Содержание
- 2. MOTIVATION “… each of us remembers and forgets in a pattern whose labyrinthing windings are an
- 3. INTRODUCTION Memory : Storage of information for later retrieval Human Memory Processes -> Strong Research Area
- 5. TYPES OF MEMORY Sensory Memory Retain impressions of sensory information Even after original stimulus ceases Short
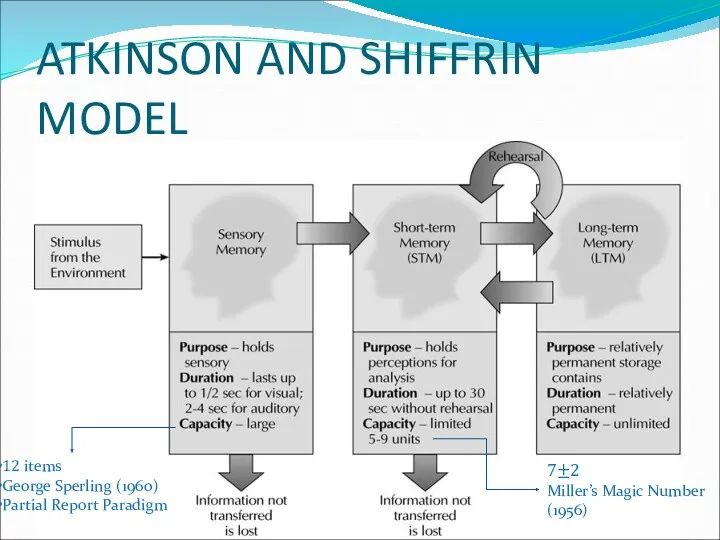
- 6. ATKINSON AND SHIFFRIN MODEL 12 items George Sperling (1960) Partial Report Paradigm 7±2 Miller’s Magic Number
- 7. EVIDENCE Anterograde amnesia Intact ability to retain small amounts of information over short time scales Ability
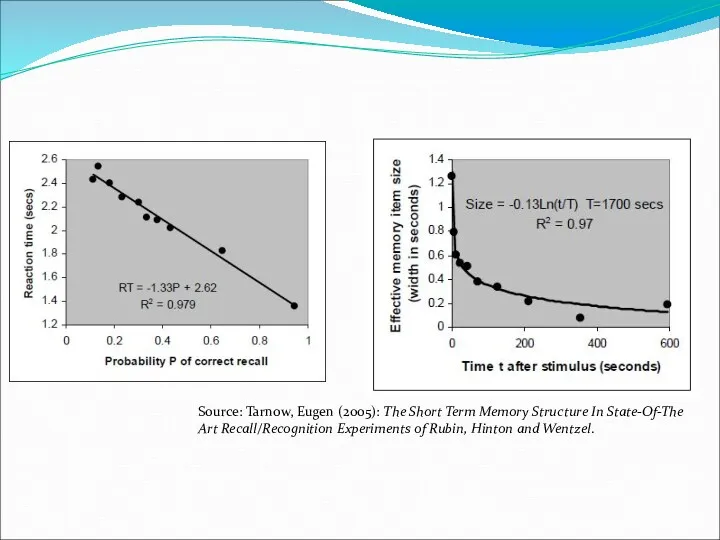
- 8. CONTRADICTIONS Tarnow’s work in 2005 The recall probability vs. latency curve is a straight line from
- 9. Source: Tarnow, Eugen (2005): The Short Term Memory Structure In State-Of-The Art Recall/Recognition Experiments of Rubin,
- 10. SHORT TERM MEMORY Memory span The longest list of items that a person can repeat back
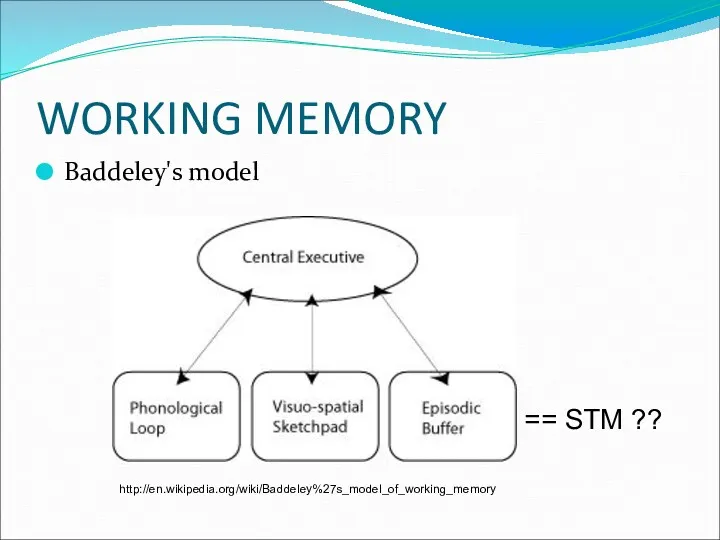
- 11. WORKING MEMORY Baddeley's model http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baddeley%27s_model_of_working_memory == STM ??
