Содержание
- 3. Classification Family Genus Species Micrococcaceae Micrococcus and Staphylococcus S. aureus S. saprophyticus S. epidermidis M. luteus
- 4. Gram-Positive Cocci Enterococcus (Group D CHO) γ hemolytic (α or β) Enterococcus faecalis, E. faecium FAMILY
- 5. Morphology
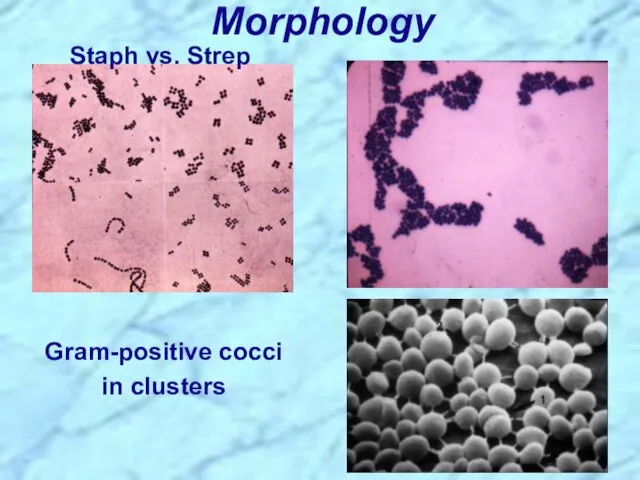
- 6. Morphology Staph vs. Strep Gram-positive cocci in clusters
- 7. Streptococcus Staphylococcus
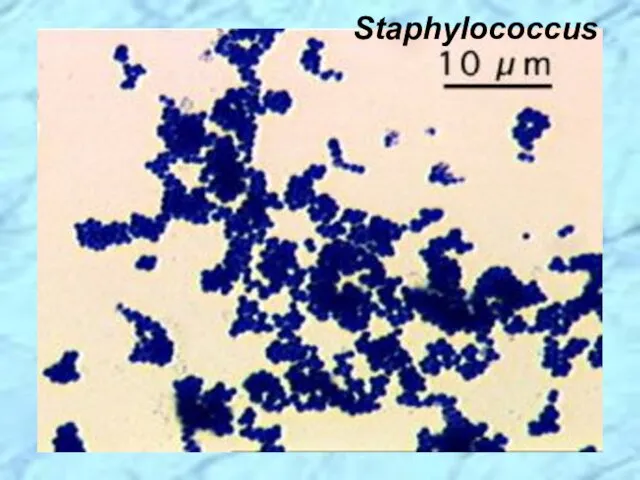
- 8. Staphylococcus
- 12. See Overheads ~~~~~~~~~~ TSS Foodborne Intoxication ~~~~~~~~~~
- 15. Cell-Associated Virulence Factors Capsule or slime layer (glycocalyx) Peptidoglycan (PG) Teichoic acid is covalently linked to
- 16. Virulence Factors Extracellular Enzymes Coagulases (bound or free) Antigenic Hyaluronidase “spreading factor” of S. aureus Nuclease
- 17. Virulence Factors: Exotoxins Cytolytic (cytotoxins; cytolysins) Alpha toxin - hemolysin Reacts with RBCs Beta toxin Sphingomyelinase
- 18. Enterotoxin Exfoliative toxin (epidermolytic toxin) Pyrogenic exotoxins Virulence Factors: Exotoxins
- 19. Pathogenesis Pass skin – first line of defense Benign infection Phagocytosis Antibody Inflammatory response Chronic infections
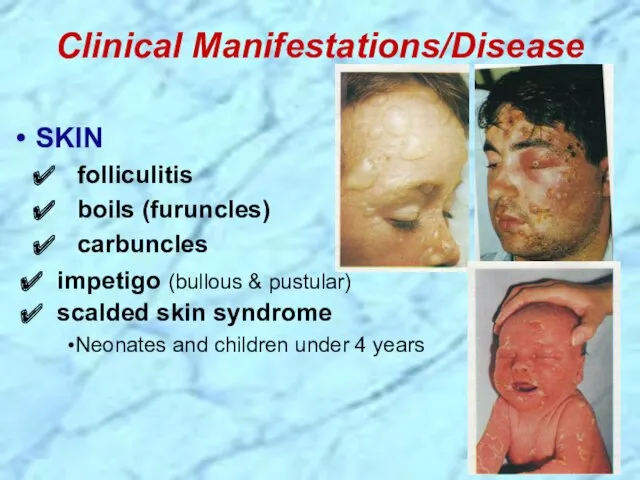
- 20. Clinical Manifestations/Disease SKIN folliculitis boils (furuncles) carbuncles impetigo (bullous & pustular) scalded skin syndrome Neonates and
- 21. Clinical Manifestations/Disease Other infections Primary staphylococcal pneumonia Food poisoning vs. foodborne disease Toxic shock syndrome
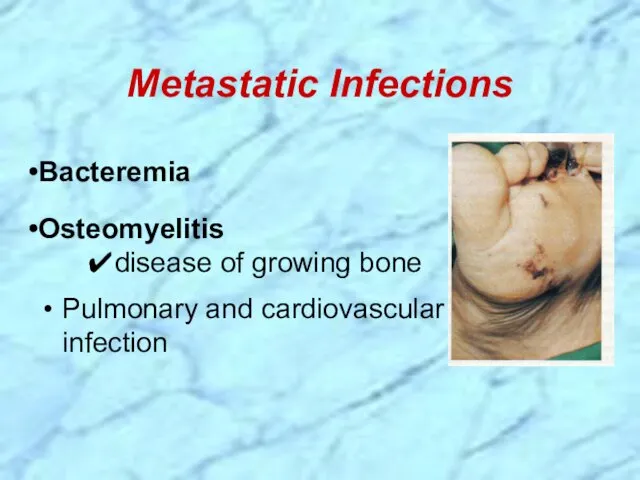
- 22. Metastatic Infections Bacteremia Osteomyelitis ✔disease of growing bone Pulmonary and cardiovascular infection
- 24. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Staphylococcus epidermidis S. saprophyticus
- 27. Staphylococcal Lab ID & Diagnostic Tests Microscopic Lab isolation Coagulase positive S. aureus
- 28. Mannitol Salts Agar (MSA) Staphylococcus aureus
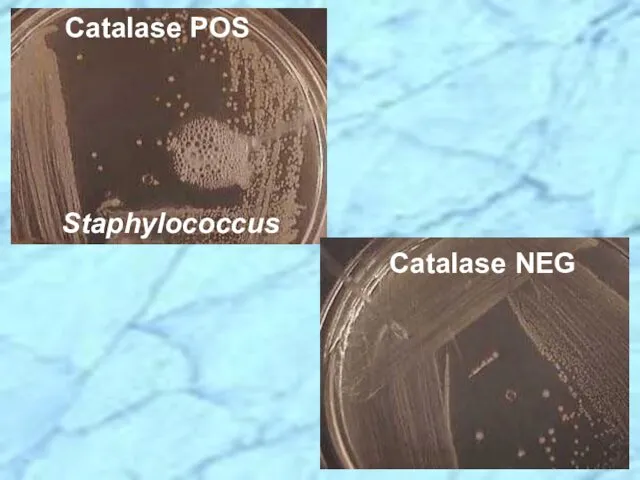
