Содержание
- 2. Understanding Inequality Inequality is the unequal access to scarce goods or resources. It is found in
- 3. Understanding Social Stratification Social stratification is the division of society into groups arranged in a social
- 4. Social Stratification Every society has some form of social stratification, but societies group people on different
- 5. Introduction to Sociology: Social Class and Inequality Systems of Stratification (Cont’d) Social class refers to a
- 6. Social Classes in the United States The upper class (capitalist class): Wealthiest people in a class
- 7. Social Classes in the United States The upper-middle class: Professionals and managers Make up about 14%
- 8. Social Classes in the United States The working (lower-middle) class: “Blue-collar” or service industry workers Less
- 9. Social Classes in the United States The lower class (the working poor): Many poor people who
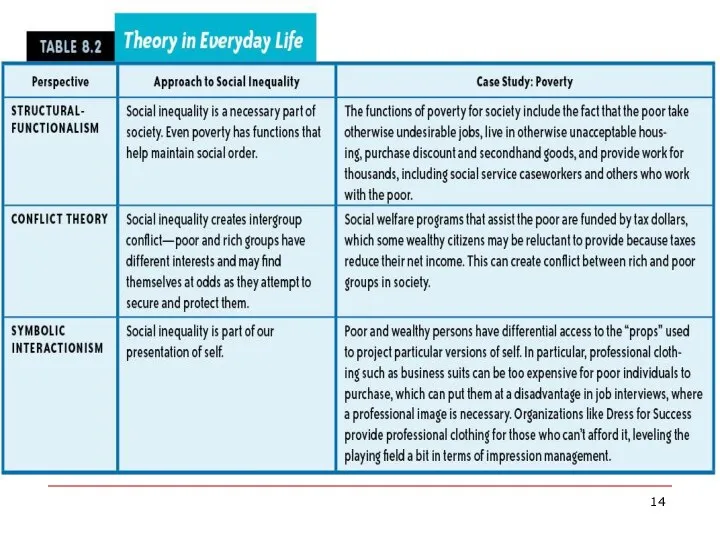
- 10. Theories of Social Class Karl Marx believed that there were two main social classes in capitalist
- 11. Theories of Social Class Max Weber offered a similar model that also included cultural factors. He
- 12. Theories of Social Class More recently, Pierre Bourdieu argued each generation acquires cultural capital (tastes, habits,
- 13. Theories of Social Class Symbolic Interactionists examine the way we use status differences to categorize ourselves
- 15. Socioeconomic Status and Life Chances Belonging to a certain social class has profound consequences for individuals
- 16. Social Mobility Social mobility is the movement of individuals or groups within the hierarchal system of
- 17. Poverty The culture of poverty refers to learned attitudes that can develop among poor communities and
- 18. Political elite In every society there is a class of people which is though small in
- 19. Characteristics of political elites Small in number Organised Monopoly over political power Open competition among different
- 20. Elitist Theorists “pluralists” or “functionalists” Mosca, Parsons Mosca's enduring contribution to political science is the observation
- 21. Lesson Quiz True or False: 1. Every society has some form of stratification. a. True b.
- 22. Lesson Quiz 2. The tendency of social classes to remain relatively stable as social class status
- 23. Lesson Quiz 3. Entrenched attitudes that can develop among poor communities and lead the poor to
- 25. Скачать презентацию





















 Командообразование
Командообразование Эмиль Дюркгейм (15 апреля 1858 — 15 ноября 1917)
Эмиль Дюркгейм (15 апреля 1858 — 15 ноября 1917) Нові явища у соціальній сфері. Зрушення у повсякденному житті населення
Нові явища у соціальній сфері. Зрушення у повсякденному житті населення Северный Управленческий округ Свердловской области об организации отдыха и оздоровления детей и подростков
Северный Управленческий округ Свердловской области об организации отдыха и оздоровления детей и подростков Вопросы кодификатора. Социальная структура общества
Вопросы кодификатора. Социальная структура общества Проект добрых дел. 7 класс
Проект добрых дел. 7 класс Презентация к уроку Мы -многонациональный народ
Презентация к уроку Мы -многонациональный народ Презентация к уроку обществознания в 8 классе по теме Что такое общество?
Презентация к уроку обществознания в 8 классе по теме Что такое общество? Социальные отношения и институты
Социальные отношения и институты The Salvation Army
The Salvation Army Теория модернизации. Мир-системный подход
Теория модернизации. Мир-системный подход Программы социальной поддержки членов профсоюза
Программы социальной поддержки членов профсоюза Значение образа жизни в формировании уровня здоровья. ОРТ и здоровый образ жизни
Значение образа жизни в формировании уровня здоровья. ОРТ и здоровый образ жизни Правовой марафон
Правовой марафон Понятие коммуникации. История изучения коммуникации. Коммуникация и общение
Понятие коммуникации. История изучения коммуникации. Коммуникация и общение Мама, Папа, Я – дружная семья!
Мама, Папа, Я – дружная семья! презентация к урокуДевиантное поведение.
презентация к урокуДевиантное поведение. Общество, как форма жизнедеятельности людей
Общество, как форма жизнедеятельности людей Духовно-нравственное воспитание в рамках предмета ОБЖ
Духовно-нравственное воспитание в рамках предмета ОБЖ Понятие общества и его основные характеристики
Понятие общества и его основные характеристики Социология личности
Социология личности Клуб активного долголетия
Клуб активного долголетия Загальношкільні батьківські збори. Підсумки року
Загальношкільні батьківські збори. Підсумки року Организация зоны проведения массовых мероприятии
Организация зоны проведения массовых мероприятии Презентация по теме Марксистское учение об обществе
Презентация по теме Марксистское учение об обществе Семейные ценности и традиции. Обществознание. 5 класс
Семейные ценности и традиции. Обществознание. 5 класс Проблемы многодетной семьи
Проблемы многодетной семьи Социальный проект Компьютер для всех поколений
Социальный проект Компьютер для всех поколений