Содержание
- 2. Embryogenesis of nervous tissue Nervous tissue is originated from dorsal ectoderm during neurulation Stages 1. Nerve
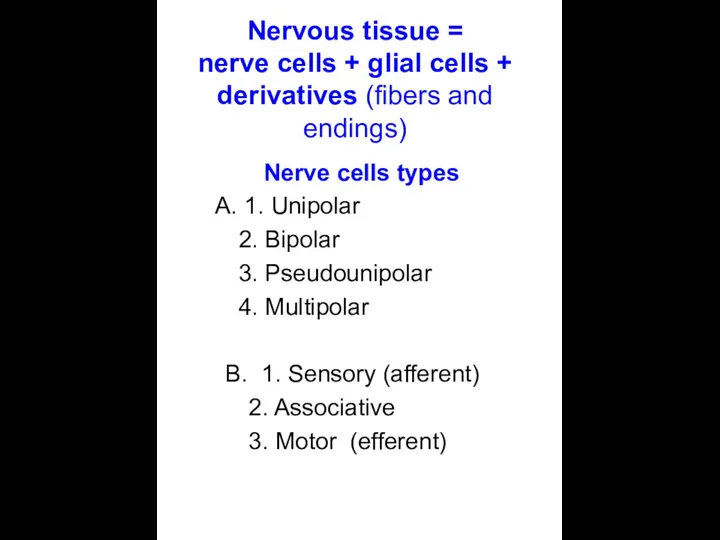
- 3. Nervous tissue = nerve cells + glial cells + derivatives (fibers and endings) Nerve cells types
