Содержание
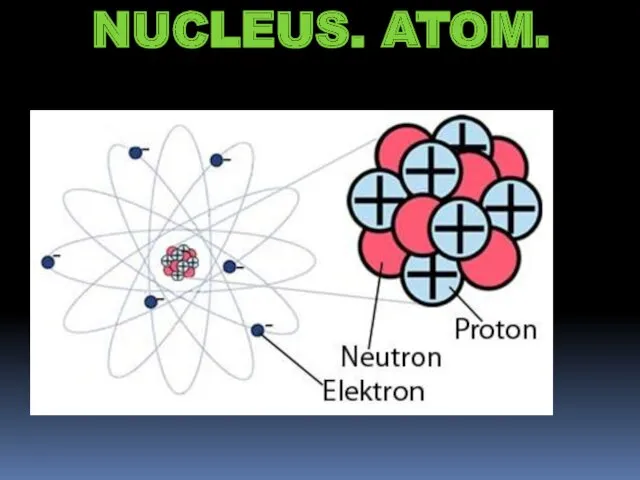
- 2. NUCLEUS. ATOM.
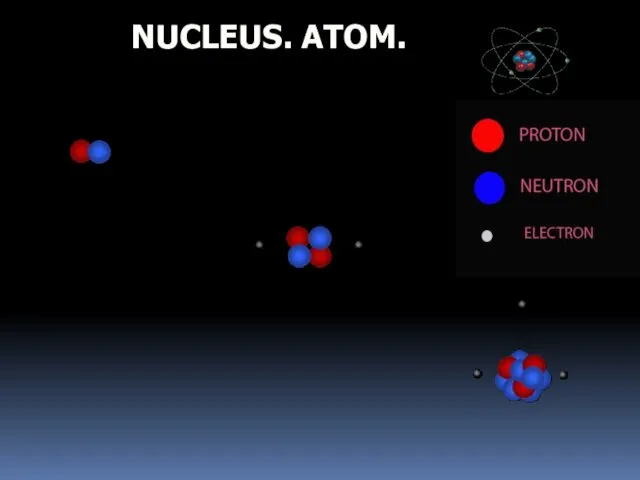
- 3. NUCLEUS. ATOM.
- 4. Parts of an Atom Each element in the Periodic Table has a different number of protons
- 5. The Hydrogen Atom One electron orbiting a nucleus 1 proton = Z = atomic number 0
- 7. Thinking deeper: The forces in the atom Electrons are bound to nucleus by the Coulomb (electromagnetic)
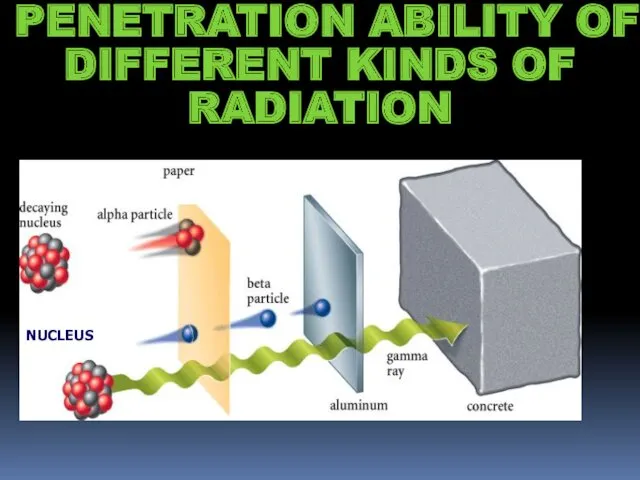
- 8. PENETRATION ABILITY OF DIFFERENT KINDS OF RADIATION
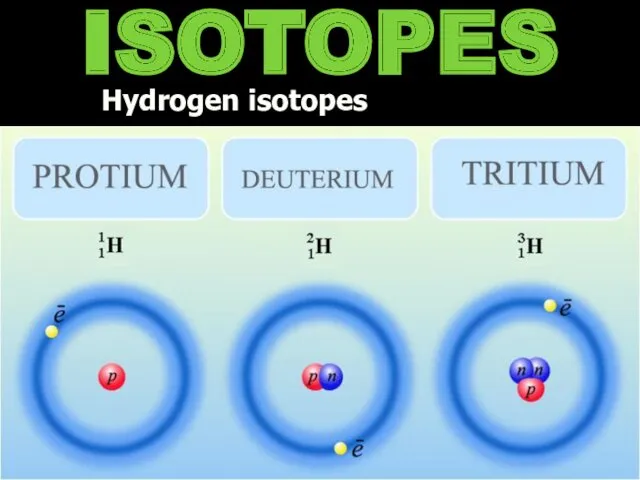
- 9. ISOTOPES Hydrogen isotopes
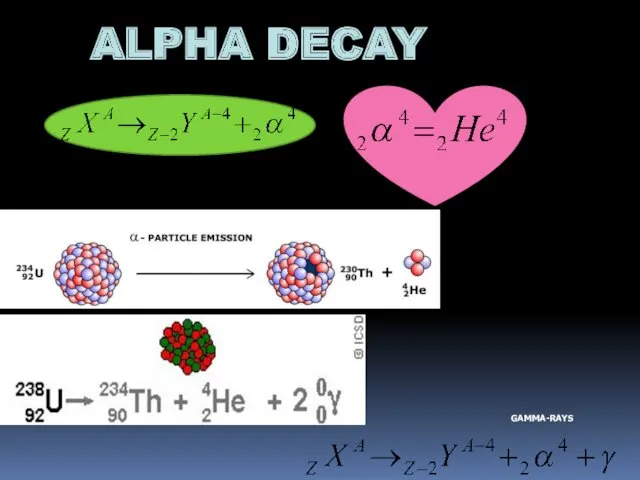
- 10. ALPHA DECAY GAMMA-RAYS
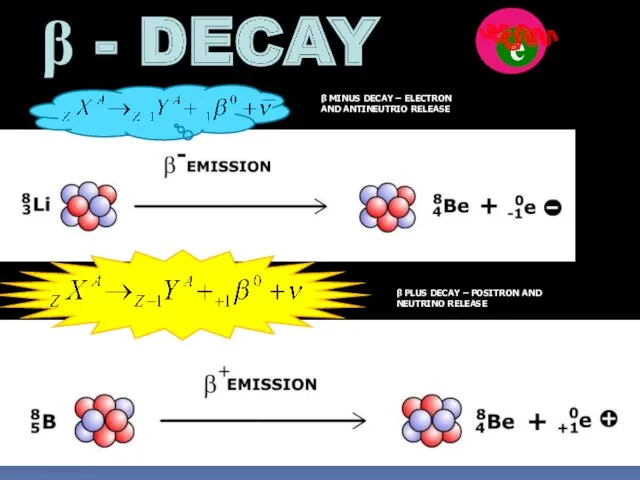
- 11. β - DECAY n е β MINUS DECAY – ELECTRON AND ANTINEUTRIO RELEASE β PLUS DECAY
- 12. ELECTRON CAPTURE
- 13. RADIOACTIVITY LAW Radioactive decay law dN – number of nuclides in radioactive decay per infinitely small
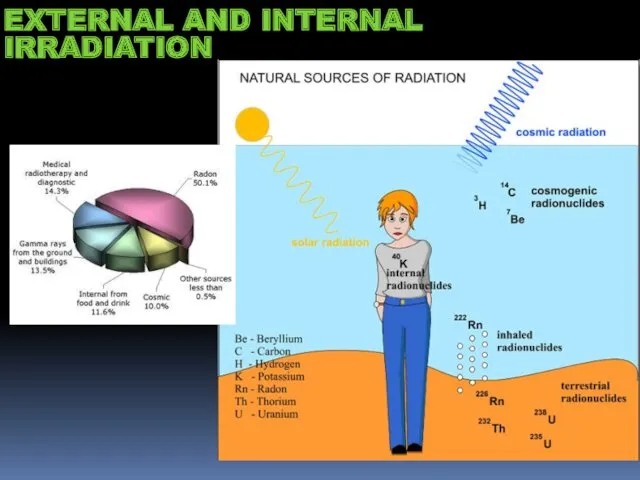