- 29. Catalase 2H2O2 ? O2 + 2H2O Streptococci vs. Staphylococci Differential Characteristics
- 31. Coagulase Fibrinogen ? Fibrin Differential Characteristics
- 33. Treatment Drain infected area Deep/metastatic infections semi-synthetic penicllins cephalosporins erythromycin clindamycin Endocarditis semi-synthetic penicillin + an
- 34. Prevention Carrier status prevents complete control Proper hygiene, segregation of carrier from highly susceptible individuals Good
- 36. REVIEW
- 37. Gram-Positive Cocci Enterococcus (Group D CHO) γ hemolytic (α or β) Enterococcus faecalis, E. faecium FAMILY
- 38. REVIEW Which features are only found in S. aureus? S. epidermidis S. aureus
- 39. REVIEW
- 40. REVIEW
- 41. REVIEW
- 42. REVIEW
- 43. REVIEW
- 45. Скачать презентацию





































 Вирусные гепатиты
Вирусные гепатиты Методика обследования хирургических больных. Операция, предоперационный и послеоперационный период
Методика обследования хирургических больных. Операция, предоперационный и послеоперационный период Депрессия. Классические критерии депрессии
Депрессия. Классические критерии депрессии Клиника алды, арнайы фармакологиялық белсенділік, токсикология, канцерогендік, мутагендік, аллергендік
Клиника алды, арнайы фармакологиялық белсенділік, токсикология, канцерогендік, мутагендік, аллергендік Мышцы областей тела. Мышцы спины поверхностный слой
Мышцы областей тела. Мышцы спины поверхностный слой Топографическая анатомия и оперативные вмешательства на органах и сосудах шеи
Топографическая анатомия и оперативные вмешательства на органах и сосудах шеи Ошибки и осложнения после протезирования на имплантатах. Гигиенические мероприятия при наличии в полости рта имплантатов
Ошибки и осложнения после протезирования на имплантатах. Гигиенические мероприятия при наличии в полости рта имплантатов Пиелонефрит. Инфекции мочевых путей
Пиелонефрит. Инфекции мочевых путей Современные подходы к осуществлению комплексного сестринского ухода за пациентами с хроническим холециститом
