Содержание
- 2. Plan 1. Definition and classification of responsibility centers 2. Requirements for RC 3. Typology of activity
- 3. 1. Definition and classification of responsibility centers Controlling system provides an accumulation and analysis of information
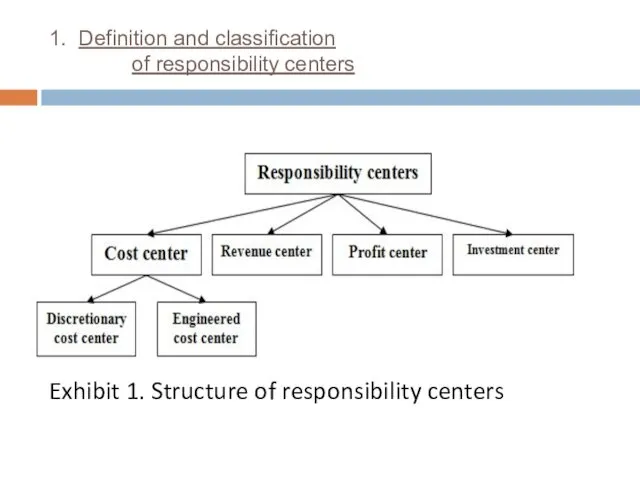
- 4. 1. Definition and classification of responsibility centers There are four major types of responsibility centers (Exhibit
- 5. 1. Definition and classification of responsibility centers Exhibit 1. Structure of responsibility centers
- 6. 1. Definition and classification of responsibility centers Cost Center - a segment of responsibility, in which
- 7. 1. Definition and classification of responsibility centers Technological costs for the center (Engineered Cost Center) may
- 8. 1. Definition and classification of responsibility centers Revenue center is responsible for the receipt of proceeds
- 9. 1. Definition and classification of responsibility centers Investment center- a center of responsibility, which head simultaneously
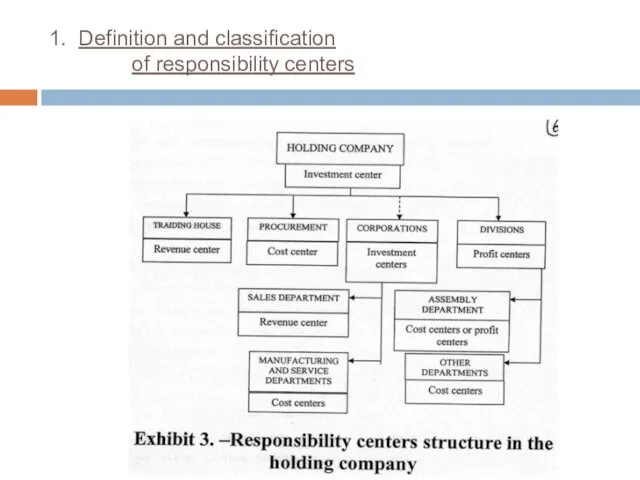
- 10. 1. Definition and classification of responsibility centers
- 11. 2. Requirements for the responsibility centers 1. The presence of the responsible for the activities of
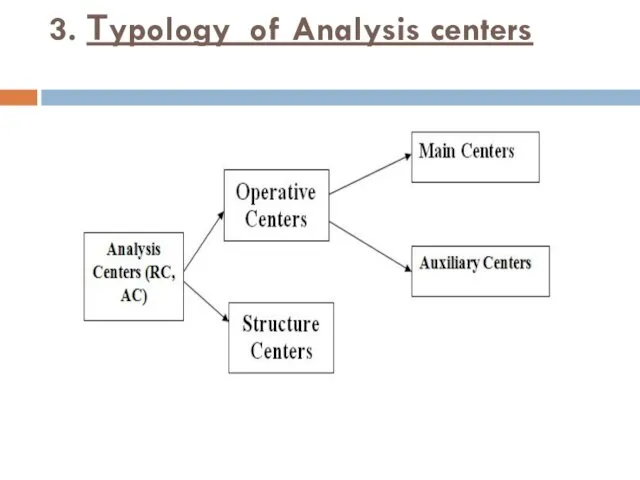
- 12. 3. Тypology of Analysis centers
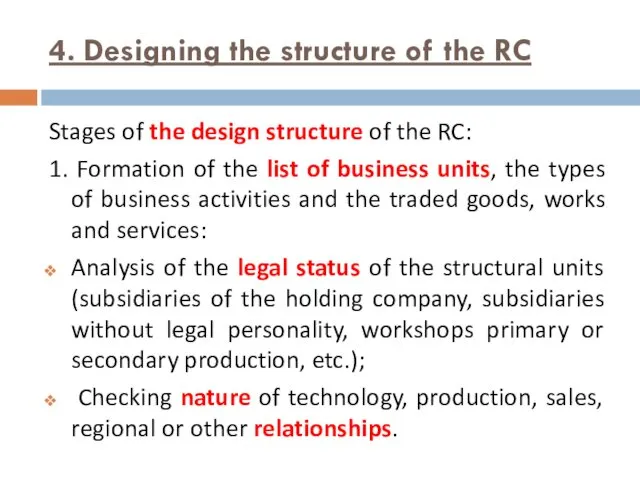
- 13. 4. Designing the structure of the RC Stages of the design structure of the RC: 1.
