Содержание
- 2. Introduction Hematopoietic stem cell disorder Clonal Characterized by proliferation Granulocytic Erythroid Megakaryocytic Interrelationship between Polycythaemia Essential
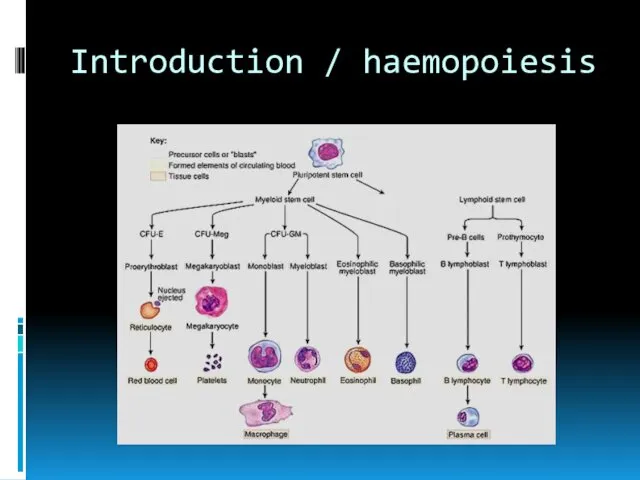
- 3. Introduction / haemopoiesis
- 4. Introduction Normal maturation (effective) Increased number of Red cells Granulocytes Platelets (Note: myeloproliferation in myelodysplastic syndrome
- 5. Rationale for classification Classification is based on the lineage of the predominant proliferation Level of marrow
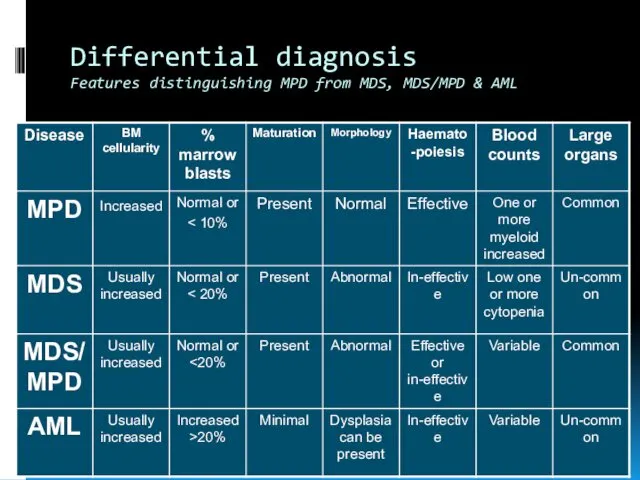
- 6. Differential diagnosis Features distinguishing MPD from MDS, MDS/MPD & AML
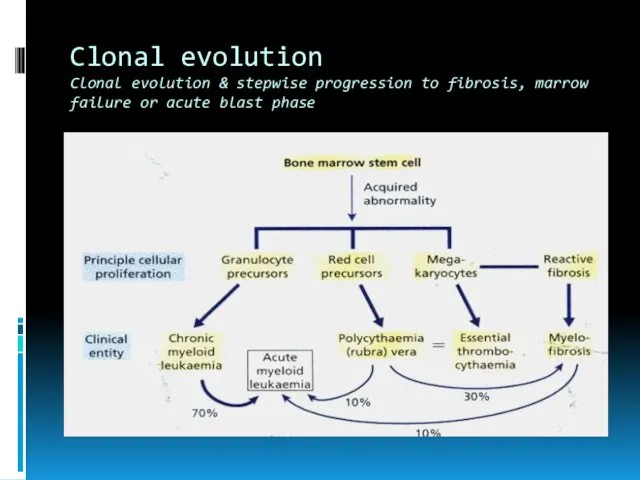
- 7. Clonal evolution Clonal evolution & stepwise progression to fibrosis, marrow failure or acute blast phase
- 8. Incidence and epidemiology Disease of adult Peak incidence in 7th decade 6-9/100,000
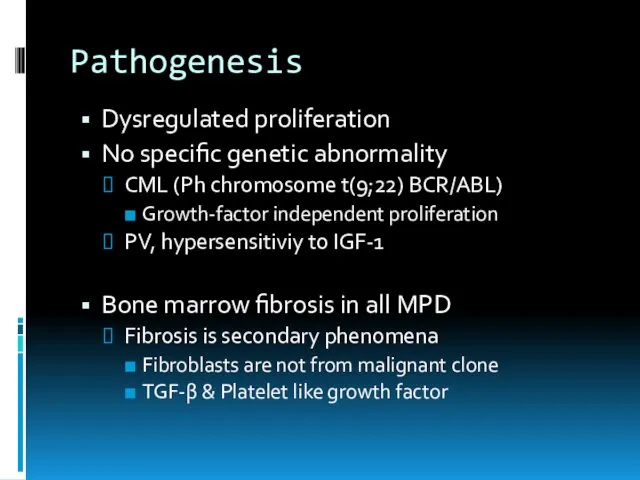
- 9. Pathogenesis Dysregulated proliferation No specific genetic abnormality CML (Ph chromosome t(9;22) BCR/ABL) Growth-factor independent proliferation PV,
- 10. Molecular basis of Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms Polycythemia Vera:~95% JAK2(V617F) Essential thrombocythemia: 50-60% JAK2(V617F) Primary myelofibrosis 50-60%
- 11. Prognosis Depends on the proper diagnosis and early treatment Role of IFN BMT Tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- 12. Polycythaemia vera (Polycythaemia rubra vera) Definition of polycythemia Raised packed cell volume (PCV / HCT) Male
- 13. Polycythaemia vera (Polycythaemia rubra vera) Polycythaemia vera is a clonal stem cell disorder characterised by increased
- 14. Polycythaemia vera (Polycythaemia rubra vera) Clinical features Age 55-60 years May occur in young adults and
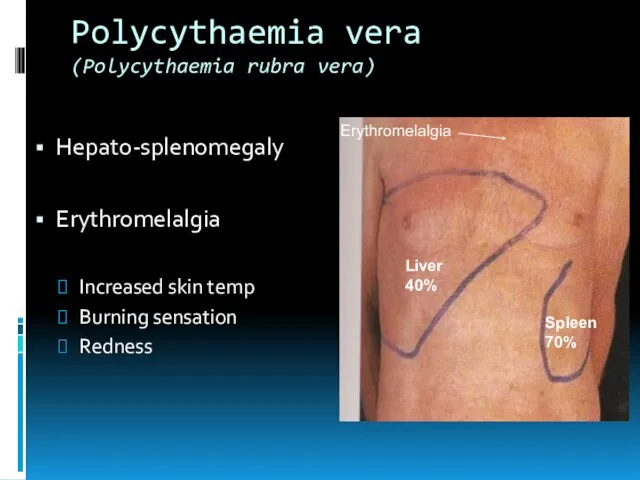
