Содержание
- 2. Multiple Pregnancy/ Multifetalpregnancy The presence of more than one fetus in the gravid uterus is called
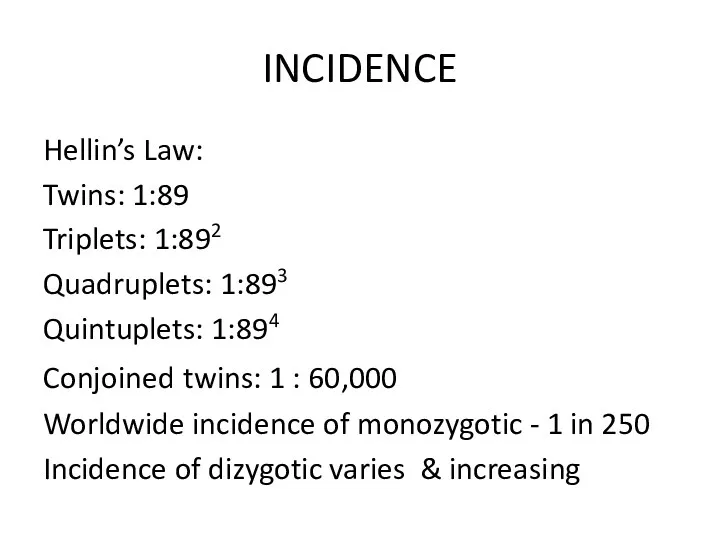
- 3. INCIDENCE Hellin’s Law: Twins: 1:89 Triplets: 1:892 Quadruplets: 1:893 Quintuplets: 1:894 Conjoined twins: 1 : 60,000
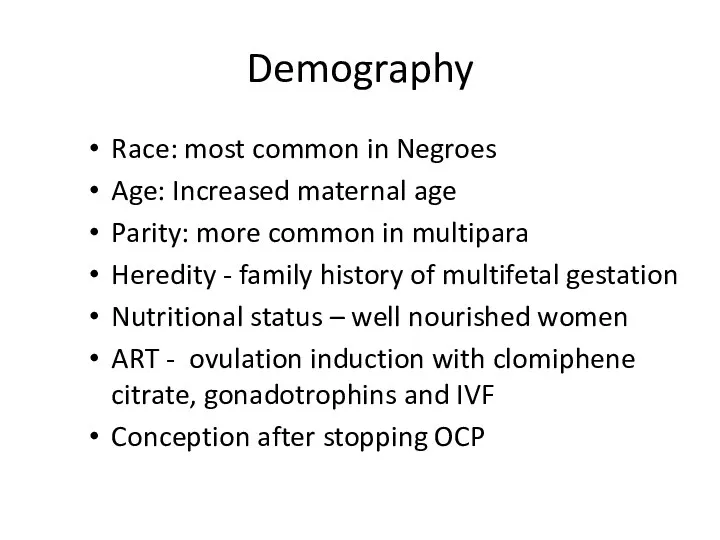
- 4. Demography Race: most common in Negroes Age: Increased maternal age Parity: more common in multipara Heredity
- 5. Twins Varieties: 1. Dizygotic twins: commonest (Two-third) 2. Monozygotic twins (one-third) Genesis of Twins: Dizygotic twins
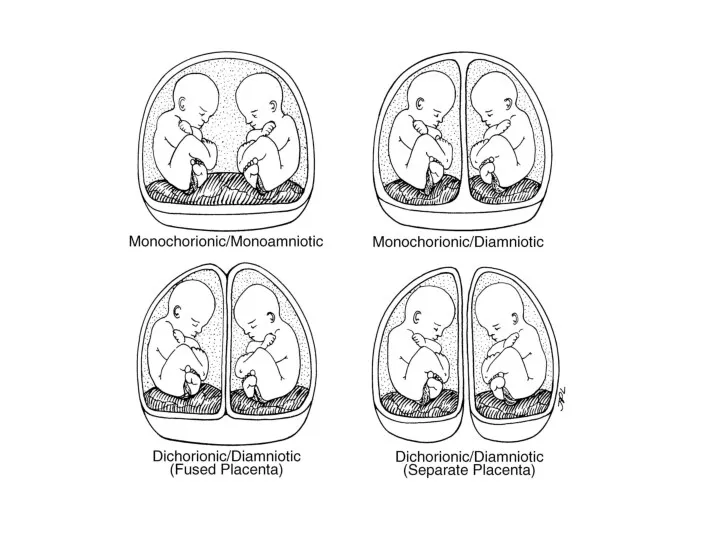
- 6. Monozygotic twins (syn: Identical, uniovular): Upto 3 days - diamniotic-dichorionic Between 4th & 7th day -
- 8. Conjoined twins Ventral: 1) Omphalopagus 2) Thoracopagus 3) Cephalopagus 4) Caudal/ ischiopagus Lateral: 1) Parapagus Dorsal:
- 9. Superfecundation Fertilization of two different ova released in the same cycle Superfetation Fertilization of two ova
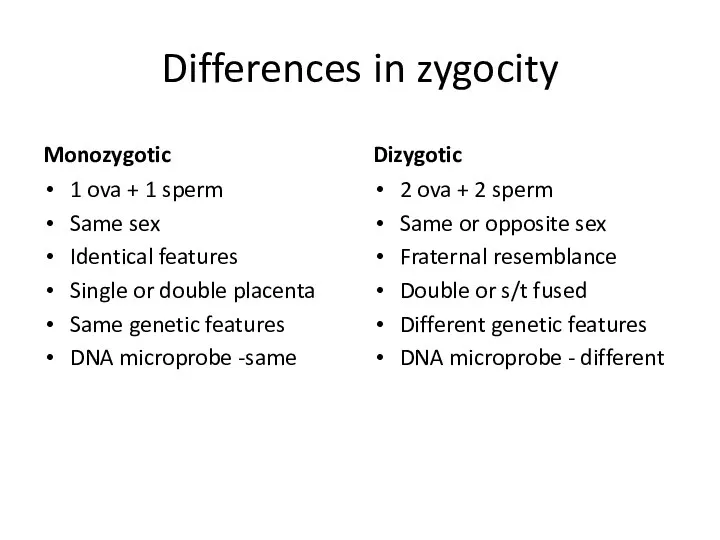
- 10. Differences in zygocity Monozygotic 1 ova + 1 sperm Same sex Identical features Single or double
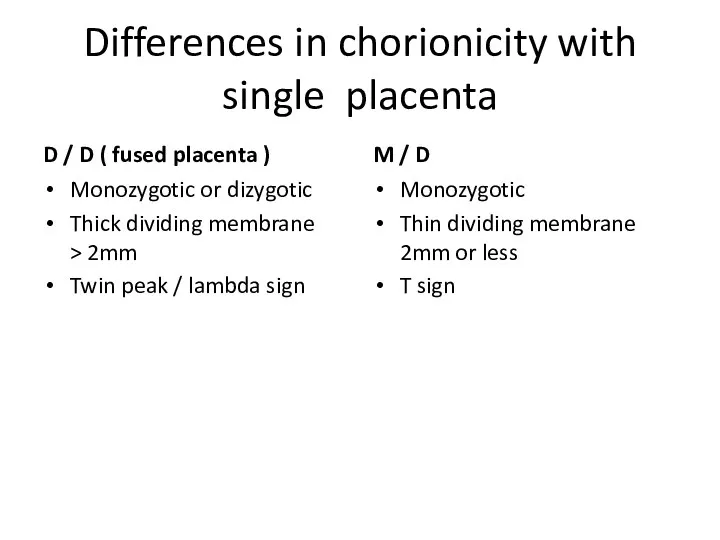
- 11. Differences in chorionicity with single placenta D / D ( fused placenta ) Monozygotic or dizygotic
- 12. Diagnosis HISTORY: History of ovulation inducing drugs specially gonadotrophins Family history of twinning (maternal side). SYMPTOMS:
- 13. GENERAL EXAMINATION: Prevalence of anaemia is more than in singleton pregnancy Unusual weight gain, not explained
- 14. Palpation: Fundal height more than the period of amenorrhoea girth more than normal Palpation of too
