Содержание
- 2. FLUKES class (TREMATODA)
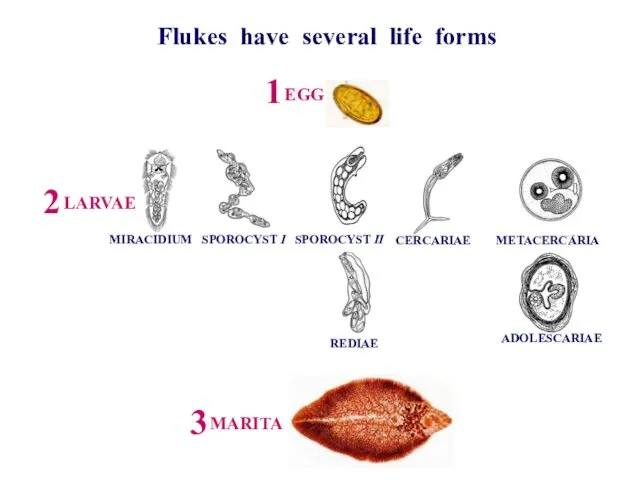
- 3. Flukes have several life forms LARVAE EGG MARITA MIRACIDIUM SPOROCYST I SPOROCYST II CERCARIAE ADOLESCARIAE REDIAE
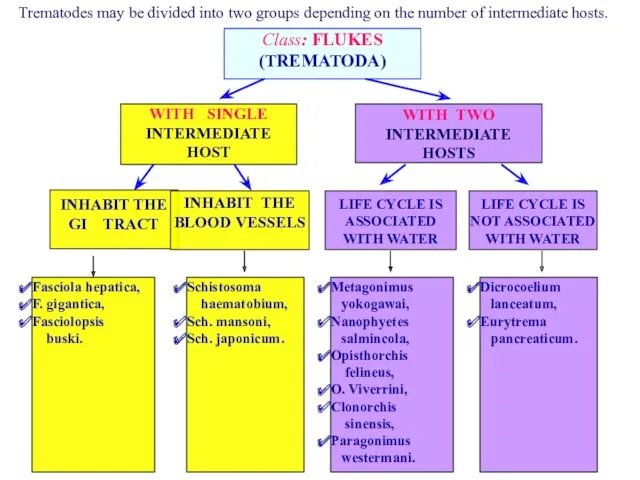
- 4. WITH SINGLE INTERMEDIATE HOST WITH TWO INTERMEDIATE HOSTS INHABIT THE GI TRACT INHABIT THE BLOOD VESSELS
- 5. All members of a subgroup have the same type of life cycles that differ only in
- 6. THE LIFE CYCLE OF TREMATODES THAT HAVE A SINGLE INTERMEDIATE HOST AND ARE LOCALIZED IN THE
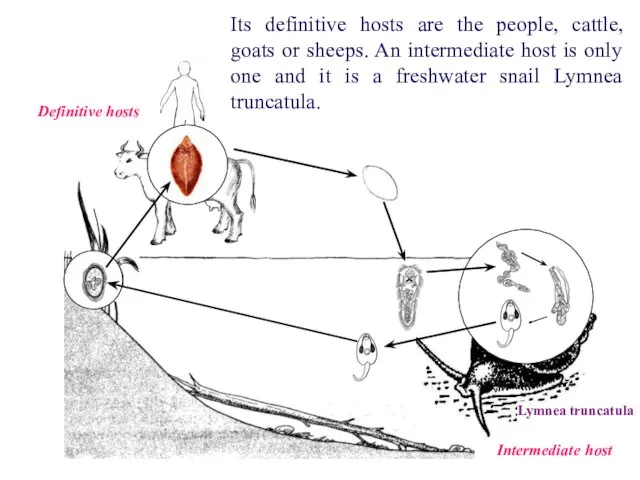
- 7. It is the causative agent of the disease, which is called “fascioliasis”. F. hepatica is localized
- 8. Definitive hosts Intermediate host Lymnea truncatula Its definitive hosts are the people, cattle, goats or sheeps.
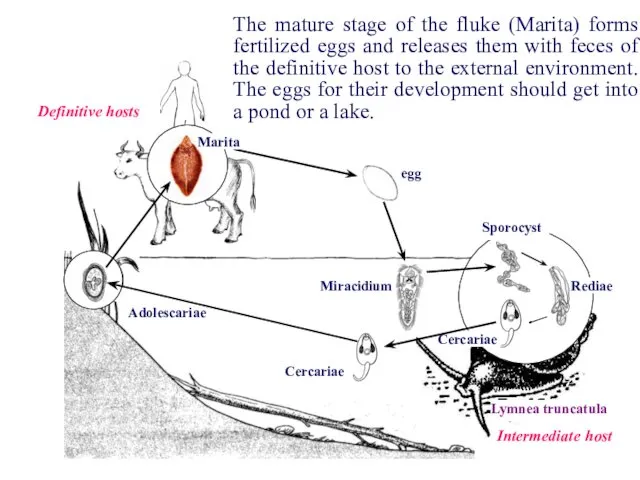
- 9. Rediae Sporocyst Cercariae Cercariae Adolescariae Miracidium Marita Definitive hosts Intermediate host Lymnea truncatula The mature stage
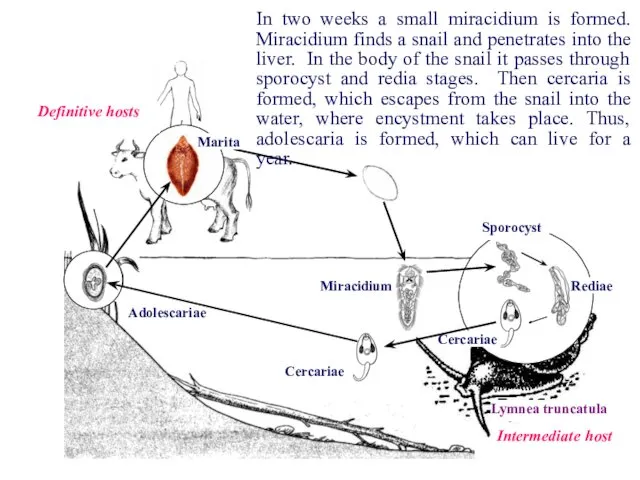
- 10. Rediae Sporocyst Cercariae Cercariae Adolescariae Miracidium Marita Definitive hosts Intermediate host Lymnea truncatula In two weeks
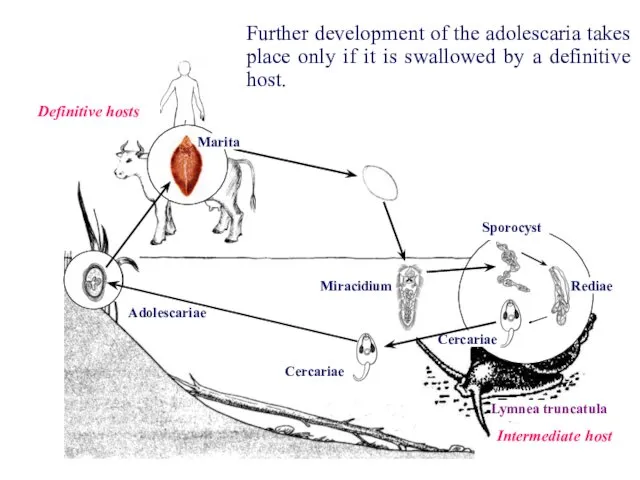
- 11. Rediae Sporocyst Cercariae Cercariae Adolescariae Miracidium Marita Definitive hosts Intermediate host Lymnea truncatula Further development of
- 12. Similarly, before enzymes in the intestine act upon a young fluke, it bores through the wall
- 13. THE LIFE CYCLE OF TREMATODES THAT HAVE A SINGLE INTERMEDIATE HOST AND ARE LOCALIZED IN THE