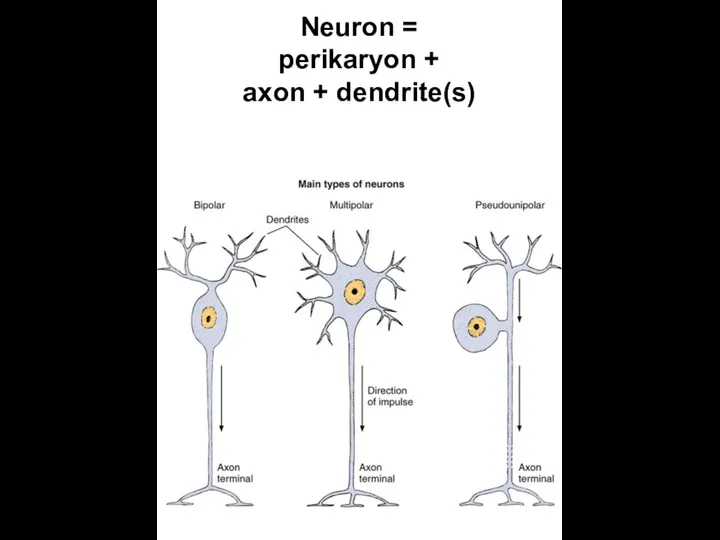
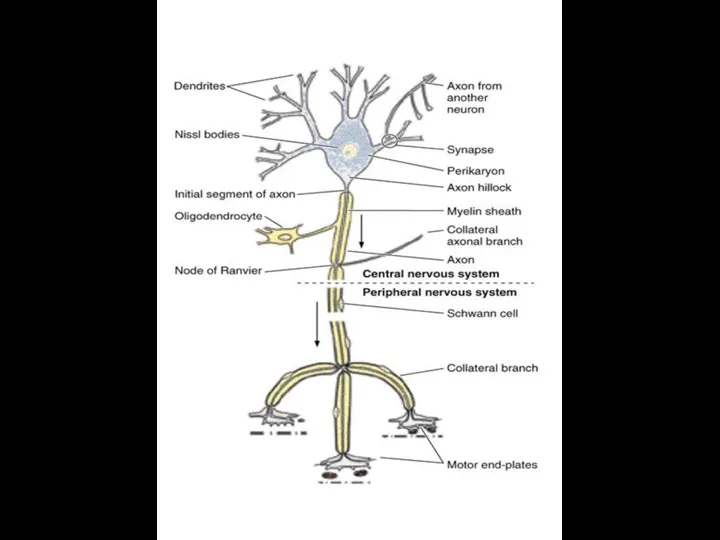
- 4. Neuron = perikaryon + axon + dendrite(s)
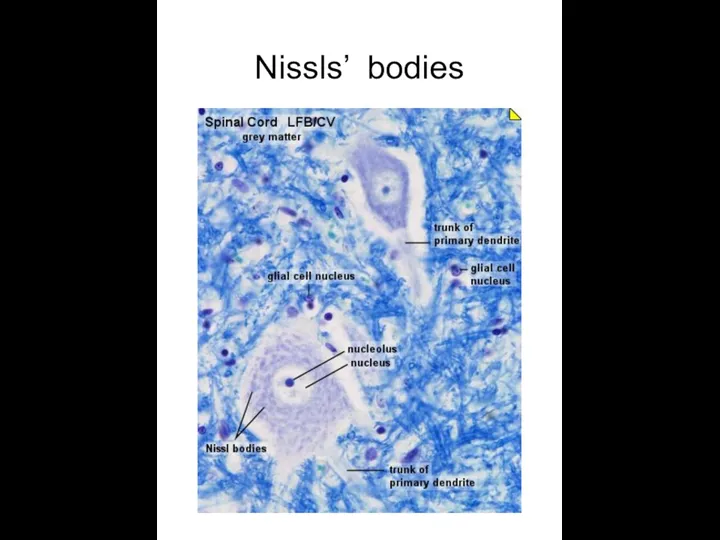
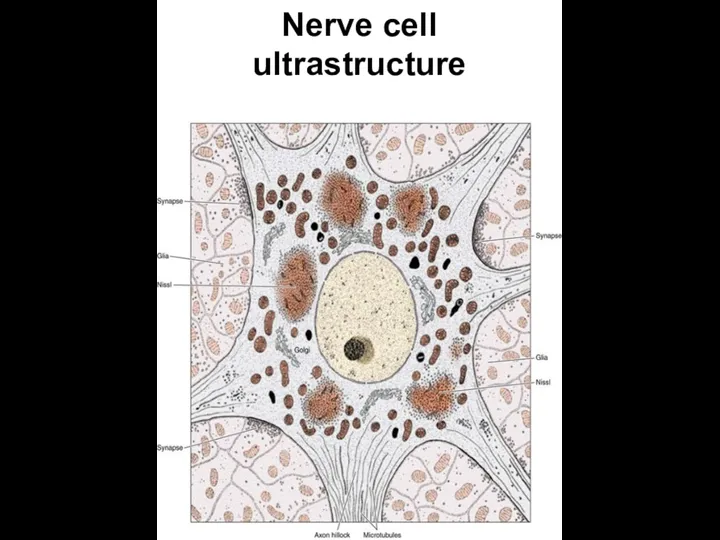
- 5. Nissls’ bodies
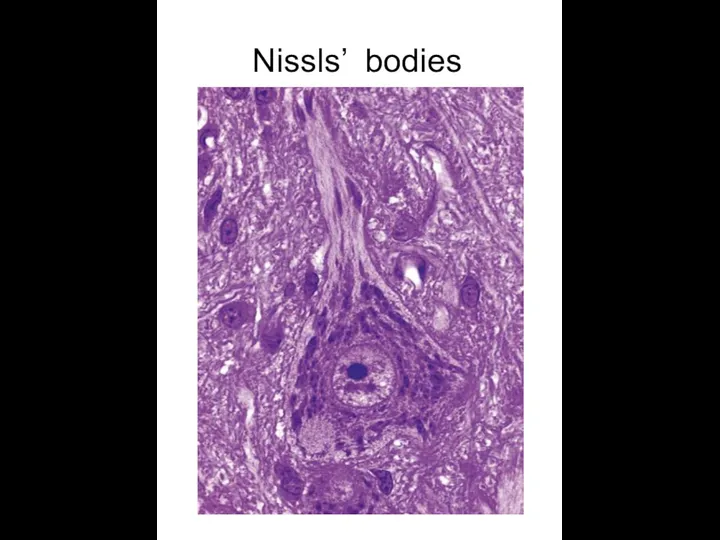
- 6. Nissls’ bodies
