Содержание
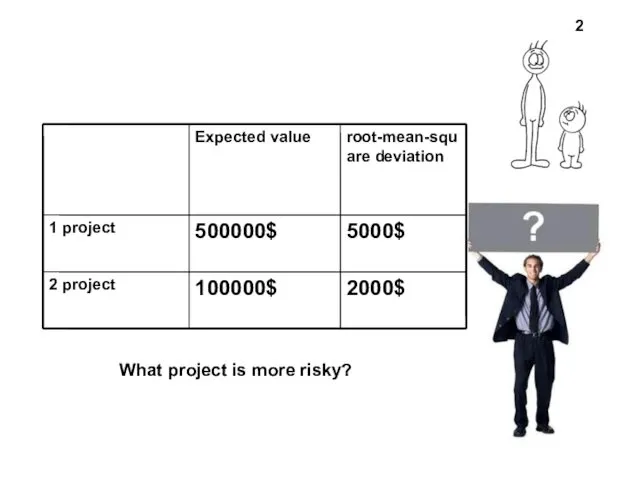
- 2. What project is more risky? 2
- 3. If taking into account root-mean-squire deviation, the first (bigger) project is more risky But if taking
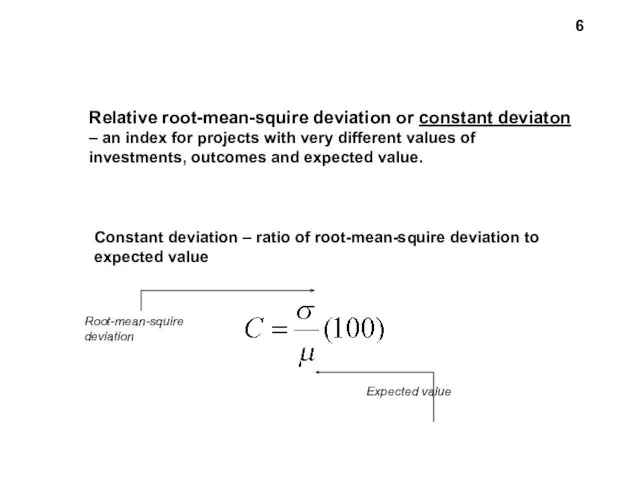
- 4. 4 In order to compare the risk of projects with very different values of investments, outcomes
- 5. Relative risk measurement: constant of variation 5
- 6. Relative root-mean-squire deviation or constant deviaton – an index for projects with very different values of
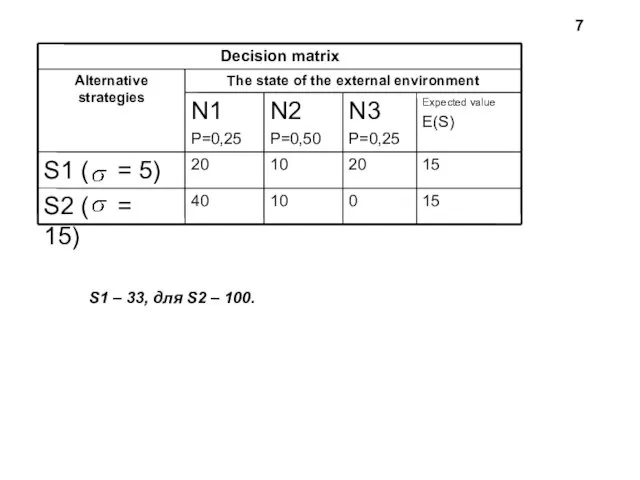
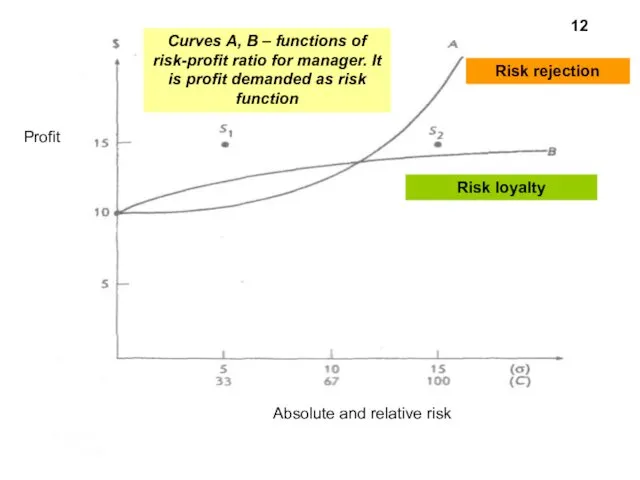
- 7. S1 – 33, для S2 – 100. 7
- 9. 9 Expected values, root-mean-squire deviation, constant of variety Risk analysis for 2 projects
- 10. A higher root-mean-squire deviation means a higher absolute risk A higher constant of variety indicates a
- 11. What index I’m taking into account and what decision I make? Depends on the attitude to
- 12. Отношение к риску -- это понятие в экономике, характеризующее склонность потребителей и инвесторов к принятию того
- 13. In the vast sea of human personalities, there are people who take risks, and people who
- 14. To risk or not to risk? Most investors and managers try to avoid risk Why? 14
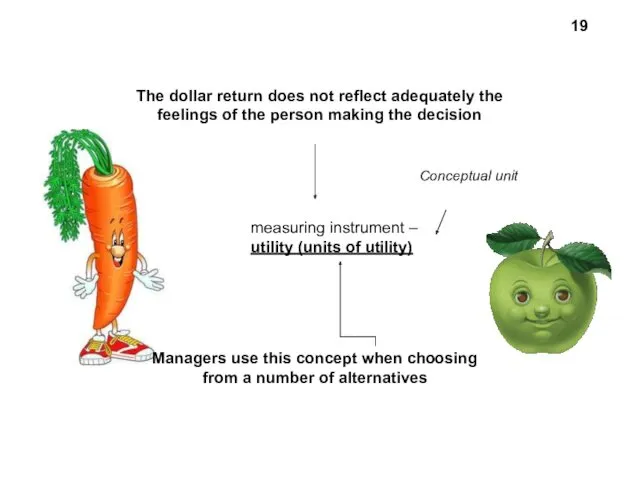
- 15. Theory of utility 15
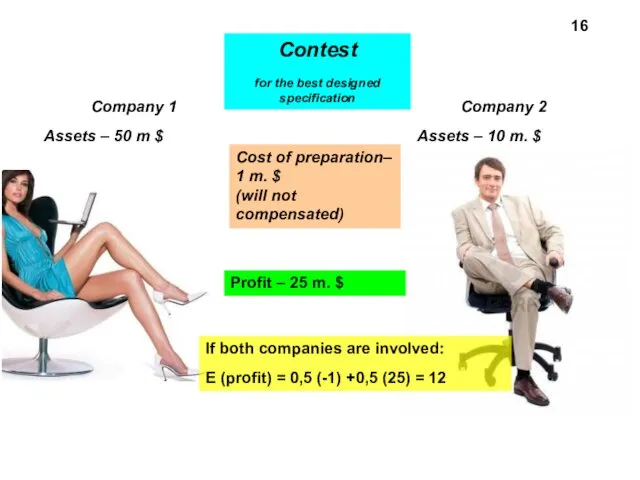
- 16. Company 1 Assets – 50 m $ Company 2 Assets – 10 m. $ Cost of
- 17. Despite 12 million $ a smaller firm may prefer not to take part in the contest
- 18. Conclusion: the conversion of dollar returns in some other incentive structure may be necessary before you
- 19. Managers use this concept when choosing from a number of alternatives The dollar return does not