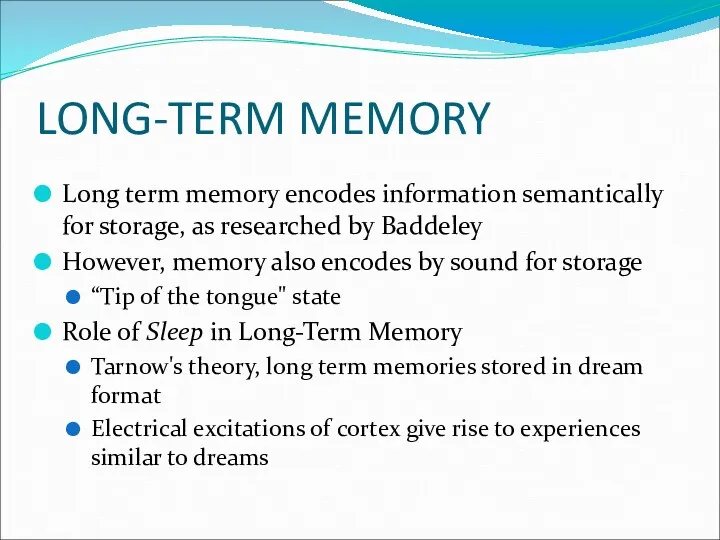
- 12. LONG-TERM MEMORY Long term memory encodes information semantically for storage, as researched by Baddeley However, memory
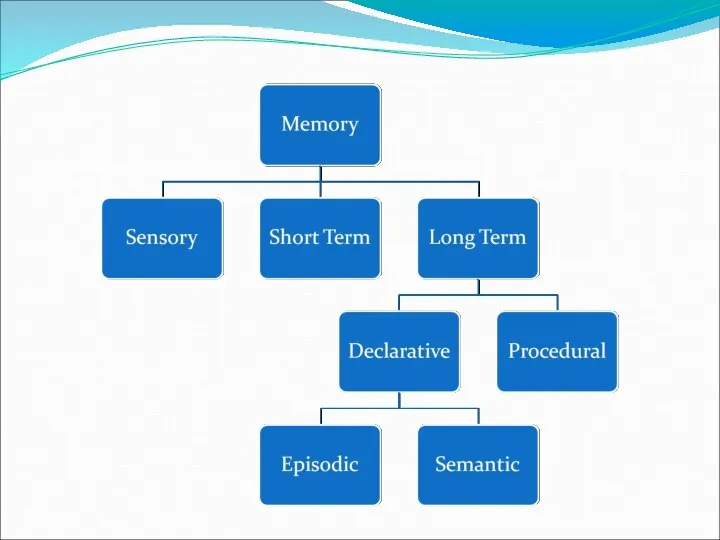
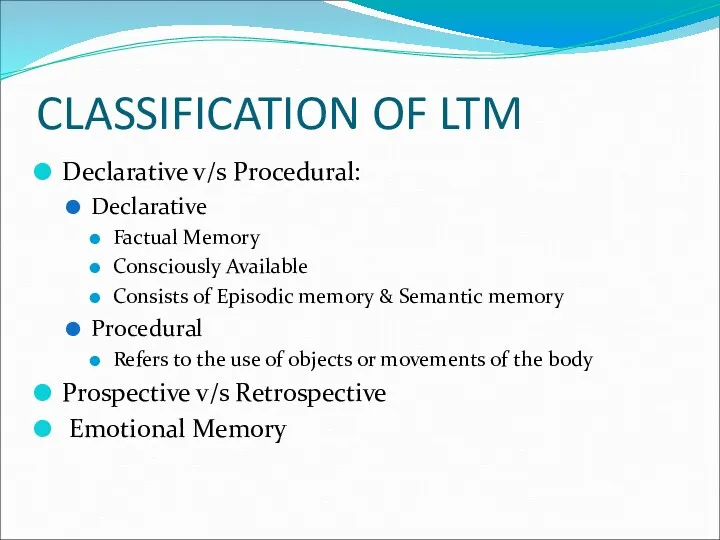
- 13. CLASSIFICATION OF LTM Declarative v/s Procedural: Declarative Factual Memory Consciously Available Consists of Episodic memory &