- 7. Nerve cell ultrastructure
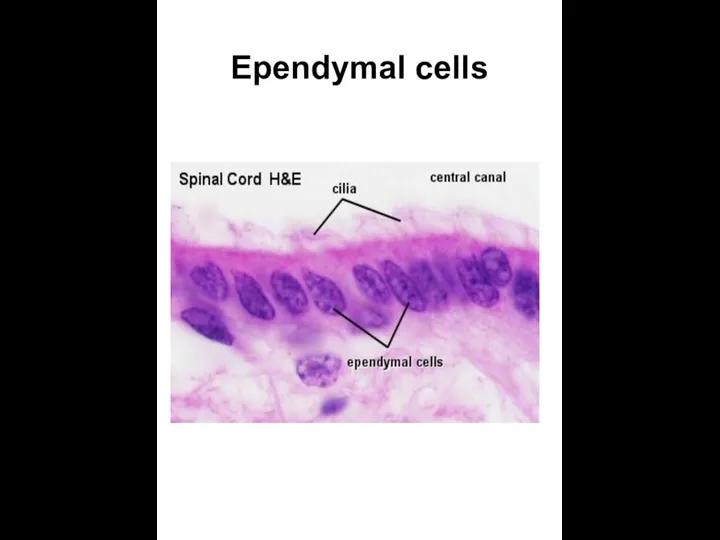
- 9. Ependymal cells
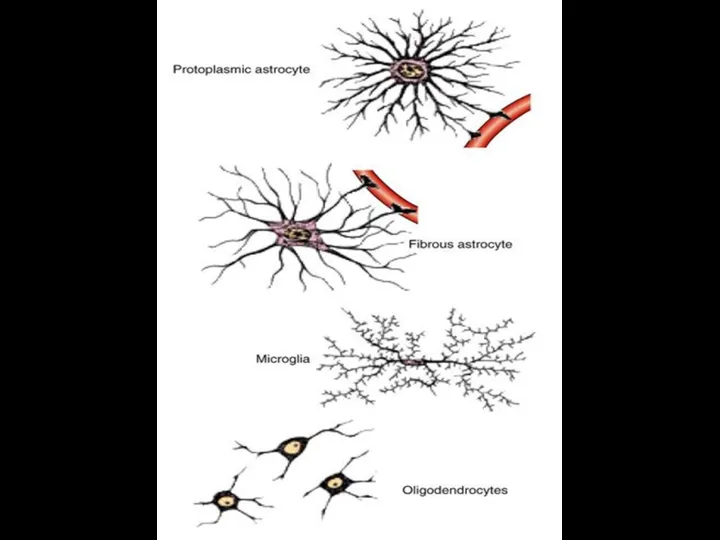
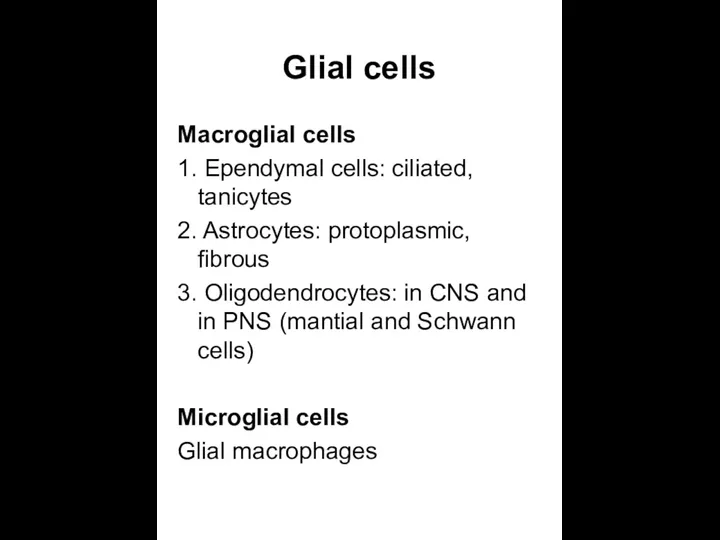
- 11. Glial cells Macroglial cells 1. Ependymal cells: ciliated, tanicytes 2. Astrocytes: protoplasmic, fibrous 3. Oligodendrocytes: in
