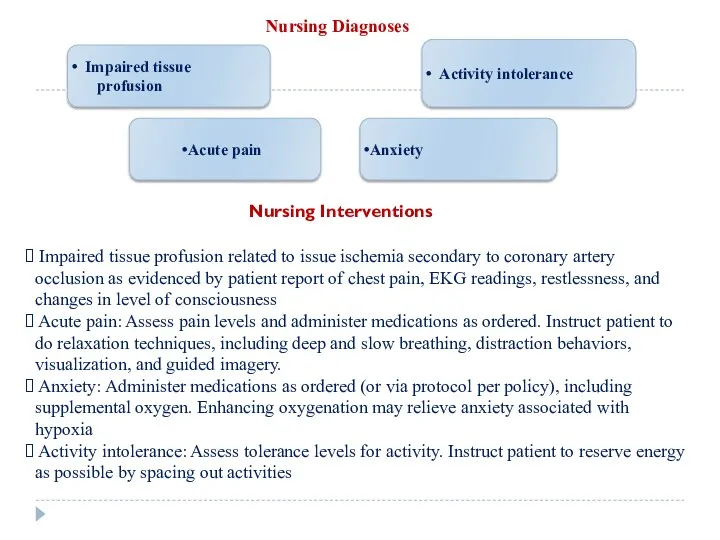
Nursing Diagnoses
Nursing Interventions
Impaired tissue profusion related to issue ischemia secondary
to coronary artery occlusion as evidenced by patient report of chest pain, EKG readings, restlessness, and changes in level of consciousness
Acute pain: Assess pain levels and administer medications as ordered. Instruct patient to do relaxation techniques, including deep and slow breathing, distraction behaviors, visualization, and guided imagery.
Anxiety: Administer medications as ordered (or via protocol per policy), including supplemental oxygen. Enhancing oxygenation may relieve anxiety associated with hypoxia
Activity intolerance: Assess tolerance levels for activity. Instruct patient to reserve energy as possible by spacing out activities
Impaired tissue
profusion
Acute pain
Anxiety
Activity intolerance
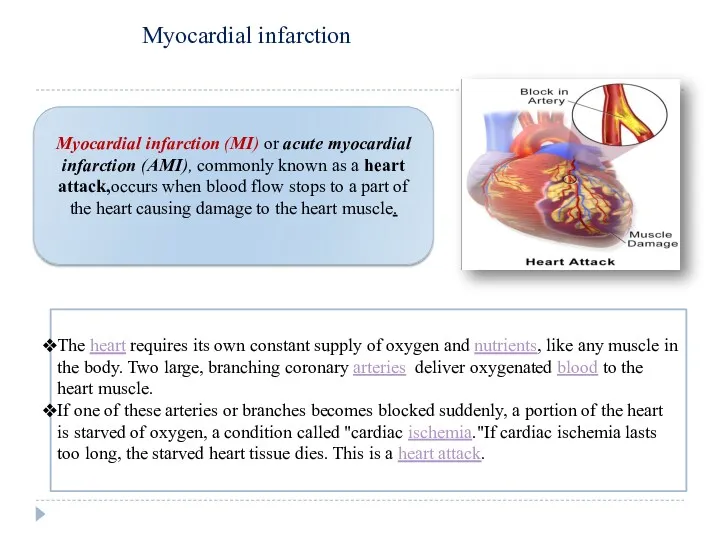
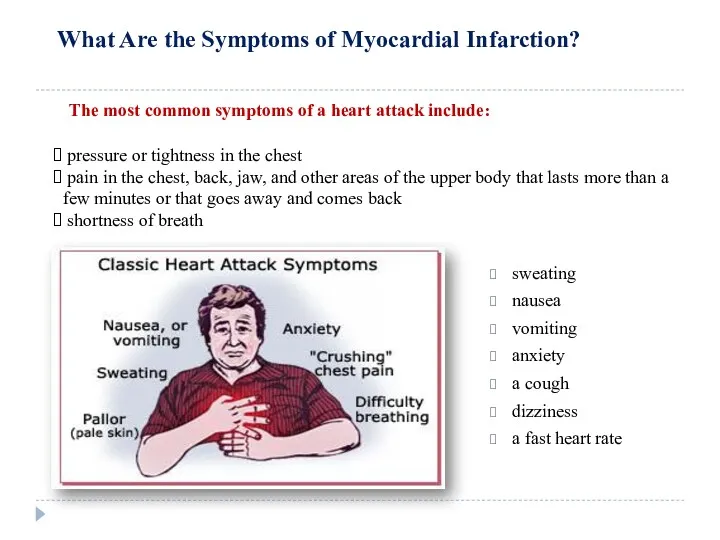
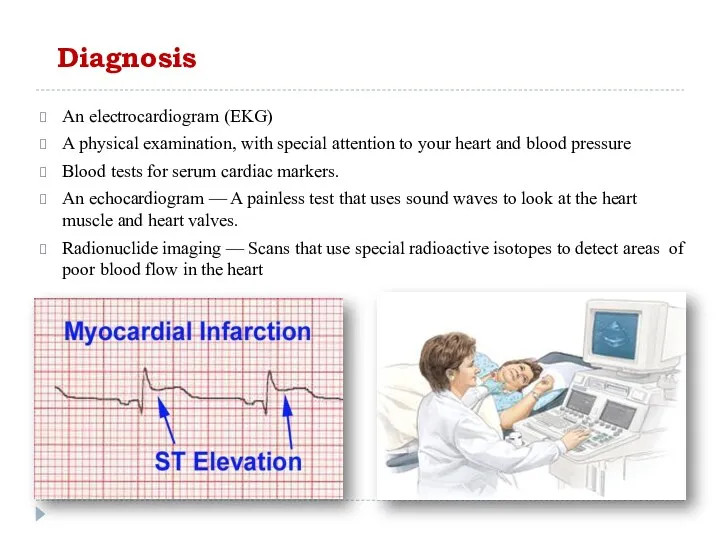
 Сердечная недостаточность
Сердечная недостаточность Медицинская реабилитация при пневонии
Медицинская реабилитация при пневонии Изготовление разборных моделей по технологии фирмы Renfert
Изготовление разборных моделей по технологии фирмы Renfert Методы определения скорости кровотока. Физические основы клинического метода измерения давления крови. Лекция 3
Методы определения скорости кровотока. Физические основы клинического метода измерения давления крови. Лекция 3 Эпидемиологиялық зерттеу этаптары
Эпидемиологиялық зерттеу этаптары Гигиена и микрофлора рук медицинского персонала
Гигиена и микрофлора рук медицинского персонала Особенности организации ухода за пациентами пожилого и старческого возраста
Особенности организации ухода за пациентами пожилого и старческого возраста Oparzenia. Rodzaje oparzeń
Oparzenia. Rodzaje oparzeń Интенсивная терапия острого гематогенного остеомиелита у детей
Интенсивная терапия острого гематогенного остеомиелита у детей Синдром скопления жидкости и воздуха в плевральной полости. Плевриты. Пневмоторакс. Легочно-сердечная недостаточность
