk Assessment in Localized Disease
- 30. The most effective therapy for clinically localized prostate cancer Surgery radiation therapy (RT) androgen deprivation therapy
- 31. Increased PSA After Radical Prostatectomy Risks Factor for Clinical Relapse 1. Doubling time The shorter the
- 33. OTHER THERAPIES Cryotherapy Laparoscopic and robotic prostatectomy
- 34. Pure germ cell tumor – one site of hystology Mixed germ cell tumor – more than
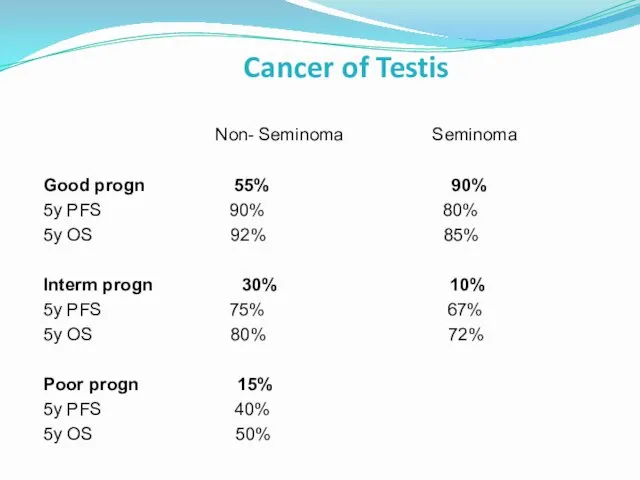
- 35. Cancer of Testis Non- Seminoma Seminoma Good progn 55% 90% 5y PFS 90% 80% 5y OS
- 36. Cancer of Testis - Staging T1- without involv of tunica vaginalis T2 –vascular/lumphovascul inv., involv tunica
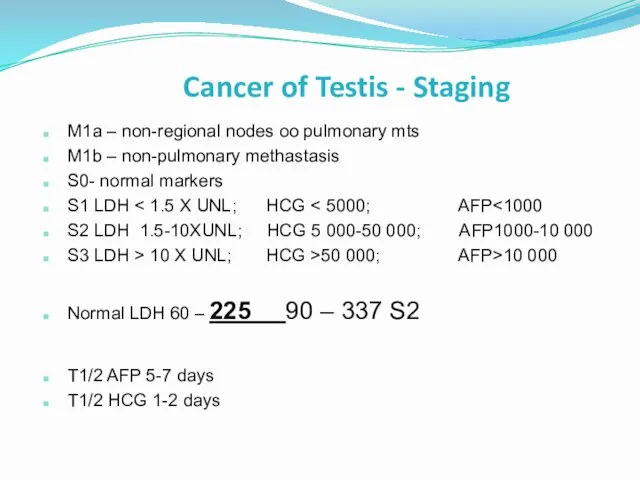
- 37. Cancer of Testis - Staging M1a – non-regional nodes oo pulmonary mts M1b – non-pulmonary methastasis
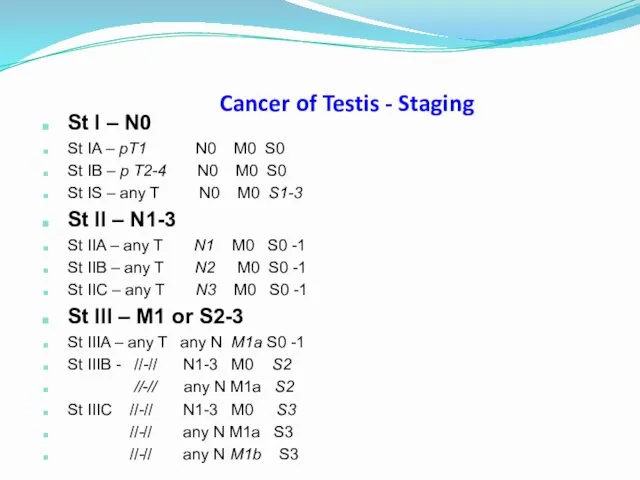
- 38. Cancer of Testis - Staging St I – N0 St IA – pT1 N0 M0 S0
- 39. Cancer of Testis – Prognostic Group Any primary, Normal alfa-FP, any HCG, LDH for both prognostic
- 40. Seminoma St I RT para-aortic (*Fossa) (*Jones) or Carbo-single dose (*Oliver) or sirveillance (*Ward)
- 41. Seminoma St II- Low- tumor burden (St IIA-B = Dog-leg 25-30 Gy + boost 5 -7.5
- 42. Seminoma St II - III – (High tumor burden= N3, supradiaphragm LN, visceral mts) Good progn.
