Содержание
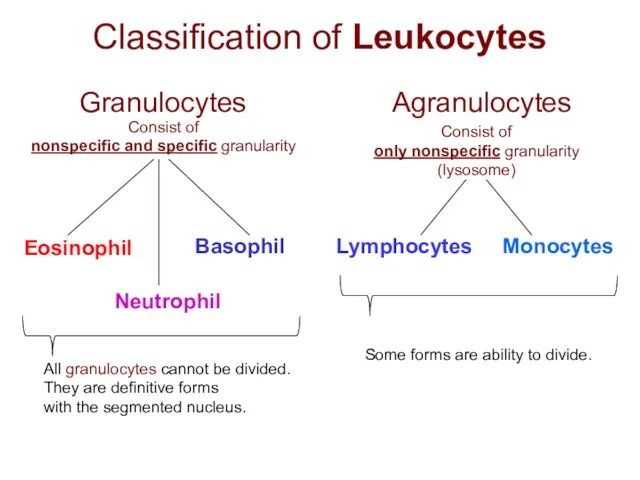
- 2. Classification of Leukocytes Granulocytes Agranulocytes Consist of nonspecific and specific granularity Consist of only nonspecific granularity
- 3. Лейкоцитарная формула Leukocytic formula Зернистые (гранулоциты) Granulocytes Незернистые (аграну-лоциты) Agranulocytes Возраст (age) % клеток (cells) Нейтрофилы
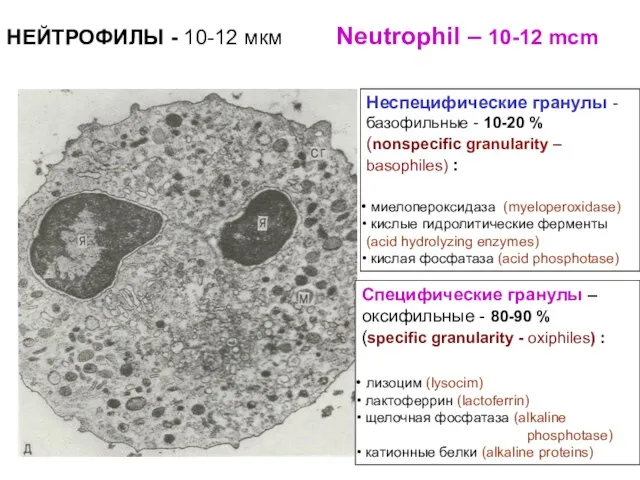
- 4. Неспецифические гранулы - базофильные - 10-20 % (nonspecific granularity – basophiles) : миелопероксидаза (myeloperoxidase) кислые гидролитические
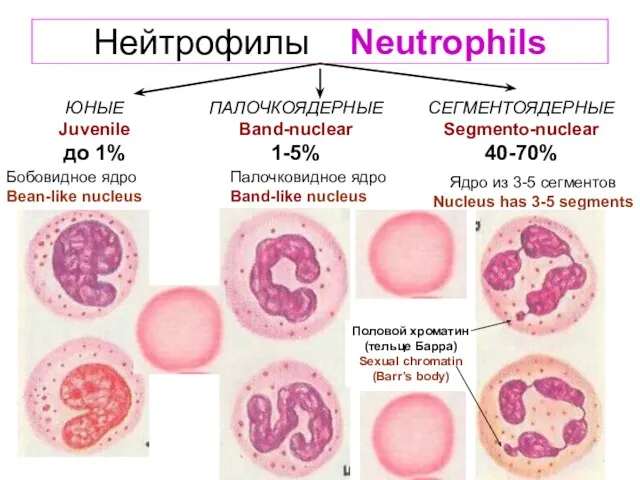
- 5. Нейтрофилы Neutrophils ЮНЫЕ Juvenile до 1% ПАЛОЧКОЯДЕРНЫЕ Band-nuclear 1-5% СЕГМЕНТОЯДЕРНЫЕ Segmento-nuclear 40-70% Бобовидное ядро Bean-like nucleus
- 6. Функции нейтрофилов Functions of Neutrophils Фагоцитоз микроорганизмов (Phagocytosis of microorganisms) 2. Разрушение бактерий и поврежденной ткани