- 14. EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL IRRADIATION
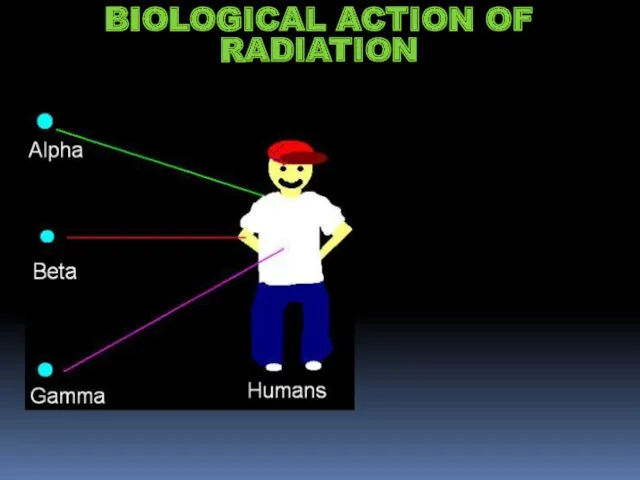
- 15. BIOLOGICAL ACTION OF RADIATION
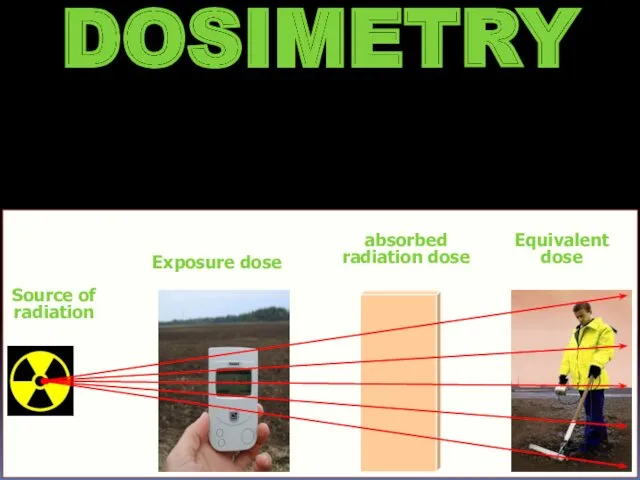
- 16. DOSIMETRY Source of radiation Exposure dose absorbed radiation dose Equivalent dose
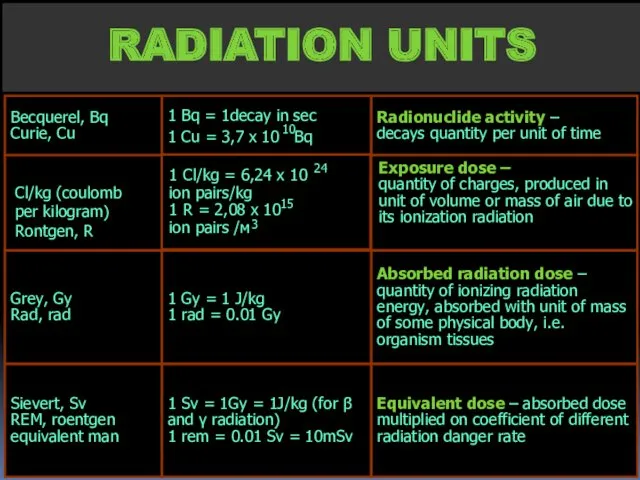
- 17. RADIATION UNITS
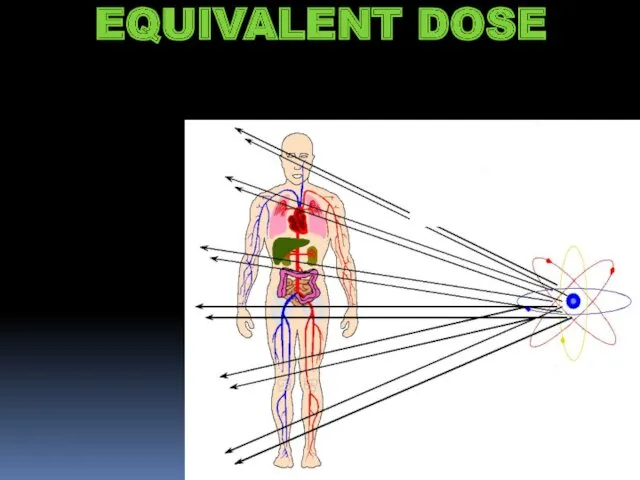
- 18. EQUIVALENT DOSE
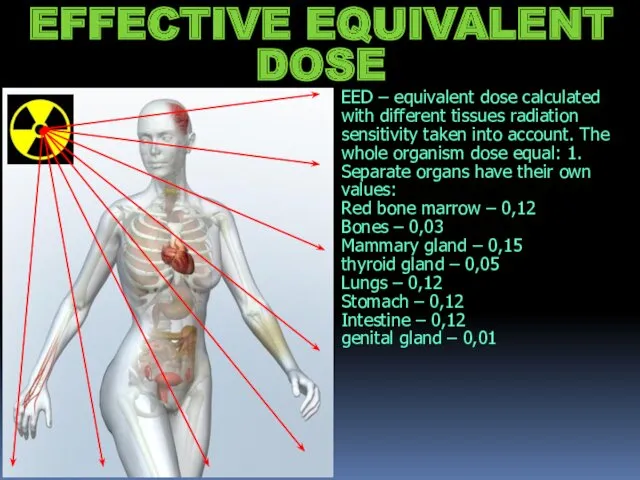
- 19. EED – equivalent dose calculated with different tissues radiation sensitivity taken into account. The whole organism
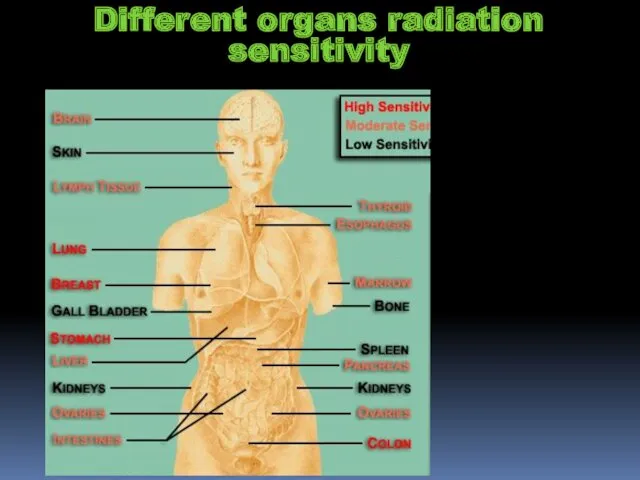
- 20. Different organs radiation sensitivity
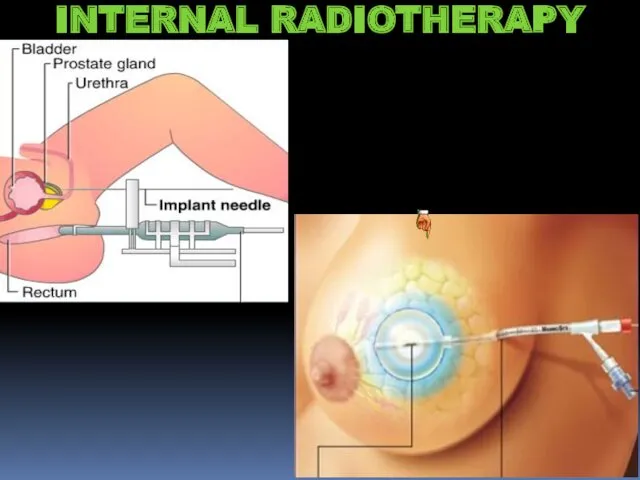
- 21. INTERNAL RADIOTHERAPY
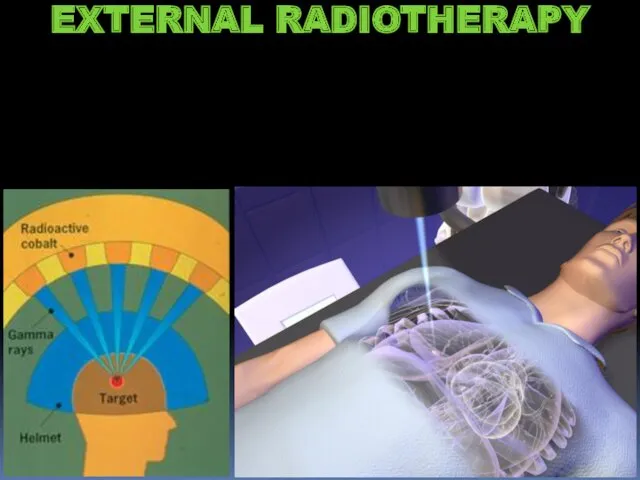
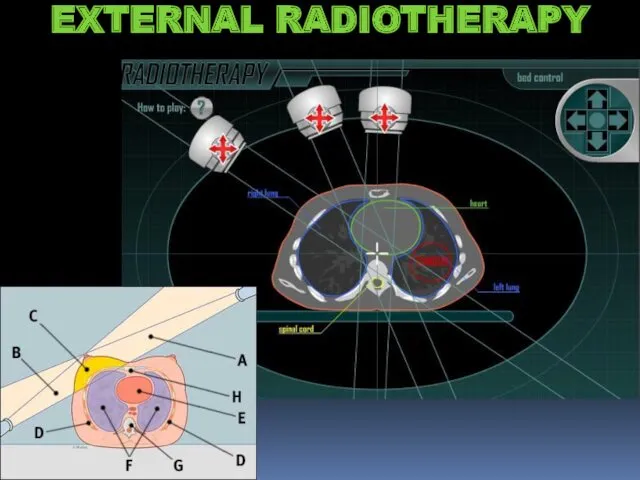
- 22. EXTERNAL RADIOTHERAPY
- 23. EXTERNAL RADIOTHERAPY
- 25. Скачать презентацию





 Сестринский процесс при заболеваниях системы крови и кроветворных органов у детей
