Содержание
- 2. 1- RBC’s count by haemocytometer Aim: The number of RBC’s is counted by haemocytometer in a
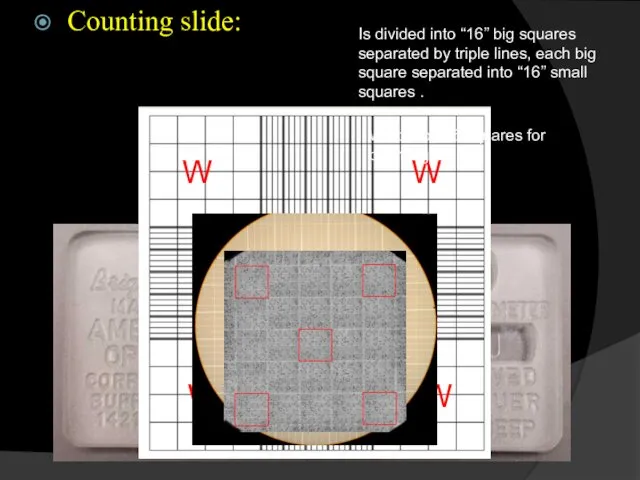
- 3. Counting slide: Is divided into “16” big squares separated by triple lines, each big square separated
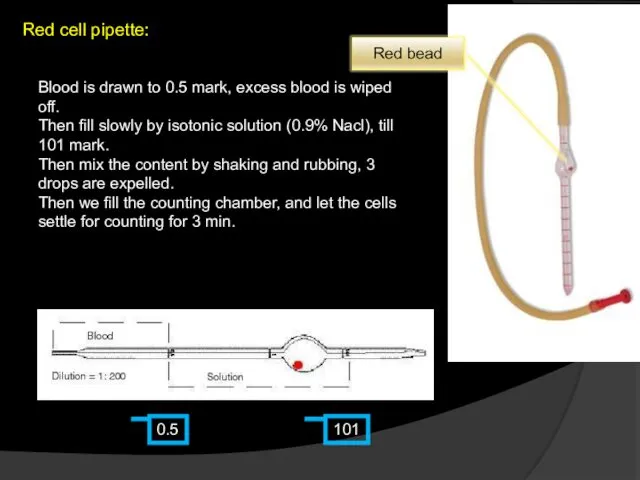
- 4. Red cell pipette: 0.5 101 Blood is drawn to 0.5 mark, excess blood is wiped off.
- 5. Shake well to mix with the hose end sealed with your finger.
- 6. Unmixed cell free fluid in the capillary portion of the pipette Empty 2-3 drops off pipette
- 8. Carefully adjust the haemocytometer on the microscope and cover
- 9. Add a small amount of the diluted RBCs to just fill the first chamber of the
- 10. It should flow in to fill the chamber by capillary action. Do not over fill. Notice
- 11. To improve your skill, repeat the dilution a second time and fill the second chamber. The