- 7. Лейкоцитарная формула Leukocytic formula Сдвиг влево (moving to the left) – Воспалительный процесс (Inflammatory process) Сдвиг
- 8. Неспецифические гранулы - базофильные (nonspecific granularity – basophiles) 10-20 %: пероксидаза (peroxidase) кислые гидролитические ферменты (acid
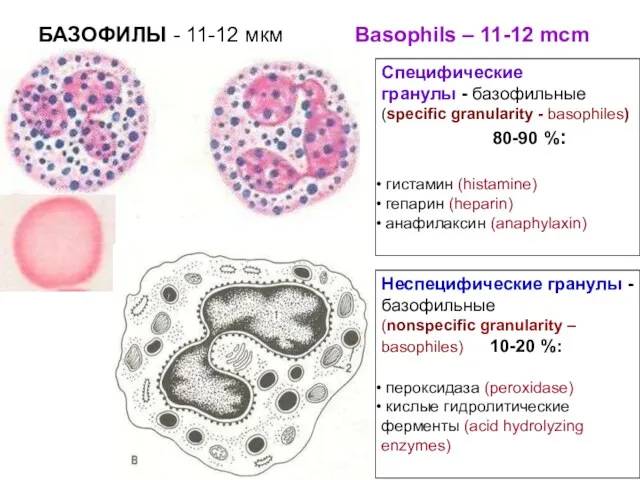
- 9. Дезинтоксикация (пероксидаза) 2. Снижение свертывания крови (гепарин) 3. Увеличение проницаемости сосудов и ткани (гистамин) 4. Развитие
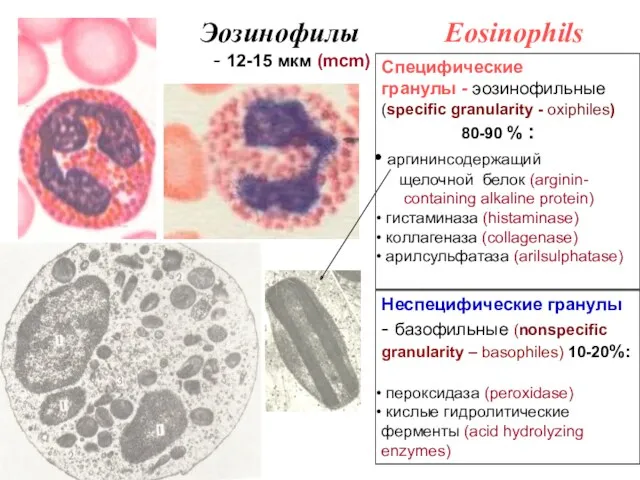
- 10. Специфические гранулы - эозинофильные (specific granularity - oxiphiles) 80-90 % : аргининсодержащий щелочной белок (arginin- containing
- 11. Функции эозинофилов Functions of Eosinophils 1. Антипаразитарная (аргининсодержащий щелочной белок) 2. Дезинтоксикация (пероксидаза) 3. Антиаллергическая (разрушение
- 12. AGRANULOCYTES are monocytes and lymphocytes. They are immunocompetent cells and participate in the immune answer.
