Содержание
- 2. The Nature of Disease – Kasallik tabiati Pathogenic Organisms – patogen organizmlar Genetic Disorders – genetik
- 3. Types of Pathogenic Organisms – patogen organizmlar tiplari Viruses - viruslar Bacteria – bakteriyalar Fungi –
- 4. Mechanisms of Disease by Pathogens – patogen kasalliklar mexanizmlari Utilization of host nutritional resources Physical damage
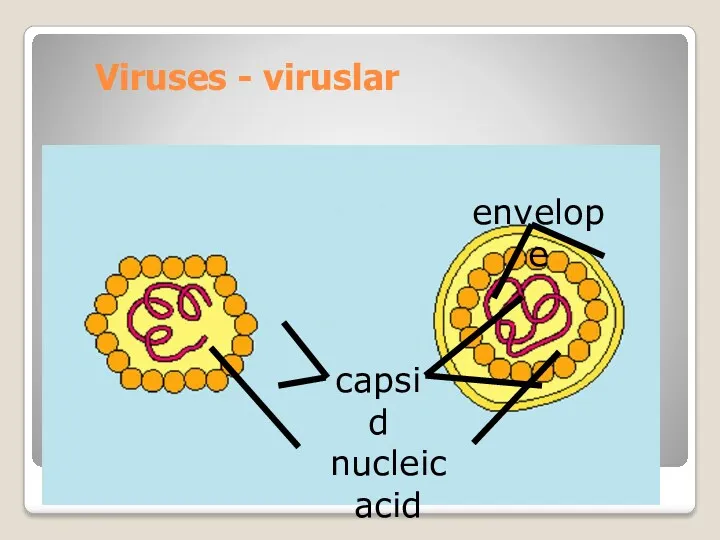
- 5. Viruses - viruslar
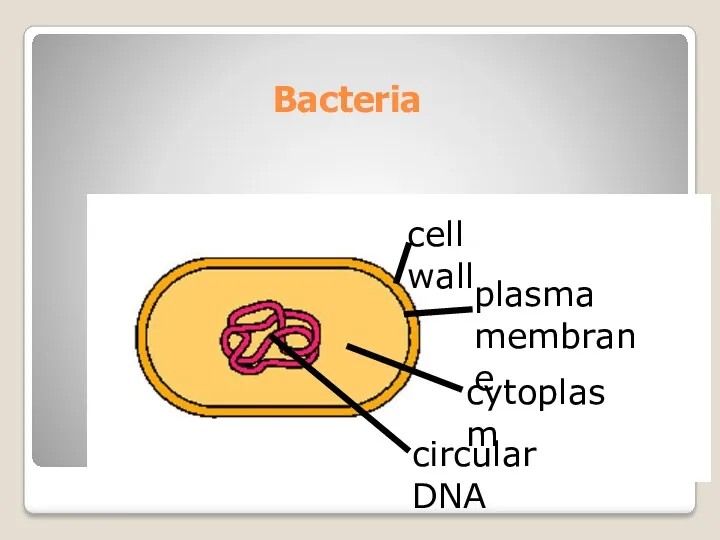
- 6. Bacteria
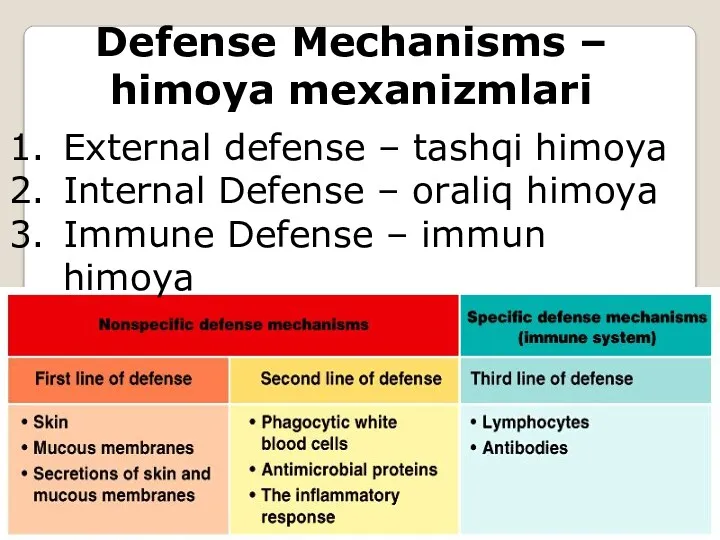
- 7. Defense Mechanisms – himoya mexanizmlari External defense – tashqi himoya Internal Defense – oraliq himoya Immune
- 8. Skin acts as barrier to microbes and viruses - sweat has a low pH - Teri
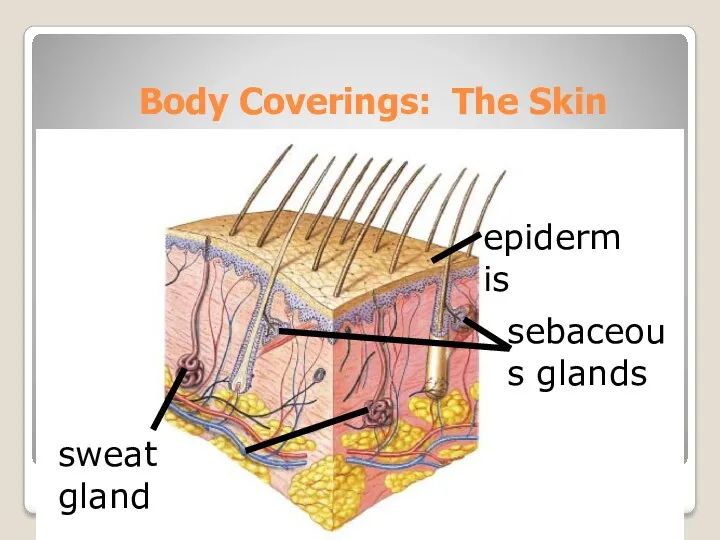
- 9. Body Coverings: The Skin
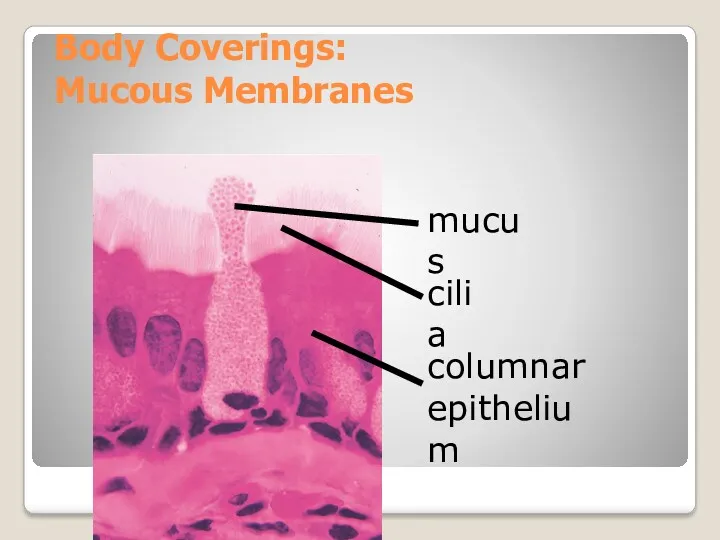
- 10. Body Coverings: Mucous Membranes
- 11. Phagocytic cells (WBCs) N L M E B Natural Killer (NK) Cells: attack virus infected cells
- 12. Nonspecific Phagocytosis Neutrophils Monocytes Eosinophils
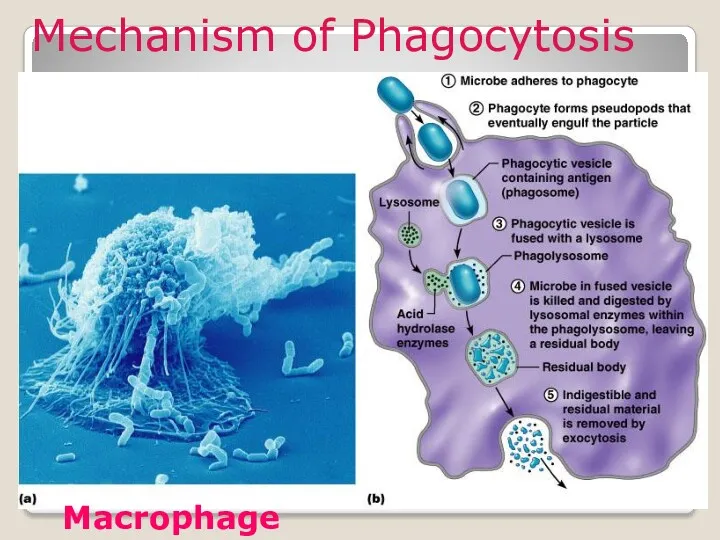
- 13. Mechanism of Phagocytosis Mechanism of Phagocytosis Macrophage
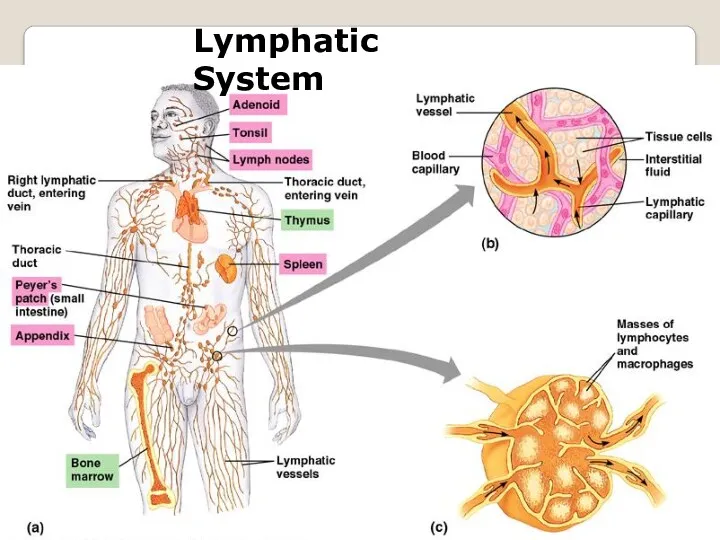
- 14. Lymphatic System
