Содержание
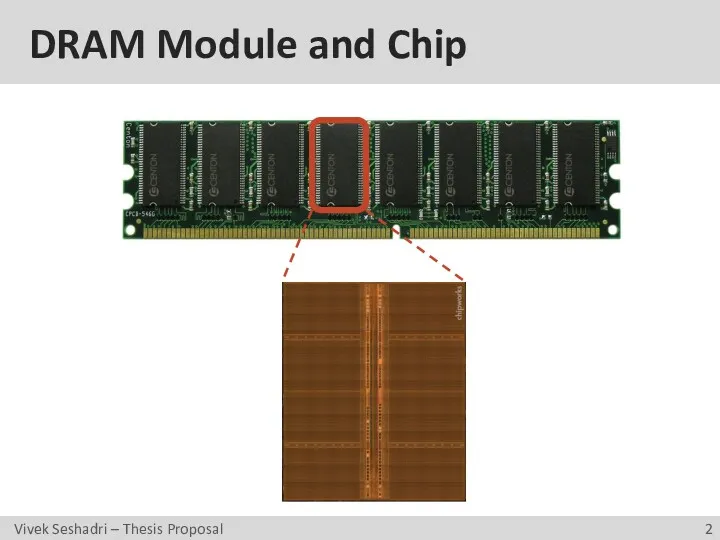
- 2. DRAM Module and Chip
- 3. Goals Cost Latency Bandwidth Parallelism Power Energy
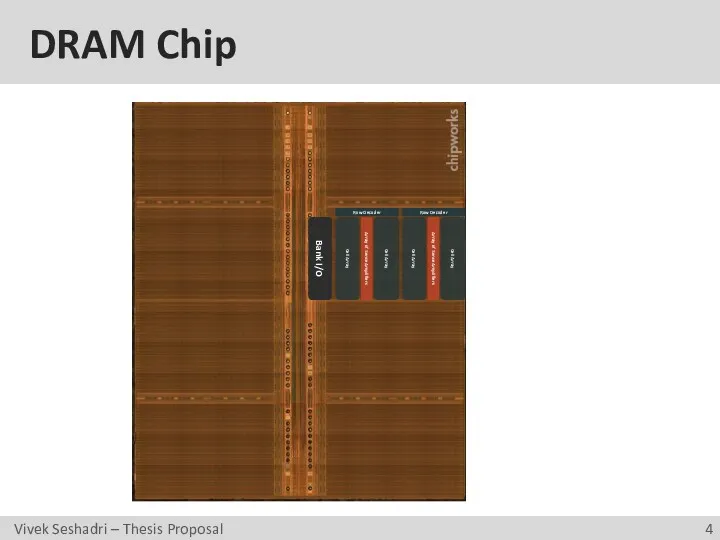
- 4. DRAM Chip
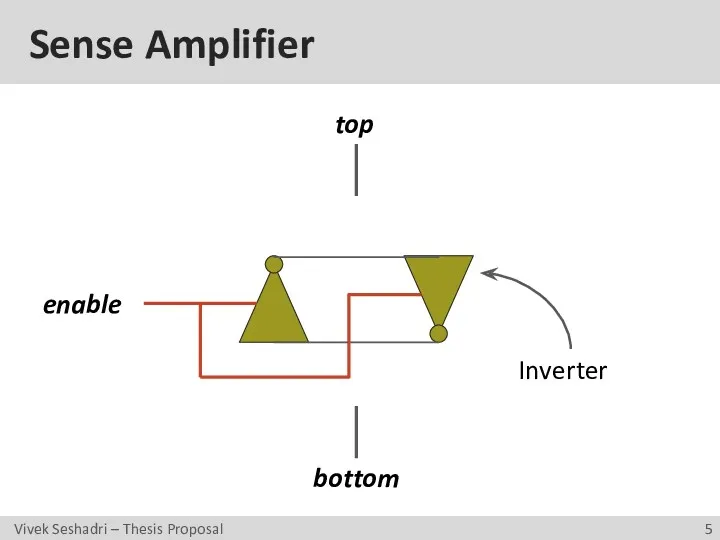
- 5. Sense Amplifier enable top bottom Inverter
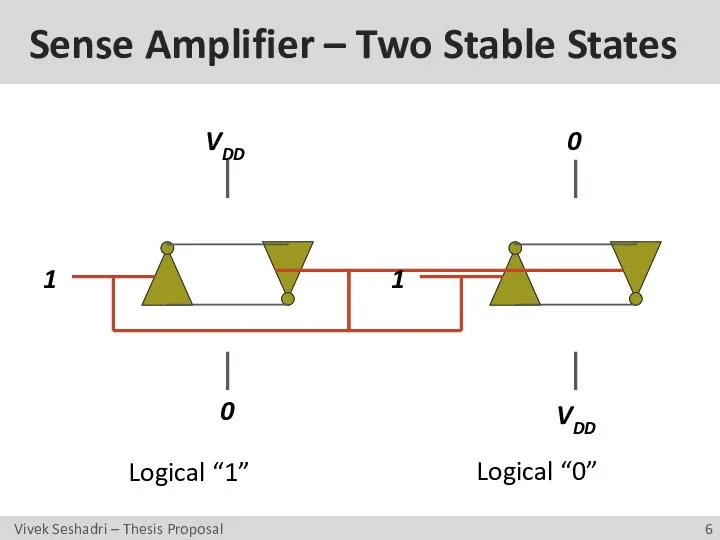
- 6. Sense Amplifier – Two Stable States 1 1 0 0 VDD VDD Logical “1” Logical “0”
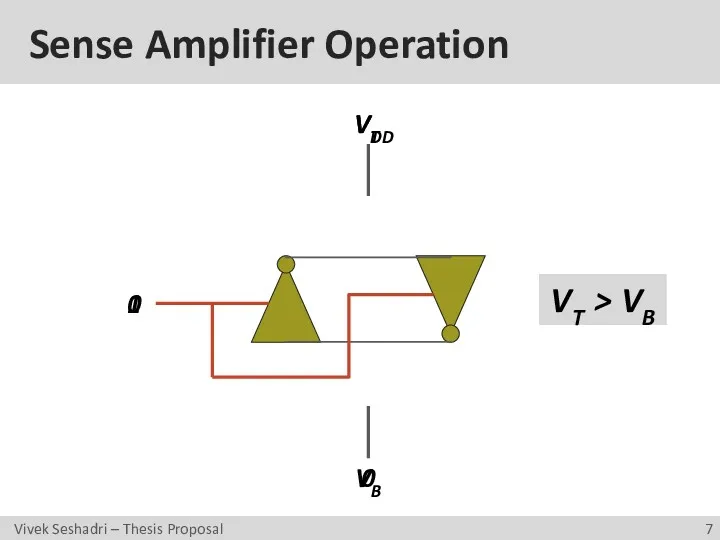