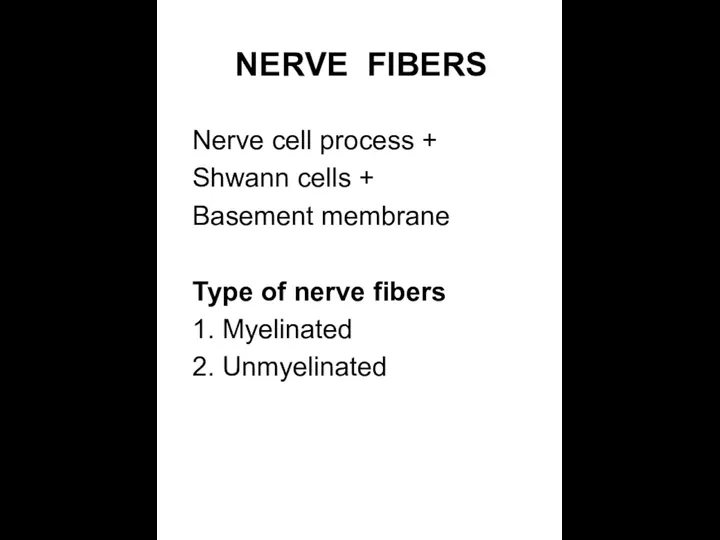
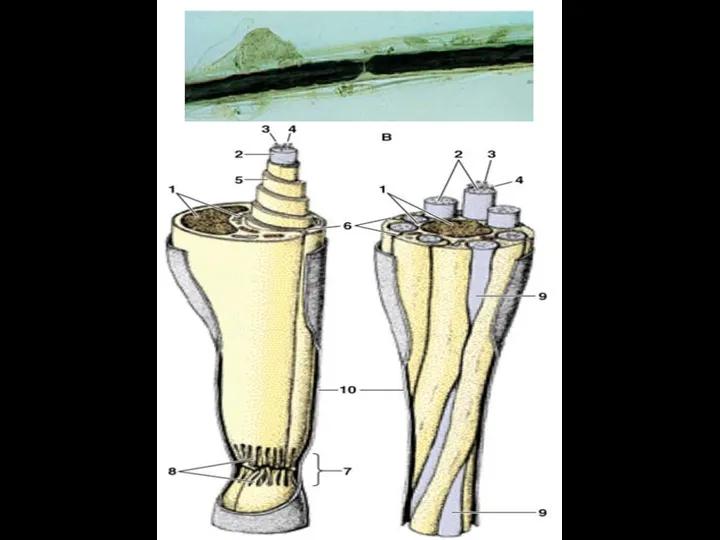
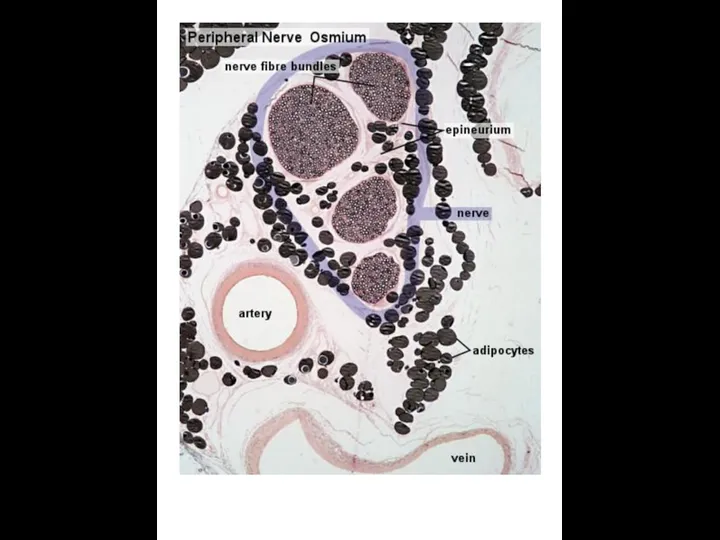
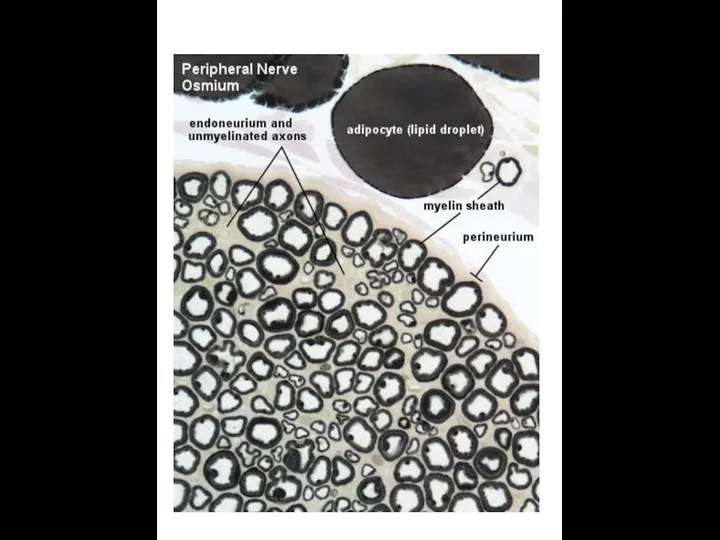
- 12. NERVE FIBERS Nerve cell process + Shwann cells + Basement membrane Type of nerve fibers 1.