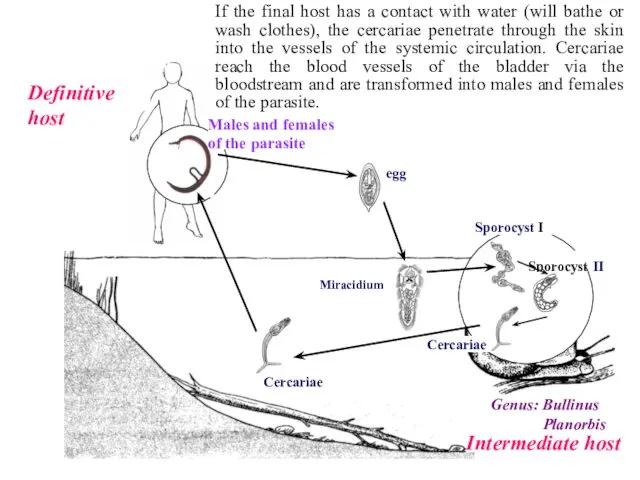
- 14. We will study this group of parasites on the example of Sh. Haematobium. It is the
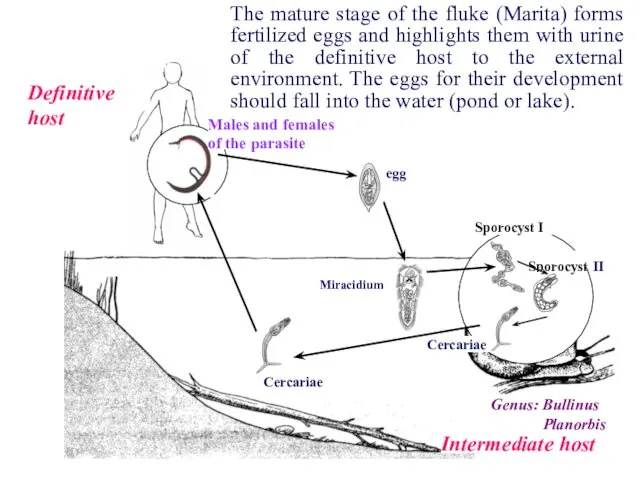
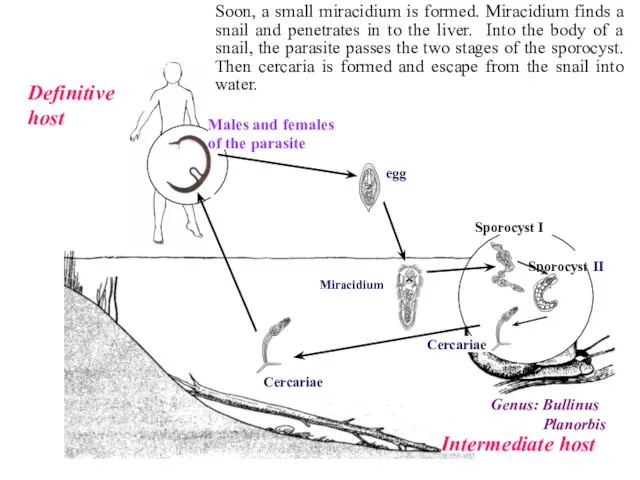
- 15. Sporocyst II Sporocyst I Cercariae Miracidium Definitive host Intermediate host Genus: Bullinus Planorbis Cercariae Males and
- 16. Sporocyst II Sporocyst I Cercariae Miracidium Definitive host Intermediate host Genus: Bullinus Planorbis Cercariae Males and
- 17. Sporocyst II Sporocyst I Cercariae Miracidium Definitive host Intermediate host Genus: Bullinus Planorbis Cercariae Males and
- 18. General Characteristics of blood flukes: Sexes of the blood flukes are separate (diecious) They are cylindrical
- 19. TREMATODES WHICH HAVE TWO INTERMEDIATE HOSTS AND WHOSE LIFE CYCLE IS NOT ASSOCIATED WITH WATER
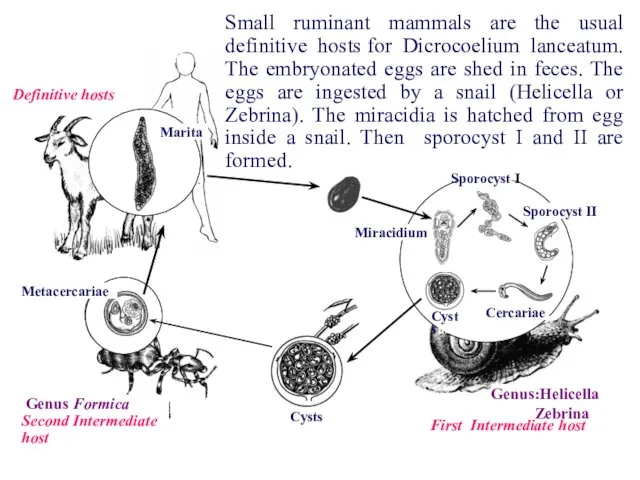
- 20. Phylum – Plathelminthes Class – Trematoda Genus - Dicrocoelium Species - D. lanceatum We will study
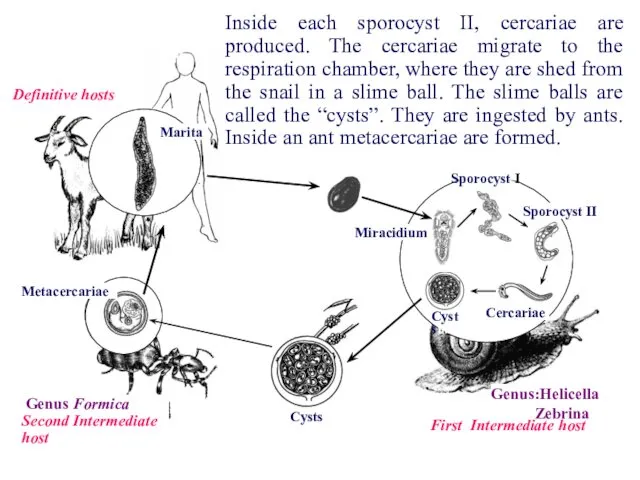
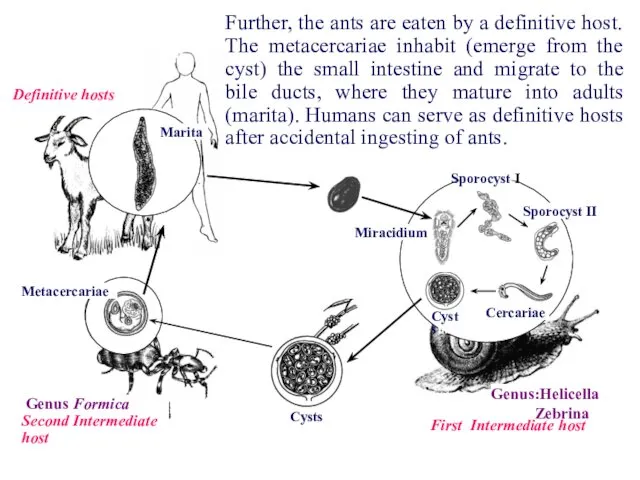
- 21. First Intermediate host Definitive hosts Marita Genus:Helicella Zebrina Sporocyst I Sporocyst II Cercariae Miracidium Cysts Cysts
- 22. First Intermediate host Definitive hosts Marita Genus:Helicella Zebrina Sporocyst I Sporocyst II Cercariae Miracidium Cysts Cysts
- 23. First Intermediate host Definitive hosts Marita Genus:Helicella Zebrina Sporocyst I Sporocyst II Cercariae Miracidium Cysts Cysts
