Содержание
- 2. CONTENTS Introduction Elements Communication Models
- 3. INTRODUCTION Communication is an exchange of facts, ideas, opinions or emotions by two or more persons
- 4. Effective Communication is to share meaning and understanding between the person sending the message and the
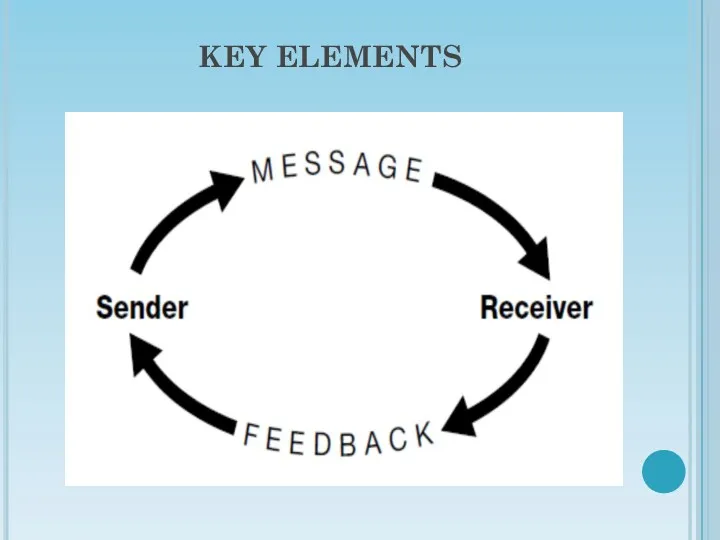
- 5. KEY ELEMENTS
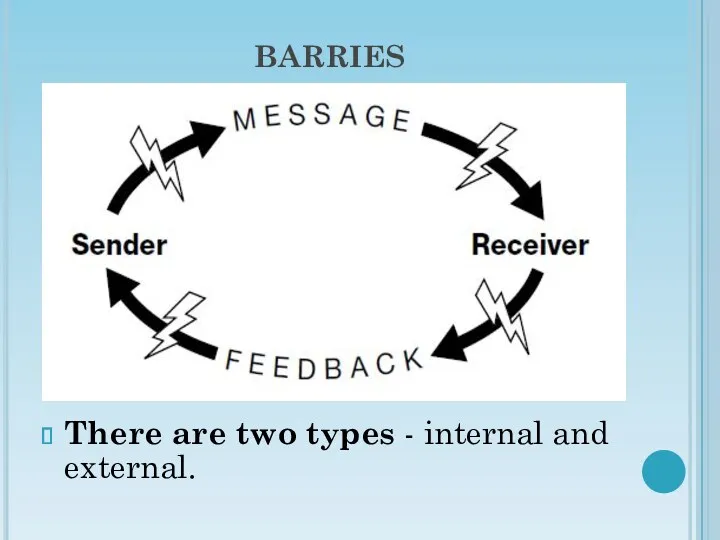
- 6. BARRIES There are two types - internal and external.
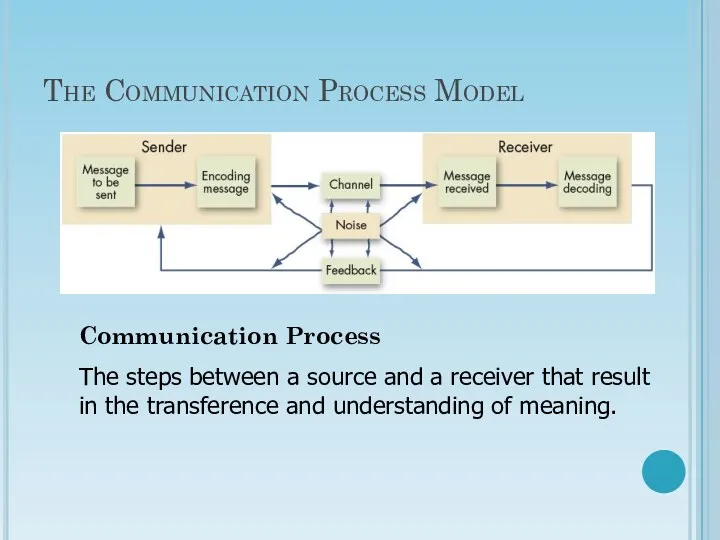
- 7. The Communication Process Model Communication Process The steps between a source and a receiver that result
- 8. Sender- Communication process starts with the sender, the person who wants to transmit the message to
- 9. Message- Messages can be verbal(spoken or written), non- verbal ( photograph, an illustration, a symbol, facial
- 10. Encoding- To change into a system of sending messages secretly or to represent in a simple
- 11. Channel- Medium or Channel used for conveying the encoded message to the receiver. The choice of
- 12. Receiver- Decodes the message on the basis of personal experience and characteristics. The sender should be
- 13. Decoding- The process of converting words or symbols of received message into ideas is called decoding.
