Содержание
- 2. Agenda Session 1: Introduction to PMP Exam Session 2: Introduction to Project Management Theory Midterm quiz
- 3. PMP® Exam Consists of 200 multiple-choice questions 4 choice per question Total 4 hours (inclusive of
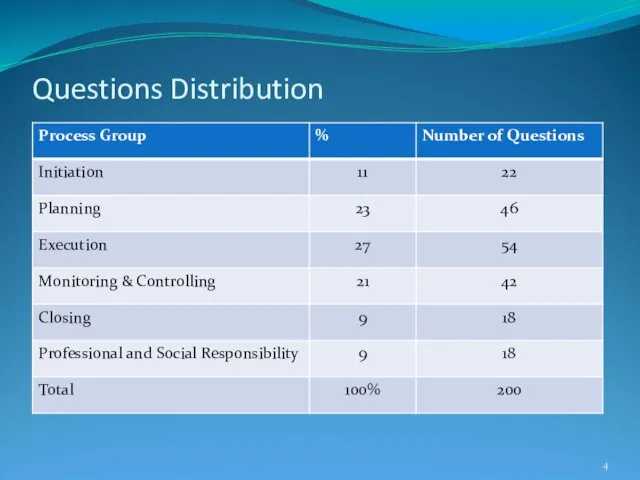
- 4. Questions Distribution
- 5. Question types Definitions Inputs, Outputs, and Tools & Techniques Network Diagram Calculations Scenario and Situational Fill
- 6. Good exam practices Read the question carefully Read the last sentence first in long questions Formulate
- 7. Introduction to Project Management
- 8. Learning Objectives Purpose of the PMBOK® - is to provide and promote a common lexicon (standard)
- 9. What is a Project? A project is “a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product,
- 10. A technician replaces ten laptops for a small department A small software development team adds a
- 11. Project Stakeholders Stakeholders are the people involved in or affected by project activities Stakeholders include: The
- 12. Process A series of actions bringing about a result Project Management Process Describe, organize and complete
- 13. What is Project Management? Project management is “the application of knowledge, skills, tools and techniques to
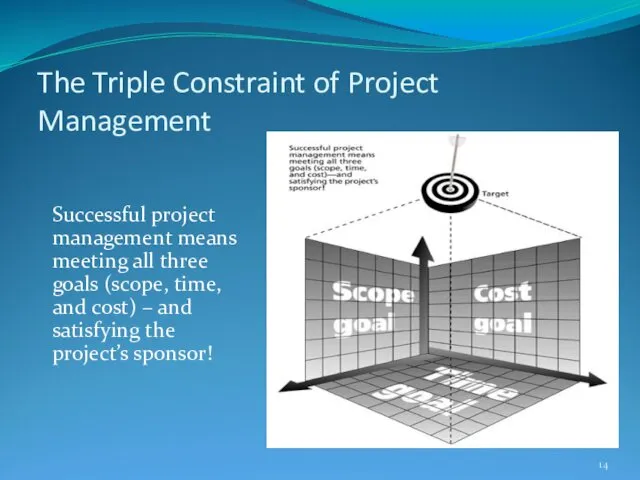
- 14. The Triple Constraint of Project Management Successful project management means meeting all three goals (scope, time,
- 15. Five Project Management Process Areas Initiating: Recognize the need and commit to action Planning: Create and
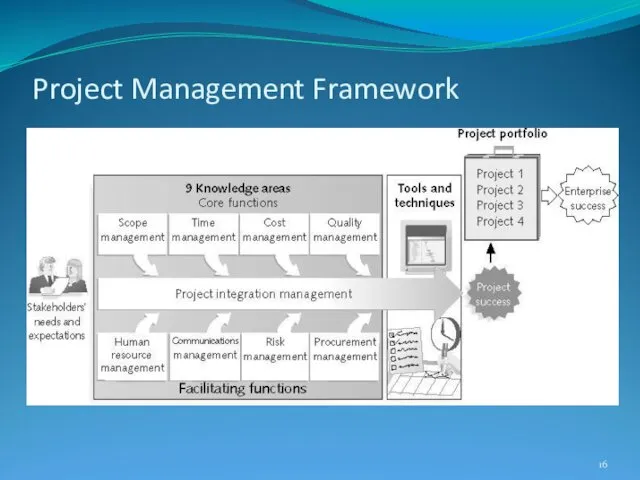
- 16. Project Management Framework
- 17. Project Management Tools and Techniques Project management tools and techniques assist project managers and their teams
- 18. Benefits of Program Management Provides a single focal point for managing scope, budget, and schedule for
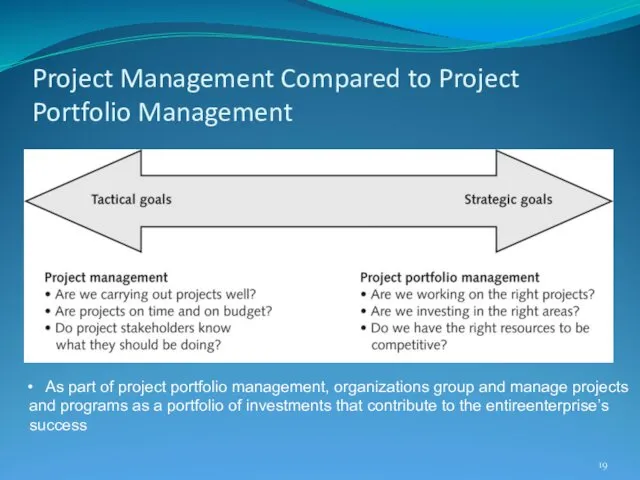
- 19. Project Management Compared to Project Portfolio Management As part of project portfolio management, organizations group and
- 20. Projects Vs Operations Projects end when their objectives have been reached or the project has been
- 21. Project Success There are several ways to define project success: The project met scope, time, and
- 22. What Helps Projects Succeed?* 1. Executive support 2. User involvement 3. Experienced project manager 4. Clear
- 23. Project Management Knowledge - Who Needs It? Project Managers Increase the chance of successfully meeting time,
- 24. Project Manager A Project Manager leads and is accountable for meeting customer requirements and obtaining the
- 25. Skills & Experience Expected from a Project Manager Relationship and Leadership Perform effective negotiations Apply communication
- 26. Summary A project is a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result
- 28. Скачать презентацию





















 Ідентифікація та документування робіт
Ідентифікація та документування робіт Совершенствование безопасности в гостинице Дружба
