Содержание
- 2. Objectives of the session: By the end of this lecture you will: understand the language levels
- 3. CEFR uses and users:
- 4. Common European Framework of Reference Framework - a system of rules, ideas, or beliefs that is
- 5. Common European Framework of Reference Framework - a set of ideas, conditions, or assumptions that determine
- 6. Common European Framework of Reference in Russian «Общеевропейские компетенции владения иностранным языком: Изучение, преподавание, оценка»
- 7. Common European Framework of Reference An international standard for describing language ability Language and context neutral
- 8. European Union: 28 countries, a diversity of languages Languages are one of the key features of
- 9. Milestones of the CEFR development 1960s and 1970s – shift from grammar-translation method to functional/notional approach
- 10. Milestones of the CEFR development (cont.) 1991 - Rüschlikon intergovernmental symposium ‘Transparency and Coherence in Language
- 11. CEFR uses and users: The overarching goal: increase transparency of language education Uses setting targets for
- 12. CEFR: structure of the document The document as available at http://www.coe.int/t/dg4/linguistic/Source/Framework_EN.pdf The CEFR states that the
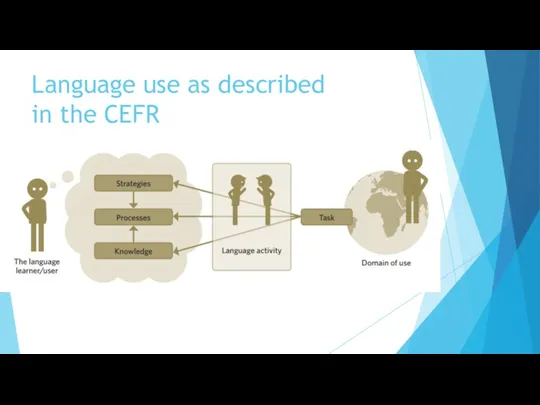
- 13. Chapter 2: “Language use, embracing language learning, comprises the actions performed by persons who as individuals
- 14. Language use as described in the CEFR
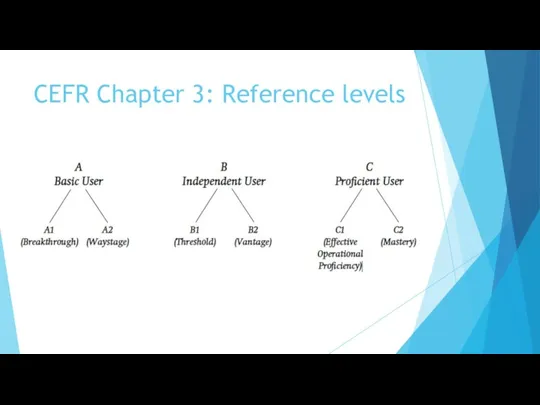
- 15. CEFR Chapter 3: Reference levels
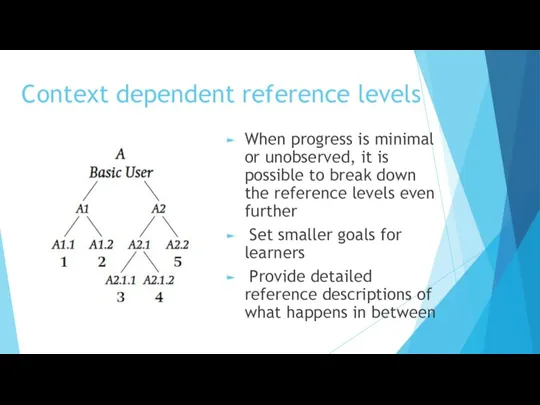
- 16. Context dependent reference levels When progress is minimal or unobserved, it is possible to break down
- 17. CEFR: a set of scales A global scale A self-assessment grid Grids for each skill, which
- 18. Global scale
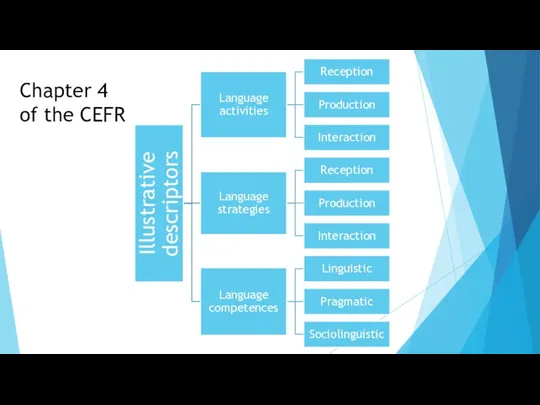
- 19. Chapter 4 of the CEFR
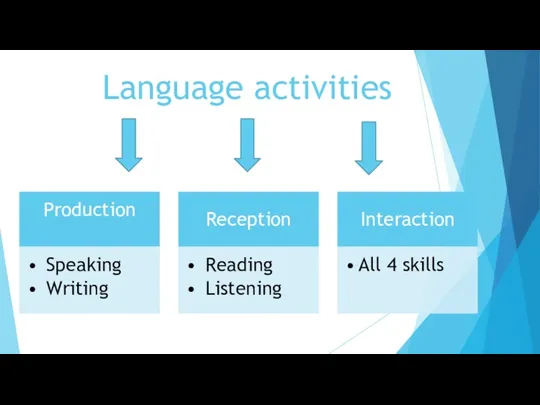
- 20. Language activities
- 21. Productive scales: Speaking
- 22. Overall oral production
- 23. Public announcements
- 24. Productive scales: Writing
- 25. Receptive scales
- 26. Receptive scales
- 27. WATCHING TV AND FILM
- 28. Interactive scales Overall spoken interaction Understanding a native speaker interlocutor Conversation Informal discussion (with a friend)
- 29. Chapter 4 of the CEFR
- 30. Language strategies
- 31. Scales for language competences
- 32. Scales for language competences
- 33. Scales for language competences
- 34. Self-Assessment Grids Allow learners to assess themselves across levels and skills using the I-Can-Do format They
- 35. Self-assessment exercise Think of a second or third language that you know. On a scale from
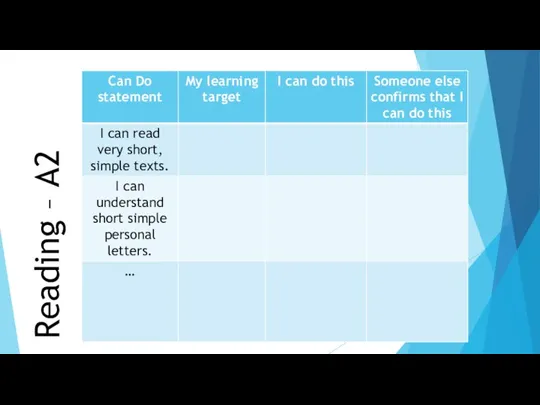
- 36. Ideas for use of CEFR scales in the classroom Reading – A2
- 37. Reading – A2
- 38. Reading – A2
- 39. Reading – A2
- 41. Critique of the CEFR CEFR descriptors are not exclusive: no description is provided for All possible
- 42. Critique of the CEFR CEFR descriptors are not necessary or sufficient specifications of what should be
- 43. English Profile A long-term research program to extend the CEFR It translates CEFR into the English
- 44. Where do I proceed from here? Define your teaching context and your learners Become familiar with
- 45. What CEFR is and is not CEFR scales are used to describe, not prescribe CEFR scales
- 46. Watch the video clip and choose the correct CEFR level for each learner What skill is
- 48. Скачать презентацию







































 Федеральный государственный образовательный стандарт дошкольного образования: штрихи к портрету