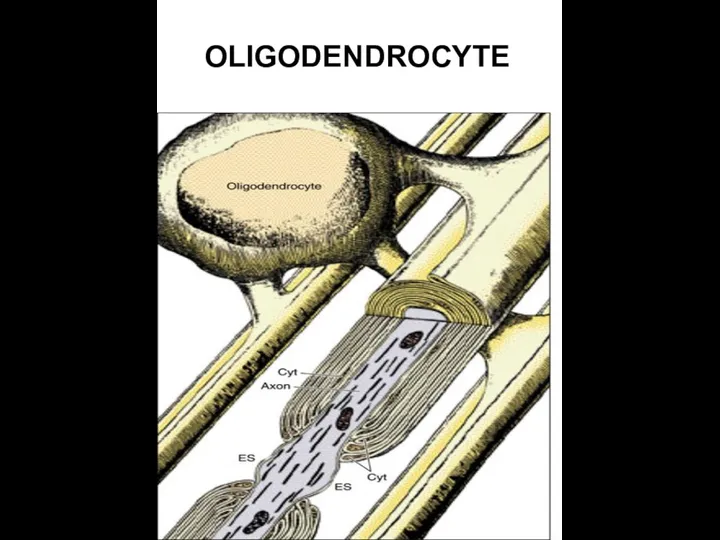
- 13. OLIGODENDROCYTE
- 14. UNMYOLINATED FIBER
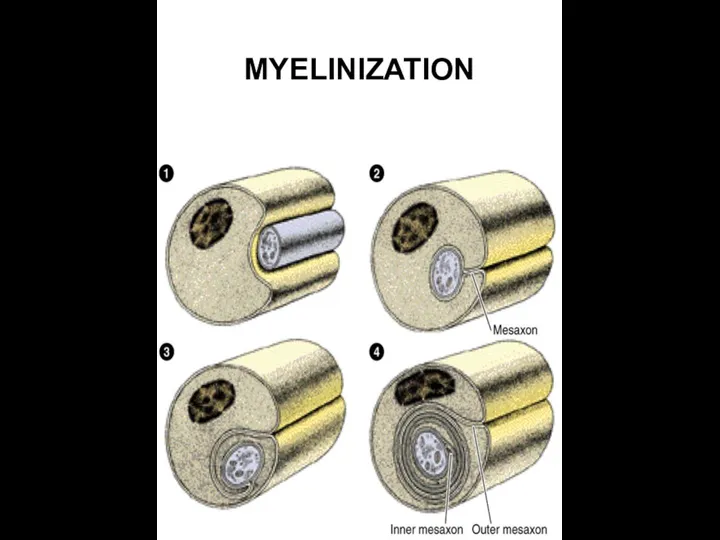
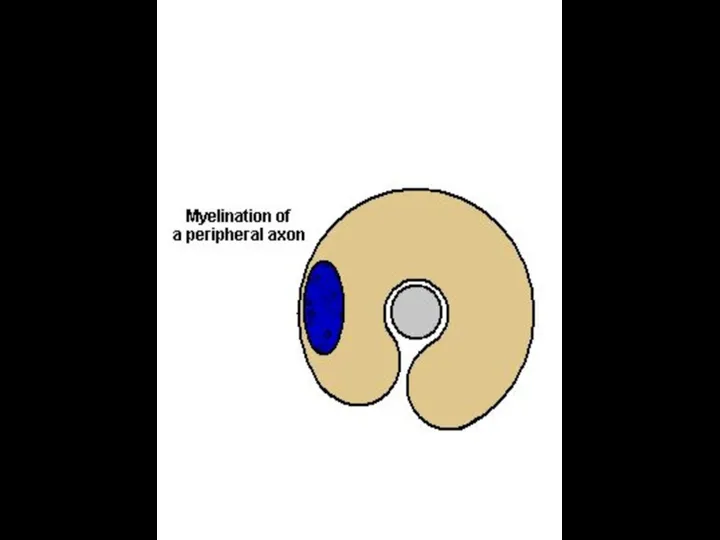
- 15. MYELINIZATION
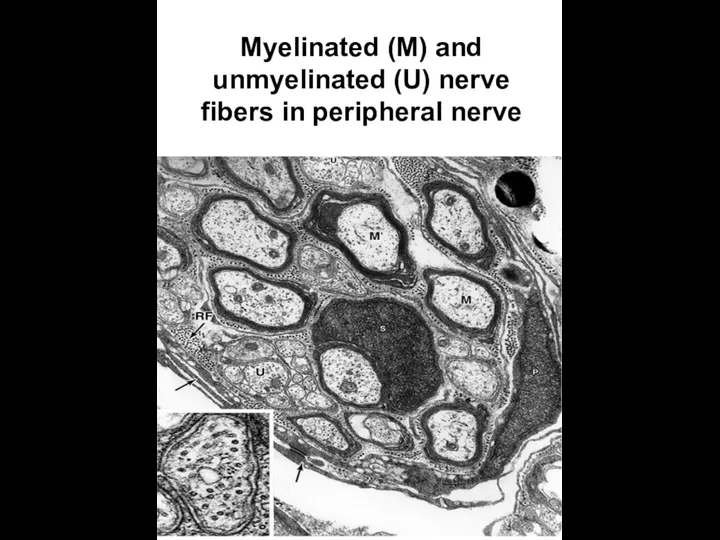
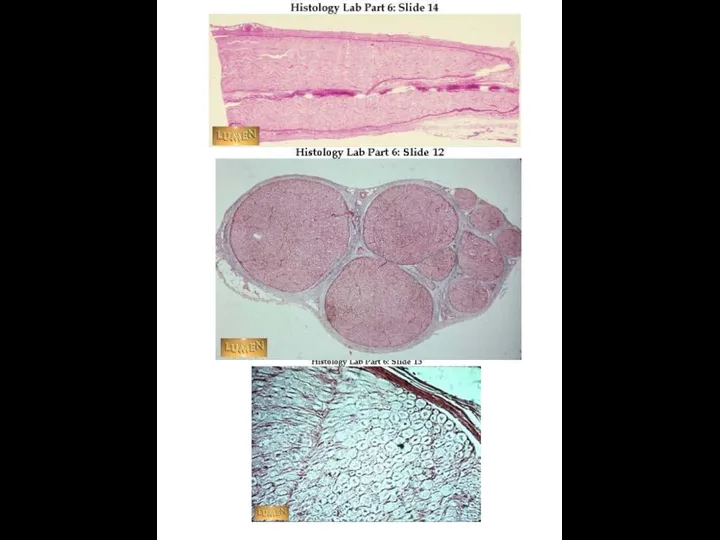