- 24. TREMATODES WHICH HAVE TWO INTERMEDIATE HOSTS AND WHOSE LIFE CYCLE IS ASSOCIATED WITH WATER
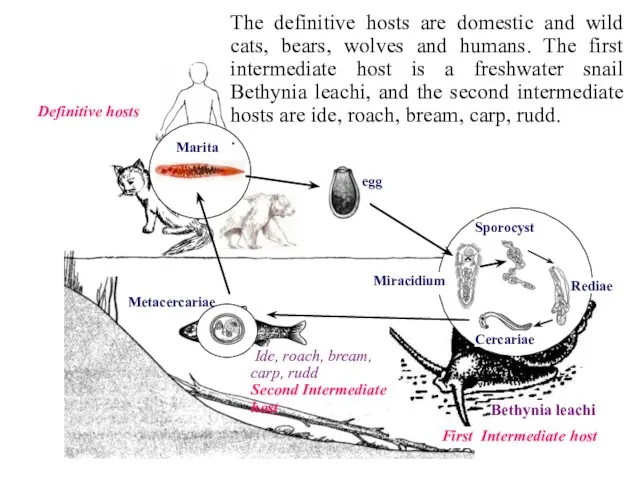
- 25. Phylum – Plathelminthes Class – Trematoda Genus - Opistorchis Species - O. felineus We will study
- 26. Rediae Sporocyst Miracidium Marita Definitive hosts First Intermediate host Bethynia leachi Cercariae Metacercariae Ide, roach, bream,
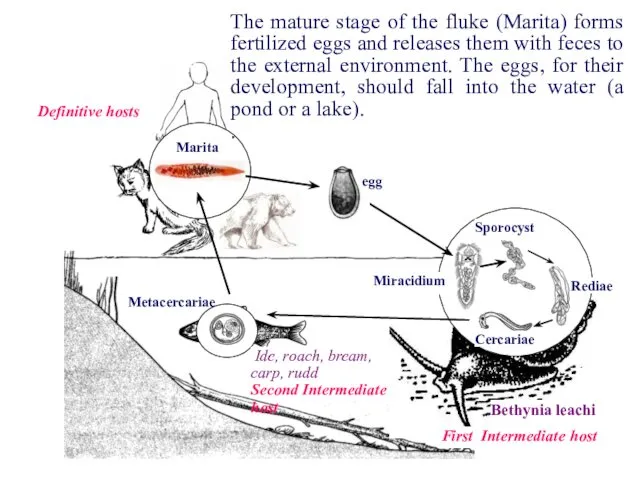
- 27. Rediae Sporocyst Miracidium Marita Definitive hosts First Intermediate host Bethynia leachi Cercariae Metacercariae Ide, roach, bream,
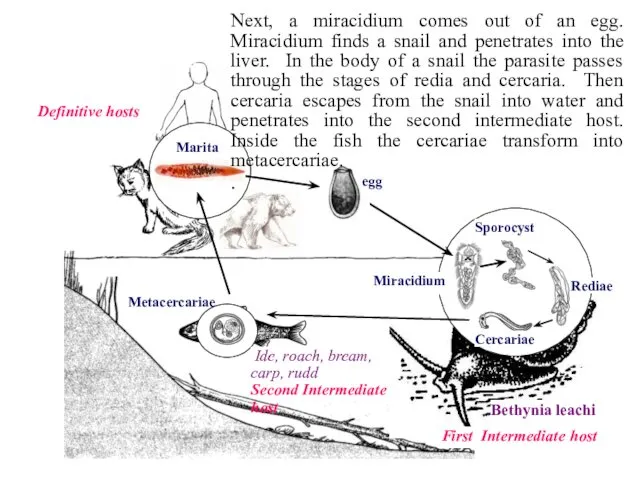
- 28. Rediae Sporocyst Miracidium Marita Definitive hosts First Intermediate host Bethynia leachi Cercariae Metacercariae Ide, roach, bream,
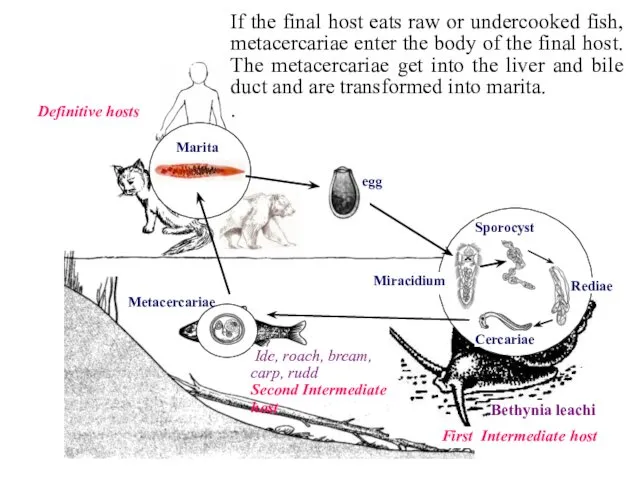
- 29. Rediae Sporocyst Miracidium Marita Definitive hosts First Intermediate host Bethynia leachi Cercariae Metacercariae Ide, roach, bream,
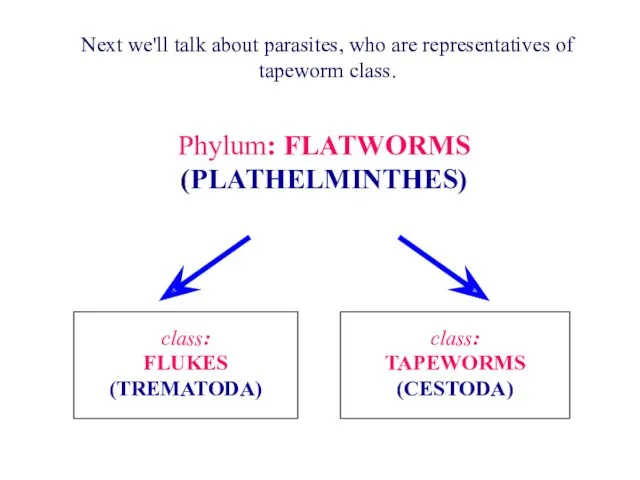
- 30. Phylum: FLATWORMS (PLATHELMINTHES) class: FLUKES (TREMATODA) class: TAPEWORMS (CESTODA) Next we'll talk about parasites, who are
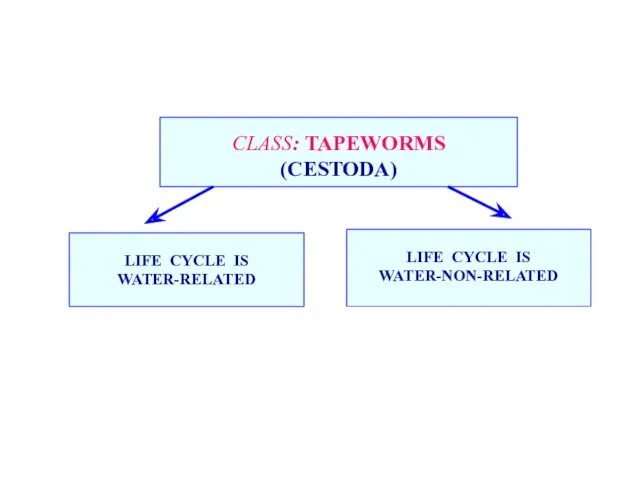
- 31. CLASS: TAPEWORMS (CESTODA) LIFE CYCLE IS WATER-RELATED LIFE CYCLE IS WATER-NON-RELATED
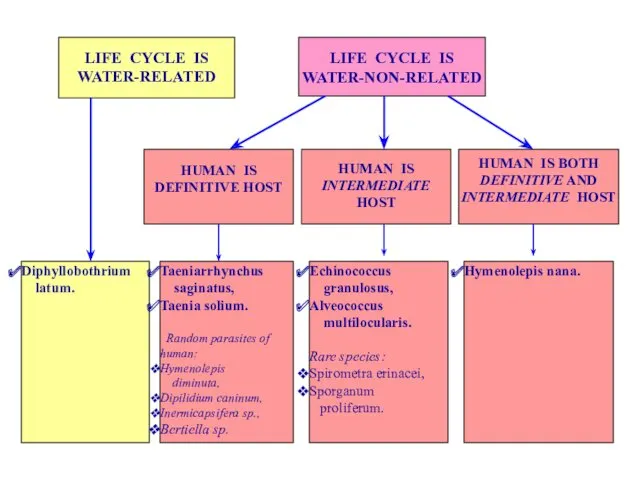
- 32. LIFE CYCLE IS WATER-RELATED LIFE CYCLE IS WATER-NON-RELATED HUMAN IS DEFINITIVE HOST HUMAN IS INTERMEDIATE HOST
- 33. 1. The class includes about 3500 species. All are parasites mainly of vertebrates. 2. Parasites have