- 7. Sense Amplifier Operation 0 VT VB VT > VB 1 0 VDD
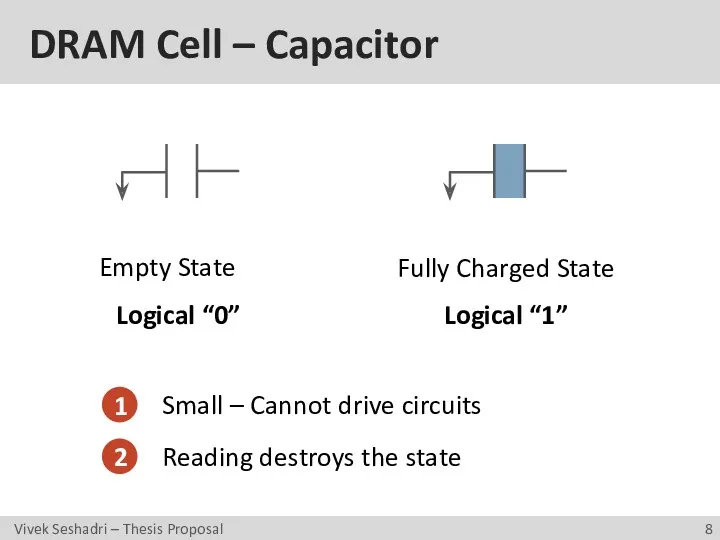
- 8. DRAM Cell – Capacitor Empty State Fully Charged State Logical “0” Logical “1” 1 2 Small
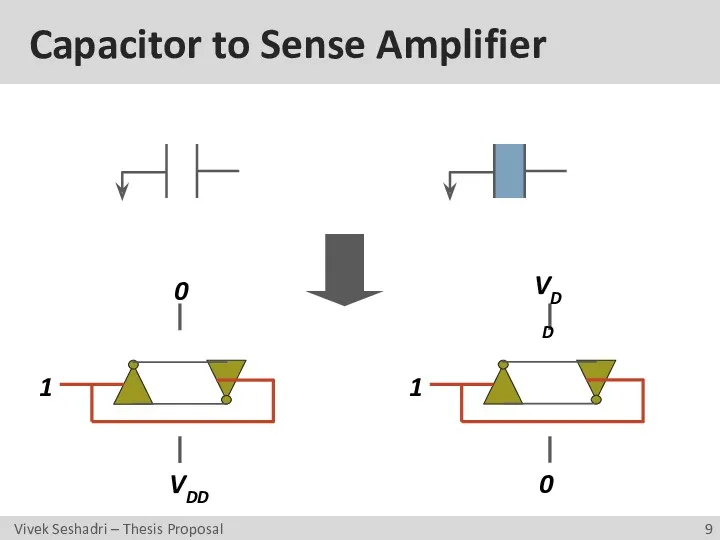
- 9. Capacitor to Sense Amplifier
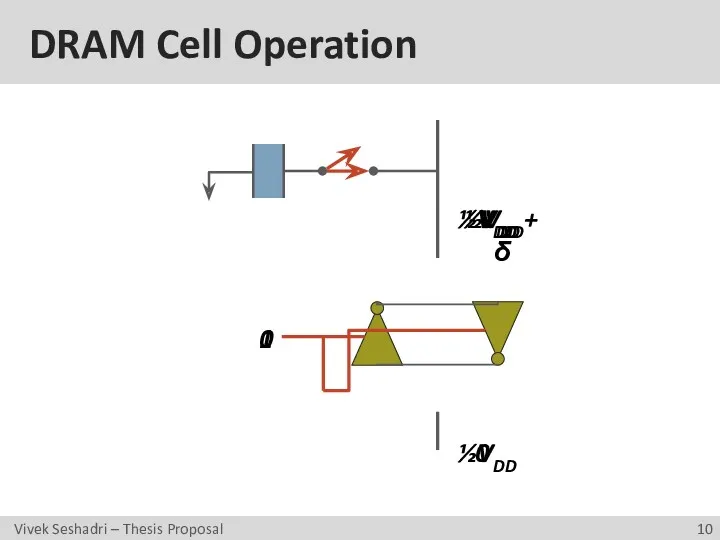
- 10. DRAM Cell Operation ½VDD ½VDD 0 1 0 VDD ½VDD+δ
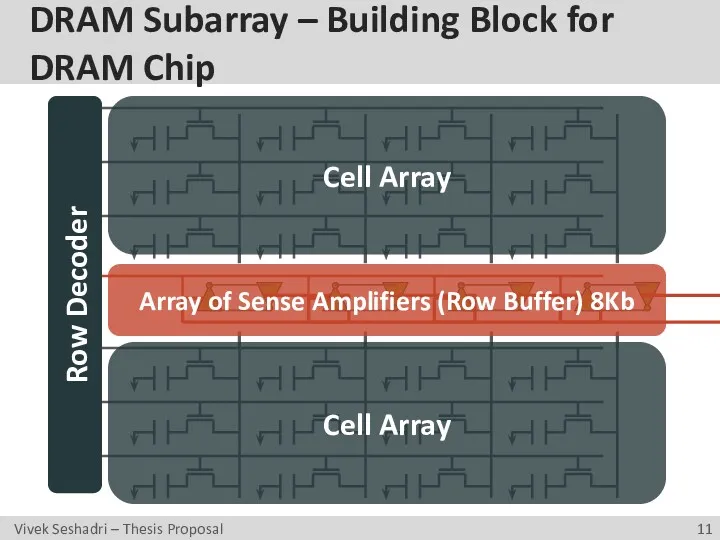