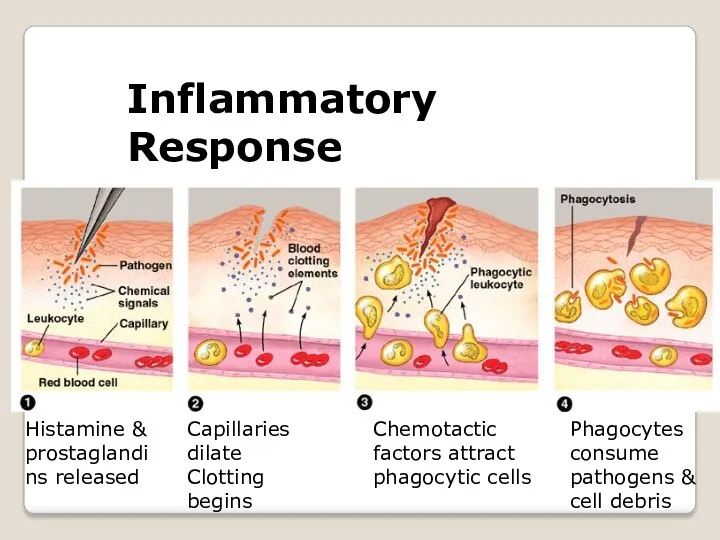
- 15. Inflammatory Response Histamine & prostaglandins released Capillaries dilate Clotting begins Chemotactic factors attract phagocytic cells Phagocytes
- 16. Characteristics of Immunity Recognition of self versus non-self – o’ziga tegishli bo’lmagan antigenni tanish Response is
- 17. Types of Immunity Active Immunity Naturally-Acquired Active Immunity – tabiiy aktiv Artificially-Acquired Active Immunity – sun’iy
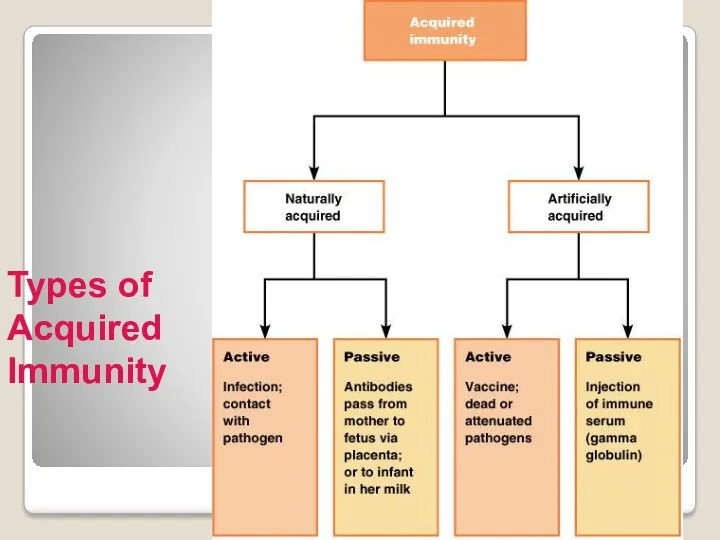
- 18. Types of Acquired Immunity
- 20. Скачать презентацию








 Медицина в период средних веков
Медицина в период средних веков Экстраинтестинальные проявления воспалительных заболеваний кишечника
Экстраинтестинальные проявления воспалительных заболеваний кишечника Радиационная безопасность персонала при работе источниками ионизирующих излучений
Радиационная безопасность персонала при работе источниками ионизирующих излучений Иммуногенетика. Открытие МНС
Иммуногенетика. Открытие МНС Причины и тактика ведения пациенток с трубно-перитонеальным бесплодием
Причины и тактика ведения пациенток с трубно-перитонеальным бесплодием Гестационный сахарный диабет
Гестационный сахарный диабет Первичный патронаж новорожденного