- 18. Myelinated (M) and unmyelinated (U) nerve fibers in peripheral nerve
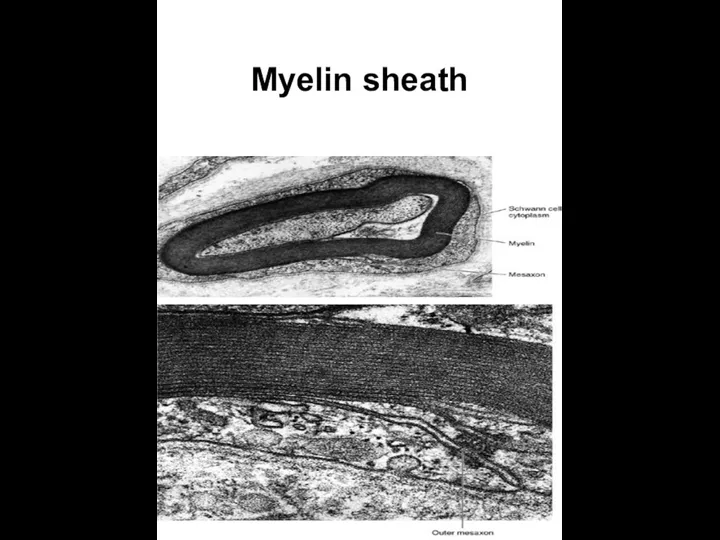
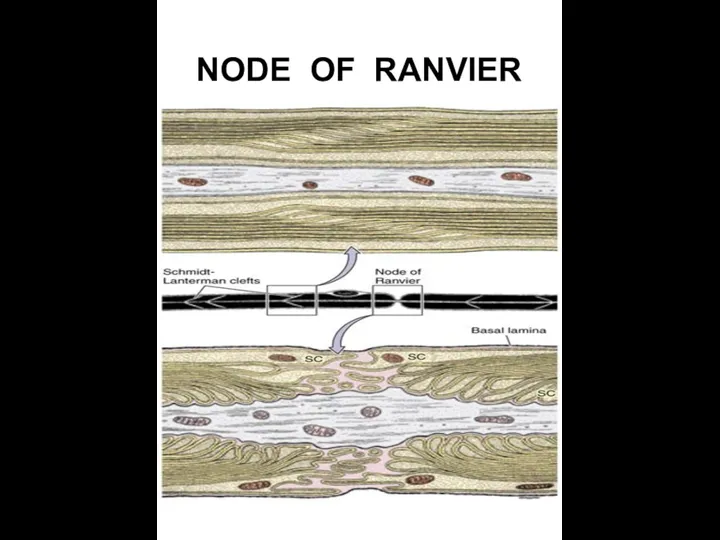
- 19. Myelin sheath
- 20. NODE OF RANVIER
- 24. NERVE ENDINGS I SENSORY (receptors) A. Location: 1. Interoceptors 2. Proprioceptors 3. Exteroceptors B. Feelings: 1.