- 15. Polycythaemia vera (Polycythaemia rubra vera) Hepato-splenomegaly Erythromelalgia Increased skin temp Burning sensation Redness Liver 40% Spleen
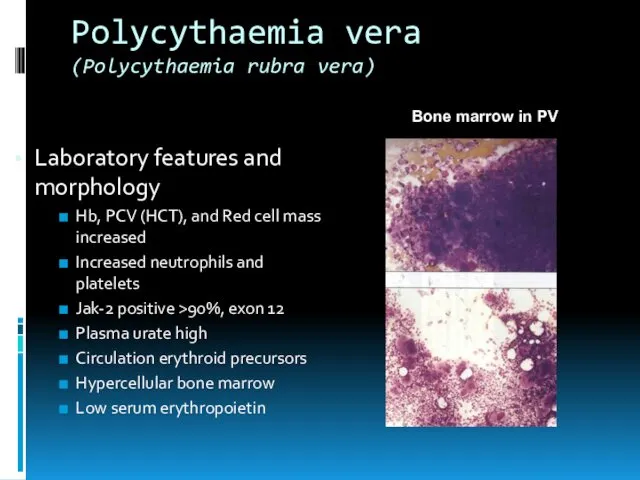
- 16. Polycythaemia vera (Polycythaemia rubra vera) Laboratory features and morphology Hb, PCV (HCT), and Red cell mass
- 17. Polycythaemia vera (Polycythaemia rubra vera) Treatment To decrease PVC (HCT) Venesection Chemotherapy Treatment of complications
- 18. Secondary polycythaemia Polycythaemia due to known causes Compensatory increased in EPO High altitude Pulmonary diseases Heart
- 19. Secondary polycythaemia Arterial blood gas Hb electrophoresis Oxygen dissociation curve EPO level Ultrasound abdomen Chest X
- 20. Relative polycythaemia Apparent polycythaemia or pseudopolycythaemia due to plasma volume contraction Causes Stress Cigarette smoker or
- 21. Myelofibrosis Chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis Progressive fibrosis of the marrow & increase connective tissue element Agnogenic myeloid
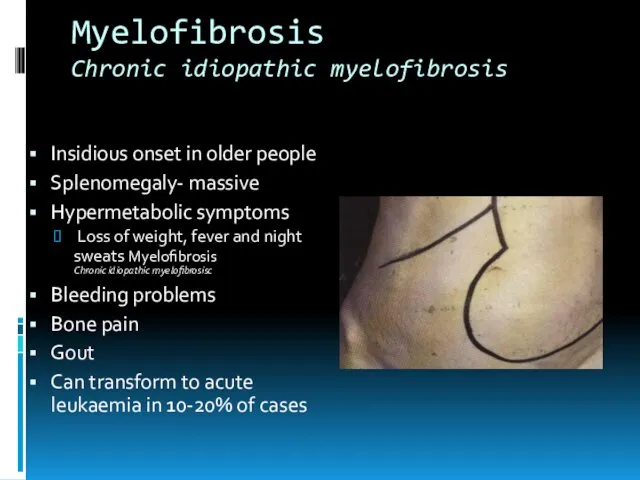
- 22. Myelofibrosis Chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis Insidious onset in older people Splenomegaly- massive Hypermetabolic symptoms Loss of weight,
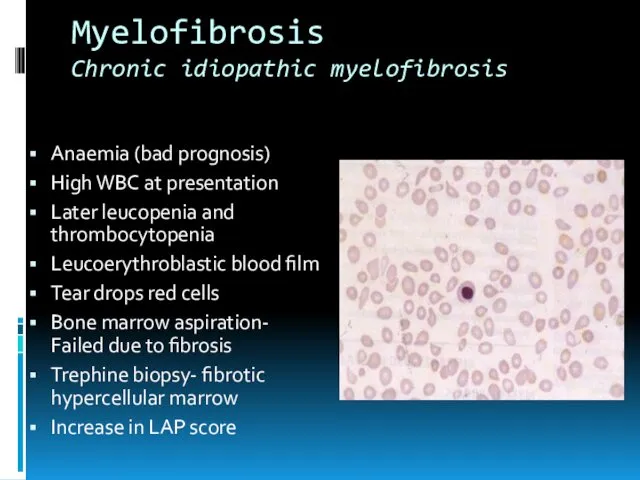
- 23. Myelofibrosis Chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis Anaemia (bad prognosis) High WBC at presentation Later leucopenia and thrombocytopenia Leucoerythroblastic
- 24. Essential thrombocythaemia Primary thrombocytosis / idiopathic thrombocytosis Clonal myeloproliferative disease of megakaryocytic lineage Sustained thrombocytosis Increase
- 25. Essential thrombocythaemia Primary thrombocytosis / idiopathic thrombocytosis Criteria of exclusion No evidence of Polycythaemia vera No
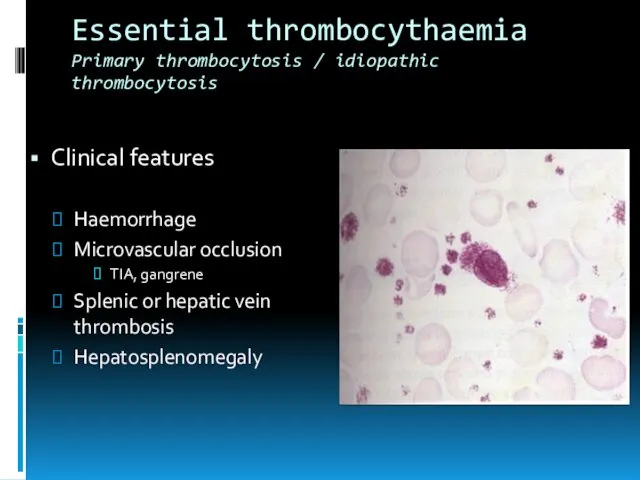