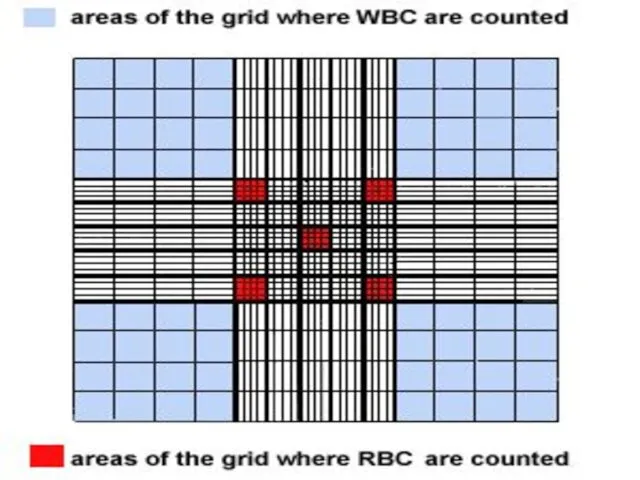
- 14. Counting chamber It is the space formed between the cover placed on the counting slide and
- 15. Calculations
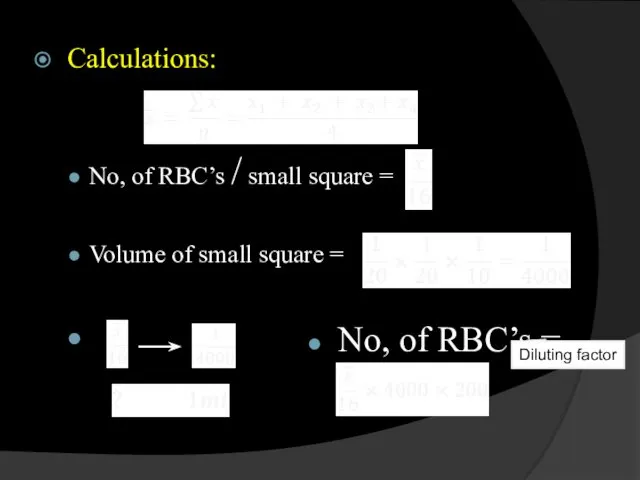
- 16. Calculations: No, of RBC’s / small square = Volume of small square = No, of RBC’s
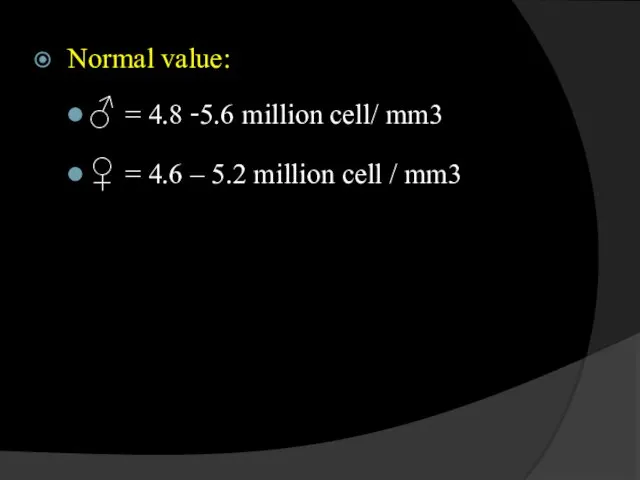
- 17. Normal value: ♂ = 4.8 -5.6 million cell/ mm3 ♀ = 4.6 – 5.2 million cell
- 18. 2- colorimetric determination of “Hb” by haemometer Aim: Determination of amount of “Hb” by change in
- 19. Principle: The haemolysis of RBC’s by using the acid “HCl” to get a free “Hb” in
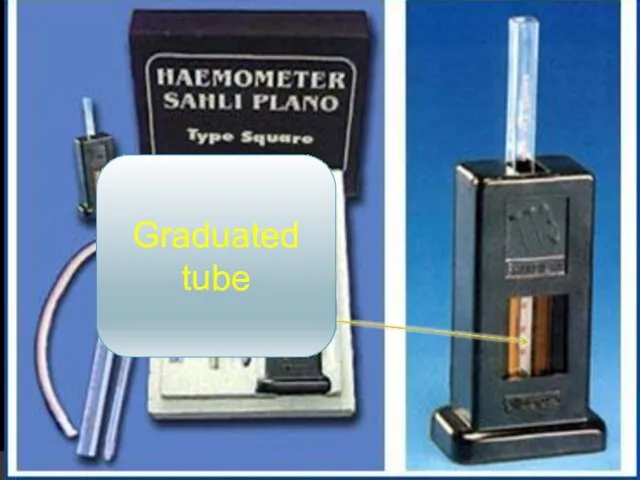
- 20. Haemometer: Consists of: “2” standard colored tubes Graduated tube Capillary tube
- 21. Standard coloured tubes
- 22. Graduated tube
- 23. Capillary tube
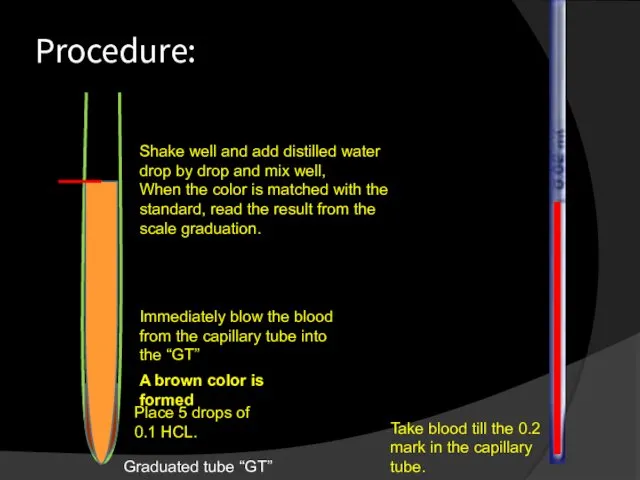