- 11. DRAM Subarray – Building Block for DRAM Chip Row Decoder Cell Array Cell Array Array of
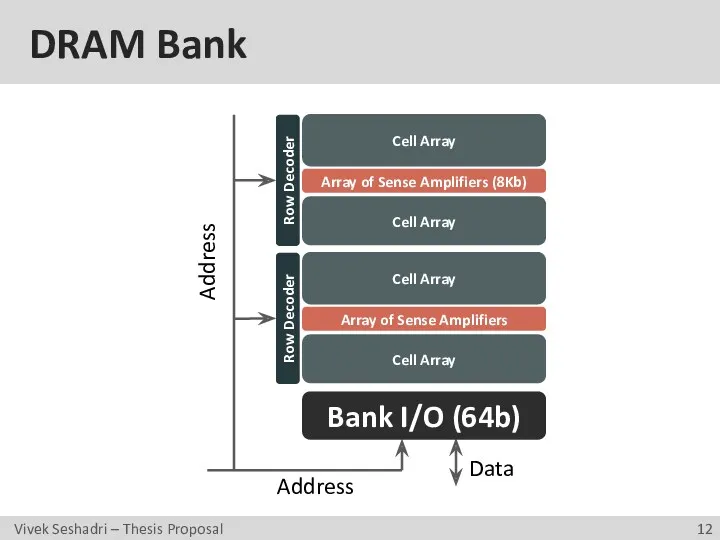
- 12. DRAM Bank Bank I/O (64b) Address Address Data
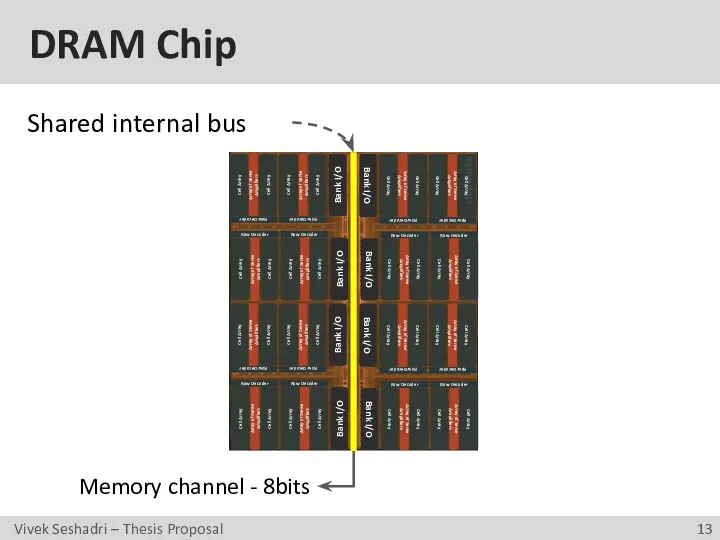
- 13. DRAM Chip Shared internal bus Memory channel - 8bits
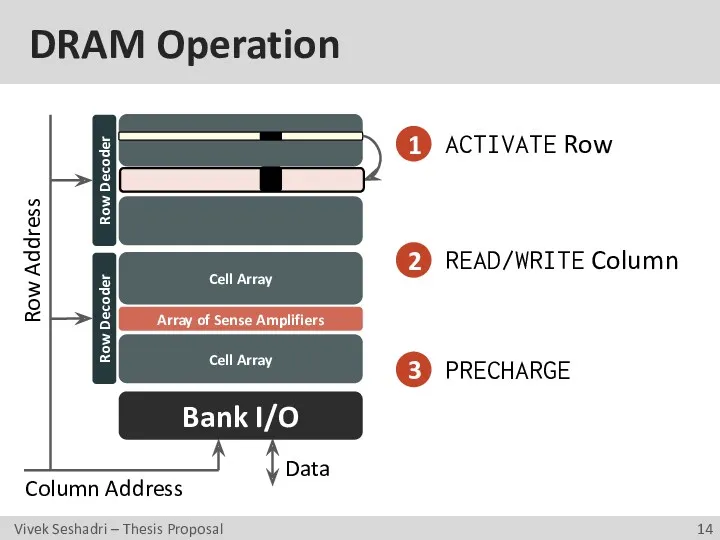
- 14. DRAM Operation Bank I/O Data 1 2 ACTIVATE Row READ/WRITE Column 3 PRECHARGE Row Address Column