- 15. D/D of increased fundal height Full bladder Wrong dates Hydramnios Macrosomia Fibroid with preg Ovarian tumor
- 16. INVESTIGATIONS Sonography: In multi fetal pregnancy it is done to obtain the following information: Suspecting twins
- 17. Fetal anomalies Fetal growth monitoring (at every 3-4 weeks interval) for IUGR Presentation and lie of
- 18. Radiography Biochemical tests: raised but not diagnostic Maternal serum chorionic gonadotrophin, Alpha fetoprotein Unconjugated oestriol
- 19. Lie and Presentation Longitudinal lie (90%) both vertex (40%) Vertex + breech (28%) breech + vertex
- 20. Complications Maternal Pregnancy Labour Puerperium Fetal MATERNAL: During pregnancy: - miscarriages Hyperemesis gravidorum Anaemia Pre-eclampsia (25%)
- 21. GDM ( 2 – 3 times) Antepartum hemorrhage – placenta previa and placental abruption Cholestasis of
- 22. During Labour: Prelabour rupture of the membranes Cord prolapse Incoordinate uterine contractions Increased operative interference Placental
- 23. FETAL – more with monochorionic Spontaneous abortion Single fetal demise Vanishing twin – before 10 weeks
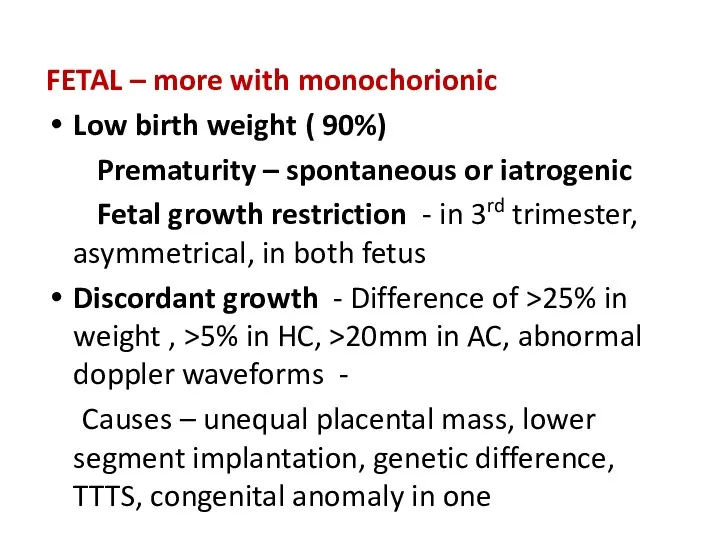
- 24. FETAL – more with monochorionic Low birth weight ( 90%) Prematurity – spontaneous or iatrogenic Fetal
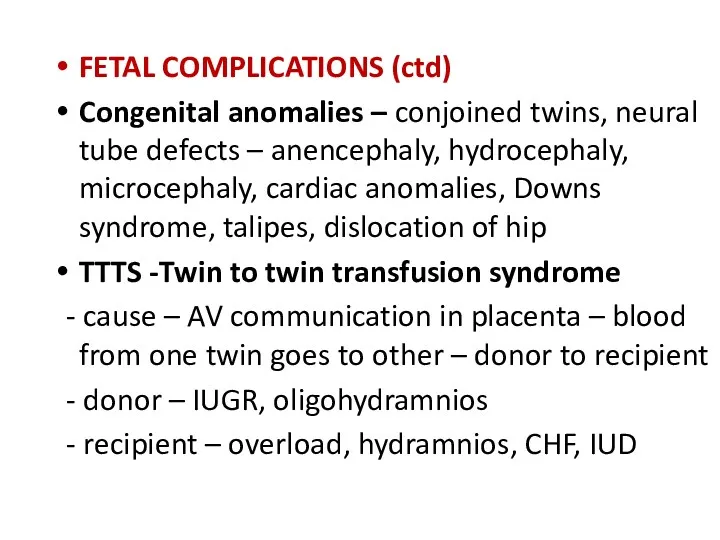
- 25. FETAL COMPLICATIONS (ctd) Congenital anomalies – conjoined twins, neural tube defects – anencephaly, hydrocephaly, microcephaly, cardiac
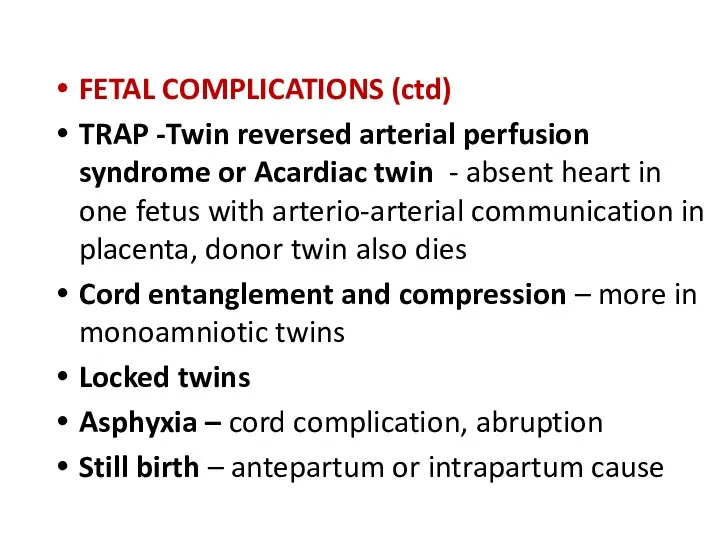
- 26. FETAL COMPLICATIONS (ctd) TRAP -Twin reversed arterial perfusion syndrome or Acardiac twin - absent heart in
- 27. Monoamniotic twins high perinatal morbidity, mortality. Causes : cord entanglement congenital anomaly preterm birth twin to
