Содержание
- 2. Clinical Removable prosthodontics 2 Fitting the Framework
- 3. WHY TRY IN of the framework? No matter how much care is taken during the clinical
- 4. WHY TRY IN of the framework? . Improvements in the materials and techniques have reduced the
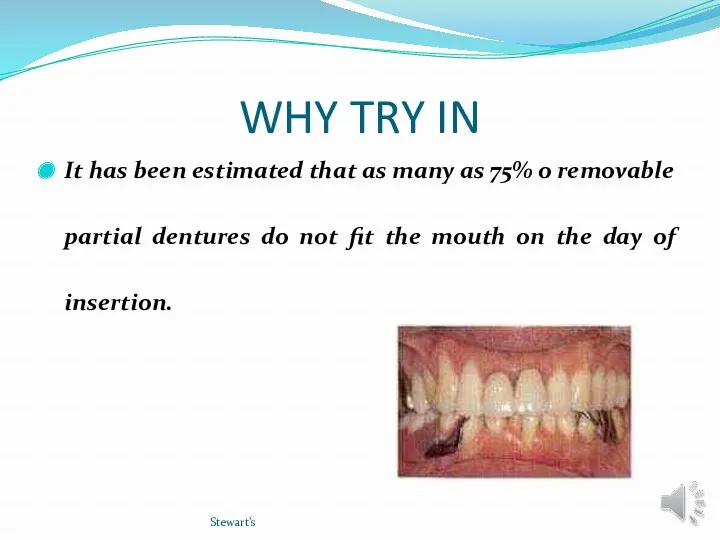
- 5. WHY TRY IN It has been estimated that as many as 75% o removable partial dentures
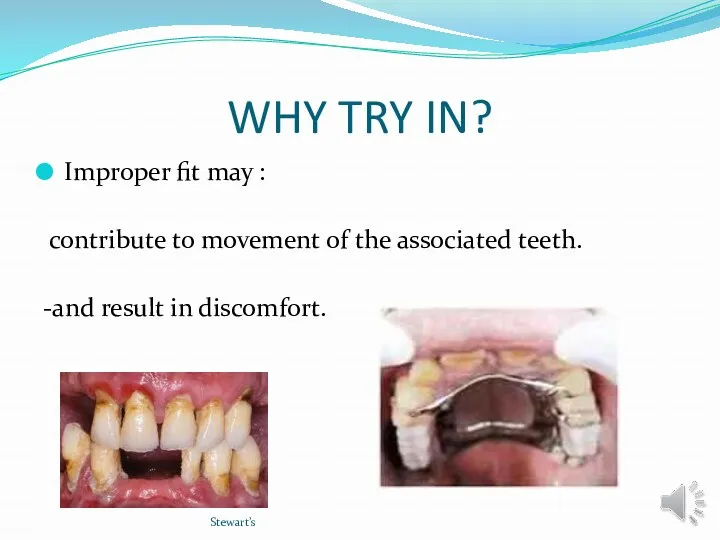
- 6. WHY TRY IN? Improper fit may : contribute to movement of the associated teeth. -and result
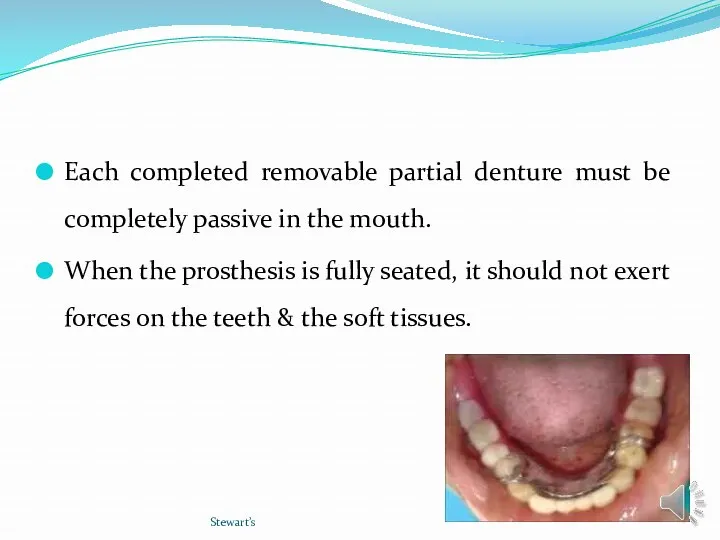
- 7. Each completed removable partial denture must be completely passive in the mouth. When the prosthesis is