- 15. RowClone Fast and Energy-Efficient In-DRAM Bulk Data Copy and Initialization Y. Kim, C. Fallin, D. Lee,
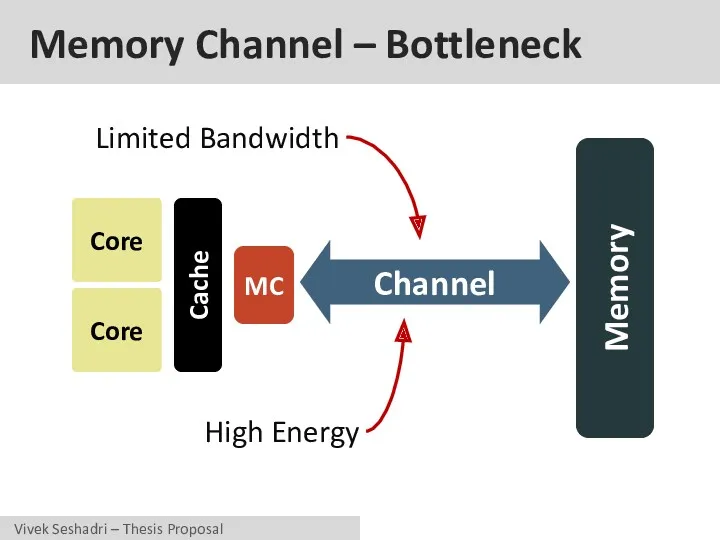
- 16. Memory Channel – Bottleneck Core Core Cache MC Memory Channel Limited Bandwidth High Energy
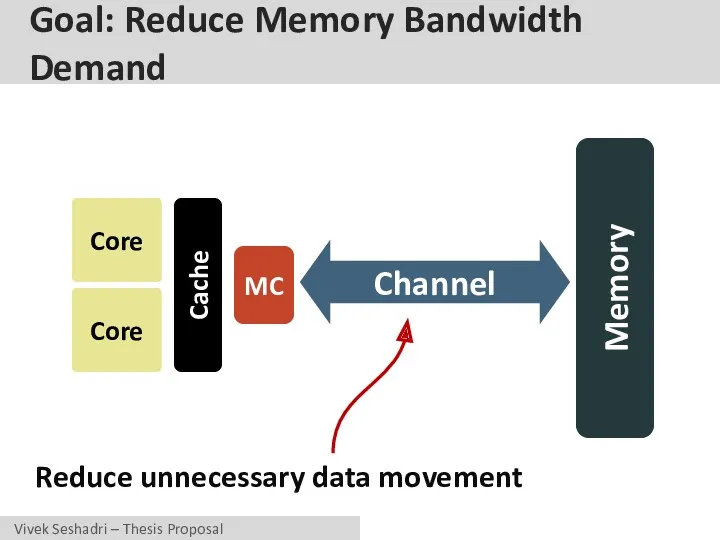
- 17. Goal: Reduce Memory Bandwidth Demand Core Core Cache MC Memory Channel Reduce unnecessary data movement
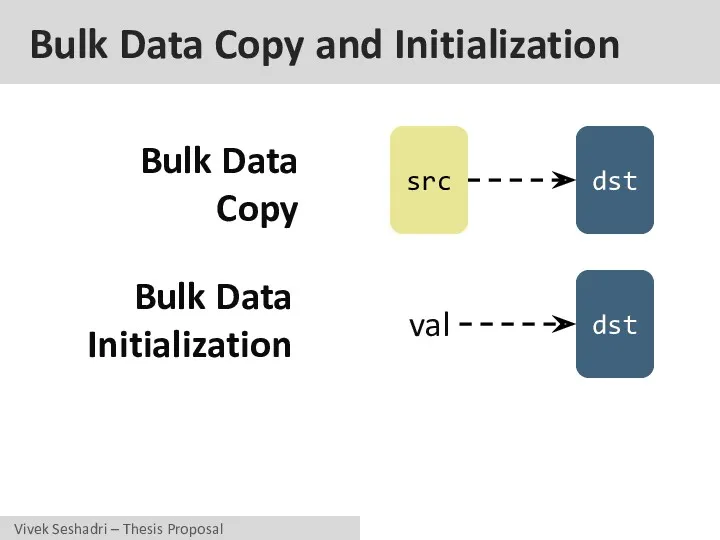