Федеральный государственный образовательный стандарт дошкольного образования: штрихи к портрету Изменение естественно-научного образования при переходе на ФГОС общего образования
Изменение естественно-научного образования при переходе на ФГОС общего образования Наука в современном обществе
Наука в современном обществе Образование
Образование Ученые степени и ученые звания в истории отечественной науки и высшего образования
Ученые степени и ученые звания в истории отечественной науки и высшего образования Сочинение по литературе в декабре 2017
Сочинение по литературе в декабре 2017 Институциональная аккредитация Международного университета информационных технологий
Институциональная аккредитация Международного университета информационных технологий Основы исследовательской и проектной деятельности школьников
Основы исследовательской и проектной деятельности школьников Медаль им. М.В. Ломоносова
Медаль им. М.В. Ломоносова Организация внеурочной деятельности в условиях введия ФГОС
Организация внеурочной деятельности в условиях введия ФГОС Порядок и формы проведения государственной итоговой аттестации выпускников 9 классов в 2022-2023 учебном году
Порядок и формы проведения государственной итоговой аттестации выпускников 9 классов в 2022-2023 учебном году Методика обучения и воспитания по профилю Биология
Методика обучения и воспитания по профилю Биология итоги работы ШМО над методической темой
итоги работы ШМО над методической темой Факультет клинической психологии. Рязанский государственный медицинский университет им. академика И.П. Павлова
Факультет клинической психологии. Рязанский государственный медицинский университет им. академика И.П. Павлова Южно-Уральский Государственный Аграрный Университет
Южно-Уральский Государственный Аграрный Университет Творческая проектная деятельность. 5 класс
Творческая проектная деятельность. 5 класс Энергетика emec энергетикалык кафедрасы
Энергетика emec энергетикалык кафедрасы Особенности развития, особые образовательные потребности и потенциальные возможности обучающихся с умственной отсталостью
Особенности развития, особые образовательные потребности и потенциальные возможности обучающихся с умственной отсталостью Balance. Детская бизнес-школа
Balance. Детская бизнес-школа Деятельность ПМПК и ПМПк
Деятельность ПМПК и ПМПк Интерпретация результатов ГИА по истории и обществознанию в целях построения национальной системы учительского роста
Интерпретация результатов ГИА по истории и обществознанию в целях построения национальной системы учительского роста ЦОР Кубанская казачья хатаЧАСТЬ 3
ЦОР Кубанская казачья хатаЧАСТЬ 3 Регламент работы общественного наблюдателя в ППЭ
Регламент работы общественного наблюдателя в ППЭ Система подготовки лидеров в детском общественном объединении
Система подготовки лидеров в детском общественном объединении Государственная итоговая аттестация по образовательным программам среднего общего образования (ГИА – 11). Апрель 2017 года
Государственная итоговая аттестация по образовательным программам среднего общего образования (ГИА – 11). Апрель 2017 года Использование модульной технологии на уроках математики
Использование модульной технологии на уроках математики Прием в образовательные организации программы ВО он набора 23-09
Прием в образовательные организации программы ВО он набора 23-09 Рабочая программа учителя химии. Методические рекомендации в свете требований новых образовательных стандартов
Рабочая программа учителя химии. Методические рекомендации в свете требований новых образовательных стандартов