Современные подходы к осуществлению комплексного сестринского ухода за пациентами с хроническим холециститом Нормы питания
Нормы питания Влияние кофеина на жизнь человека
Влияние кофеина на жизнь человека Физиологическая оптика. Оптическая система глаза
Физиологическая оптика. Оптическая система глаза Ціноутворення та регулювання цін у сфері охорони здоров’я. Оплата постачальників медичних послуг
Ціноутворення та регулювання цін у сфері охорони здоров’я. Оплата постачальників медичних послуг Фотодинамическая терапия ЗНО
Фотодинамическая терапия ЗНО Аллопластика височно-нижнечелюстного сустава
Аллопластика височно-нижнечелюстного сустава Хейлиты и предраковые заболевания слизистой оболочки
Хейлиты и предраковые заболевания слизистой оболочки Безопасность пищевых продуктов
Безопасность пищевых продуктов Виды ран и правила оказания первой медицинской помощи
Виды ран и правила оказания первой медицинской помощи Вопросы общей и клинической онкологии
Вопросы общей и клинической онкологии Болезнь Альцгеймера
Болезнь Альцгеймера Жұқпалы аурулар iндетi пайда болу қаупi төнген жағдайда шектеу шараларын қарастыру
Жұқпалы аурулар iндетi пайда болу қаупi төнген жағдайда шектеу шараларын қарастыру Жұқпалы үрдіс, анықтамасы, жұқпалы үрдіс түрлері
Жұқпалы үрдіс, анықтамасы, жұқпалы үрдіс түрлері Технология формирования тестовых заданий по дисциплине Акушерство и гинекология
Технология формирования тестовых заданий по дисциплине Акушерство и гинекология Чреспищеводная электро кардио стимуляция
Чреспищеводная электро кардио стимуляция Тромбоз. Эмболия. Лекция 6
Тромбоз. Эмболия. Лекция 6 Денсаулық сақтау объектілерін пайдалануға қойылатын санитариялық-эпидемиологиялық талаптар
Денсаулық сақтау объектілерін пайдалануға қойылатын санитариялық-эпидемиологиялық талаптар Жүрек артериялар және веналар қабырғасы құрлысының жасқа байланысты ерекшеліктері
Жүрек артериялар және веналар қабырғасы құрлысының жасқа байланысты ерекшеліктері Құтыру
Құтыру