- 8. Uncontrolled forces can produce movement of the remaining teeth and cause damage to the soft tissues
- 9. The practitioner must remember that the tip of each retentive clasp is designed to lie passively
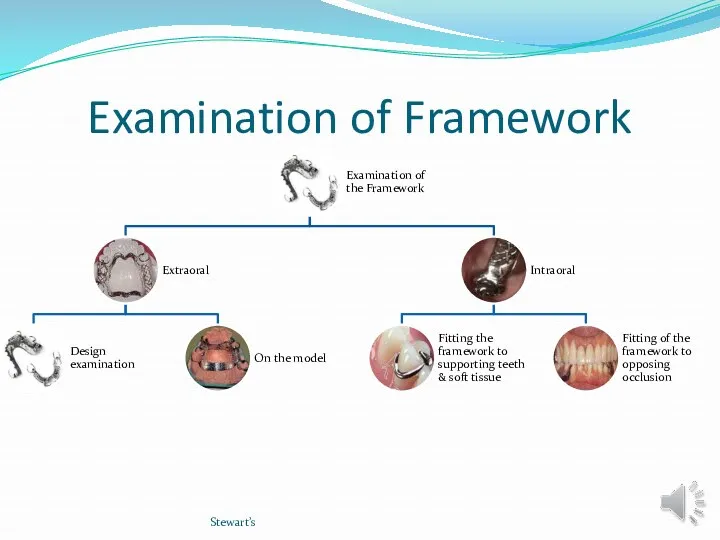
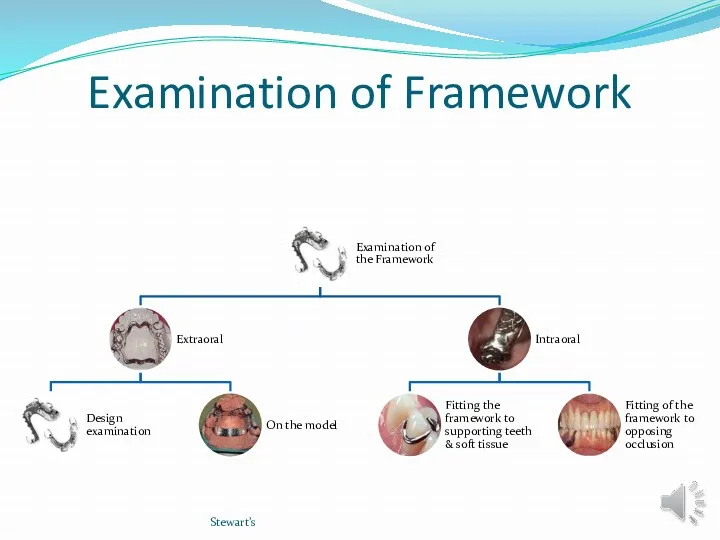
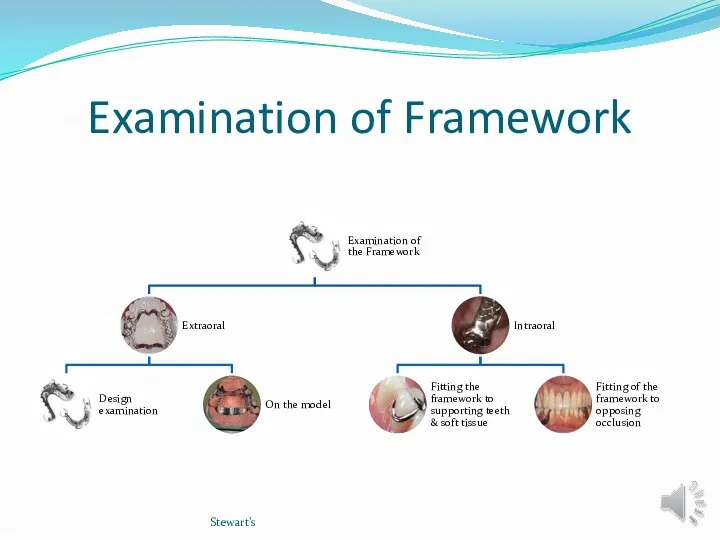
- 10. Examination of Framework Stewart’s
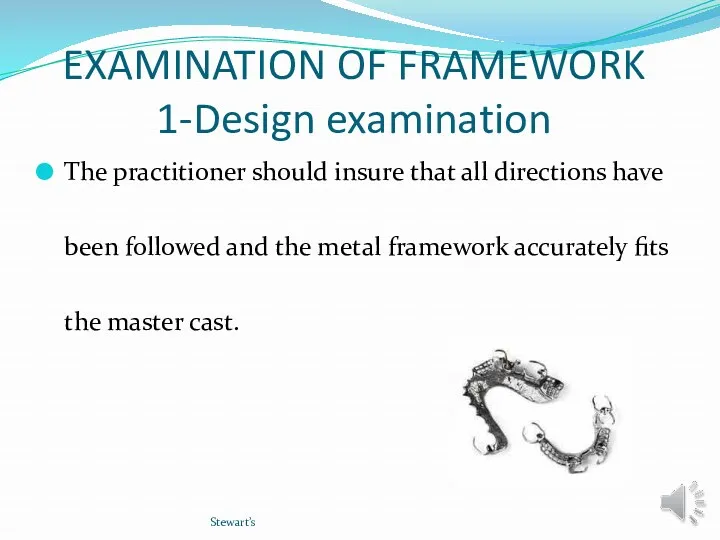
- 11. EXAMINATION OF FRAMEWORK 1-Design examination The practitioner should insure that all directions have been followed and
- 12. EXAMINATION OF FRAMEWORK 1-Design examination Was the proposed design closely followed? has the major connector been
