Содержание
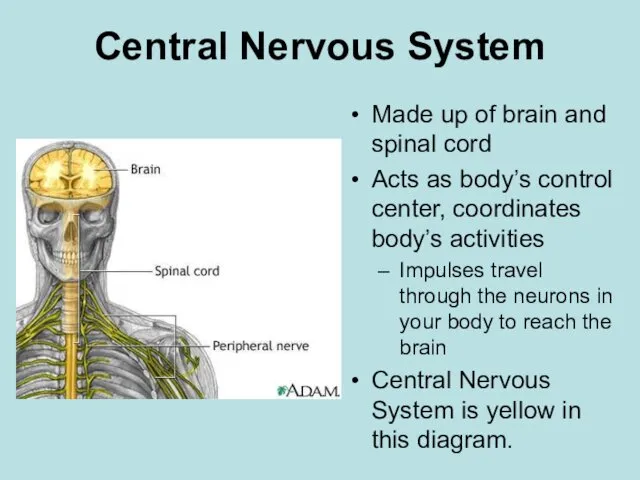
- 2. Central Nervous System Made up of brain and spinal cord Acts as body’s control center, coordinates
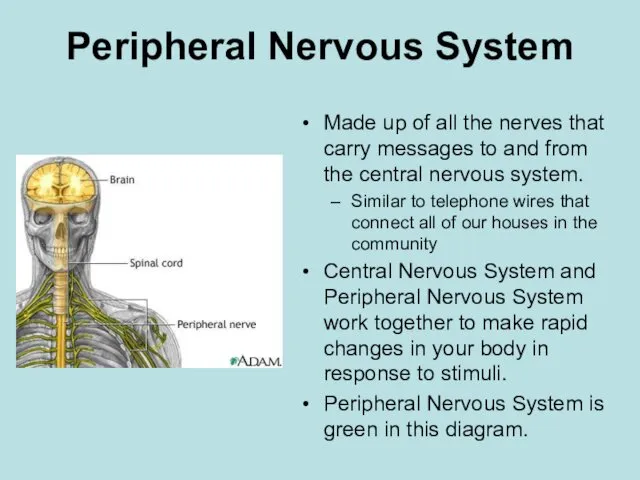
- 3. Peripheral Nervous System Made up of all the nerves that carry messages to and from the
- 4. Peripheral Nervous System: 2 parts Somatic Nervous System Relay information between skin, skeletal muscles and central
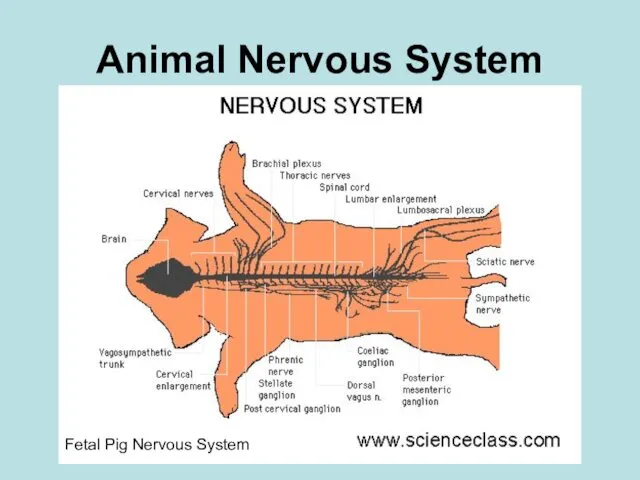
- 5. Animal Nervous System Fetal Pig Nervous System
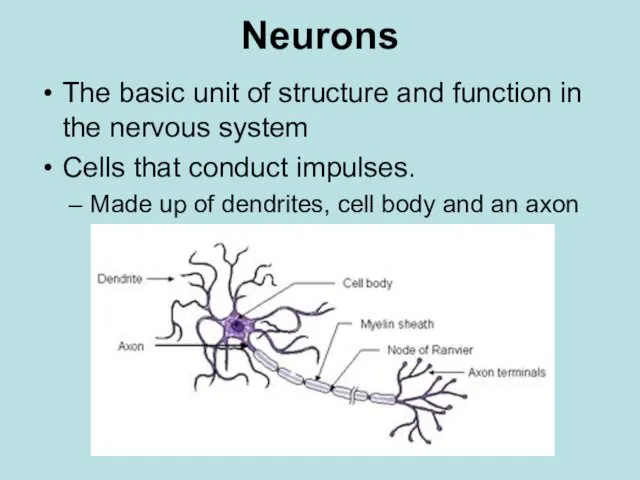
- 6. Neurons The basic unit of structure and function in the nervous system Cells that conduct impulses.