Первичный патронаж новорожденного Мутационная теория онкогенеза
Мутационная теория онкогенеза Антисептические и анальгетические лекарства
Антисептические и анальгетические лекарства Дитячі інфекційні хвороби
Дитячі інфекційні хвороби Клинические методы обследования детей в ортодонтии
Клинические методы обследования детей в ортодонтии Обезвреживание аммиака. Остаточный азот крови. Биохимия полости рта. Лекция 7
Обезвреживание аммиака. Остаточный азот крови. Биохимия полости рта. Лекция 7 Патология опухолевого роста
Патология опухолевого роста Вопросы пола в проблеме биполярного расстройства
Вопросы пола в проблеме биполярного расстройства Жүйке - бұлшық еттік синапс және бұлшық ет аурулары. Орталық жүйке жүйесінің миелинсізденген аурулары
Жүйке - бұлшық еттік синапс және бұлшық ет аурулары. Орталық жүйке жүйесінің миелинсізденген аурулары Пролежни. Организация ухода
Пролежни. Организация ухода Полный съёмный зубной протез
Полный съёмный зубной протез Первичные бактериальные менингиты
Первичные бактериальные менингиты Әскери медицина туралы түсінік. Медицина қызметін ұйымдастыру және тактикасы, ғылыми тұрғыда және пән ретінде оқып үйрену