- 24. Procedure: Graduated tube “GT” Place 5 drops of 0.1 HCL. Take blood till the 0.2 mark
- 25. Normal value: ♂ = 93 – 118 % ♀ = 83 – 107 % 1 gm
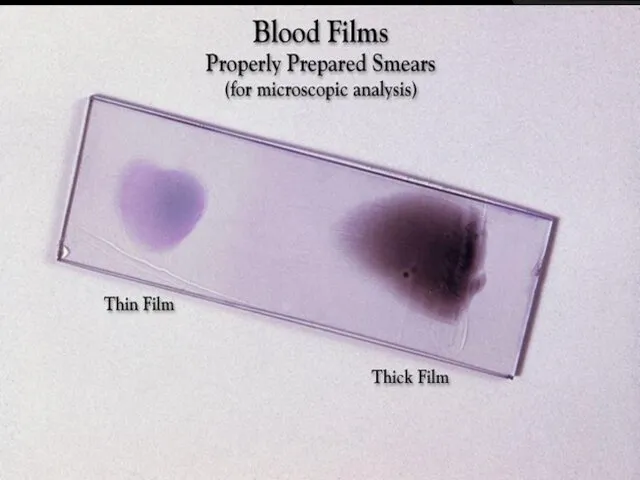
- 26. 3- Blood film Principle: A small drop of blood is placed near the end of a
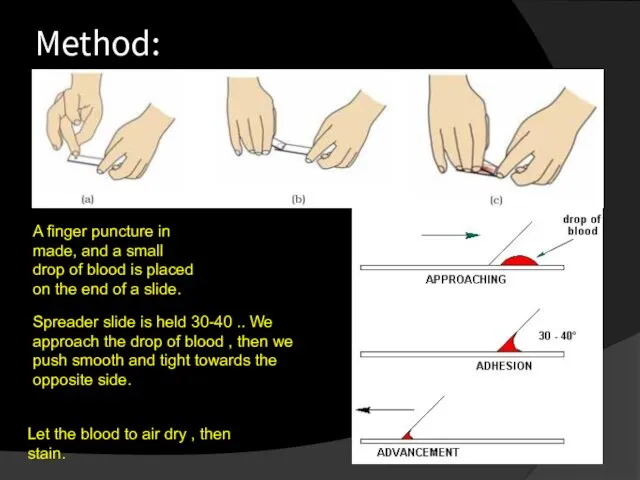
- 27. Method: A finger puncture in made, and a small drop of blood is placed on the
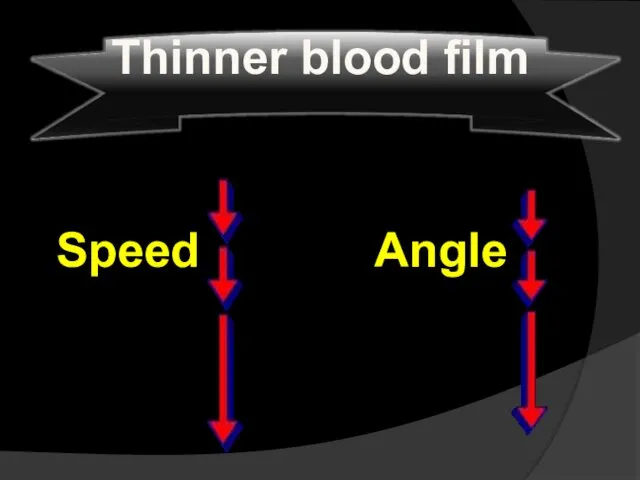
- 28. The thickness of the film can be varied by:- the spread with which the slide is
- 29. Speed Angle Thinner blood film
- 31. Stains used: Leishman Stain : and it consists of Methylene blue : It stains nuclear DNA
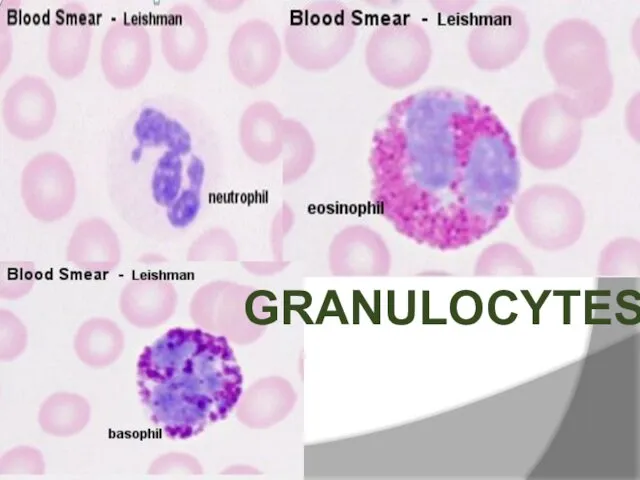
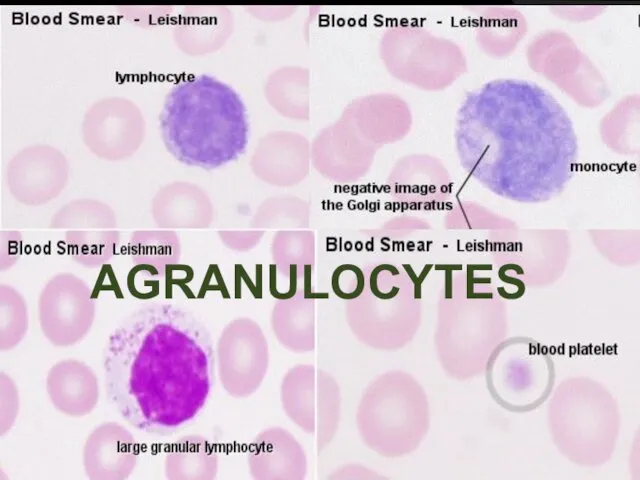
- 32. Examination of the Blood film: Evaluation of RBC’s Evaluation of platelets Differentail leucocytic count
- 33. GRANULOCYTES
- 34. AGRANULOCYTES