Синдром скопления жидкости и воздуха в плевральной полости. Плевриты. Пневмоторакс. Легочно-сердечная недостаточность Экономика, планирование, финансирование здравоохранения
Экономика, планирование, финансирование здравоохранения Scarlet fever
Scarlet fever Хронические воспалительные заболевания гортани
Хронические воспалительные заболевания гортани Құлақ құрылымы мен топографиясының жасқа байланысты ерекшеліктері және олардың құлақ патологиясындағы маңызы
Құлақ құрылымы мен топографиясының жасқа байланысты ерекшеліктері және олардың құлақ патологиясындағы маңызы Острая печеночная недостаточность
Острая печеночная недостаточность Заболевания желудочно-кишечного тракта и гепато-биларной системы у пациентов с ревматоидным артритом
Заболевания желудочно-кишечного тракта и гепато-биларной системы у пациентов с ревматоидным артритом Предмет и задачи патологии. Нозология
Предмет и задачи патологии. Нозология Понятие дезинфекция. Виды и методы дезинфекции
Понятие дезинфекция. Виды и методы дезинфекции Ангины. Хронический тонзиллит
Ангины. Хронический тонзиллит Язвенная болезнь
Язвенная болезнь Тізе буыны зақымдалуы
Тізе буыны зақымдалуы Амбулаторная хирургия и первая медицинская помощь
Амбулаторная хирургия и первая медицинская помощь Ответы на вопросы итогового тестирования-отбора на V Всероссийскую олимпиаду по оториноларингологии
Ответы на вопросы итогового тестирования-отбора на V Всероссийскую олимпиаду по оториноларингологии Хирургические заболевания органов средостения
Хирургические заболевания органов средостения Наследственные тромбофилии
Наследственные тромбофилии Черепно-мозговые нервы. Анатомо-физиологическое строение речевого аппарата
Черепно-мозговые нервы. Анатомо-физиологическое строение речевого аппарата Как лечить нейрокогнитивные расстройства при разных диагнозах?
Как лечить нейрокогнитивные расстройства при разных диагнозах? Болезни лица и шеи
Болезни лица и шеи