- 14. Feedback- It is the reversal of communication process in which receiver expresses the response to the
- 15. Types of Communication A. Self-Action or One-Way Communication: In one –way communication , there is no
- 16. Types of Communication B. Interaction or Two-Way Communication. This approach recognizes the role of the receiver
- 17. Types of Communication C. Transaction. This approach focuses on meaning and sharing by accounting for all
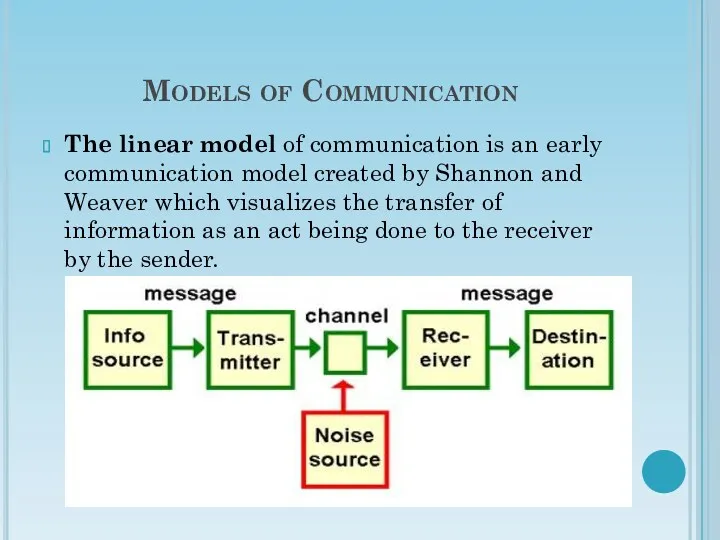
- 18. Models of Communication The linear model of communication is an early communication model created by Shannon
- 19. Linear Model of Communication Understanding several key terms is important in order to follow the model.
- 20. Advantages and Problems of Linear Model This linear model is great for electronic media, such as
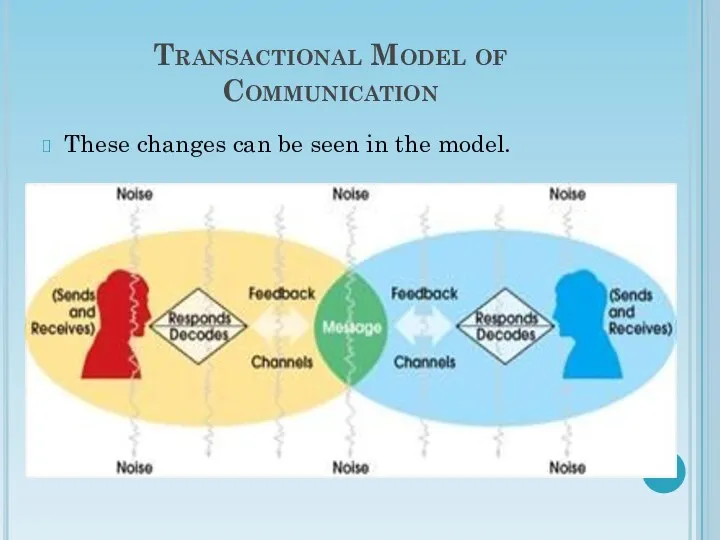
- 21. Transactional Model of Communication The transactional model, unlike the linear, recognizes that communication is a simultaneous
- 22. Transactional Model of Communication These changes can be seen in the model.