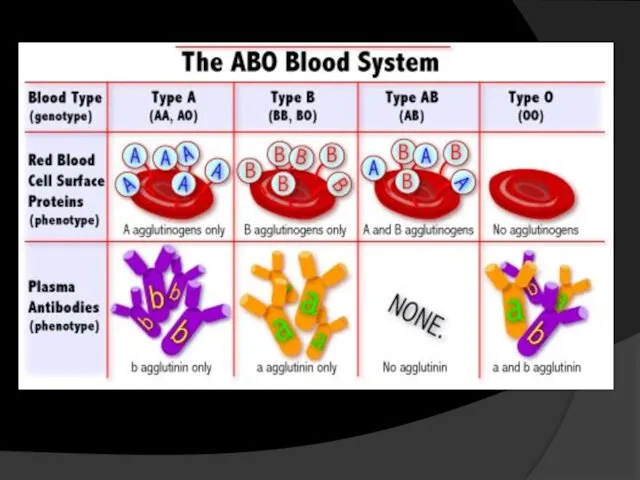
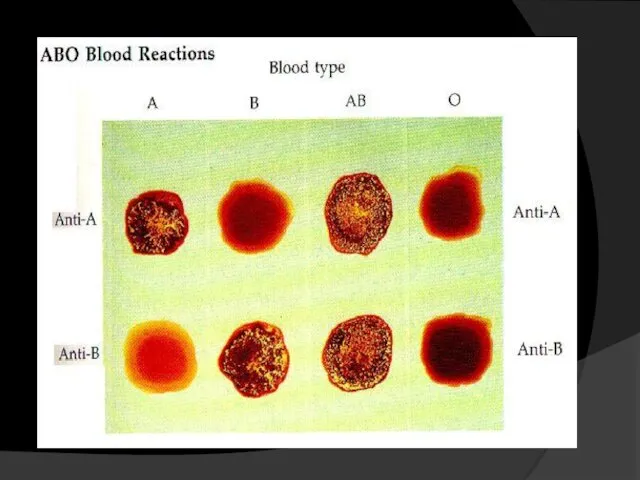
- 35. 4- Determination of blood groups Principle : The blood consists of plasma and cells (RBC’s- WBC’s-
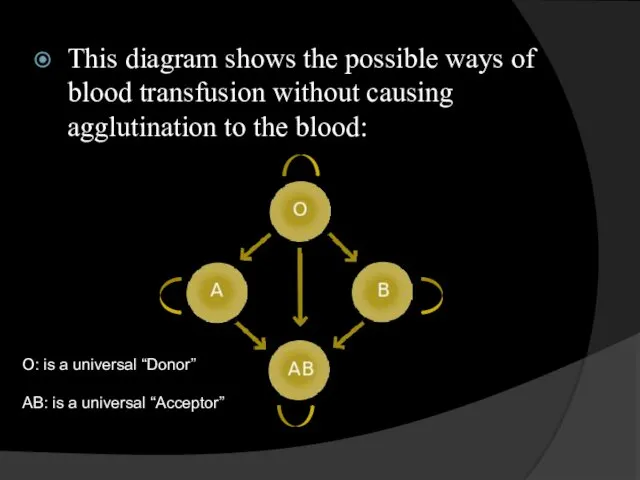
- 37. This diagram shows the possible ways of blood transfusion without causing agglutination to the blood: O:
- 38. Preparation of the slide: Add a drop of antibody A “blue” Add a drop of antibody
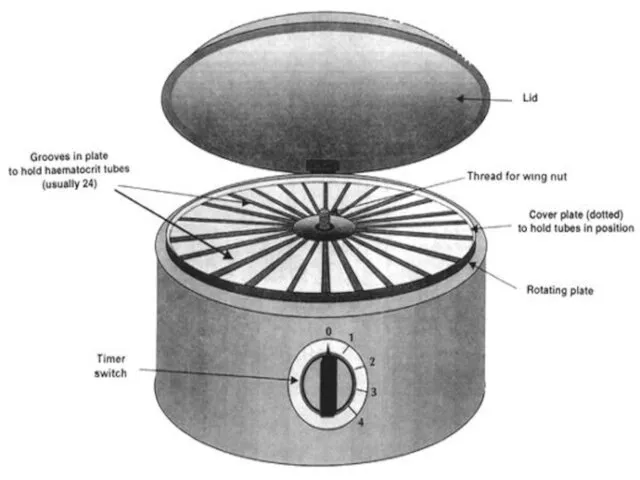
- 40. Haematocrite value
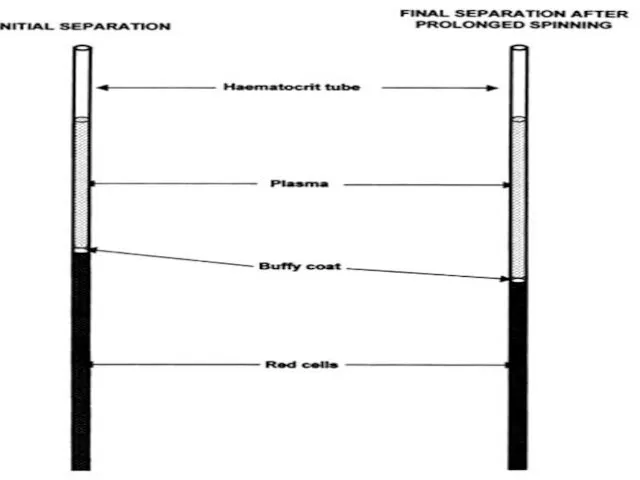
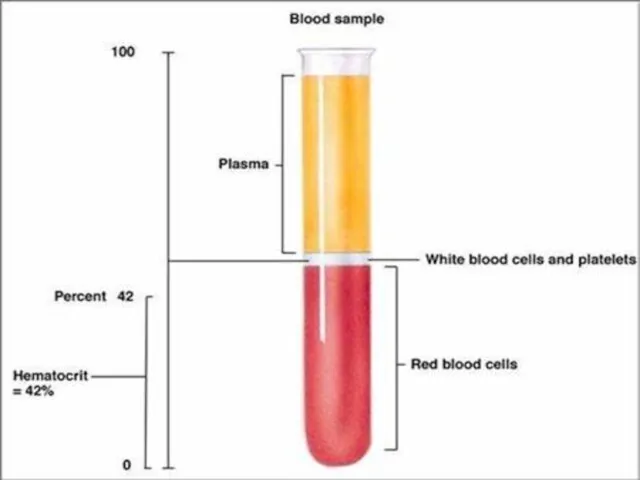
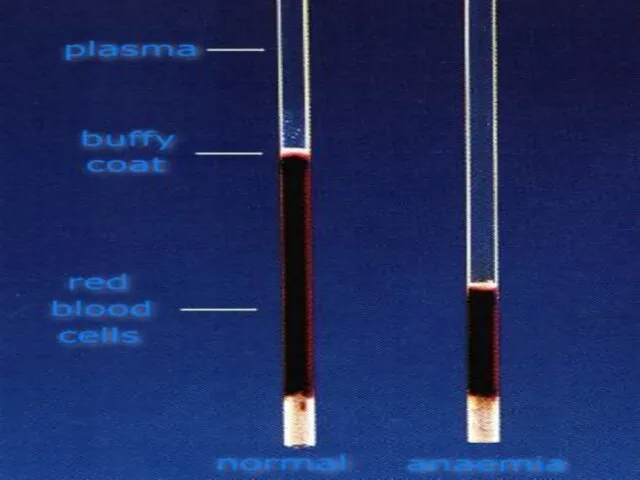
- 41. Define:- hematocrit (Ht ), also known as packed cell volume (PCV) or erythrocyte volume fraction (EVF),
- 42. How to calculate Ht/PCV? The packed cell volume (PCV) can be determined by centrifugingThe packed cell