- 43. Seminoma St II-III High- tumor burden Chemo +/- surgery RPLND * good prognosis BEPX3 (PEX4) *interm
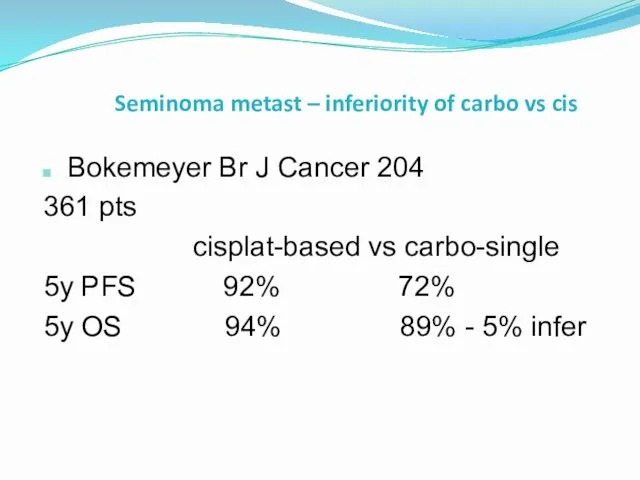
- 44. Seminoma metast – inferiority of carbo vs cis Bokemeyer Br J Cancer 204 361 pts cisplat-based
- 45. Non-Seminoma Good and interm progn: testis/retroperitoneal primary And No nonpulmonary visceral metastasis And : S1 for
- 47. Скачать презентацию


















 Периоды родов
Периоды родов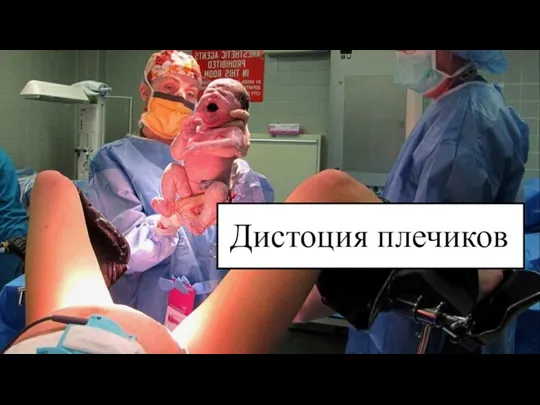 Дистоция плечиков
Дистоция плечиков Вторичный туберкулёз. Макропрепараты
Вторичный туберкулёз. Макропрепараты Голотопия желудка
Голотопия желудка Состояния, сопровождающиеся потерей сознания
Состояния, сопровождающиеся потерей сознания Организация предметно-количественного учета лекарственных препаратов
Организация предметно-количественного учета лекарственных препаратов Врожденный гипертрофический стеноз привратника
Врожденный гипертрофический стеноз привратника Балалар анемиясы
Балалар анемиясы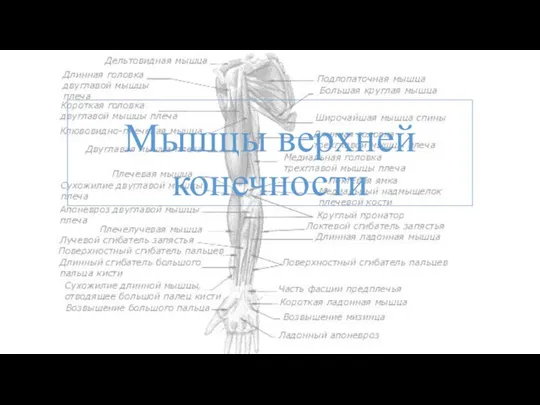 Мышцы верхней конечности
Мышцы верхней конечности Патология эндометрия. Гиперпластические процессы, рак эндометрия
Патология эндометрия. Гиперпластические процессы, рак эндометрия Первая медицинская помощь на занятиях физической культуры
Первая медицинская помощь на занятиях физической культуры Федеральный закон № 61-ФЗ Об обращении лекарственных средств
Федеральный закон № 61-ФЗ Об обращении лекарственных средств Диспансерное наблюдение детей и подростков с хронической патологией ЖКТ
Диспансерное наблюдение детей и подростков с хронической патологией ЖКТ Оболочки головного и спинного мозга. Ликвор и ликвородинамика
Оболочки головного и спинного мозга. Ликвор и ликвородинамика Көмекші материалдар: Қалыптық материалдар: Балауыздар. Жіктелуі. Құрамы, қасиеті және қолданыстары
Көмекші материалдар: Қалыптық материалдар: Балауыздар. Жіктелуі. Құрамы, қасиеті және қолданыстары Физическое развитие детей. Психомоторное развитие. Нервная система. АФО кожи и подкожно-жировой клетчатки
Физическое развитие детей. Психомоторное развитие. Нервная система. АФО кожи и подкожно-жировой клетчатки Оздоровление детей в условиях горного курорта Казахстана
Оздоровление детей в условиях горного курорта Казахстана Первая медицинская помощь при сердечной недостаточности и инсульте
Первая медицинская помощь при сердечной недостаточности и инсульте Недоношенные дети
Недоношенные дети Демография. Статика, динамика. Медицинская демография. Медико-социальные аспекты демографии. (Тема 5)
Демография. Статика, динамика. Медицинская демография. Медико-социальные аспекты демографии. (Тема 5) Казеозды пневмония
Казеозды пневмония Твердые лекарственные формы и их рецептурное оформление
Твердые лекарственные формы и их рецептурное оформление Гражданско-правовая ответственность медицинских работников
Гражданско-правовая ответственность медицинских работников Сбор, хранение и транспортировка материала для микробиологических исследований
Сбор, хранение и транспортировка материала для микробиологических исследований Профилактика, диагностика и лечение новой коронавирусной инфекции COVID-19
Профилактика, диагностика и лечение новой коронавирусной инфекции COVID-19 Гипертензивные расстройства. Преэклампсия. Эклампсия
Гипертензивные расстройства. Преэклампсия. Эклампсия Хронический гепатит
Хронический гепатит Периодическая аккредитация специалистов
Периодическая аккредитация специалистов