Содержание
- 2. The skin has a surface area of 1.6-2 m2 This area enables the enhancement of systemic
- 3. What are the parameters that should be considered for cutaneous drug administration Age of patient Area
- 4. What are dermatologic vehicles? Powder Paste Shake lotion Ointment Hydrophilic ointment, cream or lotion Water
- 5. When do we use topical treatment? If a patient has a skin disorder covering
- 6. Choice of vehicles Three main determinants to choose the right vehicle are: Patient’s skin type Degree
- 7. Choice of vehicles Skin type: About 50% of individuals have oily skin or seborrhea. They do
- 8. Choice of vehicles for different lesions Lesion Recommended Avoided Acute erythema shake lotion, Ointment, lotion, cream
- 9. Topical agents Keratolytic agents Cytotatic agents: Podophyllin, 5-fluorouracil Retinoids Antibiotics, antifungals, antiviral agents Corticosteroids Combination products
- 10. Topical corticosteroids Class I (weakest): Hydrocortisone, prednisolone Class II: Methylprednisolone aceponate, triamcinolone Class III: Betamethasone 17-valerate
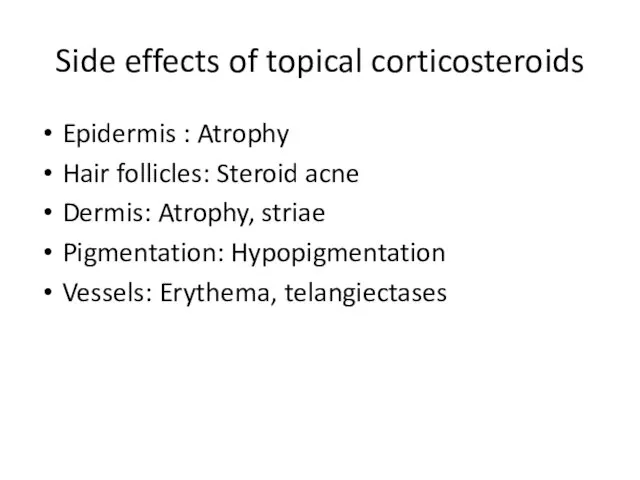
- 11. Side effects of topical corticosteroids Epidermis : Atrophy Hair follicles: Steroid acne Dermis: Atrophy, striae Pigmentation:
- 12. What would you prescribe for: An infant having flares of erythema and small papules on the
- 13. What would you prescribe for: A burn (with hot water) involving the wrist, with erythema and
- 19. Скачать презентацию














 Рак желудка
Рак желудка Технология гомеопатических таблеток. Викторина
Технология гомеопатических таблеток. Викторина Художественное творчество больных шизофренией и эпилепсией
Художественное творчество больных шизофренией и эпилепсией Эпителиальные злокачественные опухоли поджелудочной железы
Эпителиальные злокачественные опухоли поджелудочной железы Вибрационная болезнь
Вибрационная болезнь Государственная система управления здравоохранением. Современные формы управления в системе здравоохранения
Государственная система управления здравоохранением. Современные формы управления в системе здравоохранения Анатомія нервової системи
Анатомія нервової системи Health and safety legislation
Health and safety legislation Алынбайтын протездер
Алынбайтын протездер Заболевания периферической нервной системы
Заболевания периферической нервной системы Здоровое питание
Здоровое питание Сифилис
Сифилис Атипичное удаление зубов
Атипичное удаление зубов Кровотечение
Кровотечение Витамин Д зависимый рахит, витамин Д резистентный рахит
Витамин Д зависимый рахит, витамин Д резистентный рахит Концепция охраны репродуктивного здоровья и активного социального долголетия
Концепция охраны репродуктивного здоровья и активного социального долголетия ЭКГ при электролитных нарушениях в организме
ЭКГ при электролитных нарушениях в организме Ожирение среди подростков. Ожирение - хроническое заболевание
Ожирение среди подростков. Ожирение - хроническое заболевание Patologik anatomiya mavzu: distrofiya
Patologik anatomiya mavzu: distrofiya Ауески ауруы
Ауески ауруы Заболевания вен, нижних конечностей
Заболевания вен, нижних конечностей Преимущество естественного вскармливания перед искусственным
Преимущество естественного вскармливания перед искусственным Физика в моей будущей профессии
Физика в моей будущей профессии Анемия. Классификация анемий
Анемия. Классификация анемий Фармакогенетика негіздері. Дәрілік препараттағы ағзаның тұқым қуалау негізделген полимарфизм реакциясы
Фармакогенетика негіздері. Дәрілік препараттағы ағзаның тұқым қуалау негізделген полимарфизм реакциясы Эритроциттегі глюкоза-6-фосфатдегидрогеназа ферменті тапшылығына байланысты туындайтын гемолиздік анемия
Эритроциттегі глюкоза-6-фосфатдегидрогеназа ферменті тапшылығына байланысты туындайтын гемолиздік анемия Острая почечная недостaточность
Острая почечная недостaточность Коленный сустав. Биомеханика, физиология
Коленный сустав. Биомеханика, физиология