- 28. Antenatal Management Diet: additional 300 K cal per day, increased proteins, 60 to 100 mg of
- 29. Management During Labour Place of delivery: tertiary level hospital FIRST STAGE: blood to be cross matched
- 30. Management During Labour SECOND STAGE –delivery of first baby as in singleton pregnancy start an IV
- 31. Management During Labour Delivery of second twin – problems & interventions -inadequate contraction- augmentation – ARM,
- 33. Скачать презентацию






















 Медиастинит. Этиология және патогенез
Медиастинит. Этиология және патогенез Патанатомия неспецифического язвенного колита, аппендицита
Патанатомия неспецифического язвенного колита, аппендицита Основы медицинской протозоологии. Тип простейшие. Представители классов споровики и инфузории
Основы медицинской протозоологии. Тип простейшие. Представители классов споровики и инфузории ОМС АО Страховая компания СОГАЗ-Мед. Обязательное медицинское страхование
ОМС АО Страховая компания СОГАЗ-Мед. Обязательное медицинское страхование Аудиологический скрининг новорожденных. Генетические аспекты тугоухости
Аудиологический скрининг новорожденных. Генетические аспекты тугоухости Язвенная болезнь желудка и двенадцатиперстной кишки
Язвенная болезнь желудка и двенадцатиперстной кишки Психиатриялық науқастарды тексеру әдістері
Психиатриялық науқастарды тексеру әдістері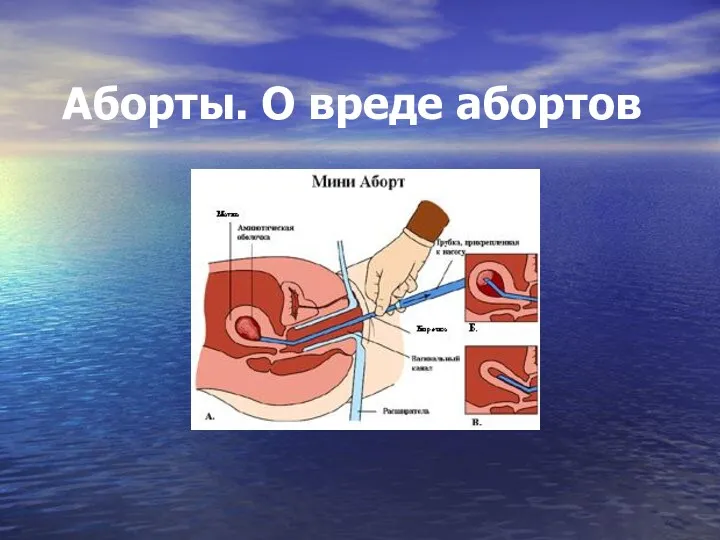 Аборты. О вреде абортов
Аборты. О вреде абортов Antimicrobial drugs
Antimicrobial drugs Көз туберкулезі
Көз туберкулезі Фонетико-фонематическое недоразвитие
Фонетико-фонематическое недоразвитие Анксиолитики (транквилизаторы)
Анксиолитики (транквилизаторы) Психические расстройства позднего возраста