Әскери медицина туралы түсінік. Медицина қызметін ұйымдастыру және тактикасы, ғылыми тұрғыда және пән ретінде оқып үйрену Лечение кислотозависимых заболеваний в условиях резистентности Helicobacter pylori
Лечение кислотозависимых заболеваний в условиях резистентности Helicobacter pylori Эпителиальные злокачественные опухоли поджелудочной железы
Эпителиальные злокачественные опухоли поджелудочной железы Жировые дистрофии (липидозы)
Жировые дистрофии (липидозы) Клинические рекомендации пациенту с заболеванием мочеполовой системы. Тактика ведения пациента на уровне ПМСП
Клинические рекомендации пациенту с заболеванием мочеполовой системы. Тактика ведения пациента на уровне ПМСП Организация работы по профилактике ВИЧ/СПИДа в молодежной среде
Организация работы по профилактике ВИЧ/СПИДа в молодежной среде Организация медицинского освидетельствования граждан при постановке их на воинский учёт
Организация медицинского освидетельствования граждан при постановке их на воинский учёт Анатомия мозжечка и корковых узлов мозга
Анатомия мозжечка и корковых узлов мозга Болезнь Гентингтона
Болезнь Гентингтона Роль анаэробной инфекции в развитии гнойно-воспалительных заболеваний челюстно-лицевой области
Роль анаэробной инфекции в развитии гнойно-воспалительных заболеваний челюстно-лицевой области