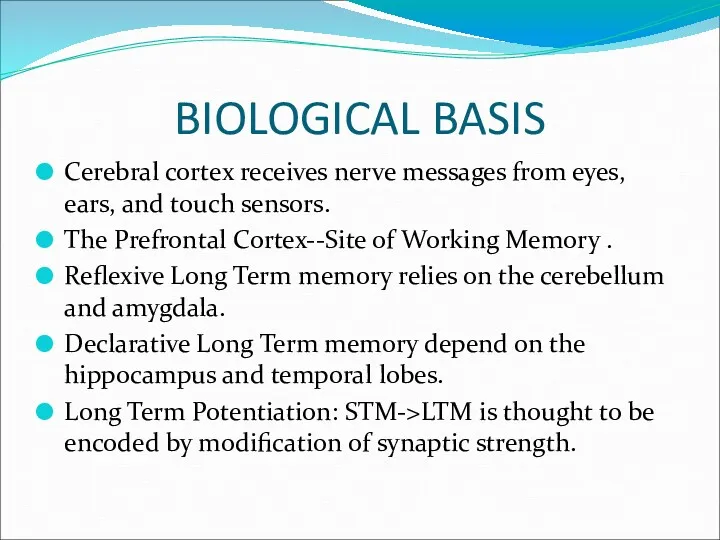
- 14. BIOLOGICAL BASIS Cerebral cortex receives nerve messages from eyes, ears, and touch sensors. The Prefrontal Cortex--Site
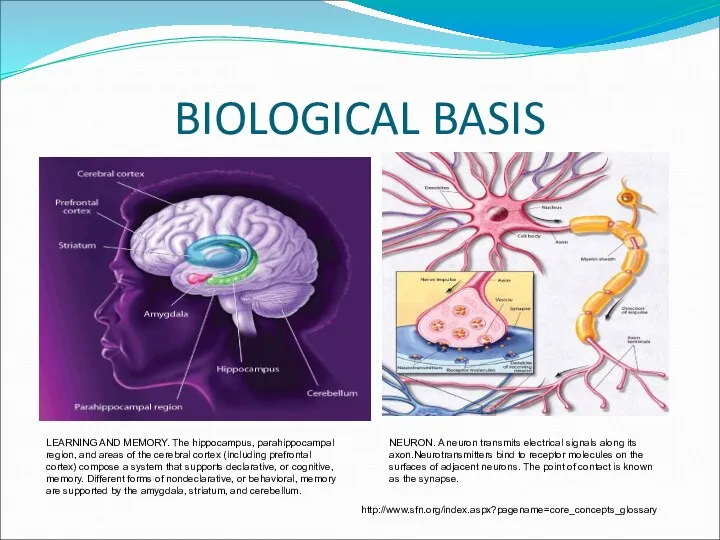
- 15. BIOLOGICAL BASIS LEARNING AND MEMORY. The hippocampus, parahippocampal region, and areas of the cerebral cortex (including
- 16. MEMORY AND A.I.