- 49. Rate of sedimentation (ESR=Erythrocyte sedimentation rate)
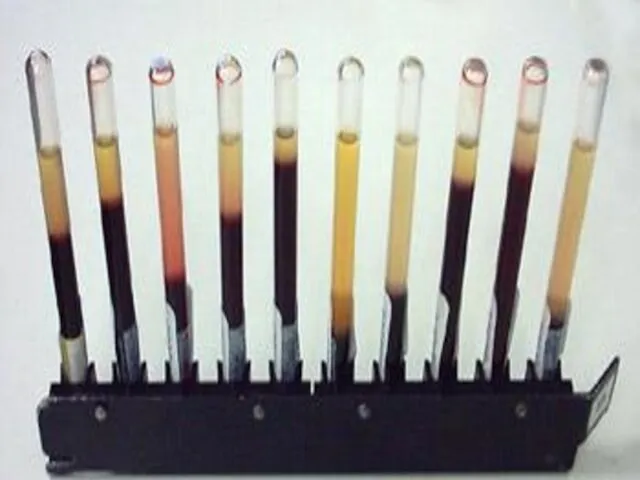
- 50. Define:- Rate of sedimentation is the rate at which red blood cells sediment in a period
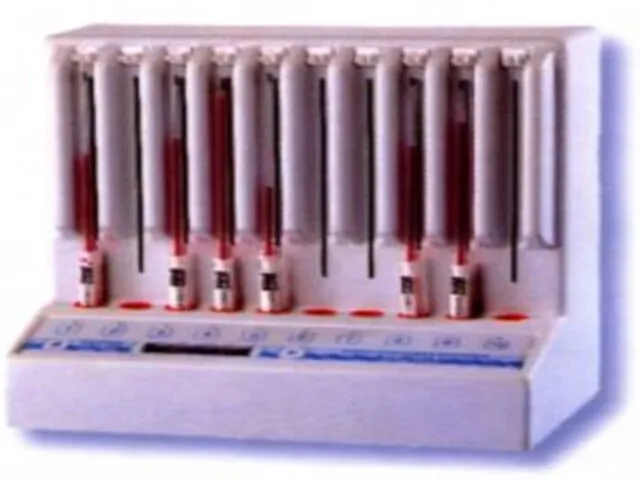
- 51. How To perform the test? Anticoagulated blood is placed in an upright tube, known as a
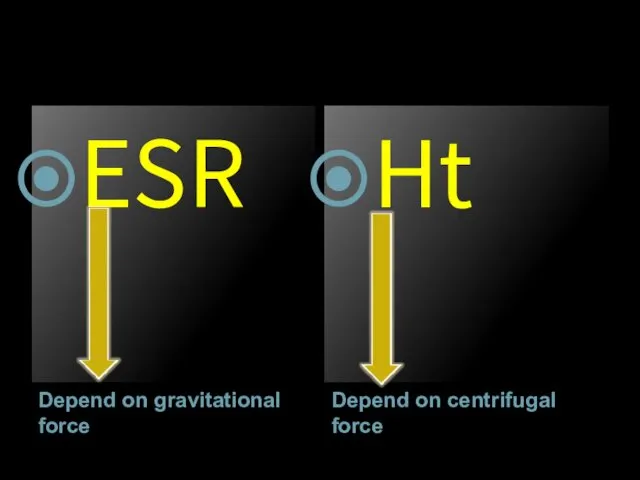
- 54. Depend on gravitational force Depend on centrifugal force ESR Ht
- 56. Скачать презентацию





























 Кардиогенный шок. Дефиниции: термины и понятия
Кардиогенный шок. Дефиниции: термины и понятия Жанұя денсаулығы. Бала денсаулығы
Жанұя денсаулығы. Бала денсаулығы Подходы к организации логопедической работы с детьми при нарушении зрения
Подходы к организации логопедической работы с детьми при нарушении зрения Пищевая аллергия
Пищевая аллергия Балалардағы ішек дисбактериозы