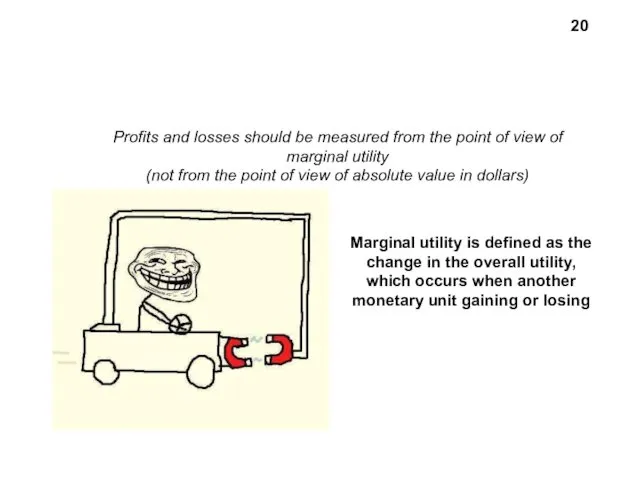
- 20. Profits and losses should be measured from the point of view of marginal utility (not from
- 21. The smaller company has appointed a greater marginal utility to the potentially lost dollars, not to
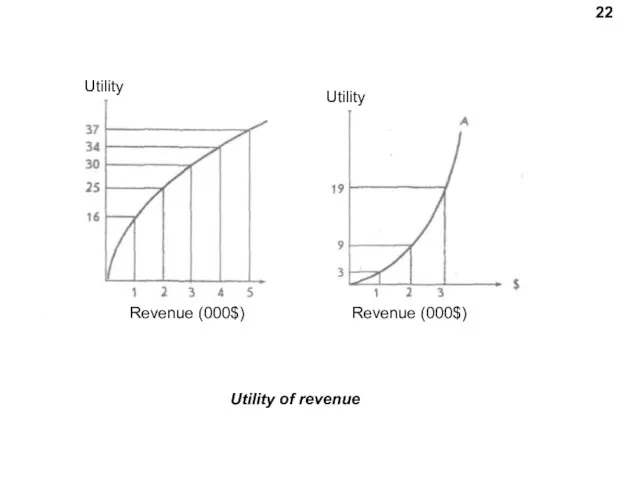
- 22. Utility of revenue 22 Utility Utility Revenue (000$) Revenue (000$)
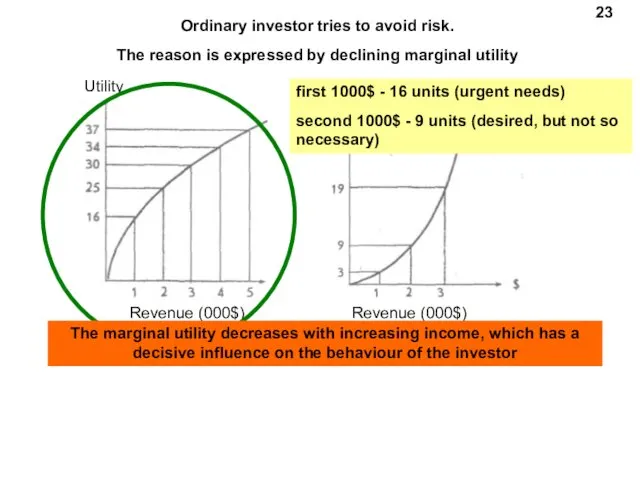
- 23. Revenue (000$) Utility Revenue (000$) Utility 23 Ordinary investor tries to avoid risk. The reason is
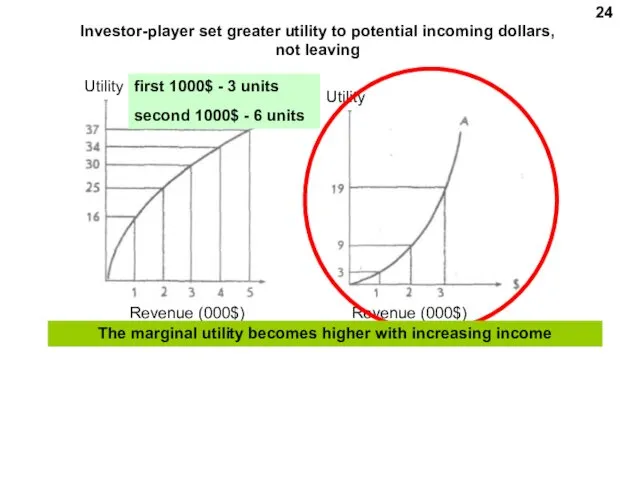
- 24. Revenue (000$) Utility 24 Investor-player set greater utility to potential incoming dollars, not leaving Utility Revenue
- 25. Leaders may be of different types Most of the leaders belong to type "a". They feel
- 27. Скачать презентацию












 Личность и мотивация
Личность и мотивация Беседа по эффективности
Беседа по эффективности Менеджер проекта: координатор, лидер или начальник
Менеджер проекта: координатор, лидер или начальник Strategic Human Resource Management Research Methods
Strategic Human Resource Management Research Methods Анализ состояния нормирования труда в организации
Анализ состояния нормирования труда в организации Turistik deneyim
Turistik deneyim Стиль руководства
Стиль руководства Транспортировка в логистических системах
Транспортировка в логистических системах Соотношение государственного управления и исполнительной власти
Соотношение государственного управления и исполнительной власти Организация работы закусочной Блинная на 75 мест
Организация работы закусочной Блинная на 75 мест Фармацевтикалық ұйымдарды логистикалық жүйе арқылы басқару
Фармацевтикалық ұйымдарды логистикалық жүйе арқылы басқару ОИП_стандарт