- 18. Bulk Data Copy and Initialization Bulk Data Copy Bulk Data Initialization src dst dst val
- 19. Bulk Data Copy and Initialization Bulk Data Copy Bulk Data Initialization src dst dst val
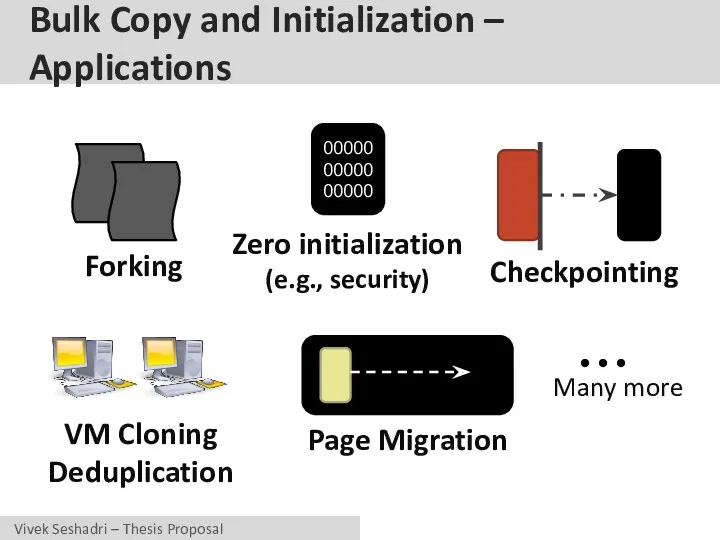
- 20. Bulk Copy and Initialization – Applications Many more
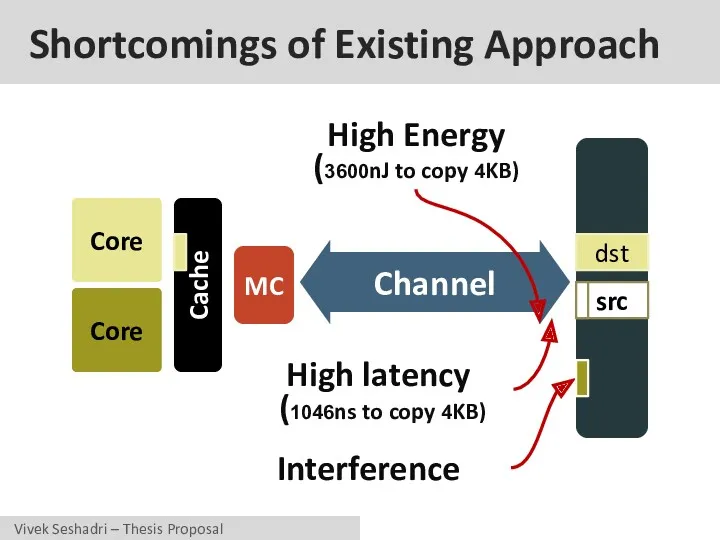
- 21. Shortcomings of Existing Approach Core Core Cache MC Channel src dst High latency (1046ns to copy