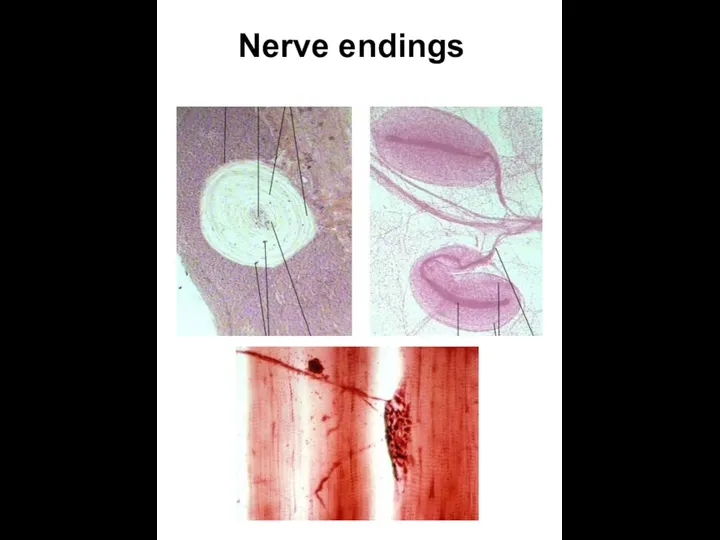
- 25. Nerve endings
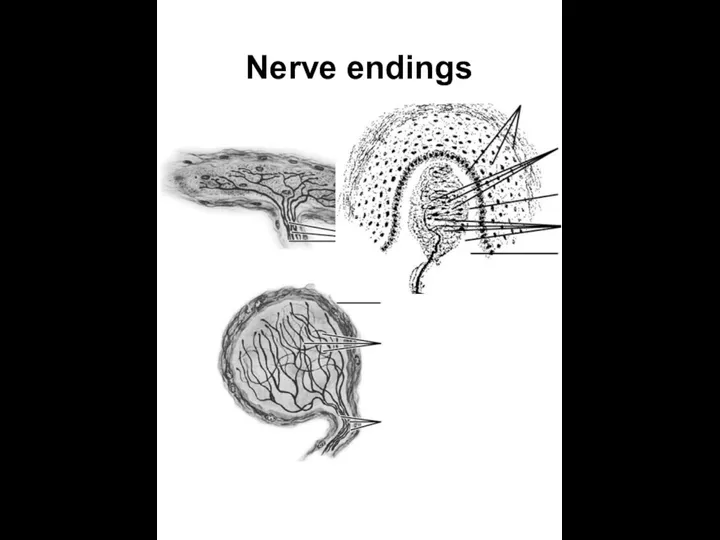
- 26. Nerve endings
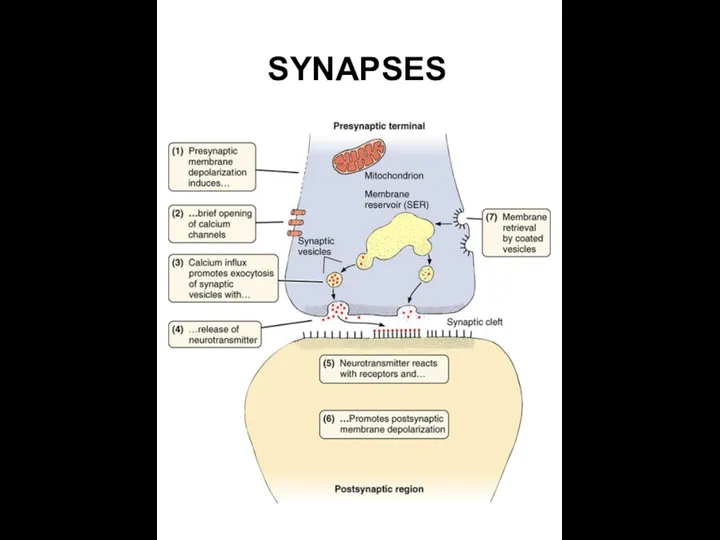
- 27. SYNAPSES
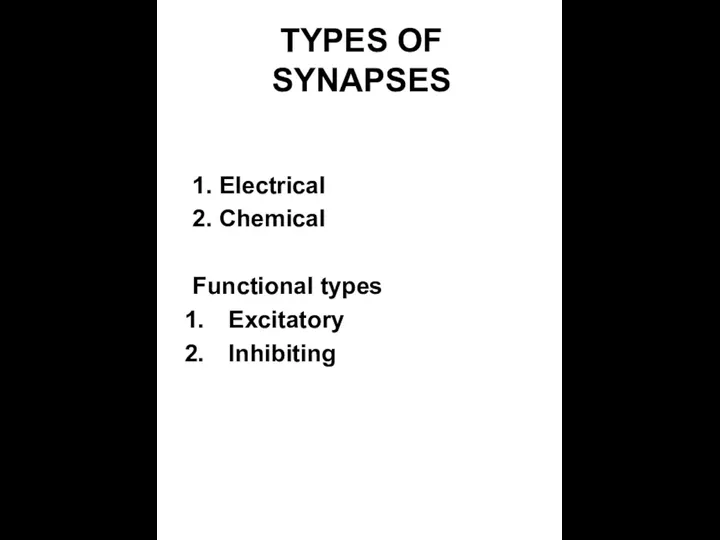
- 28. TYPES OF SYNAPSES 1. Electrical 2. Chemical Functional types Excitatory Inhibiting
- 29. SYNAPTIC COMMUNICATION The synapse is responsible for the unidirectional transmission of nerve impulses. Synapses are the
- 31. Скачать презентацию




 Синдром Ангельмана
Синдром Ангельмана Мимические мышцы лица
Мимические мышцы лица Спортивная медицина. Содержание и методы врачебно-педагогических наблюдений
Спортивная медицина. Содержание и методы врачебно-педагогических наблюдений Бірыңғай ұлттық денсаулық сақтау жүйесі
Бірыңғай ұлттық денсаулық сақтау жүйесі Хроническая ишемия мозга. Транзиторная ишемическая атака
Хроническая ишемия мозга. Транзиторная ишемическая атака Инфекционный мононуклеоз
Инфекционный мононуклеоз Коррекция нарушений звукопроизношения у детей
Коррекция нарушений звукопроизношения у детей Функциональная анатомия лимфатической системы
Функциональная анатомия лимфатической системы Плацентарная недостаточность. Гипоксия плода. Синдром задержки роста плода
Плацентарная недостаточность. Гипоксия плода. Синдром задержки роста плода Кератоконус. Классификация, симптомы
Кератоконус. Классификация, симптомы Профілактика захворювань нервової системи
Профілактика захворювань нервової системи Продукция медицинской промышленности. Технологический регламент производства
Продукция медицинской промышленности. Технологический регламент производства Гигиенические требования к выбору и планировке больничного участка. Системы строительства больниц, их преимущества и недостатки
Гигиенические требования к выбору и планировке больничного участка. Системы строительства больниц, их преимущества и недостатки Зачет 1. Повреждение. Нарушения кровообращения