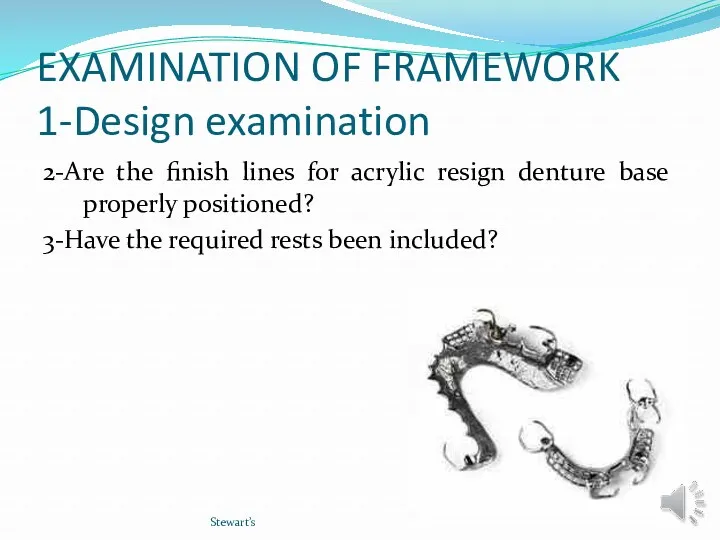
- 13. EXAMINATION OF FRAMEWORK 1-Design examination 2-Are the finish lines for acrylic resign denture base properly positioned?
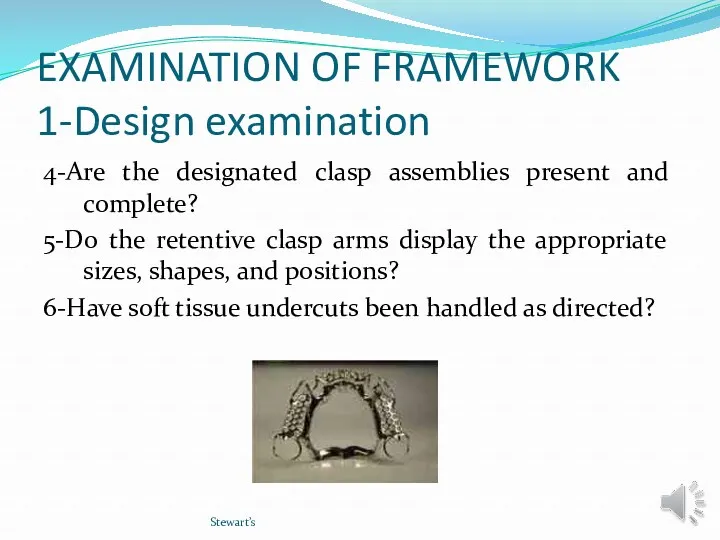
- 14. EXAMINATION OF FRAMEWORK 1-Design examination 4-Are the designated clasp assemblies present and complete? 5-Do the retentive
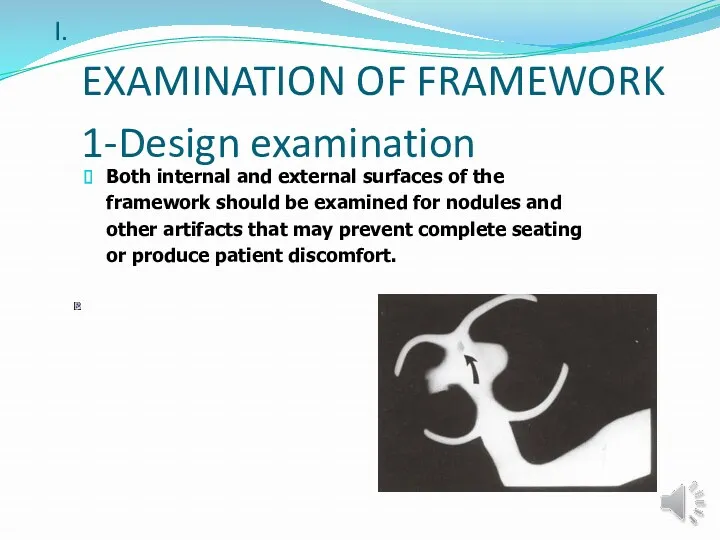
- 15. EXAMINATION OF FRAMEWORK 1-Design examination Both internal and external surfaces of the framework should be examined
- 16. Examination of Framework Stewart’s