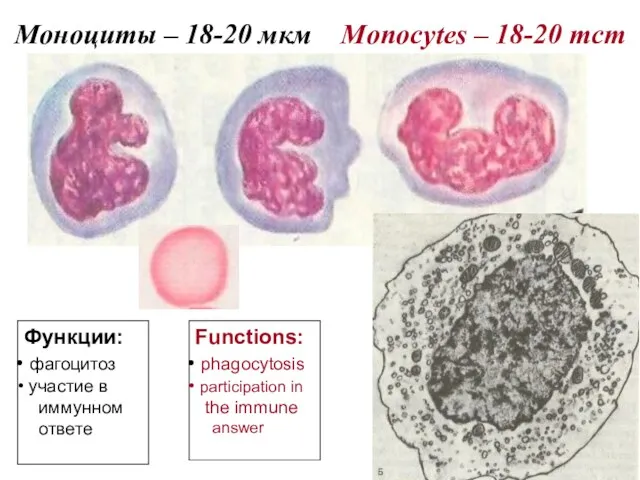
- 13. Моноциты – 18-20 мкм Monocytes – 18-20 mcm Функции: фагоцитоз участие в иммунном ответе Functions: phagocytosis
- 14. Иммунный ответ – специфическая реакция организма, направленная на уничтожение генетически чужеродного вещества – АНТИГЕНА. The immune
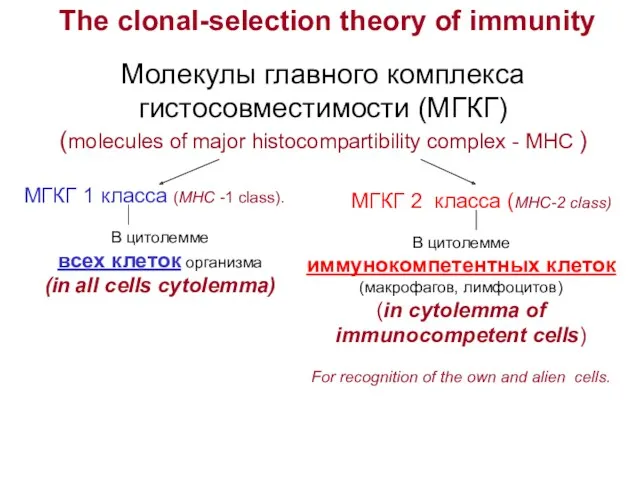
- 15. Молекулы главного комплекса гистосовместимости (МГКГ) (molecules of major histocompartibility complex - MHC ) МГКГ 1 класса
- 16. Monocytes, macrophages are an antigene-representing cells or A-cells Функции А-клеток (Functions of A-cells): Узнают антиген (по
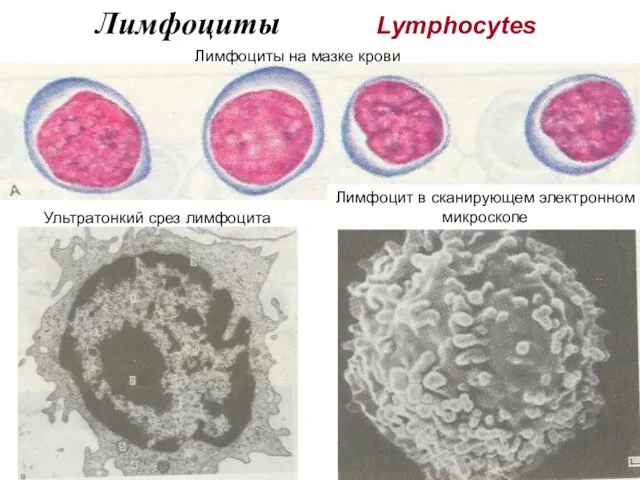
- 17. Лимфоциты Lymphocytes Ультратонкий срез лимфоцита Лимфоцит в сканирующем электронном микроскопе Лимфоциты на мазке крови
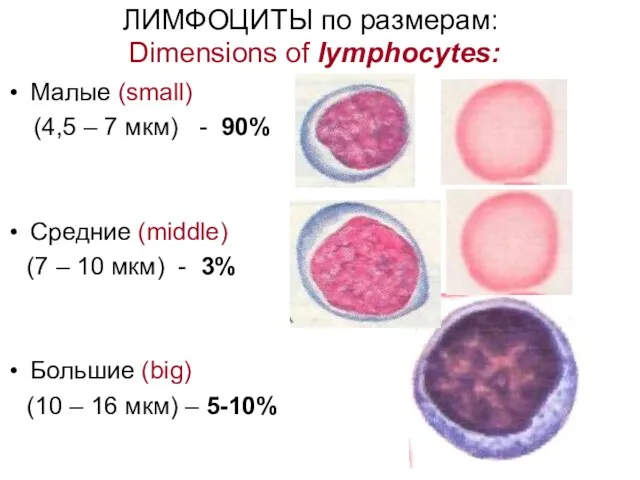
- 18. ЛИМФОЦИТЫ по размерам: Dimensions of lymphocytes: Малые (small) (4,5 – 7 мкм) - 90% Средние (middle)
- 19. Виды иммунного ответа: Гуморальный - связывание антигенных белков антителами (осуществляют В-лимфоциты) Humoral - linkage of AG-proteins
- 20. Т-лимфоциты В-лимфоциты Естественные клетки-киллеры (ЕКК, NK) ЛИМФОЦИТЫ LYMPHOCYTES (по функциям): (on functions) : Т- lymphocytes (thymus-dependent)
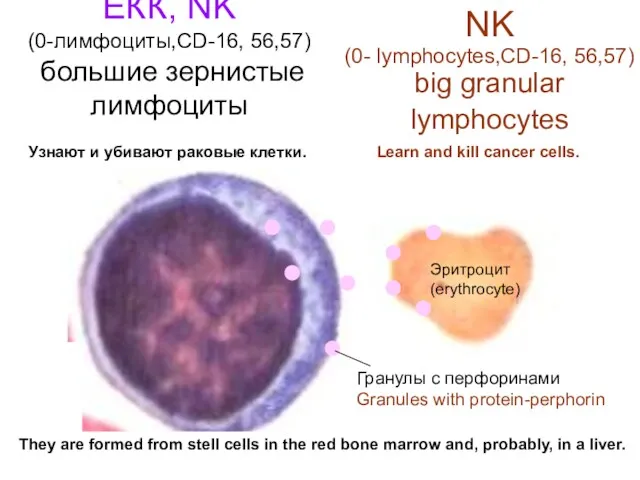
- 21. ЕКК, NK (0-лимфоциты,CD-16, 56,57) большие зернистые лимфоциты Гранулы с перфоринами Granules with protein-perphorin Узнают и убивают
- 22. Виды Т-лимфоцитов: Постоянно образуются в тимусе Т-хелперы (Th–CD4+) (малые, циркулируют в крови) Т-супрессоры (Ts–CD8) (средние, мигрируют
- 23. Бласттрансформация – трансформация (превращение) лимфоцитов в лимфобласты под влиянием антигенов (АГ) Blast-transformation – transformation of lymphocytes
