Содержание
- 2. Definition KFD is a tick-borne viral haemorrhagic fever endemic (constant presence of disease) in Karnataka State,
- 3. Definition KFDV was first identified in 1957, when an illness occurred in monkeys (the black faced
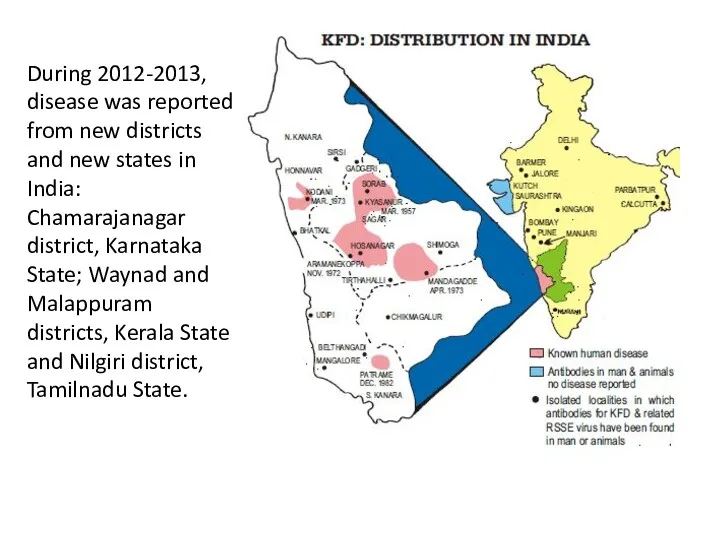
- 4. During 2012-2013, disease was reported from new districts and new states in India: Chamarajanagar district, Karnataka
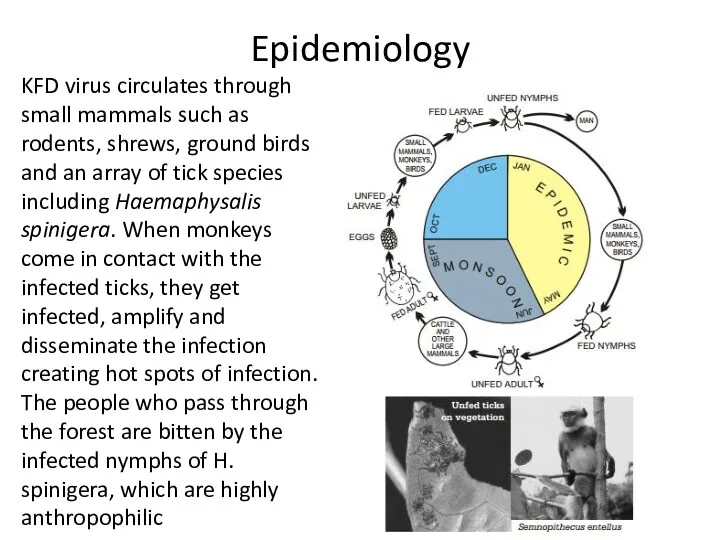
- 5. Epidemiology KFD virus circulates through small mammals such as rodents, shrews, ground birds and an array
- 6. Clinical features The onset is sudden with chills, frontal headache and high fever about 40 C.
- 7. Clinical features Diarrhoea and vomiting occur by the third or fourth day of illness. Bleeding from
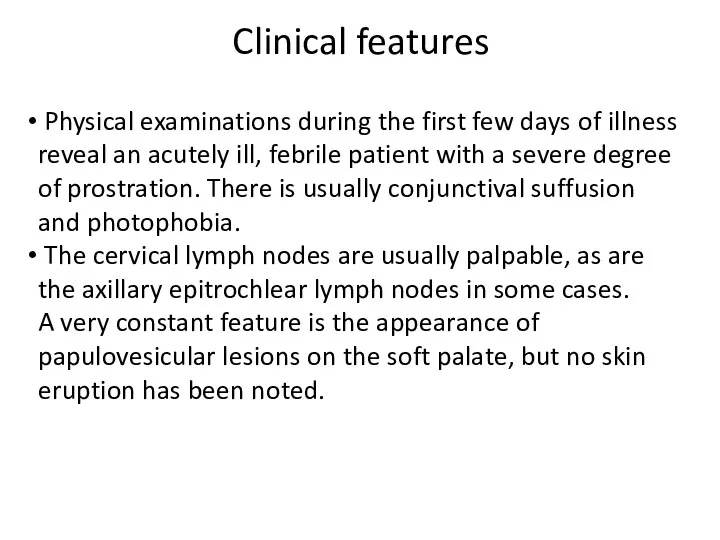
- 8. Clinical features Physical examinations during the first few days of illness reveal an acutely ill, febrile
- 9. Clinical features The convalescent phase of the disease is prolonged. Often, the disease runs a biphasic
- 10. Diagnosis Diagnosis is mainly syndromic. Laboratory tests include Hemagglutination inhibition, immunofluorescence and neutralization tests. Neutralization test
- 12. Скачать презентацию






 Cистема кровообращения
Cистема кровообращения ВИЧ вирус иммунодефицита человека
ВИЧ вирус иммунодефицита человека ЭКГ-диагностика ишемической болезни сердца - стенокардии и инфаркта миокарда
ЭКГ-диагностика ишемической болезни сердца - стенокардии и инфаркта миокарда Лекарственные растения в нашей жизни
Лекарственные растения в нашей жизни Методы детоксикации организма
Методы детоксикации организма Дети с нарушением интеллекта
Дети с нарушением интеллекта Геморагический инсульт
Геморагический инсульт Внезапная сердечная смерть
Внезапная сердечная смерть Илік заттар (немесе тұтқыр заттар), тітіркендіруші заттар.қаптаушы заттар, адсорбциялаушы заттар
Илік заттар (немесе тұтқыр заттар), тітіркендіруші заттар.қаптаушы заттар, адсорбциялаушы заттар Кровь: состав, свойства и функции. Свёртывание крови
Кровь: состав, свойства и функции. Свёртывание крови МРТ в диагностики ишемического инсульта. Сосудистая патология. Лекция 3
МРТ в диагностики ишемического инсульта. Сосудистая патология. Лекция 3 Регенерация костной ткани
Регенерация костной ткани Специальные методы исследования вен
Специальные методы исследования вен Анатомо-физиологические основы массажа
Анатомо-физиологические основы массажа ГБУЗ Городская больница №2 г.Волжский
ГБУЗ Городская больница №2 г.Волжский ВИЧ-инфекция
ВИЧ-инфекция Виразкова хвороба у дітей
Виразкова хвороба у дітей Психосоциальные факторы риска сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний
Психосоциальные факторы риска сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний Кесар тілігінен кейінгі перитонит. Акушерлік перитонит. Септикалық инфекция
Кесар тілігінен кейінгі перитонит. Акушерлік перитонит. Септикалық инфекция СРС: Диагностика Рахита
СРС: Диагностика Рахита Botkin’s Disease
Botkin’s Disease Кровоснабжение проводящей системы сердца
Кровоснабжение проводящей системы сердца Общая фармакология. Формулярная система
Общая фармакология. Формулярная система Понятие про иммунитет. СПИД и ВИЧ-инфекция
Понятие про иммунитет. СПИД и ВИЧ-инфекция Плеврит. Механизм развития
Плеврит. Механизм развития Сифилис. Часть I
Сифилис. Часть I Развитие коммуникативного поведения детей с нарушением опорно-двигательного аппарата
Развитие коммуникативного поведения детей с нарушением опорно-двигательного аппарата Хирургиялық науқастарды тамақтандыру
Хирургиялық науқастарды тамақтандыру