Содержание
- 2. 1. Introduction to EMI/EMC
- 3. EMI in the Sky On a flight from New York City’s La Guardia airport to Chicago’s
- 5. ESD on a PC A Workstation Support person was attending to a call regarding a PC
- 6. ESD on a Motor Vehicle A “Vehicle Safety Recall” was issued by a well-known motor vehicle
- 8. [Source: Electronics Australia]
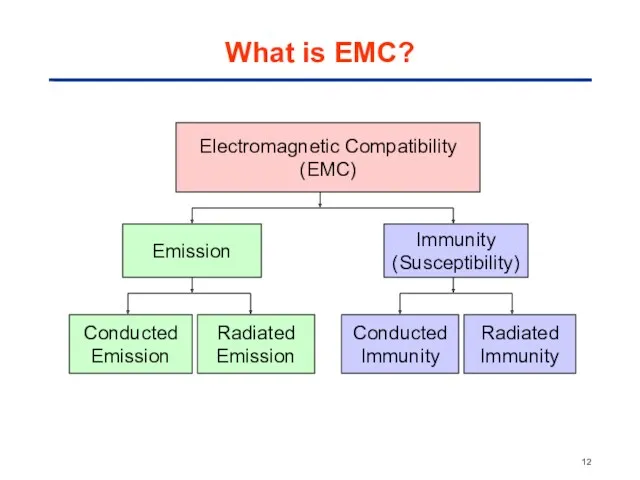
- 9. What is EMC? EMC = Electromagnetic compatibility Definition [IEC 61000-1-1] The ability of a device, unit
- 10. European EMC Directive 89/336/EEC, ... 92/31/EEC, ... 2004/108/EC* The electromagnetic disturbance generated by an apparatus does
- 11. Two Aspects to Consider Emission the ability to operate without interfering with others Immunity the ability
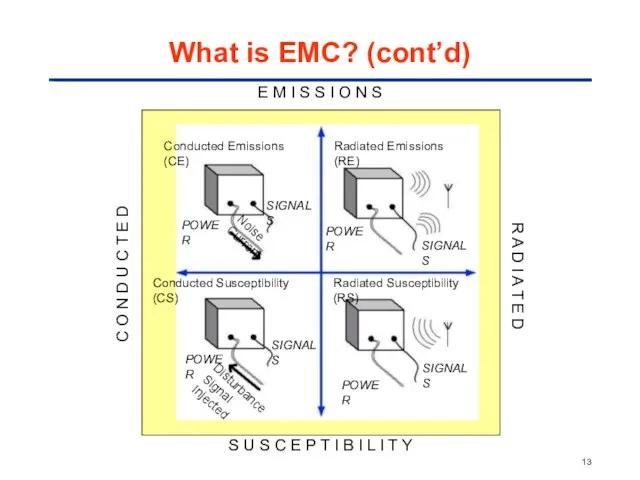