- 7. Neurons Dendrites: branch-like extensions that receive impulses and carry them toward cell body. Axon: single extension
- 8. In other words, there’s a lot of traffic going on in the neurons of your Central
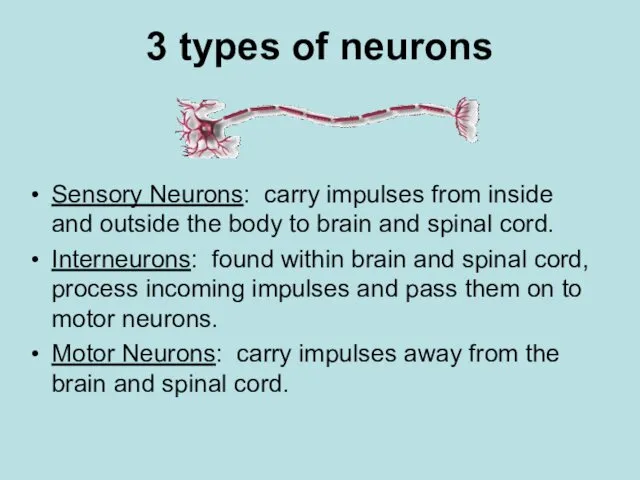
- 9. 3 types of neurons Sensory Neurons: carry impulses from inside and outside the body to brain
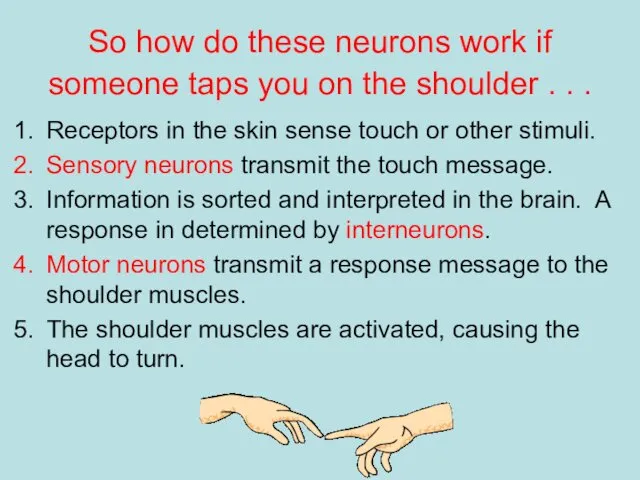
- 10. So how do these neurons work if someone taps you on the shoulder . . .
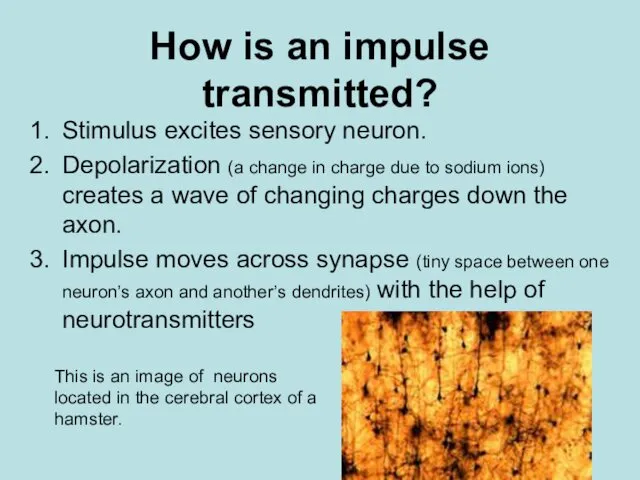
- 11. How is an impulse transmitted? Stimulus excites sensory neuron. Depolarization (a change in charge due to
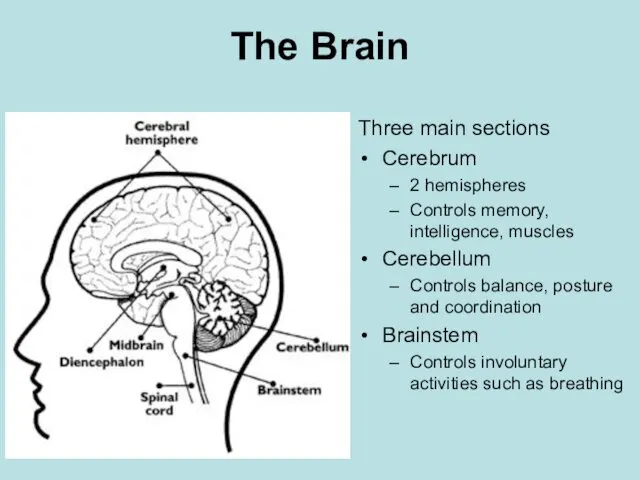
- 12. The Brain Three main sections Cerebrum 2 hemispheres Controls memory, intelligence, muscles Cerebellum Controls balance, posture
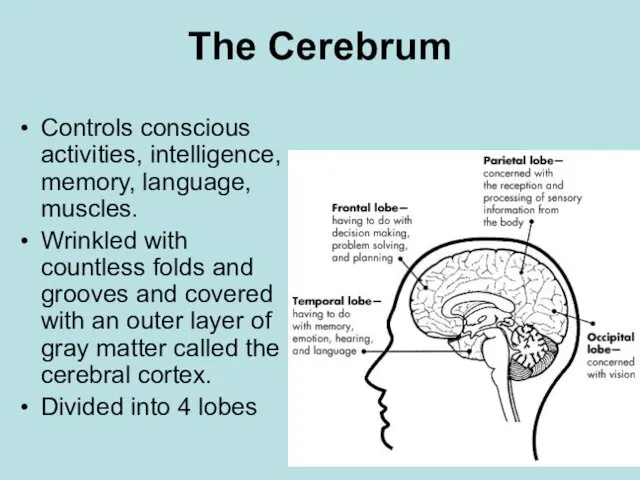
- 13. The Cerebrum Controls conscious activities, intelligence, memory, language, muscles. Wrinkled with countless folds and grooves and
- 14. The Cerebellum Muscle coordination is developed here as well as the memory of physical skills. If
- 15. The Brainstem Made up of the medulla oblongata, pons and midbrain. Medulla oblongata controls involuntary activities
- 16. Show what you know! 1. The Central Nervous System consists of what two parts? 2. What
- 17. Show what you know! 3. The Peripheral Nervous System consists of what? 4. What is the
- 18. Show what you know! 5. Draw a neuron and label the axon, dendrite and cell body.
- 19. Show what you know! 7. What are the three types of neurons? 8. What is the
- 20. Show what you know! 9. What does the cerebrum enable us to do? 10. Compare and
- 22. Скачать презентацию









 ЖИТС және жүктілік
ЖИТС және жүктілік Амбулаторлы жағдайда жаңа туылған нәрестелерге емдік-профилактикалық шараларды ұйымдастыру
Амбулаторлы жағдайда жаңа туылған нәрестелерге емдік-профилактикалық шараларды ұйымдастыру Геморрагический синдром. Острый лейкоз
Геморрагический синдром. Острый лейкоз Энтеробактерии. Классификация
Энтеробактерии. Классификация Физиология выделения
Физиология выделения Клиническая анатомия лицевого нерва. Топическая диагностика периферических поражений лицевого нерва