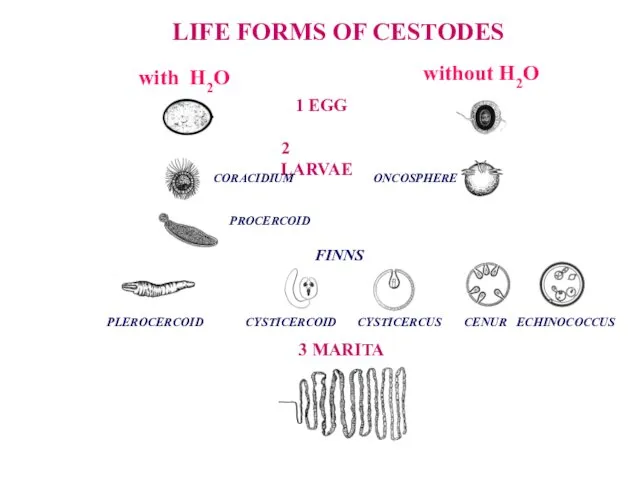
- 34. LIFE FORMS OF CESTODES 2 LARVAE 1 EGG 3 MARITA ONCOSPHERE CORACIDIUM FINNS PROCERCOID with Н2О
- 35. CESTODES WHICH HAVE WATER-RELATED LIFE CYCLE
- 36. Fish tapeworm is widely distributed in the lake areas of Europe, Asia, Far East, North America,
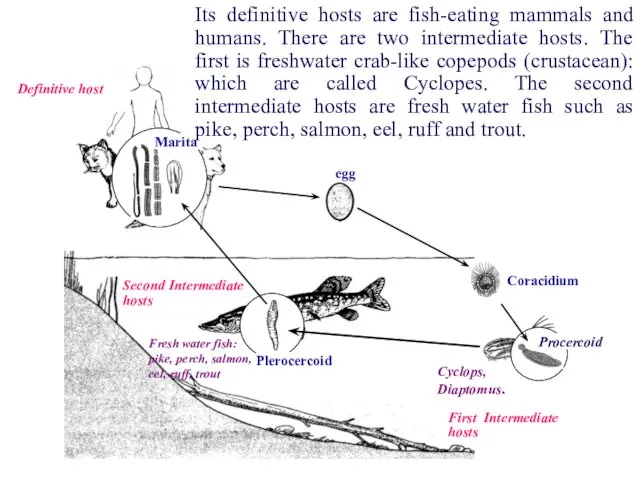
- 37. Definitive host Its definitive hosts are fish-eating mammals and humans. There are two intermediate hosts. The
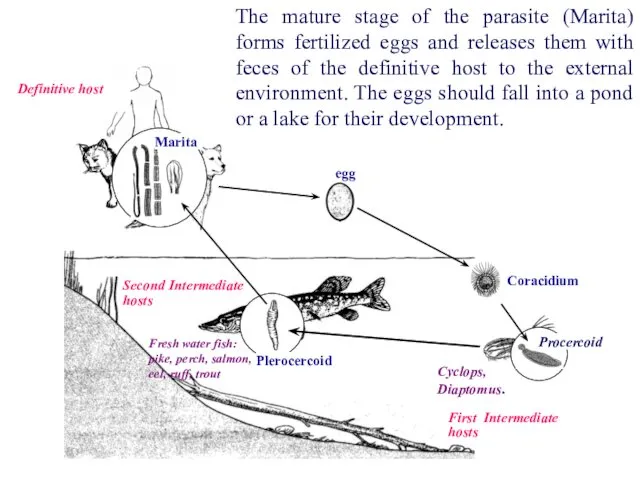
- 38. Definitive host The mature stage of the parasite (Marita) forms fertilized eggs and releases them with
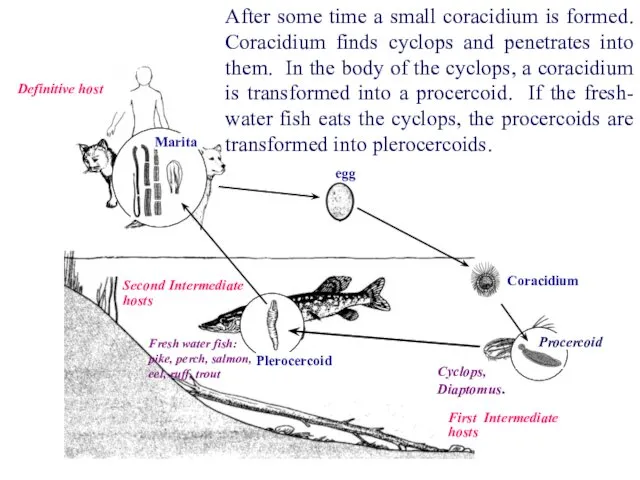
- 39. Definitive host After some time a small coracidium is formed. Coracidium finds cyclops and penetrates into
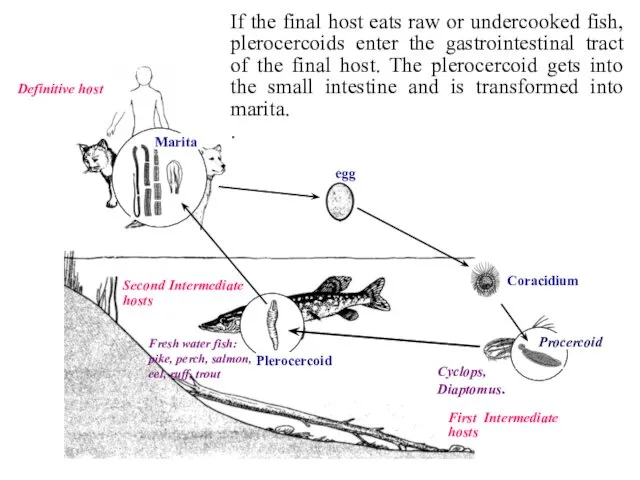
- 40. Definitive host If the final host eats raw or undercooked fish, plerocercoids enter the gastrointestinal tract
- 41. The major symptoms of the diphillobotriasis are: abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, loss of weight, intestinal obstruction,
- 42. CESTODES WHICH HAVE WATER-NON RELATED LIFE CYCLE MAN IS A DEFINITIVE HOST
- 43. Beef tapeworm is widespread in the regions of the world where the cattle is bred. The
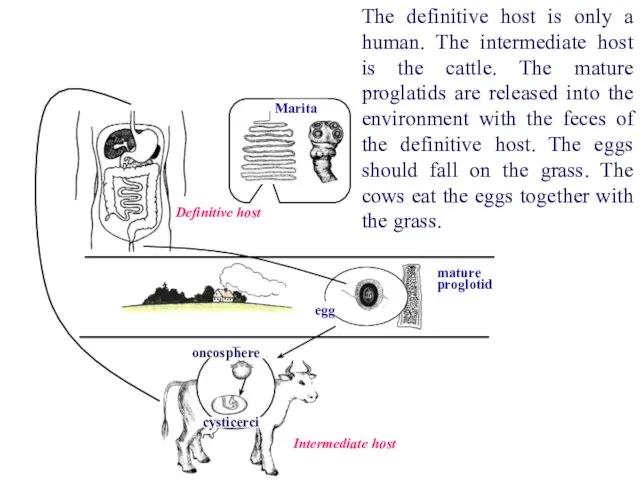
- 44. Definitive host Marita oncosphere cysticerci Intermediate host The definitive host is only a human. The intermediate
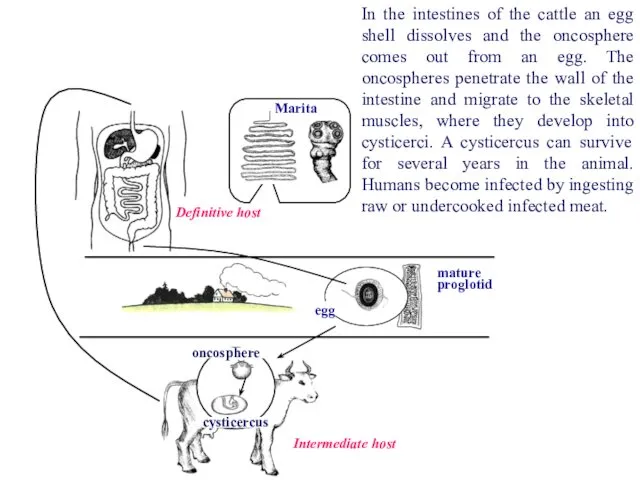