- 12. Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Emission Immunity (Susceptibility) Conducted Emission Radiated Emission Conducted Immunity Radiated Immunity What is
- 13. E M I S S I O N S S U S C E P T
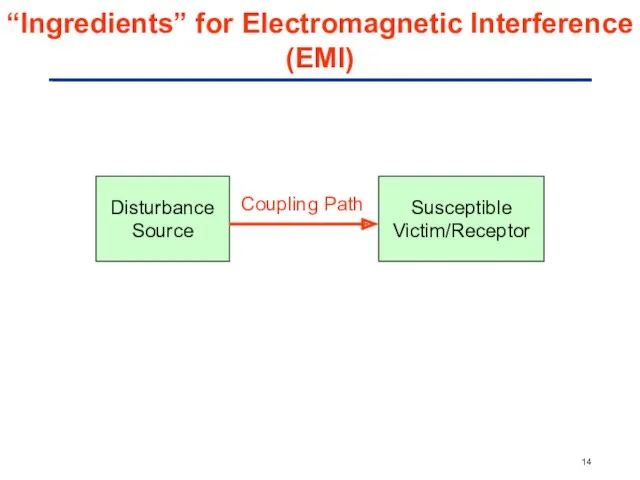
- 14. “Ingredients” for Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Disturbance Source Susceptible Victim/Receptor Coupling Path
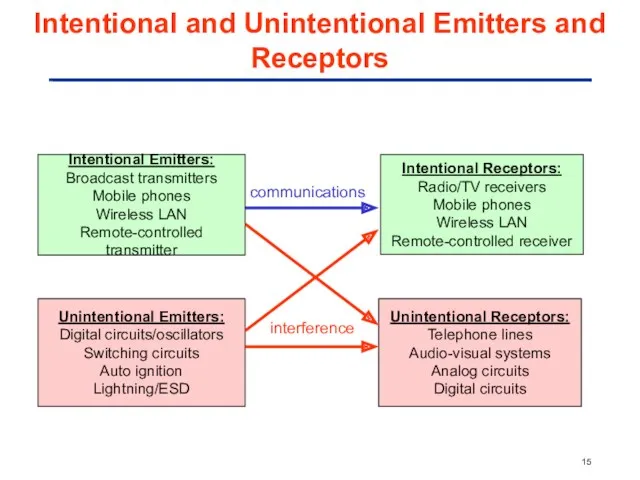
- 15. Intentional and Unintentional Emitters and Receptors Intentional Emitters: Broadcast transmitters Mobile phones Wireless LAN Remote-controlled transmitter
- 16. Lightning an example of a naturally occurring noise source Brisbane 19 May 2005 [Image Source: Wikipedia,
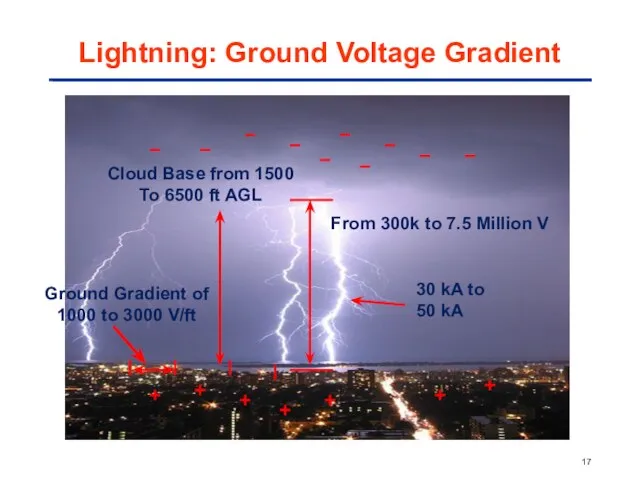
- 17. Lightning: Ground Voltage Gradient