- 23. Transactional Model of Communication Another change you will notice in the transactional model is the overlap
- 24. Transactional Model of Communication In the linear model, noise is solely external noise; for example, loud
- 26. Скачать презентацию


















 Воспитание культуры радости как одна из задач позитивной социализации дошкольников
Воспитание культуры радости как одна из задач позитивной социализации дошкольников Психология (психологические основы реализации ФГОС)
Психология (психологические основы реализации ФГОС) Закономерности, динамика и механизмы психического развития личности в онтогенезе (продолжение)
Закономерности, динамика и механизмы психического развития личности в онтогенезе (продолжение) Введение в чакрамную систему.Рабочая тетрадь 5 дня
Введение в чакрамную систему.Рабочая тетрадь 5 дня Технология проведения тренинга социально-психологической безопасности студентов
Технология проведения тренинга социально-психологической безопасности студентов Теоретические аспекты психологической готовности детей с ОВЗ к школьному обучению
Теоретические аспекты психологической готовности детей с ОВЗ к школьному обучению Принципы здоровьясбережения.
Принципы здоровьясбережения. Темперамент и профессия. Определение темперамента. Урок 2
Темперамент и профессия. Определение темперамента. Урок 2 Герман Эббингауз. Монография О памяти
Герман Эббингауз. Монография О памяти Особенности сиблинговых отношений
Особенности сиблинговых отношений Здоровье ваших детей изначально является вашей зоной ответственности
Здоровье ваших детей изначально является вашей зоной ответственности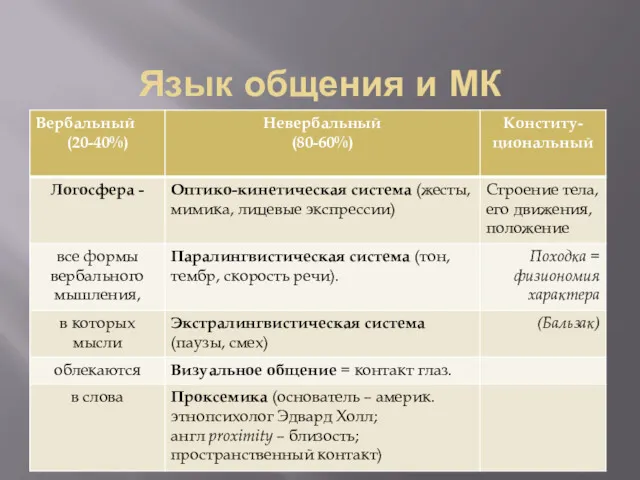 Язык общения и МК
Язык общения и МК Общение и коммуникация
Общение и коммуникация Lecture: Impression Formation & Interpersonal Perception
Lecture: Impression Formation & Interpersonal Perception Вербальное и невербальное общение: ключи к вашему успеху
Вербальное и невербальное общение: ключи к вашему успеху Способности и прирожденные условия развития способностей
Способности и прирожденные условия развития способностей Психологическое строение индивидуальной деятельности (по А.Н.Леонтьеву)
Психологическое строение индивидуальной деятельности (по А.Н.Леонтьеву) Проблема самосознания в психологии
Проблема самосознания в психологии Школьная служба примирения
Школьная служба примирения Критерии отбора актуальных проблем теоретической и практической психологии
Критерии отбора актуальных проблем теоретической и практической психологии Психология развития личности
Психология развития личности Коррекция страхов у детей с аутизмом
Коррекция страхов у детей с аутизмом Презентация к занятию по этике и психологии семейных отношений 10кл
Презентация к занятию по этике и психологии семейных отношений 10кл Тело чувств
Тело чувств Теоретические основы психологии горя
Теоретические основы психологии горя Психологическая подготовка к экзаменам
Психологическая подготовка к экзаменам Теория перспектив. Д.Канеман -4
Теория перспектив. Д.Канеман -4 Проблемы девиантного поведения детей и подростков в системе образования
Проблемы девиантного поведения детей и подростков в системе образования