Клиническая анатомия лицевого нерва. Топическая диагностика периферических поражений лицевого нерва Спинной мозг. Проводящие пути
Спинной мозг. Проводящие пути Как бросить курить. Тест на выраженность никотиновой зависимости. Фармакологические препараты, облегчающие отказ от курения
Как бросить курить. Тест на выраженность никотиновой зависимости. Фармакологические препараты, облегчающие отказ от курения Лихорадка, уход за лихорадящими пациентами.Температура тела и ее измерение
Лихорадка, уход за лихорадящими пациентами.Температура тела и ее измерение Иммунология и иммунитет
Иммунология и иммунитет Нарушения кровообращения
Нарушения кровообращения Возбудители туберкулеза, микобактериозов, лепры
Возбудители туберкулеза, микобактериозов, лепры Доброкачественные и злокачественные опухоли почек
Доброкачественные и злокачественные опухоли почек Принципы терапии острой почечной недостаточности. Патогенетические сдвиги, клиническая картина
Принципы терапии острой почечной недостаточности. Патогенетические сдвиги, клиническая картина Возбудители микозов
Возбудители микозов Хроническая надпочечниковая недостаточность
Хроническая надпочечниковая недостаточность Методы лучевой диагностики. (Лекция 1)
Методы лучевой диагностики. (Лекция 1) Первая медицинская помощь на занятиях физической культуры
Первая медицинская помощь на занятиях физической культуры Рак полового члена
Рак полового члена Основы трансплантологии
Основы трансплантологии Микробиологическая диагностика брюшного тифа, паратифов и сальмонеллёзных гастроэнтеритов
Микробиологическая диагностика брюшного тифа, паратифов и сальмонеллёзных гастроэнтеритов Дезинфекция. Методы дезинфекции
Дезинфекция. Методы дезинфекции Саркома Юинга
Саркома Юинга Жамбас – сан буынының туберкулезінің дифференциальды диагностикасы
Жамбас – сан буынының туберкулезінің дифференциальды диагностикасы Проводящая система сердца
Проводящая система сердца Влияние быстрой еды на организм человека
Влияние быстрой еды на организм человека Философия сестринского дела
Философия сестринского дела Акушерство для линейных бригад скорой помощи
Акушерство для линейных бригад скорой помощи