Зачет 1. Повреждение. Нарушения кровообращения Еркін қозғалыс жүйесі. Қозғалыс анализаторының анатомо-физиологиялық ерекшеліктері. Орталық және шеткі салдану белгілері
Еркін қозғалыс жүйесі. Қозғалыс анализаторының анатомо-физиологиялық ерекшеліктері. Орталық және шеткі салдану белгілері Зубочелюстные аномалии у подростков и взрослых, методы их лечения, особенности ортопедического лечения
Зубочелюстные аномалии у подростков и взрослых, методы их лечения, особенности ортопедического лечения Қанның тамырлар бойымен қозғалысының гемодинамикалық заңдылықтары. Қанның реологиялық қасиеттері
Қанның тамырлар бойымен қозғалысының гемодинамикалық заңдылықтары. Қанның реологиялық қасиеттері Врожденные аномалии роговицы
Врожденные аномалии роговицы Иценко-Кушинг синдромы
Иценко-Кушинг синдромы Деформация зубных рядов. Зубочелюстная аномалия
Деформация зубных рядов. Зубочелюстная аномалия Гемобластозы опухоли кроветворной системы
Гемобластозы опухоли кроветворной системы Пылевые болезни легких. Пневмокониозы
Пылевые болезни легких. Пневмокониозы COLLOST- Специфика применения, приоритетные зоны, особенности работы в косметологии
COLLOST- Специфика применения, приоритетные зоны, особенности работы в косметологии Фармакологическая кардиоверсия аритмий сердца
Фармакологическая кардиоверсия аритмий сердца Тұрақты электротоктардың медицинада қолданылуы
Тұрақты электротоктардың медицинада қолданылуы Деонтология в онкологии
Деонтология в онкологии Острый панкреатит. Выбор срока хирургического вмешательства при остром панкреатите
Острый панкреатит. Выбор срока хирургического вмешательства при остром панкреатите Tuberculosis. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Tuberculosis. Mycobacterium tuberculosis