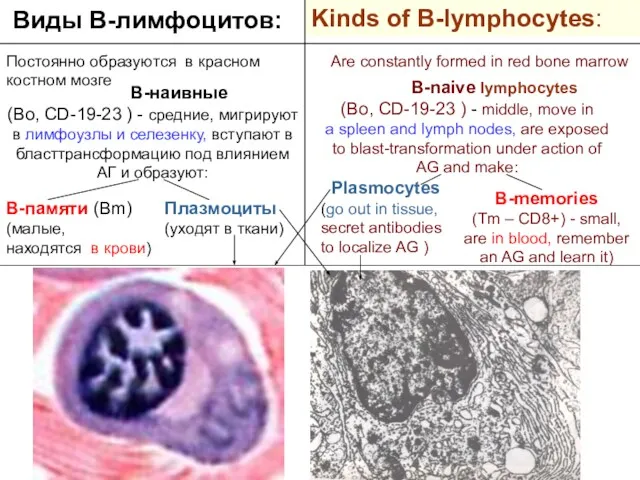
- 24. Kinds of B-lymphocytes: Виды В-лимфоцитов: Постоянно образуются в красном костном мозге В-наивные (Во, CD-19-23 ) -
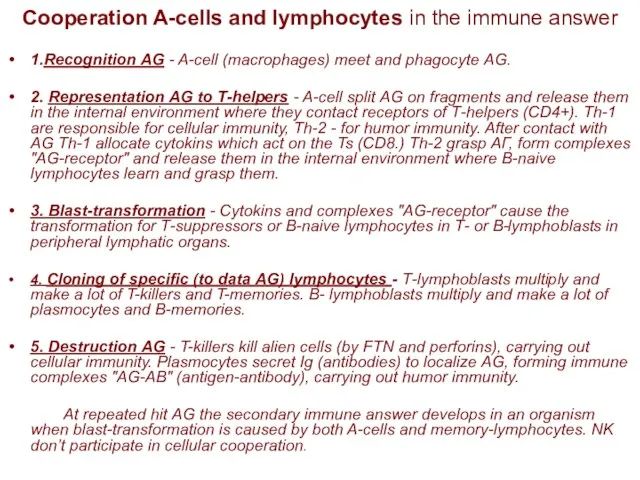
- 25. Cooperation A-cells and lymphocytes in the immune answer 1.Recognition АG - A-cell (macrophages) meet and phagocyte
- 27. Скачать презентацию












 Клиническая анатомия конечностей. Современная ангиология
Клиническая анатомия конечностей. Современная ангиология Аритмиялар (өміріне қауіп төндірген аритмия кезінде ауруханаға жатқызғанға дейін шұғыл және жедел көмек көрсету)
Аритмиялар (өміріне қауіп төндірген аритмия кезінде ауруханаға жатқызғанға дейін шұғыл және жедел көмек көрсету) Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in adults and adolescents
Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in adults and adolescents Катаракта. Причины катаракты
Катаракта. Причины катаракты Сүйек және буын туберкулезі
Сүйек және буын туберкулезі Повреждение костей таза и тазовых органов
Повреждение костей таза и тазовых органов Профилактика внутрибольничных инфекций, связанных и оказанием медицинской помощи
Профилактика внутрибольничных инфекций, связанных и оказанием медицинской помощи Рахит. Этиопатогенез рахита
Рахит. Этиопатогенез рахита Урология. Несеп-жыныс жүйесінің жарақаты
Урология. Несеп-жыныс жүйесінің жарақаты Дифтерия: этиология, классификация, клиника, лечение
Дифтерия: этиология, классификация, клиника, лечение Сестринский уход при сахарном диабете. Часть 1
Сестринский уход при сахарном диабете. Часть 1 Реакция отторжения трансплантата