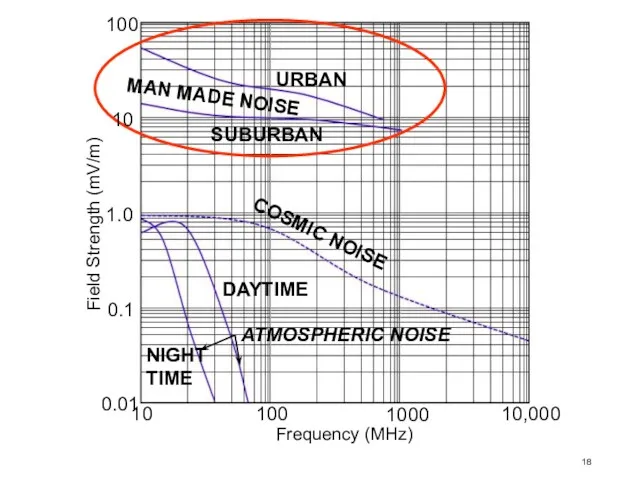
- 18. Field Strength (mV/m)
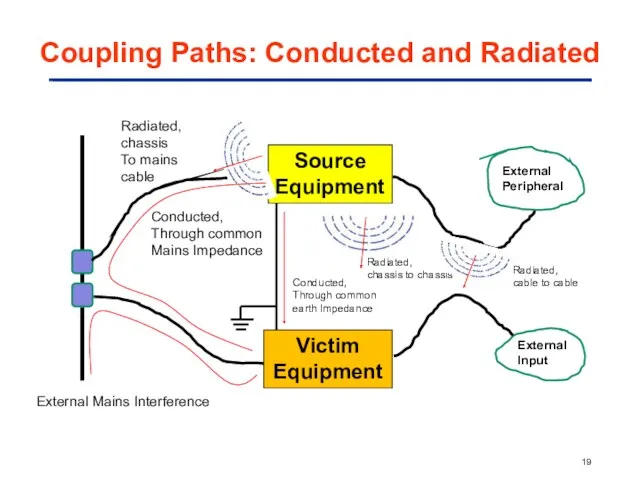
- 19. Coupling Paths: Conducted and Radiated
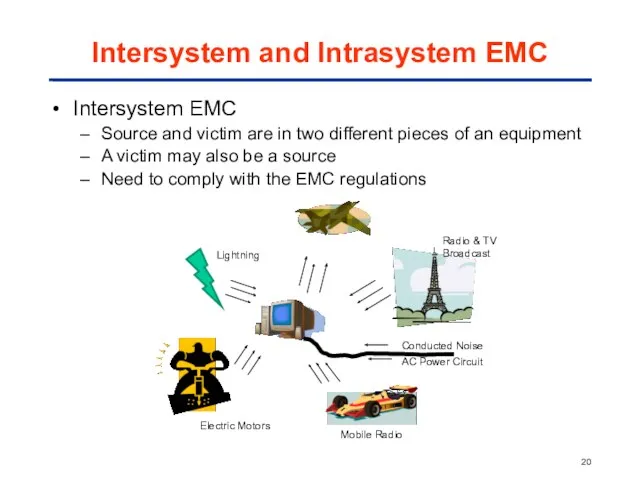
- 20. Intersystem and Intrasystem EMC Intersystem EMC Source and victim are in two different pieces of an
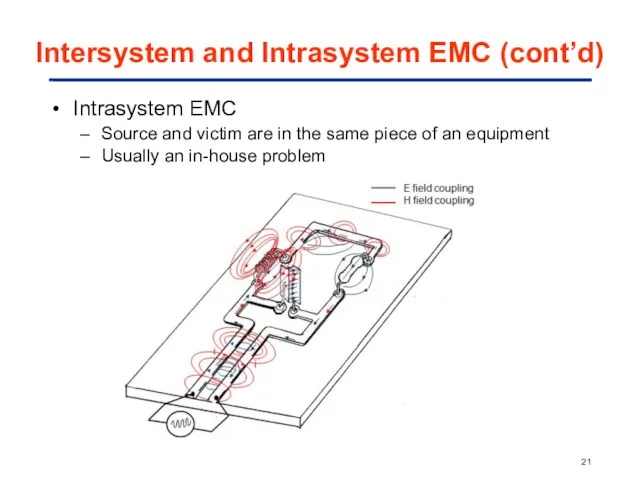
- 21. Intersystem and Intrasystem EMC (cont’d) Intrasystem EMC Source and victim are in the same piece of
- 22. EMI Mitigation Methods Separation in SPACE Separation in TIME Separation in FREQUENCY Application of the Design
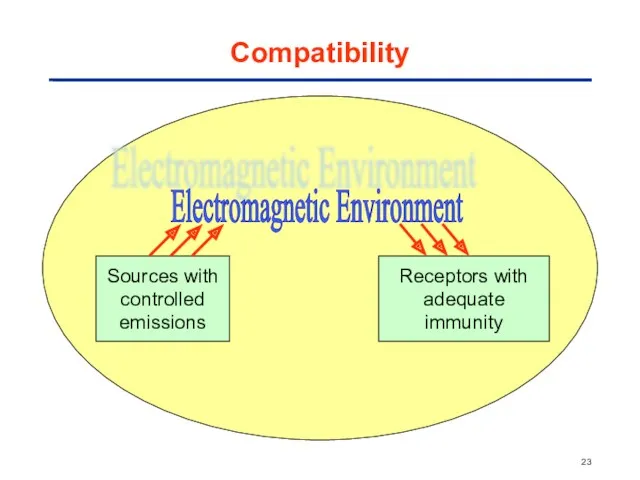
- 23. Compatibility Sources with controlled emissions Receptors with adequate immunity Electromagnetic Environment
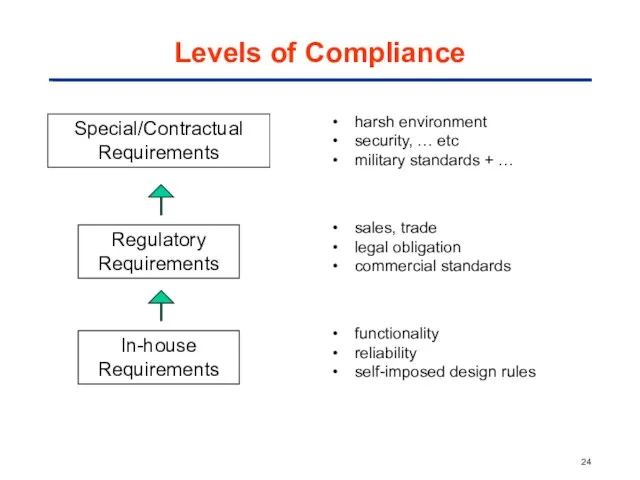