- 17. 2-Does the framework fit the master cast accurately? A properly constructed framework should fit tightly against
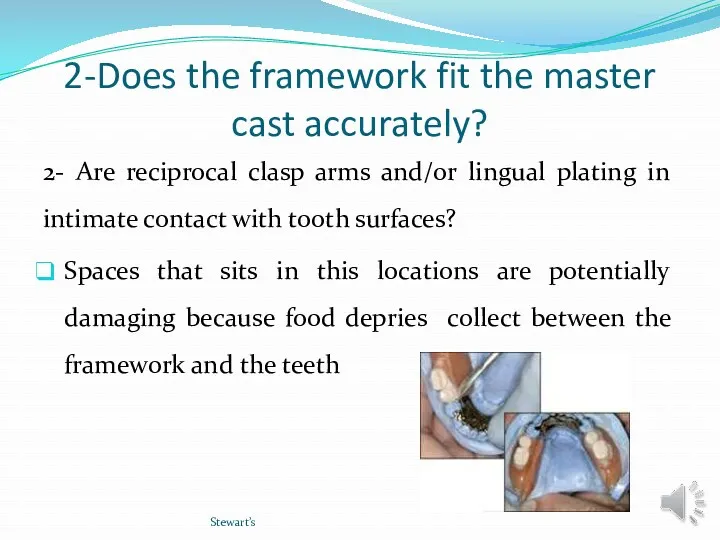
- 18. 2-Does the framework fit the master cast accurately? 2- Are reciprocal clasp arms and/or lingual plating
- 19. 2-Does the framework fit the master cast accurately? 3- Have finishing and polishing procedures been carried
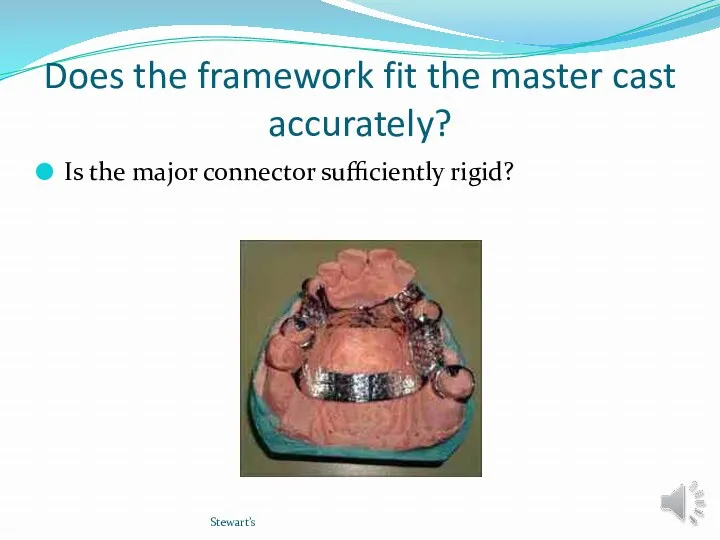
- 20. Does the framework fit the master cast accurately? Is the major connector sufficiently rigid? Stewart’s
- 21. Examination of Framework Stewart’s
- 22. B-INTRAORAL EXAMINATION Objectives: Fit the framework to the teeth and soft tissues of the supporting arch.
