Содержание
- 2. Objectives To understand: The need and reason for pharmaceutical air handling systems The technical requirements for
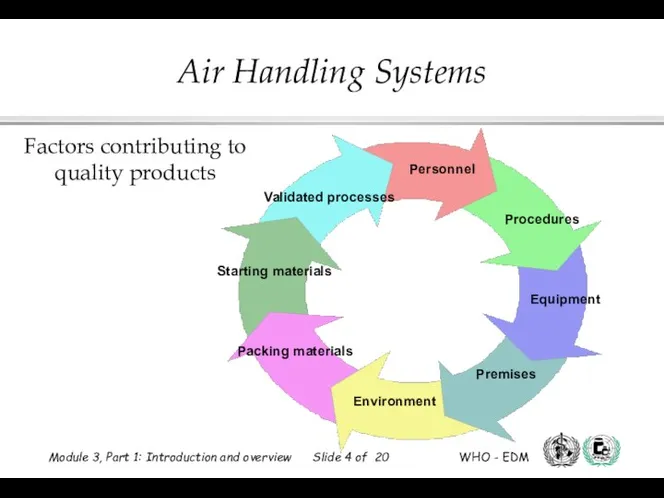
- 3. Factors that contribute to quality products: Starting materials and packaging materials Validated processes Personnel Procedures Equipment
- 4. Factors contributing to quality products
- 5. The manufacturing environment is critical for product quality Light Temperature Humidity Air movement Microbial contamination Particulate
- 6. What are contaminants ? Contaminants are Products or substances other than product manufactured Foreign products Particulate
- 7. Cross-Contamination (1) What is Cross-Contamination ? Definition of Cross-Contamination: Contamination of a starting material, intermediate product,
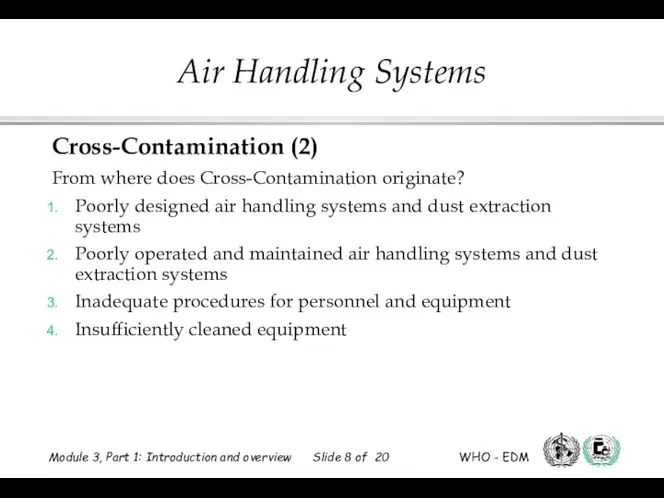
- 8. Cross-Contamination (2) From where does Cross-Contamination originate? Poorly designed air handling systems and dust extraction systems
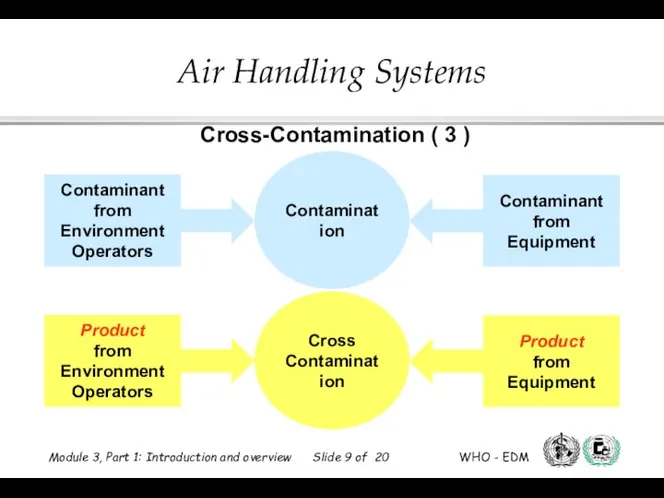
- 9. Cross-Contamination ( 3 )
- 10. Cross-Contamination (4) Cross-contamination can be minimized by: Personnel procedures Adequate premises Use of closed production systems
- 11. Level of Protection Concept Defines environmental requirements Helps prevent contamination and cross-contamination Allows production under optimal
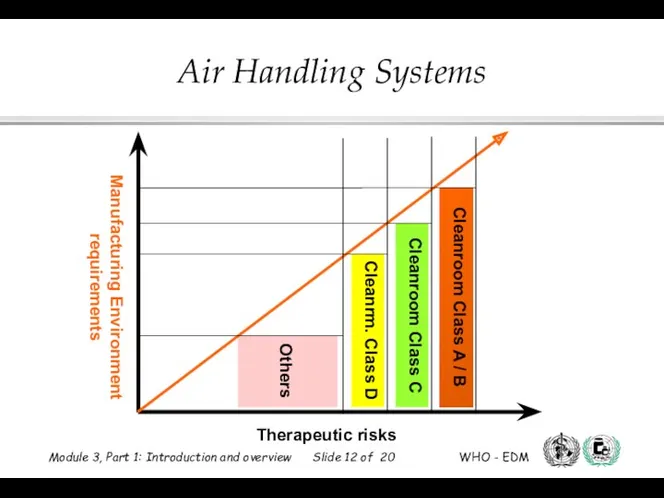
- 12. Therapeutic risks Manufacturing Environment requirements Cleanroom Class A / B Cleanroom Class C Cleanrm. Class D
- 13. Levels of Protection Parameters to be defined: Air cleanliness requirements (filters type and position, air changes,
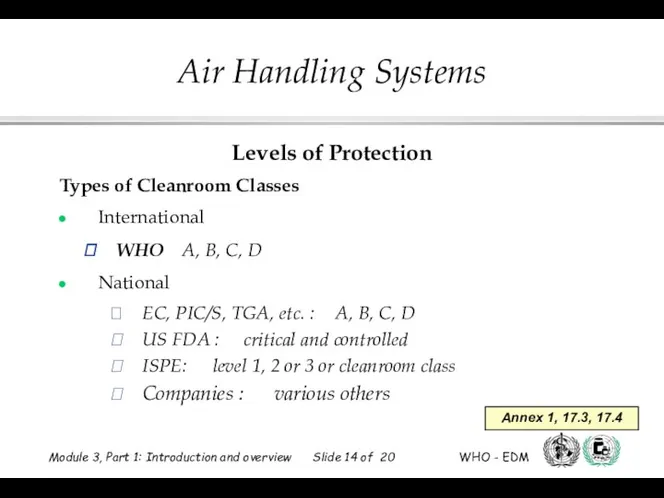
- 14. Levels of Protection Types of Cleanroom Classes International WHO A, B, C, D National