ОИП_стандарт Создание и продвижение музыкального проекта
Создание и продвижение музыкального проекта Басшылық және ықпал ету
Басшылық және ықпал ету Управление транспортными системами. Технико-экономическая характеристика магистральных видов транспорта
Управление транспортными системами. Технико-экономическая характеристика магистральных видов транспорта Понятие стратегического менеджмента
Понятие стратегического менеджмента Анализ рынка. Состояние. Тренды
Анализ рынка. Состояние. Тренды Активные методы обучения
Активные методы обучения Системный подход к управлению качеством. Система управления качеством процессов на основе стандартов ИСО серии 9000: 2000-2008
Системный подход к управлению качеством. Система управления качеством процессов на основе стандартов ИСО серии 9000: 2000-2008 Спортивный бизнес, как новое явление российской экономики
Спортивный бизнес, как новое явление российской экономики История управленческой и организационной мысли
История управленческой и организационной мысли Планирование и организация логистического процесса в организациях
Планирование и организация логистического процесса в организациях Визначення і концепції управління проектами. (Тема 2)
Визначення і концепції управління проектами. (Тема 2) Планирование и управление закупками и выбором поставщиков в логистической системе на предприятии ООО Оконные системы
Планирование и управление закупками и выбором поставщиков в логистической системе на предприятии ООО Оконные системы Правила деловых отношений
Правила деловых отношений Управление качеством
Управление качеством Этика руководителя. (Лекция 6)
Этика руководителя. (Лекция 6) Помещения гостиниц и их оборудование
Помещения гостиниц и их оборудование