- 23. B-INRAORAL EXMINATION 1-Fit the framework to the teeth and soft tissues of the supporting arch. Stewart’s
- 24. B-INTRAORAL EXAMINATION Disclosing Media
- 25. Disclosing Media To properly adjust a removable partial denture framework, the practitioner must identify areas of
- 26. Disclosing Media Tow types of disclosing media 1-spray type. 2-disclosing wax Stewart’s
- 27. Disclosing Media 1-Spray-type disclosing media are often used during fitting procedures. While sprays are convenient, they
- 28. Stewart’s 2-disclosing wax Advantage: The greatest advantage of disclosing wax over other disclosing agents is it
- 29. Stewart’s Application and use of disclosing wax armamentarium A- disclosing wax itself, B-a heat source, C-
- 30. Stewart’s NB: To prevent contamination of the remaining material, a small amount of disclosing wax is
- 31. Stewart’s STEPS: 1-A number seven wax spatula or a roach carver is then heated and used
- 32. Stewart’s 2- The melted disclosing wax is applied to framework surfaces that will contact the teeth.
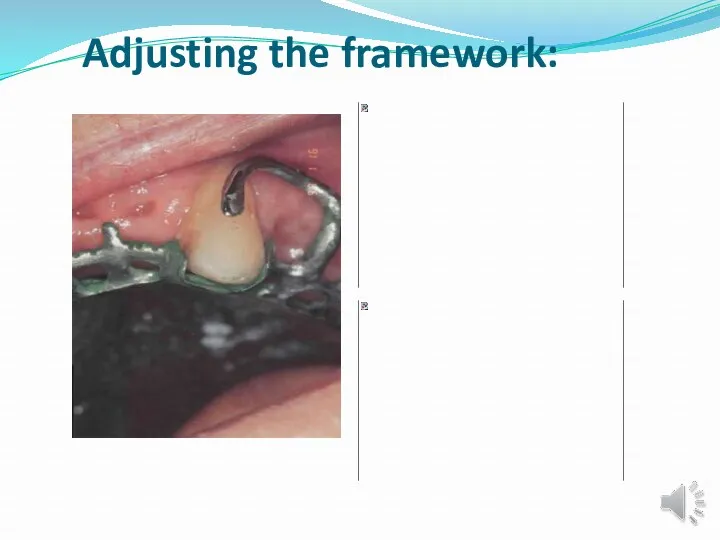
- 33. Adjusting the framework:
- 34. Adjusting the framework:
- 35. Stewart’s 4-If significant resistance is met, the framework should be removed and examined for signs of
- 36. Stewart’s NB: In case of a distal extension framework, no pressure should be applied over the
- 37. Stewart’s Areas of show-through represent interferences that prevent complete seating of the framework. The most common
- 38. Stewart’s Areas that have been defined as true interferences must be carefully machined. This is accomplished
- 39. Stewart’s 2-Fitting the framework to the opposing occlusion The simplest and most reliable method for correcting
- 40. Stewart’s In a clinical setting, one framework is positioned in the mouth and the patient is
- 41. Stewart’s Undesirable contact is eliminated by grinding the offending areas of the metal framework. To promote
- 42. Stewart’s When the patient’s original contacts have been reestablished, the practitioner should evaluate all eccentric movements.