- 14. 4. Designing the structure of the RC 2. Determining the type of organizational structure (divisional, linear-functional
- 15. 4. Designing the structure of the RC 4. Delineation of zones of competence and responsibility, the
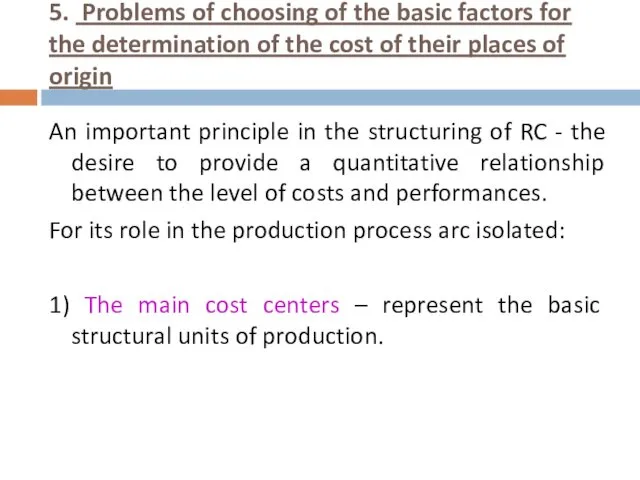
- 16. 5. Problems of choosing of the basic factors for the determination of the cost of their
- 17. 5. Problems of choosing of the basic factors for the determination of the cost of their
- 18. 5. Problems of choosing of the basic factors for the determination of the cost of their
- 19. 5. Problems of choosing of the basic factors for the determination of the cost of their
- 20. 5. Problems of choosing of the basic factors for the determination of the cost of their
- 21. 6.Advantages of the management by the centers of responsibility Controlling system provides an accumulation and analysis
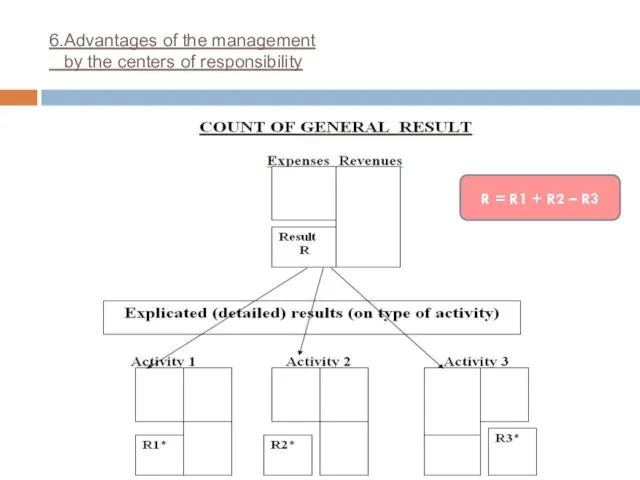
- 22. 6.Advantages of the management by the centers of responsibility R = R1 + R2 – R3
- 23. 6.Advantages of the management by the centers of responsibility Advantages: Provides a process for effective delegation
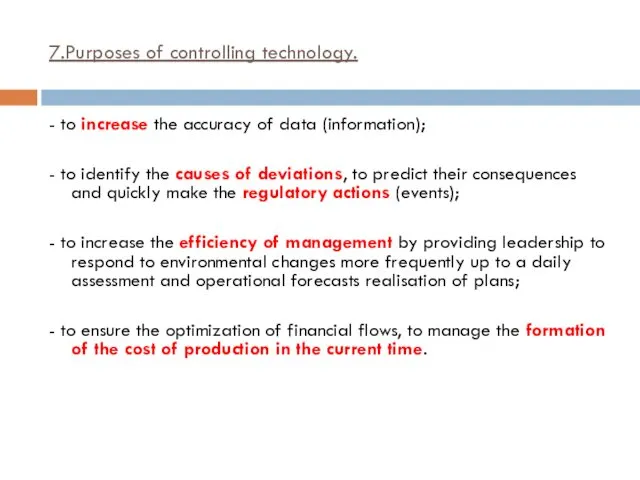
- 24. 7.Purposes of controlling technology. Controlling technology allows: - to link business strategy with operational management: to
- 25. 7.Purposes of controlling technology. - to increase the accuracy of data (information); - to identify the
- 26. 8. Characteristic (role) of specialist for controlling in the firm Controlling integrates knowledge from all disciplines
- 27. 8. Role of specialist for controlling in the firm - an organizer, able to coordinate a
- 29. Скачать презентацию
















 Где логика
Где логика Школа молодого родителя
Школа молодого родителя Музыкальный эрудит
Музыкальный эрудит Выбор профессии. Горный инженер
Выбор профессии. Горный инженер Студия Calligraphy Курган. Каллиграфия
Студия Calligraphy Курган. Каллиграфия В поисках смысла жизни
В поисках смысла жизни Педагогическая диагностика