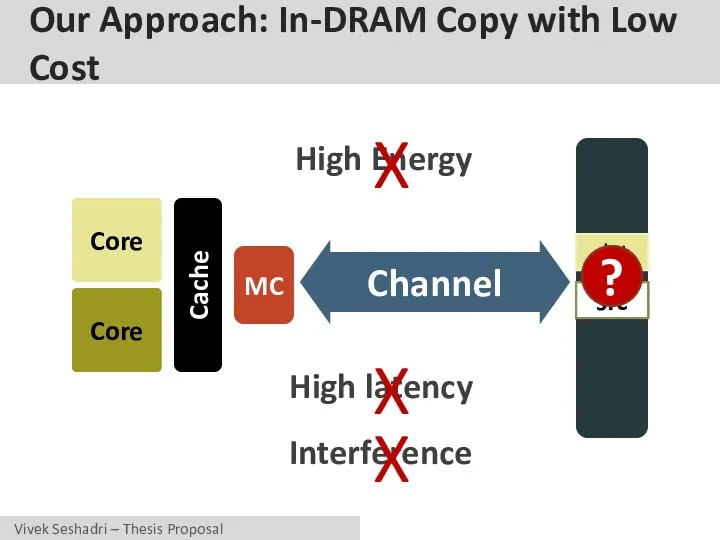
- 22. Our Approach: In-DRAM Copy with Low Cost Core Core Cache MC Channel dst High latency Interference
- 23. RowClone: In-DRAM Copy
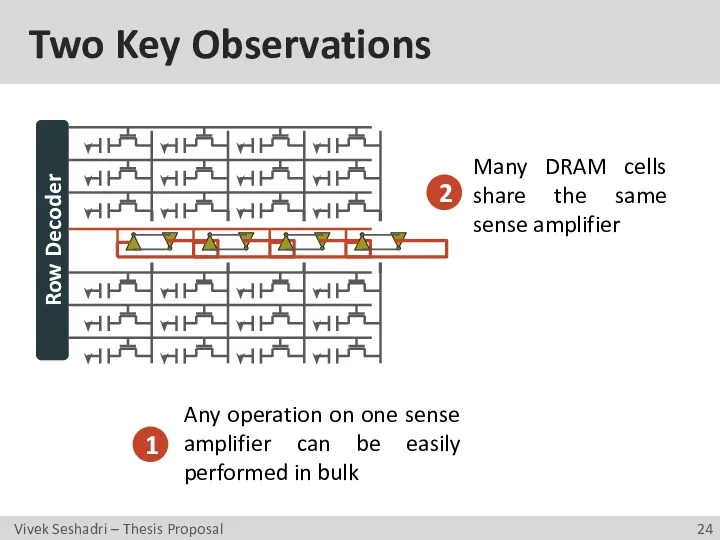
- 24. Two Key Observations Any operation on one sense amplifier can be easily performed in bulk Many
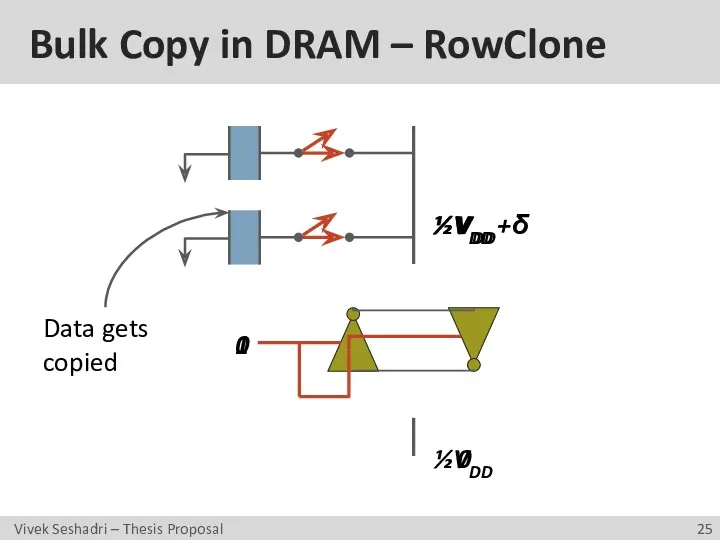
- 25. Bulk Copy in DRAM – RowClone ½VDD ½VDD 0 1 0 VDD ½VDD +δ Data gets