- 45. Definitive host Marita oncosphere cysticercus Intermediate host In the intestines of the cattle an egg shell
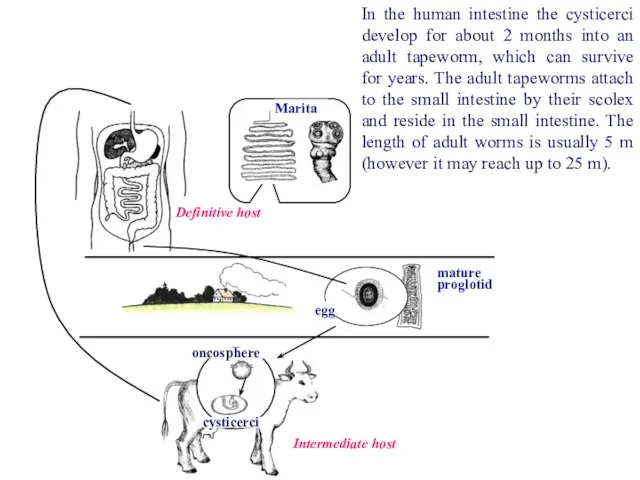
- 46. Definitive host Marita oncosphere cysticerci Intermediate host In the human intestine the cysticerci develop for about
- 47. Beef tapeworm can cause digestive problems including abdominal pain, loss of appetite, weight loss, and upset
- 48. Pork tapeworm is widespread in the regions of the world where pigs are bred. The parasite
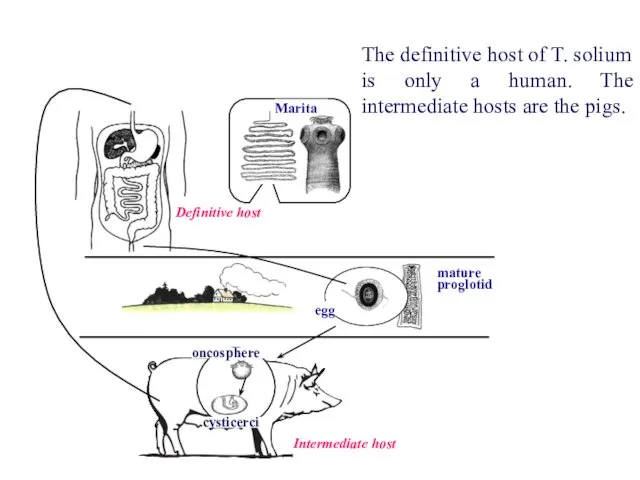
- 49. Definitive host Marita oncosphere cysticerci Intermediate host The definitive host of T. solium is only a
- 50. The marita of the pork tapeworm secretes very toxic products of its metabolism. Therefore, in patients
- 51. If the human brain is affected by cysticerci, severe headaches, vision loss and seizures are observed.
- 52. CESTODES WHICH HAS A WATER-NON RELATED LIFE CYCLE MAN IS AN INTERMEDIATE HOST
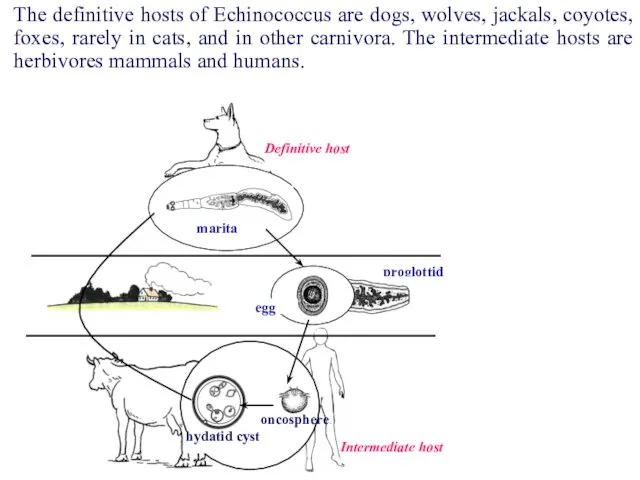
- 53. Echinococcus granulosus is widespread in various regions of the World: Europe, East Africa, the Middle East,
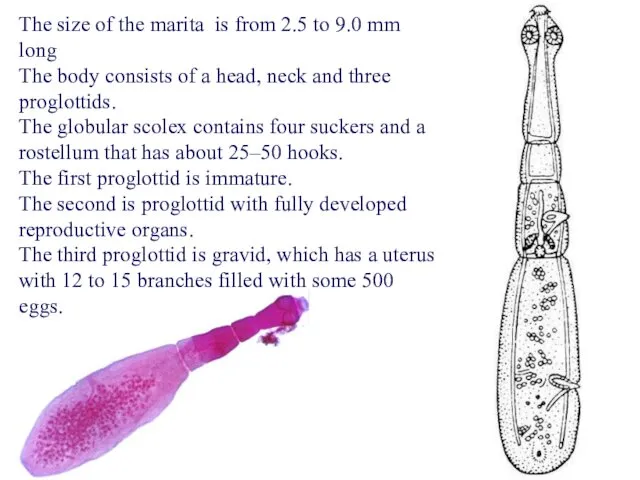
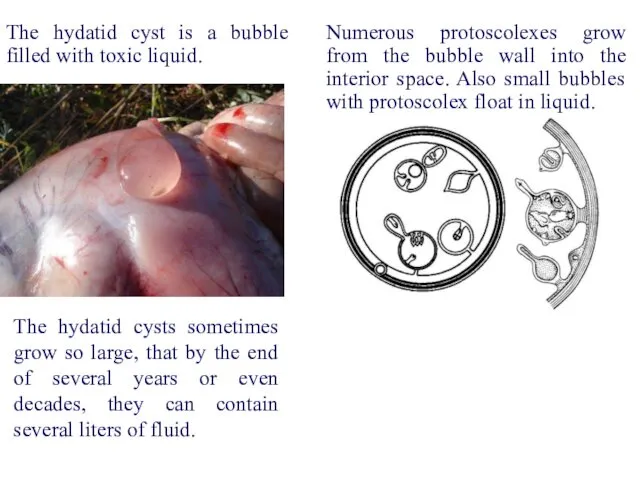
- 54. The size of the marita is from 2.5 to 9.0 mm long The body consists of
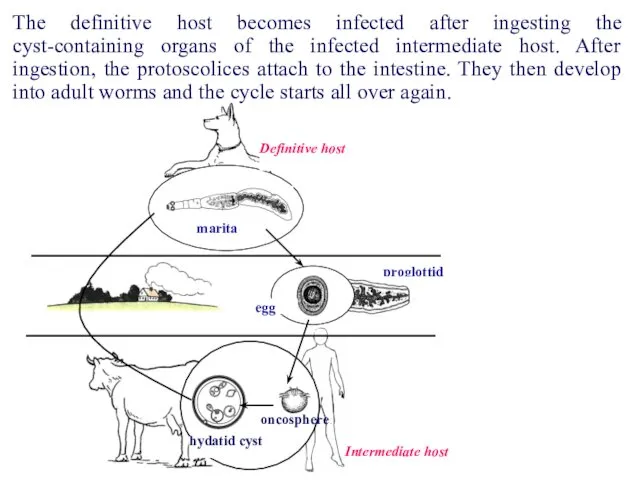
- 55. proglottid egg marita Definitive host Intermediate host hydatid cyst oncosphere The definitive hosts of Echinococcus are
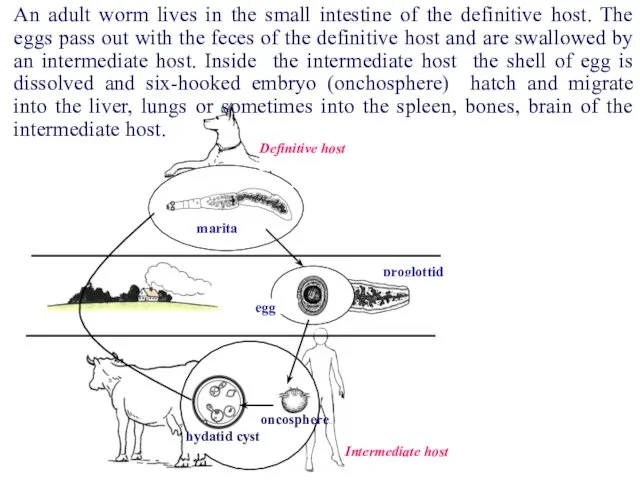
- 56. proglottid egg marita Definitive host Intermediate host hydatid cyst oncosphere An adult worm lives in the