Реакция отторжения трансплантата Острые тромбозы и эмболии аорты и магистральных артерий
Острые тромбозы и эмболии аорты и магистральных артерий Патологиялық анатомия. Кардиосклероз
Патологиялық анатомия. Кардиосклероз Табиғи ошақты және антропозоонозды инвазиялар
Табиғи ошақты және антропозоонозды инвазиялар Перевязочные материалы. Виды, потребительские свойства, оценка качества
Перевязочные материалы. Виды, потребительские свойства, оценка качества Лекарственные растения. Берёзовая роща
Лекарственные растения. Берёзовая роща Кардиальный синдром Х. Микроваскулярная стенокардия small vessel disease, дистальный тип поражения коронарного русла
Кардиальный синдром Х. Микроваскулярная стенокардия small vessel disease, дистальный тип поражения коронарного русла Актиномицеты сем. Actinomycetaceae
Актиномицеты сем. Actinomycetaceae Основные клинико-лабораторные методы оценки качества зубных щеток
Основные клинико-лабораторные методы оценки качества зубных щеток Отечественный опыт медицинского обслуживания международных спортивных мероприятий на примере Республики Татарстан
Отечественный опыт медицинского обслуживания международных спортивных мероприятий на примере Республики Татарстан Особенности этиопатогенетических факторов у пациентов с различными видами нехимических зависимостей
Особенности этиопатогенетических факторов у пациентов с различными видами нехимических зависимостей Introduction about ticks
Introduction about ticks Иммунопатология
Иммунопатология Вакцинация и ревакцинация. Вакцина БЦЖ
Вакцинация и ревакцинация. Вакцина БЦЖ Артериалды гипертензия
Артериалды гипертензия Мочевой синдром
Мочевой синдром 16_Polovye_gormony
16_Polovye_gormony