- 15. Levels of Protection All operations within a pharmaceutical facilility must be correlated to well-defined cleanroom classes,
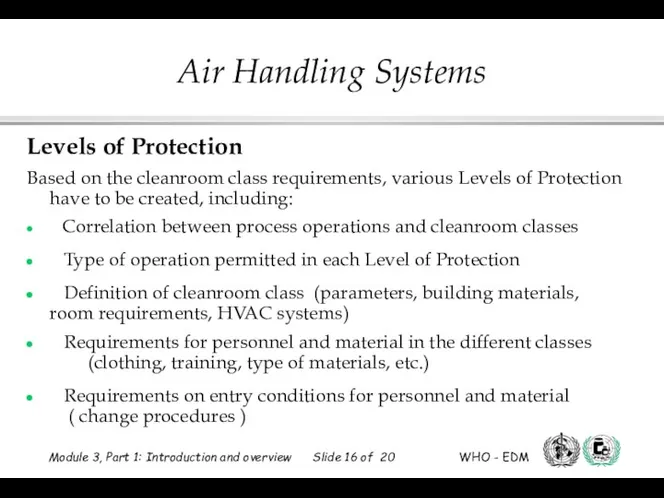
- 16. Levels of Protection Based on the cleanroom class requirements, various Levels of Protection have to be
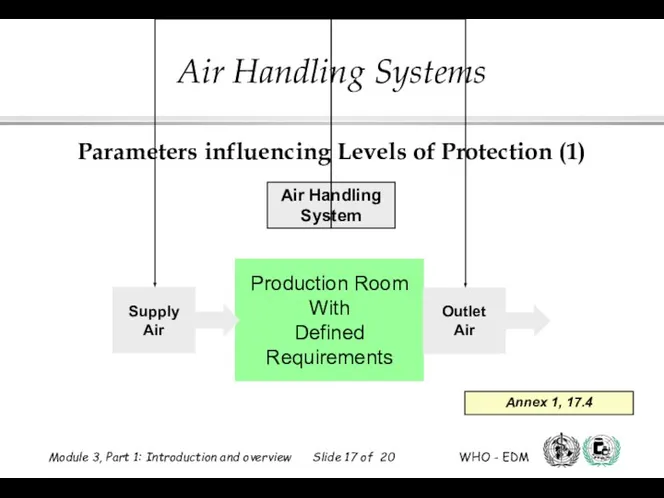
- 17. Parameters influencing Levels of Protection (1) Annex 1, 17.4
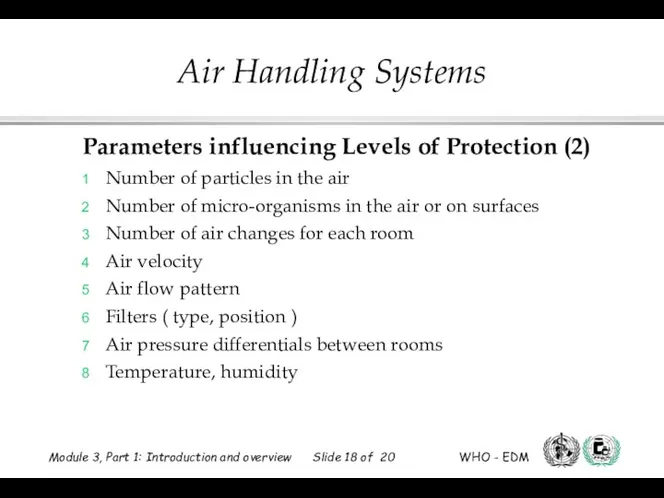
- 18. Parameters influencing Levels of Protection (2) Number of particles in the air Number of micro-organisms in
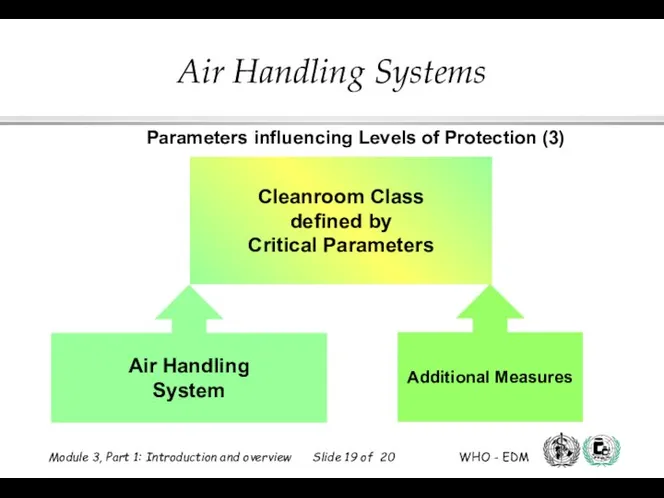
- 19. Cleanroom Class defined by Critical Parameters Air Handling System Additional Measures Parameters influencing Levels of Protection
- 21. Скачать презентацию









 Вакцинація. Найпоширеніші міфи
Вакцинація. Найпоширеніші міфи Космическое путешествие
Космическое путешествие Роль домашнего задания в самообразовании школьника
Роль домашнего задания в самообразовании школьника e0f2d-a27ace3f
e0f2d-a27ace3f Disneyland is a dream of each child! Welcome to disneyland!!!
Disneyland is a dream of each child! Welcome to disneyland!!! Функции управления
Функции управления Конфликт воспитатель-родитель. Причины возникновения и пути решения
Конфликт воспитатель-родитель. Причины возникновения и пути решения Достоинства и недостатки ГЭС
Достоинства и недостатки ГЭС Inventions that shook the world
Inventions that shook the world Духовная сфера общества. Подготовка к ЕГЭ
Духовная сфера общества. Подготовка к ЕГЭ Социальная структура общества. Социология
Социальная структура общества. Социология Масленица
Масленица Карта електроенергетика