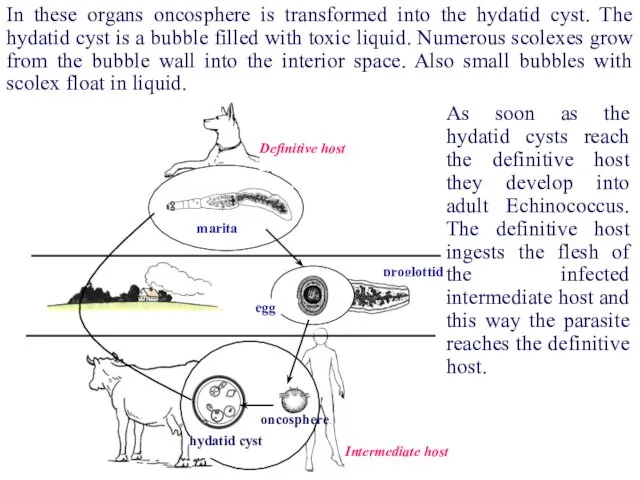
- 57. proglottid egg marita Definitive host Intermediate host hydatid cyst oncosphere In these organs oncosphere is transformed
- 58. Numerous protoscolexes grow from the bubble wall into the interior space. Also small bubbles with protoscolex
- 59. proglottid egg marita Definitive host Intermediate host hydatid cyst oncosphere The definitive host becomes infected after
- 60. In the film you can see an echinococcus cyst removal from the patient's liver.
- 61. FOR DIAGNOSIS OF ECHINOCOCCOSIS X-RAY EXAMINATIONS, ULTRASONIC EXAMINATION AND SEROLOGICAL TESTS ARE USED
- 62. CESTODES WHICH HAVE A WATER-NON-RELATED LIFE CYCLE MAN IS BOTH A DEFINITIVE AND AN INTERMEDIATE HOST
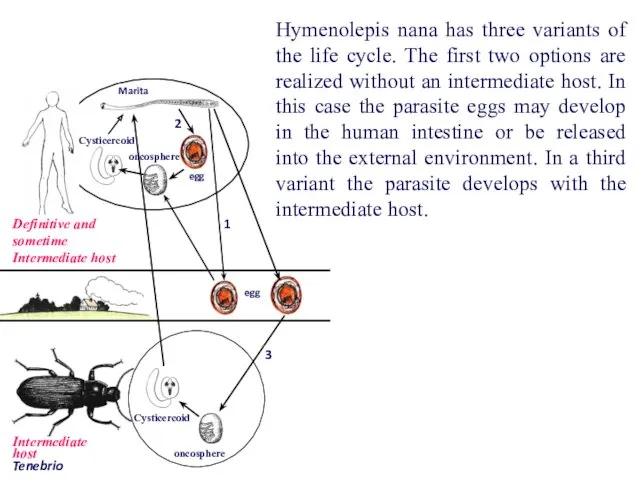
- 63. Dwarf tapeworm is found worldwide. It is most often seen in children in countries in which
- 64. The habitat of the worm is the upper two thirds of the ileum. Its life-time is
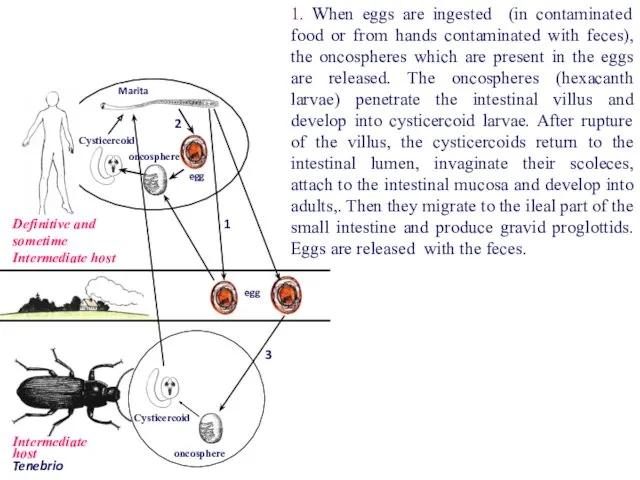
- 65. egg Род: Tenebrio egg oncosphere Marita oncosphere Cysticercoid Cysticercoid Definitive and sometime Intermediate host 2 1
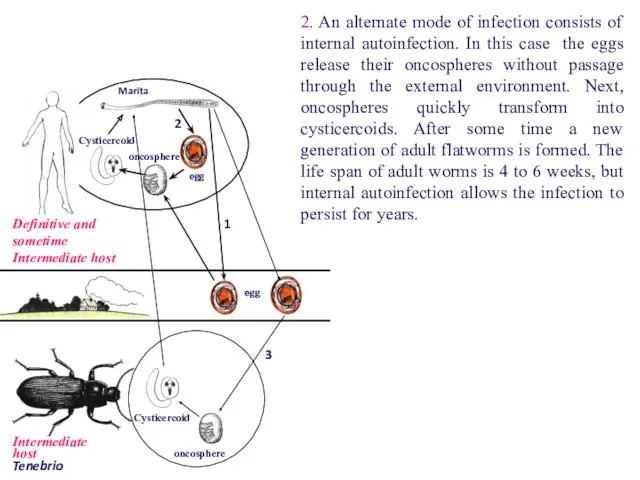
- 66. egg egg oncosphere Marita oncosphere Cysticercoid Cysticercoid Definitive and sometime Intermediate host Intermediate host Tenebrio 2
- 67. egg egg oncosphere Marita oncosphere Cysticercoid Cysticercoid Definitive and sometime Intermediate host 2 1 3 2.
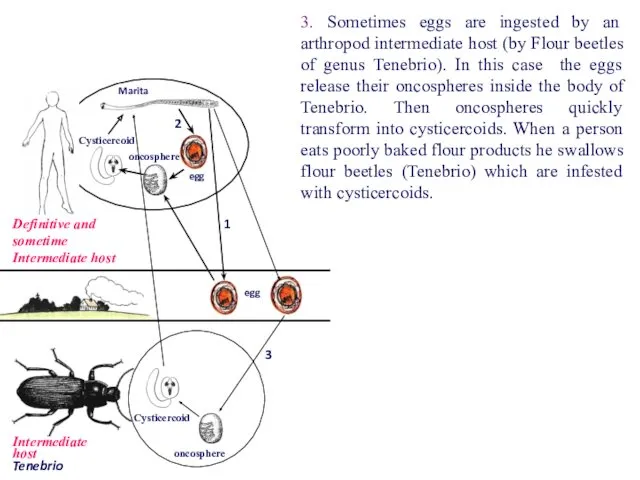