- 26. Essential thrombocythaemia Primary thrombocytosis / idiopathic thrombocytosis Clinical features Haemorrhage Microvascular occlusion TIA, gangrene Splenic or
- 27. Essential thrombocythaemia Primary thrombocytosis / idiopathic thrombocytosis Treatment Anticoagulant Chemotherapy Role of aspirin Disease course and
- 29. Скачать презентацию













 Саркома Юинга
Саркома Юинга Условно-рефлекторные методы исследования слуха
Условно-рефлекторные методы исследования слуха Группы крови, резус-фактор
Группы крови, резус-фактор Природжені дефекти та деформації ЩЛД у дітей їх профілактика. Сучасні принципи диспансерезації,лікування та реабілітації
Природжені дефекти та деформації ЩЛД у дітей їх профілактика. Сучасні принципи диспансерезації,лікування та реабілітації Язвенная болезнь
Язвенная болезнь Дәрумендер, олардың балалардың дұрыс дамуындағы маңызы, дәрумендерге жас ерекшеліктеріне байланысты физиологиялық мұқтаждығы
Дәрумендер, олардың балалардың дұрыс дамуындағы маңызы, дәрумендерге жас ерекшеліктеріне байланысты физиологиялық мұқтаждығы Мерез. Эпидемиологиясы
Мерез. Эпидемиологиясы Твердые лекарственные формы и их рецептурное оформление
Твердые лекарственные формы и их рецептурное оформление Физиология целенаправленного поведения и организации произвольных движений
Физиология целенаправленного поведения и организации произвольных движений Пневмония у детей
Пневмония у детей Лабораторная и инструментальная диагностика заболеваний органов дыхания
Лабораторная и инструментальная диагностика заболеваний органов дыхания Мышечная топография. Значение топографии мышц для практической медицины
Мышечная топография. Значение топографии мышц для практической медицины Наркомания. Три вида химических веществ, которые вызывают зависимость
Наркомания. Три вида химических веществ, которые вызывают зависимость Черепно-мозговая травма