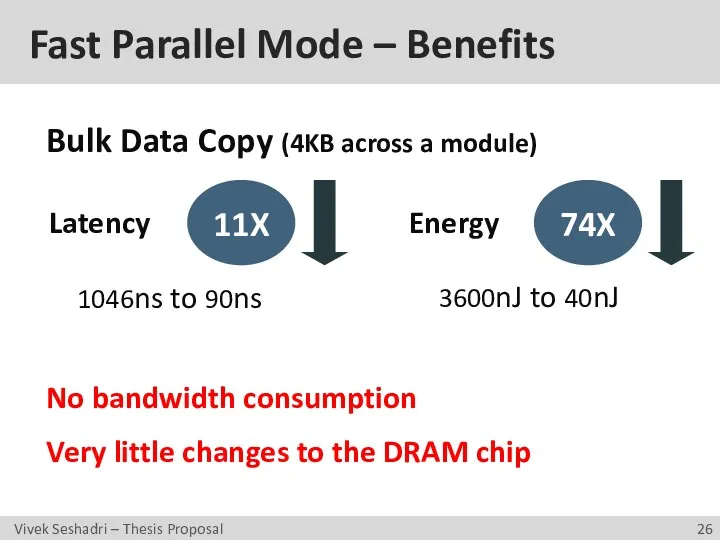
- 26. Fast Parallel Mode – Benefits Latency Energy Bulk Data Copy (4KB across a module) 1046ns to
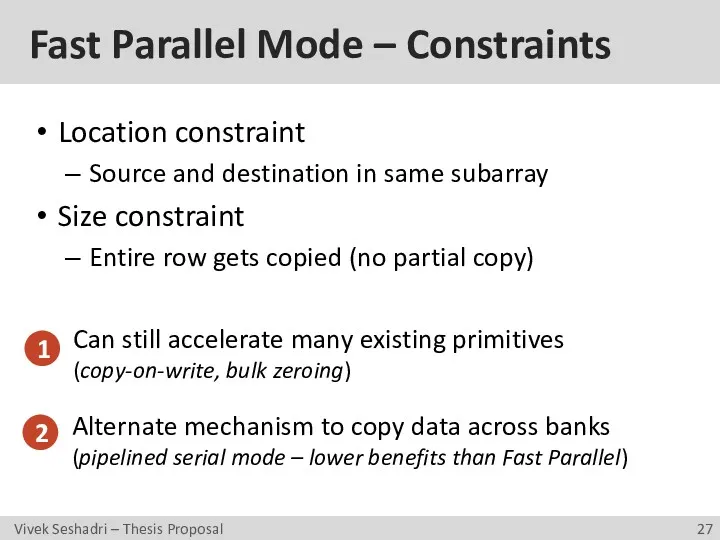
- 27. Fast Parallel Mode – Constraints Location constraint Source and destination in same subarray Size constraint Entire
- 28. End-to-end System Design Software interface memcpy and meminit instructions Managing cache coherence Use existing DMA support!