- 43. NEW TREND Occlusal interferences can also be detected using T.B SCAN Stewart’s
- 44. Stewart’s If maxillary and mandibular frameworks have been constructed, the framework should be fitted individually. After
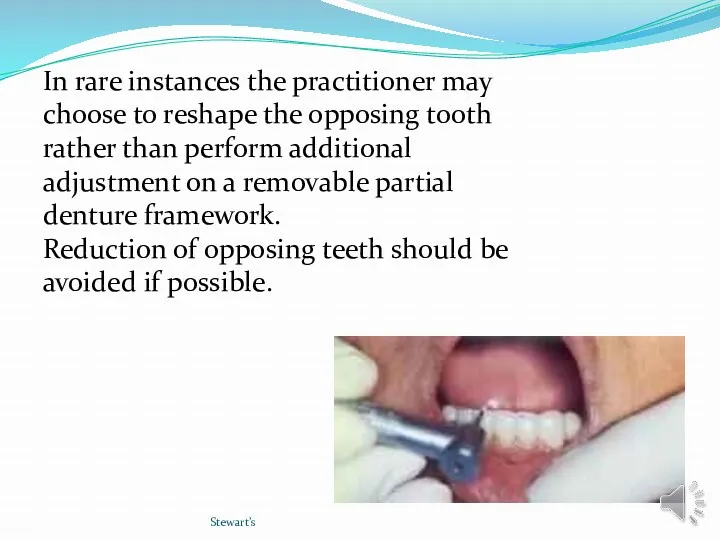
- 45. Stewart’s In rare instances the practitioner may choose to reshape the opposing tooth rather than perform
- 46. Stewart’s Finishing and polishing ground surfaces
- 47. Stewart’s After the frame work has been fitted to the supporting teeth, and opposing occlusal surfaces,
- 50. Скачать презентацию

































 Безопасное материнство и эффективная перинатальная помощь. (Модуль 1)
Безопасное материнство и эффективная перинатальная помощь. (Модуль 1) Строение атома. Испускание и поглощение света. Рентгеновское излучение. Радиоактивность. Лазеры. Лекция 6
Строение атома. Испускание и поглощение света. Рентгеновское излучение. Радиоактивность. Лазеры. Лекция 6 Инородное тело гортани и трахеи
Инородное тело гортани и трахеи Заболевания лимфатических узлов
Заболевания лимфатических узлов Ранний токсикоз беременных
Ранний токсикоз беременных Рак легкого
Рак легкого Революции в фармакологии: XX-XXI век
Революции в фармакологии: XX-XXI век Характеристики основных видов твердых лекарственных форм
Характеристики основных видов твердых лекарственных форм Омыртқа жотасының қисаюы
Омыртқа жотасының қисаюы Брюшной тиф
Брюшной тиф Нарушение терморегуляции. Лихорадка
Нарушение терморегуляции. Лихорадка Репродуктивное здоровье населения и национальная безопасность России
Репродуктивное здоровье населения и национальная безопасность России Тканевая совместимость и переливание крови
Тканевая совместимость и переливание крови Гравидограмма интерпритациясы
Гравидограмма интерпритациясы Public health. Medicare and medicaid. Law and poverty
Public health. Medicare and medicaid. Law and poverty Основы патологии. Гипоксия. Нарушение терморегуляции. Голодание
Основы патологии. Гипоксия. Нарушение терморегуляции. Голодание Тема 5.5. Роль ЦНС в процессе адаптации. Стресс, фазы и механизмы стресса
Тема 5.5. Роль ЦНС в процессе адаптации. Стресс, фазы и механизмы стресса Балалардың асқазан - ішек аурулары туралы түсінік беру. Балаларда ішек жұқпасының көріністері
Балалардың асқазан - ішек аурулары туралы түсінік беру. Балаларда ішек жұқпасының көріністері Дыхательная недостаточность
Дыхательная недостаточность Оказание первой медицинской помощи детям
Оказание первой медицинской помощи детям Parainfluenza
Parainfluenza Балалардағы ерін мен тіл аурулары. Клиникасы, нақтамасы, емі. Лекция 8
Балалардағы ерін мен тіл аурулары. Клиникасы, нақтамасы, емі. Лекция 8 Эпидемиологическая ситуация по туберкулезу и реализация мер профилактики в Атбасарском районе
Эпидемиологическая ситуация по туберкулезу и реализация мер профилактики в Атбасарском районе Особенности течения и лечения артериальной гипертензии у беременных
Особенности течения и лечения артериальной гипертензии у беременных Центральная линия
Центральная линия Эндометриоз. Актуальность проблемы
Эндометриоз. Актуальность проблемы Сладкая жизнь. Опасность сахарного диабета
Сладкая жизнь. Опасность сахарного диабета Современные представления о заболеваниях пародонта. Классификации заболеваний пародонта. Клиника. Диагностика
Современные представления о заболеваниях пародонта. Классификации заболеваний пародонта. Клиника. Диагностика