Психические расстройства позднего возраста Взаимодействие лекарственных препаратов
Взаимодействие лекарственных препаратов Жасушалық иммунитет жүйесінің негізгі қызметтері. Иммунологиялық төзімділік
Жасушалық иммунитет жүйесінің негізгі қызметтері. Иммунологиялық төзімділік Дискинезия желчевыводящих путей у детей
Дискинезия желчевыводящих путей у детей Патологиялык анатомияның заманауи зерттеу әдістері. Қр патологиялық анатомиялық қызметі
Патологиялык анатомияның заманауи зерттеу әдістері. Қр патологиялық анатомиялық қызметі Психическая предрасположенность к развитию зависимости от ПАВ
Психическая предрасположенность к развитию зависимости от ПАВ Питание кормящей матери
Питание кормящей матери Отек легких
Отек легких Развитие отечественной медицины в годы Первой мировой войны
Развитие отечественной медицины в годы Первой мировой войны Симптоматика урологических заболеваний (изменения мочи)
Симптоматика урологических заболеваний (изменения мочи) Наружные кишечные свищи
Наружные кишечные свищи Клинический случай вестибулярного синдрома. Плоскоклеточная карцинома (SCC) слюнной железы у кошки
Клинический случай вестибулярного синдрома. Плоскоклеточная карцинома (SCC) слюнной железы у кошки Первая помощь при повреждениях головы и позвоночника
Первая помощь при повреждениях головы и позвоночника Тканевая совместимость и переливание крови
Тканевая совместимость и переливание крови Парентералды жолмен берілетін вирусты аурулар (ЖИТС) және олардың алдын алу шаралары
Парентералды жолмен берілетін вирусты аурулар (ЖИТС) және олардың алдын алу шаралары Гнатология. Основные задачи современной гнатологии
Гнатология. Основные задачи современной гнатологии