Балалардағы ішек дисбактериозы Профилактика внутрибольничной инфекции
Профилактика внутрибольничной инфекции Бюгельные протезы
Бюгельные протезы Нурофен для детей
Нурофен для детей Жидкие лекарственные формы
Жидкие лекарственные формы Стероид резистентті нефротикалық синдром
Стероид резистентті нефротикалық синдром Становление естественнонаучных знаний в эпоху Возрождения
Становление естественнонаучных знаний в эпоху Возрождения Перикардит. Перикардиттің даму себептері мен жіктелісі
Перикардит. Перикардиттің даму себептері мен жіктелісі Аборт – экстренная контрацепция или убийство?
Аборт – экстренная контрацепция или убийство? СУ при кровотечениях
СУ при кровотечениях Ақшаның мәні және атқаратын қызметтері
Ақшаның мәні және атқаратын қызметтері Адам ағзасындағы фотохимиялық түрленулер
Адам ағзасындағы фотохимиялық түрленулер Хронические гепатиты у детей
Хронические гепатиты у детей
 Қан құюдан кейінгі асқынулар. Уақытында диагностикалау. Емдеу тактикасы
Қан құюдан кейінгі асқынулар. Уақытында диагностикалау. Емдеу тактикасы Рак шейки матки (клиника, диагностика, лечение)
Рак шейки матки (клиника, диагностика, лечение) Инфекциялық үрдістің патофизиологиясы
Инфекциялық үрдістің патофизиологиясы Психология пациента
Психология пациента Вирус ГРИППа
Вирус ГРИППа Pacienta komforta nodrošinājums un pacienta drošība
Pacienta komforta nodrošinājums un pacienta drošība История, предмет и задачи гигиены и экологии человека
История, предмет и задачи гигиены и экологии человека Чистые руки
Чистые руки Вторичный период сифилиса. Скрытый сифилис. Серологическая диагностика сифилиса
Вторичный период сифилиса. Скрытый сифилис. Серологическая диагностика сифилиса Хроническая сердечная недостаточность
Хроническая сердечная недостаточность