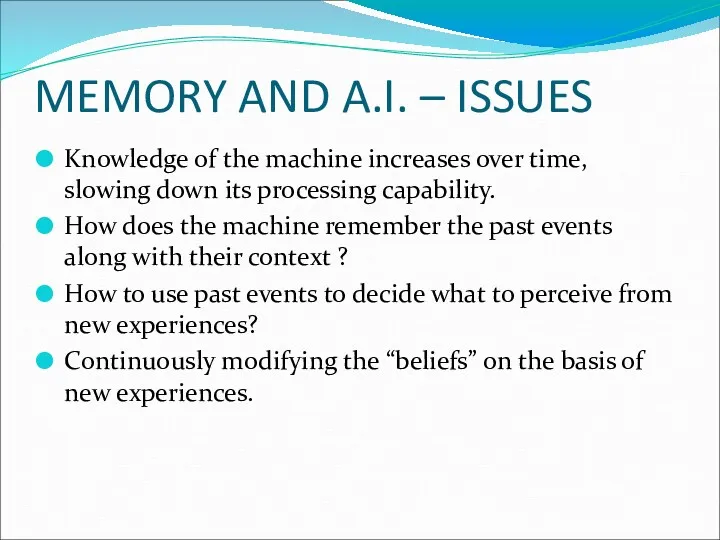
- 17. MEMORY AND A.I. – ISSUES Knowledge of the machine increases over time, slowing down its processing
- 18. (CONTD..) Some terms: Knowledge is the information about a domain that is used for solving problems
- 19. INCREASING SET OF BELIEFS The point of view is therefore emulationist and not simulationist. The idea
- 20. REMEMBERING PAST EVENTS What is remembering? How does the machine remember the past? Clancey(1997) writes that
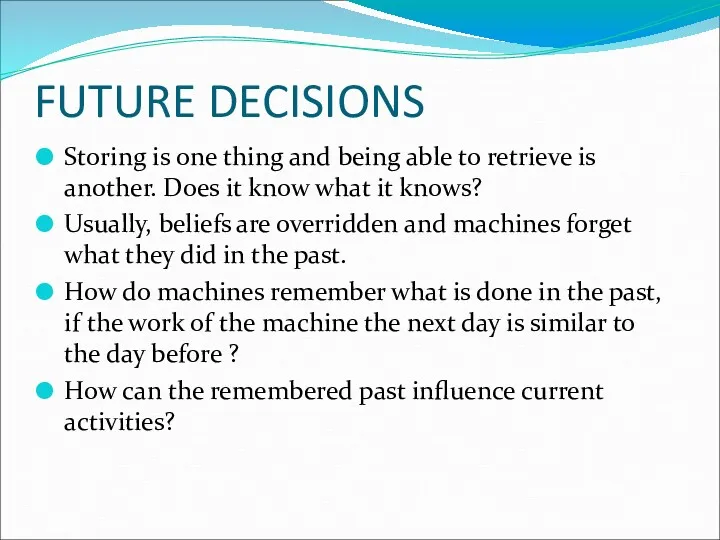
- 21. FUTURE DECISIONS Storing is one thing and being able to retrieve is another. Does it know
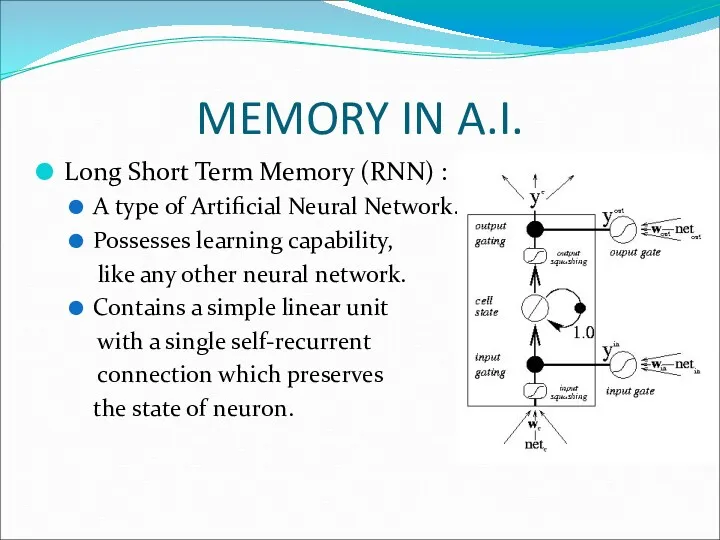
- 22. MEMORY IN A.I. Long Short Term Memory (RNN) : A type of Artificial Neural Network. Possesses
- 23. MEMORY AS ART ! Subject of interest from Historic times. Memory not a static entity. It
- 24. IMPROVING MEMORY From a Student’s perspective: Rephrase and explain. Be emotionally involved. Schedule and read in
- 25. REFERENCES Cite ^ Davelaar, E. J., Goshen-Gottstein, Y., A., A., Haarmann, H. J., & Usher, M.