Педагогическая диагностика Команда: Охотники за тайнами. МОБУ Гимназия 3 г. Кудымкар
Команда: Охотники за тайнами. МОБУ Гимназия 3 г. Кудымкар Идеальный учитель XXI века
Идеальный учитель XXI века Формирование нравственных качеств личности ребенка через игры с правилами
Формирование нравственных качеств личности ребенка через игры с правилами Изготовление снеговика из искусственного снега
Изготовление снеговика из искусственного снега Podkhody_i_printsipy_obuchenia_IYa
Podkhody_i_printsipy_obuchenia_IYa Использование здоровьесберегающих технологий в режиме дня в первой младшей группе
Использование здоровьесберегающих технологий в режиме дня в первой младшей группе Основы методики преподавания изобразительного искусства
Основы методики преподавания изобразительного искусства Презентация Осенние месяцы 4
Презентация Осенние месяцы 4 Открытка к 23 февраля
Открытка к 23 февраля Коррекция и профилактика дизорфографических ошибок у учащихся с ОВЗ
Коррекция и профилактика дизорфографических ошибок у учащихся с ОВЗ Скоро в школу я пойду (для дошкольников)
Скоро в школу я пойду (для дошкольников) Звездный час. Интеллектуальная игра по профессиональной ориентации
Звездный час. Интеллектуальная игра по профессиональной ориентации Личность современного учителя
Личность современного учителя Диалогическое обучение при преподавании естественных наук
Диалогическое обучение при преподавании естественных наук Волшебное преображение
Волшебное преображение Организация предметно-развивающей среды в первой младшей группе по ФГОС
Организация предметно-развивающей среды в первой младшей группе по ФГОС Символ 2019 года своими руками
Символ 2019 года своими руками Игра Встречаем Новый год
Игра Встречаем Новый год Коучинг технология
Коучинг технология Особенности организации адаптивной физической культуры с детьми с ограниченными возможностями здоровья
Особенности организации адаптивной физической культуры с детьми с ограниченными возможностями здоровья Мы здоровью скажем - ДА! Диск Диск
Мы здоровью скажем - ДА! Диск Диск