Сестринский процесс при заболеваниях системы крови и кроветворных органов у детей Стромалық-қантамырлық диспротеиноздар: мукоидті ісіну, фибриноидті ісіну, гиалиноз. Амилаидоз
Стромалық-қантамырлық диспротеиноздар: мукоидті ісіну, фибриноидті ісіну, гиалиноз. Амилаидоз № 2 Симптомдық артериальды гипертензия. № 3 вариант: Иценко-Кушинг синдромы кезіндегі
№ 2 Симптомдық артериальды гипертензия. № 3 вариант: Иценко-Кушинг синдромы кезіндегі Aspecte contemporane în diagnosticul şi tratamentul bronhopneumopatiei cronice obstructive
Aspecte contemporane în diagnosticul şi tratamentul bronhopneumopatiei cronice obstructive Ішкі сәулеленуден медициналық қорғану
Ішкі сәулеленуден медициналық қорғану Лучевые методы диагностики заболеваний органов дыхания
Лучевые методы диагностики заболеваний органов дыхания Методика адаптивного физического воспитания для обучающихся с задержкой психического развития
Методика адаптивного физического воспитания для обучающихся с задержкой психического развития Патогенные и условно патогенные микроорганизмы
Патогенные и условно патогенные микроорганизмы Острая печеночная недостаточность
Острая печеночная недостаточность Функциональные показатели деятельности сердца. Регуляция сердца
Функциональные показатели деятельности сердца. Регуляция сердца Илья Ильич Мечников
Илья Ильич Мечников Заболевания глотки, гортани и трахеи
Заболевания глотки, гортани и трахеи ҚР бала тұрғындарына амбулаторлық көмек көрсетуді ұйымдастыру. Ана және нәресте қлімін
ҚР бала тұрғындарына амбулаторлық көмек көрсетуді ұйымдастыру. Ана және нәресте қлімін Анемиясы бар балаларды
Анемиясы бар балаларды Этиловый спирт и его влияние на организм человека
Этиловый спирт и его влияние на организм человека Рахит. Классификация рахита
Рахит. Классификация рахита Планирование лечения
Планирование лечения Несеп жолдарының туа біткен аномалиялары
Несеп жолдарының туа біткен аномалиялары Неатложный помощь при судорожном и гипертермическом синдроме у детей
Неатложный помощь при судорожном и гипертермическом синдроме у детей Мероприятия по профилактике агрессивных действий у пациентов, страдающих психическими расстройствами
Мероприятия по профилактике агрессивных действий у пациентов, страдающих психическими расстройствами Электромагниттік терапия
Электромагниттік терапия Ферментные лекарственные средства
Ферментные лекарственные средства Диабетическая полинейропатия
Диабетическая полинейропатия Кровоснабжение головного мозга
Кровоснабжение головного мозга Токсикоз беременных (гестоз)
Токсикоз беременных (гестоз) Диагностика клинических синдромов в пульмонологии
Диагностика клинических синдромов в пульмонологии Симптомы, признаки и профилактика СПИДА
Симптомы, признаки и профилактика СПИДА Организация работы специализированных и линйных бригад скорой медицинской помощи
Организация работы специализированных и линйных бригад скорой медицинской помощи