- 27. Скачать презентацию











 Классный час: Деловое общение. Законы решения конфликтов
Классный час: Деловое общение. Законы решения конфликтов Исторические этапы развития различных видов коммуникации
Исторические этапы развития различных видов коммуникации Память как процесс приема, сохранения и переработки информации
Память как процесс приема, сохранения и переработки информации Психолого-педагогическое сопровождение учащихся младших классов с трудностями в обучении
Психолого-педагогическое сопровождение учащихся младших классов с трудностями в обучении Особенности проффесиональной и корпоративной морали
Особенности проффесиональной и корпоративной морали Базовые коммуникативные навыки в профессиональной деятельности врача общей практики
Базовые коммуникативные навыки в профессиональной деятельности врача общей практики Суицидальное поведение
Суицидальное поведение Нақты қылмыстардың себептері, шарттары және механизмдері
Нақты қылмыстардың себептері, шарттары және механизмдері Социальная психология
Социальная психология Нормы поведения в общественных местах
Нормы поведения в общественных местах Як працювати з дітьми з різним типом темпераменту
Як працювати з дітьми з різним типом темпераменту Закономерности, динамика и механизмы психического развития личности в онтогенезе (продолжение)
Закономерности, динамика и механизмы психического развития личности в онтогенезе (продолжение) Деятельность. Основные характеристики деятельности. Структура деятельности. Мотивация. Многообразие деятельности
Деятельность. Основные характеристики деятельности. Структура деятельности. Мотивация. Многообразие деятельности Қарым-қатынастың коммуникациялық жағының сипатамасы
Қарым-қатынастың коммуникациялық жағының сипатамасы Особенности эмоциональной сферы у детей с ЗПР
Особенности эмоциональной сферы у детей с ЗПР Общение, как обмен информацией
Общение, как обмен информацией Конфликты между родителями и детьми в семье
Конфликты между родителями и детьми в семье Манипуляция и способы противостоять ей
Манипуляция и способы противостоять ей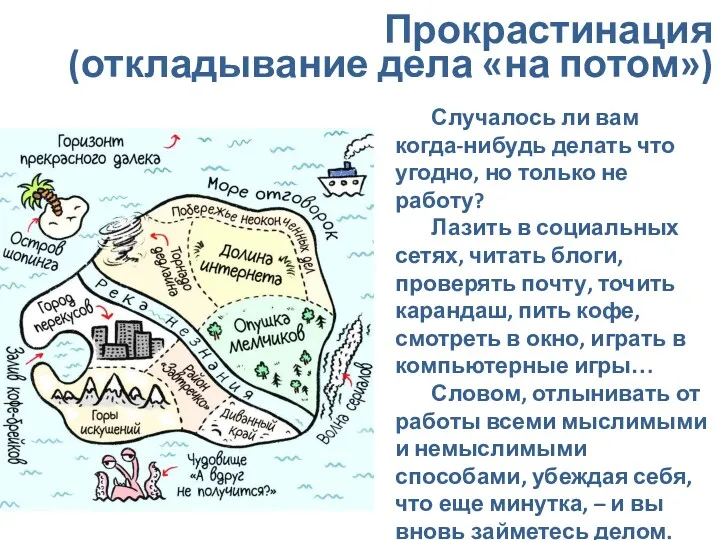 Прокрастинация. Откладывание дела на потом
Прокрастинация. Откладывание дела на потом Сценарий родительского собрания Россия без жестокости к детям
Сценарий родительского собрания Россия без жестокости к детям Основы психологических знаний в практике бизнеса и делового общения
Основы психологических знаний в практике бизнеса и делового общения Воздействие рекламы на сознание ребенка
Воздействие рекламы на сознание ребенка Агрессивное поведение у детей
Агрессивное поведение у детей Психолого-педагогические проблемы профессионального консультрования
Психолого-педагогические проблемы профессионального консультрования Родительские директивы.
Родительские директивы. Внушение народу определённых чувств и мыслей средствами искусства
Внушение народу определённых чувств и мыслей средствами искусства Деятельность педагога по созданию благоприятного психологического климата в коллективе младших школьников
Деятельность педагога по созданию благоприятного психологического климата в коллективе младших школьников Основы психологического анализа конфликтов
Основы психологического анализа конфликтов