Совершенствование безопасности в гостинице Дружба Формирование и совершенствование гостиничного продукта. Понятие и специфика продукта индустрии
Формирование и совершенствование гостиничного продукта. Понятие и специфика продукта индустрии Лидерство в системе управления профсоюзной организацией
Лидерство в системе управления профсоюзной организацией Организация работы с персоналом государственной службы
Организация работы с персоналом государственной службы Современные тенденции в менеджменте
Современные тенденции в менеджменте Технологические документы службы эксплуатации номерного фонда гостиницы
Технологические документы службы эксплуатации номерного фонда гостиницы Сертификация продукции и систем качества. Правовые вопросы в области качества. (Лекция 3)
Сертификация продукции и систем качества. Правовые вопросы в области качества. (Лекция 3) Организация и аттестация рабочих мест. (Лекция 3)
Организация и аттестация рабочих мест. (Лекция 3) Производственная логистика
Производственная логистика Пути снижения затрат подразделения промышленного предприятия (ОАО НПО Сатурн)
Пути снижения затрат подразделения промышленного предприятия (ОАО НПО Сатурн) Федеральное агентство по туризму (Ростуризм)
Федеральное агентство по туризму (Ростуризм) Процессы мониторинга и контроля, процессы завершения проекта
Процессы мониторинга и контроля, процессы завершения проекта Организационная культура
Организационная культура Генезис науки менеджмент
Генезис науки менеджмент Инновационный процесс и инновационная деятельность
Инновационный процесс и инновационная деятельность Понятие проект. Проект устойчивого развития
Понятие проект. Проект устойчивого развития Тарифы в транспортной логистике
Тарифы в транспортной логистике Управление развитием сферы физической культуры и спорта в МО Курагинский район
Управление развитием сферы физической культуры и спорта в МО Курагинский район Планування розвитку управлінських інформаційних систем. Управління інформаційними системами в організації
Планування розвитку управлінських інформаційних систем. Управління інформаційними системами в організації Корпоративный кодекс
Корпоративный кодекс Разработка автоматизированной информационной системы для учета документов ООО Малыш
Разработка автоматизированной информационной системы для учета документов ООО Малыш Комплекс услуг по агентированию судов. Управляющая компания Максима
Комплекс услуг по агентированию судов. Управляющая компания Максима Отбор персонала в организацию
Отбор персонала в организацию Транспортная обеспеченность и система управления транспортом
Транспортная обеспеченность и система управления транспортом Теоретичні основи управління інноваційним розвитком. Тема 1
Теоретичні основи управління інноваційним розвитком. Тема 1 Показатели качества продукции. Методы и инструменты управления качеством
Показатели качества продукции. Методы и инструменты управления качеством организация снабжения и складского хозяйства на предприятиях общественного питания
организация снабжения и складского хозяйства на предприятиях общественного питания