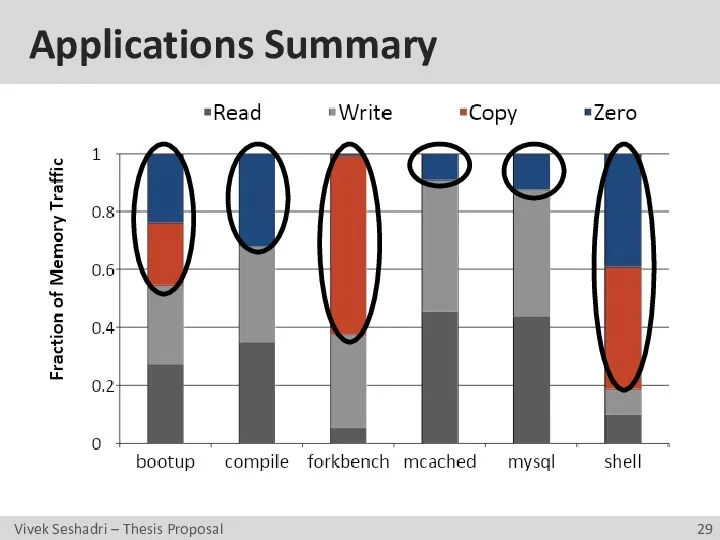
- 29. Applications Summary
- 31. Скачать презентацию



 Адміністративне право. Курс лекцій
Адміністративне право. Курс лекцій Смотр знаний Генетическая связь между основными классами неорганических соединений.
Смотр знаний Генетическая связь между основными классами неорганических соединений. Экзистенциализм
Экзистенциализм Портфолио класса
Портфолио класса Oil and gas industry segments. Part 1
Oil and gas industry segments. Part 1 Технологии презентаций
Технологии презентаций Тригонометрические выражения
Тригонометрические выражения Урок-игра Углеводороды
Урок-игра Углеводороды Урок-38
Урок-38 Евгений Онегин. Автор и его образ. Лирические отступления
Евгений Онегин. Автор и его образ. Лирические отступления Задачи на проценты. Подготовка к ЕГЭ. Задания В1
Задачи на проценты. Подготовка к ЕГЭ. Задания В1 Описание Сморгонского района
Описание Сморгонского района Обыкновенные и десятичные дроби
Обыкновенные и десятичные дроби Кубань - Любимый уголок земли.
Кубань - Любимый уголок земли. Структура строительного комплекса. Типы предприятий строительных изделий и конструкций, производственная структура предприятий
Структура строительного комплекса. Типы предприятий строительных изделий и конструкций, производственная структура предприятий What day is it today?
What day is it today? Медико-биологические и социальные основы здоровья
Медико-биологические и социальные основы здоровья Материалы внешней отделки в архитектуре музеев
Материалы внешней отделки в архитектуре музеев Основные изменения законодательства Российской Федерации по налогу на имущество физических лиц (2015)
Основные изменения законодательства Российской Федерации по налогу на имущество физических лиц (2015) Конкурс чтецов
Конкурс чтецов Конструкции плоских перекрытий. Классификация
Конструкции плоских перекрытий. Классификация Хирургиялық деонтология
Хирургиялық деонтология Органы растений
Органы растений Стабилизация нефти. Этапы сбора и подготовки нефти на промыслах
Стабилизация нефти. Этапы сбора и подготовки нефти на промыслах Военные реформы в истории Российского государства: опыт и уроки
Военные реформы в истории Российского государства: опыт и уроки Снегири на ветках.
Снегири на ветках. Агрессивные дети
Агрессивные дети Рабочая тетрадь
Рабочая тетрадь