Карта електроенергетика DVB-T2. Стандарт наземного цифрового телевизионного вещания второго поколения
DVB-T2. Стандарт наземного цифрового телевизионного вещания второго поколения Основные аспекты иммунопрофилактики инфекционных заболеваний
Основные аспекты иммунопрофилактики инфекционных заболеваний Жыпылықтаушы аритмиясы бар науқастардың өмір сүру сапасы
Жыпылықтаушы аритмиясы бар науқастардың өмір сүру сапасы Правила заполнения корректирующих форм cведений (раздел 6 расчета РСВ-1)
Правила заполнения корректирующих форм cведений (раздел 6 расчета РСВ-1) Презентация к уроку по теме: Дикие и домашние животные
Презентация к уроку по теме: Дикие и домашние животные Варианты системы обнаружения утечек межпромыслового нефтепровода УПСВ Северный Савинобор
Варианты системы обнаружения утечек межпромыслового нефтепровода УПСВ Северный Савинобор Награды Великой Отечественной войны
Награды Великой Отечественной войны Публицистический стиль речи
Публицистический стиль речи презентация на тему: Современный урок в свете внедрения ФГОС второго поколения
презентация на тему: Современный урок в свете внедрения ФГОС второго поколения Аффект. Виды аффектов
Аффект. Виды аффектов Описание и преобразование управляющих процессов. Сети Петри и их модификация
Описание и преобразование управляющих процессов. Сети Петри и их модификация Социально-экономические проблемы региона. Химическая и нефтехимическая промышленность Республики Татарстан
Социально-экономические проблемы региона. Химическая и нефтехимическая промышленность Республики Татарстан Возможность жизни на других планетах
Возможность жизни на других планетах Етика і деонтологія в професійній діяльності лікаря
Етика і деонтологія в професійній діяльності лікаря Эрнест Хемингуэй
Эрнест Хемингуэй