Содержание
- 2. CONTENTS
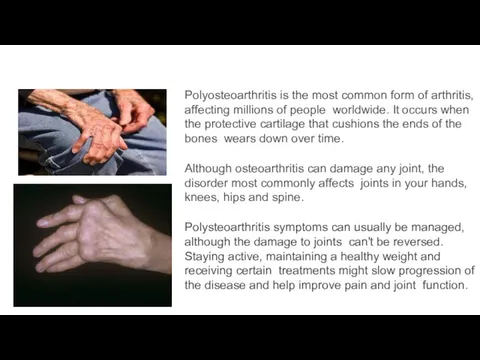
- 3. Polyosteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis, affecting millions of people worldwide. It occurs when
- 4. Polyosteoarthritis is a term used when five or more joints are affected with joint pain. There
- 5. Causes 1 2 3 4 5 6
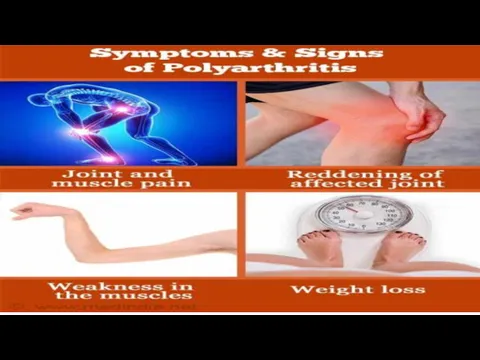
- 6. CLINICAL FEATURES Pain. Affected joints of patient hurt during or after movement. Stiffness. patient Joint stiffness
- 7. PART 01 REPAIR OF SHOUIDER AND NECK The user can perform the presentation on a projector
- 8. Biochemical changes observed in the polyosteoarthritic articular cartilage It is generally believed that degeneration of cartilage
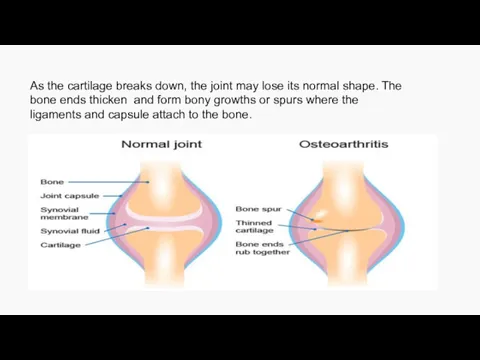
- 9. As the cartilage breaks down, the joint may lose its normal shape. The bone ends thicken
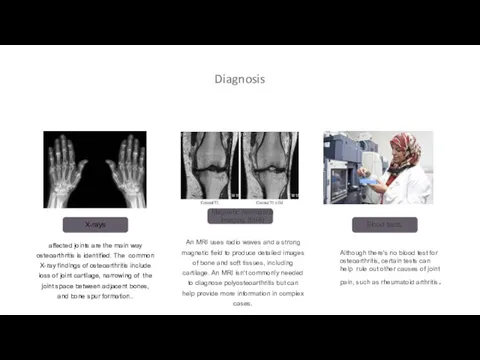
- 10. Diagnosis affected joints are the main way osteoarthritis is identified. The common X-ray findings of osteoarthritis
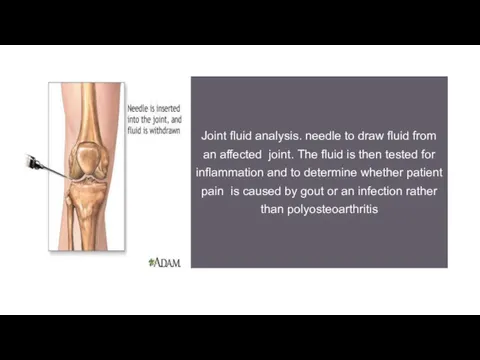
- 11. Joint fluid analysis. needle to draw fluid from an affected joint. The fluid is then tested
- 12. Treatment Medications that can help relieve polyosteoarthritis symptoms, primarily pain, include: Acetaminophen. Acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) has
- 13. Therapy Physical therapy. patient should exercise to strengthen the muscles around their joint, increase flexibility and
- 14. Surgery Lubrication injections. Injections of hyaluronic acid might relieve pain by providing some cushioning in your
- 15. Prevention Keep a healthy body weight. Extra weight puts stress on your joints. ... Control your
- 16. Prognosis The prognosis for osteoarthritis patients depends on which joints are affected and the level of
- 17. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/osteoarthritis/diagnosis- treatment/drc-20351930 https://www.aafp.org/afp/2012/0101/p49.html https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osteoarthritis References
- 19. Скачать презентацию











 Особенности ВНД человека. Познавательные процессы
Особенности ВНД человека. Познавательные процессы Технологии проектирования информационных систем
Технологии проектирования информационных систем Национальный проект Производительность труда и поддержка занятости
Национальный проект Производительность труда и поддержка занятости Методическая разработка занятия с применением современных образовательных технологий. Тема: Коллективная работа: Улица нашего города.
Методическая разработка занятия с применением современных образовательных технологий. Тема: Коллективная работа: Улица нашего города. Умножение десятичной дроби на обыкновенную
Умножение десятичной дроби на обыкновенную Наладка технологического оборудования на производстве
Наладка технологического оборудования на производстве Заболевания кишечника. Болезнь Крона. Язвенный колит
Заболевания кишечника. Болезнь Крона. Язвенный колит Организация самостоятельной работы обучающихся на уроках химии в 9 классе
Организация самостоятельной работы обучающихся на уроках химии в 9 классе Транспортное средство на электродинамической подвеске
Транспортное средство на электродинамической подвеске Фізика у професіях
Фізика у професіях классный час Жевательная резинка. Польза или вред презентация
классный час Жевательная резинка. Польза или вред презентация Углерод
Углерод Полный факторный эксперимент. Электрическая схема стенда
Полный факторный эксперимент. Электрическая схема стенда Презентация к уроку природоведения 5 класс Лекарственные растения
Презентация к уроку природоведения 5 класс Лекарственные растения Проект Олимпийская неделя 2014 г.
Проект Олимпийская неделя 2014 г. VSA Option. Курс по торговле Бинарными опционами
VSA Option. Курс по торговле Бинарными опционами Экономическая целесообразность покупки новых компьютеров и улучшения старых для курсов 3D моделирования
Экономическая целесообразность покупки новых компьютеров и улучшения старых для курсов 3D моделирования Я то, что я ем
Я то, что я ем Восприятие. Мышление
Восприятие. Мышление Волшебные свойства бумаги
Волшебные свойства бумаги презентация к уроку Углеводороды и их природные источники.Природный газ для 10 класса
презентация к уроку Углеводороды и их природные источники.Природный газ для 10 класса 16+
16+ Методическая активность
Методическая активность Технологическая схема оборудования ГРП. Требования к помещениям ГРП
Технологическая схема оборудования ГРП. Требования к помещениям ГРП Quel temps fait-il? Leçon 8
Quel temps fait-il? Leçon 8 Иллюстрированный словарь архитектурных терминов
Иллюстрированный словарь архитектурных терминов Раздельный сбор мусора (1)
Раздельный сбор мусора (1) Топонимы Пензенской области
Топонимы Пензенской области