Черепно-мозговая травма Эндодонтиялық тәжірибеде лазерлі сәулені қолдан
Эндодонтиялық тәжірибеде лазерлі сәулені қолдан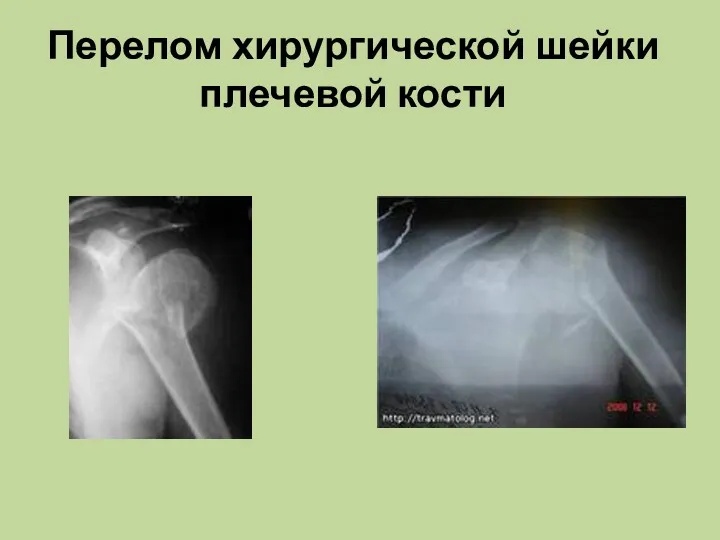 Перелом хирургической шейки плечевой кости
Перелом хирургической шейки плечевой кости Сестринский процесс при нейрохирургических операциях, операциях на сосудах, урологических операций
Сестринский процесс при нейрохирургических операциях, операциях на сосудах, урологических операций Анемии
Анемии Пациент пен отбасы мүшелерін реабилитациялық тәсілдерге үйрету
Пациент пен отбасы мүшелерін реабилитациялық тәсілдерге үйрету Hardening - a factor of strengthening and maintaining the health of children
Hardening - a factor of strengthening and maintaining the health of children Оптическая когерентная томография в оценке структурных изменений сетчатки глаза у пациентов с ко-инфекцией (ВИЧ/туберкулез)
Оптическая когерентная томография в оценке структурных изменений сетчатки глаза у пациентов с ко-инфекцией (ВИЧ/туберкулез) Классификация дефектов зубных рядов. Показания к применению несъемных мостовидных протезов
Классификация дефектов зубных рядов. Показания к применению несъемных мостовидных протезов Манифестация скрытой формы болезни Грейвса у больной с пароксизмальной формой фибрилляции предсердий
Манифестация скрытой формы болезни Грейвса у больной с пароксизмальной формой фибрилляции предсердий Инфекционный мононуклеоз
Инфекционный мононуклеоз Задержка полового созревания центрального генеза
Задержка полового созревания центрального генеза Гастроэзофагеальная рефлюксная болезнь (ГЭРБ)
Гастроэзофагеальная рефлюксная болезнь (ГЭРБ) Гормональные препараты
Гормональные препараты Ұрықтың антенатальды қорғауы. Ұрықтың даму ақауларының пренатальды диагностикасы
Ұрықтың антенатальды қорғауы. Ұрықтың даму ақауларының пренатальды диагностикасы