- 68. egg egg oncosphere Marita oncosphere Cysticercoid Cysticercoid Definitive and sometime Intermediate host 2 1 3 3.
- 69. Ordinarily in hymenolepiasis there is no material damage to the intestinal mucosa, but enteritis may be
- 71. Скачать презентацию






























 Қанның тасымалдаушы липопротеиндерінің құрамы, құрылысы және жіктелуі
Қанның тасымалдаушы липопротеиндерінің құрамы, құрылысы және жіктелуі Задачи принципы организации диетического питания
Задачи принципы организации диетического питания Ерте кезеңдегі ұлы дәрігерлер
Ерте кезеңдегі ұлы дәрігерлер Chronic gastritis
Chronic gastritis Болевой синдром и его лечение в ОВП
Болевой синдром и его лечение в ОВП Коматозды жағдайлардың патофизиологиясы
Коматозды жағдайлардың патофизиологиясы Медициналық сұхбаттасу техникасы
Медициналық сұхбаттасу техникасы Анемия. Эритроциттердің формасы мен көлемі
Анемия. Эритроциттердің формасы мен көлемі Хронические обструктивные заболевания легких. Бронхиты
Хронические обструктивные заболевания легких. Бронхиты Лекция 11. Ненаркотические анальгетики
Лекция 11. Ненаркотические анальгетики Основы психосоматики и психологии больного. Сестринское дело. Переподготовка
Основы психосоматики и психологии больного. Сестринское дело. Переподготовка Профилактика ВИЧ-инфекции. СПИД
Профилактика ВИЧ-инфекции. СПИД Ошибки и осложнения после протезирования на имплантатах. Гигиенические мероприятия при наличии в полости рта имплантатов
Ошибки и осложнения после протезирования на имплантатах. Гигиенические мероприятия при наличии в полости рта имплантатов Роль гормонов в обменных процессах, нервно-гуморальная регуляция, её нарушения
Роль гормонов в обменных процессах, нервно-гуморальная регуляция, её нарушения Внутривенные наркотики. Героиновая наркомания. Заменители героина
Внутривенные наркотики. Героиновая наркомания. Заменители героина Опыт хирургического лечения опухолей надпочечников у детей
Опыт хирургического лечения опухолей надпочечников у детей ЭКГ - диагностика при подозрении на инфаркт миокарда
ЭКГ - диагностика при подозрении на инфаркт миокарда Отравление алкоголем и его суррогатами
Отравление алкоголем и его суррогатами NIR
NIR Acquired Immunodeficiency syndrome
Acquired Immunodeficiency syndrome Особенности ведения преждевременных родов
Особенности ведения преждевременных родов Общая характеристика и эпидемиология новообразований ЛОР-органов
Общая характеристика и эпидемиология новообразований ЛОР-органов Цукровий діабет у дітей
Цукровий діабет у дітей Особенности капсульной эндоскопии
Особенности капсульной эндоскопии Дезинфекционные мероприятия при новой коронавирусной инфекции (2019-nCoV)
Дезинфекционные мероприятия при новой коронавирусной инфекции (2019-nCoV) Травмы. Травматический шок
Травмы. Травматический шок Методические указания по приготовлению дезинфицирующим растворов. Отбор проб дезинфектантов
Методические указания по приготовлению дезинфицирующим растворов. Отбор проб дезинфектантов Общий алгоритм подбора очковой коррекции
Общий алгоритм подбора очковой коррекции