- 24. Levels of Compliance Special/Contractual Requirements Regulatory Requirements In-house Requirements harsh environment security, … etc military standards
- 25. Why Do We Need EMC Regulations? Safeguard the consumers Protect the environment Market forces International trade
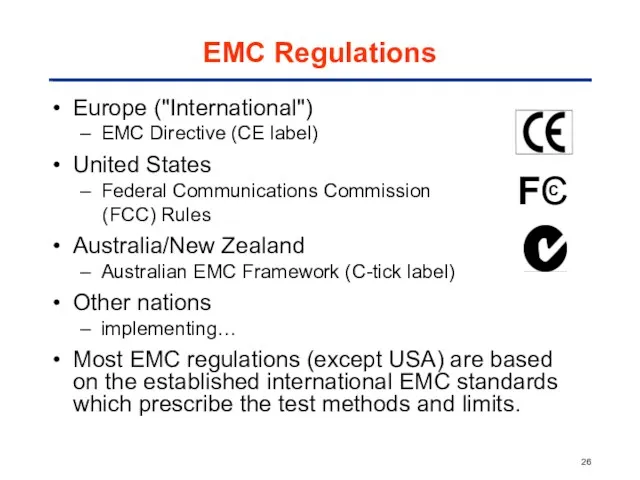
- 26. EMC Regulations Europe ("International") EMC Directive (CE label) United States Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Rules Australia/New
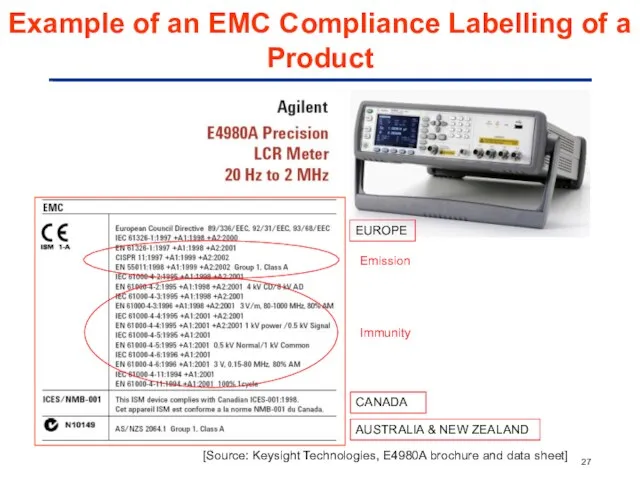
- 27. Emission Immunity CANADA AUSTRALIA & NEW ZEALAND Example of an EMC Compliance Labelling of a Product
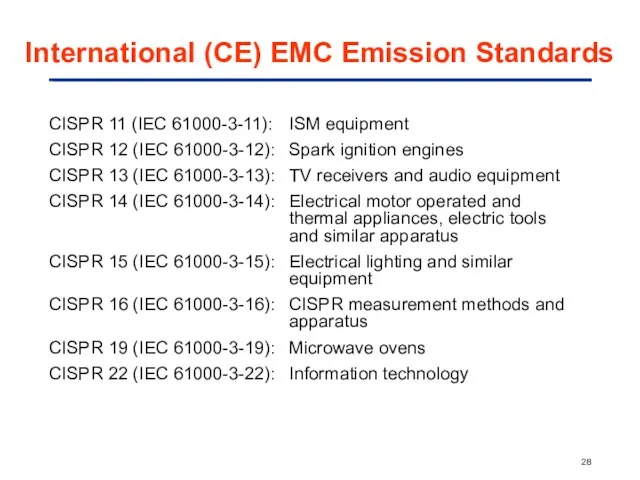
- 28. International (CE) EMC Emission Standards CISPR 11 (IEC 61000-3-11): ISM equipment CISPR 12 (IEC 61000-3-12): Spark
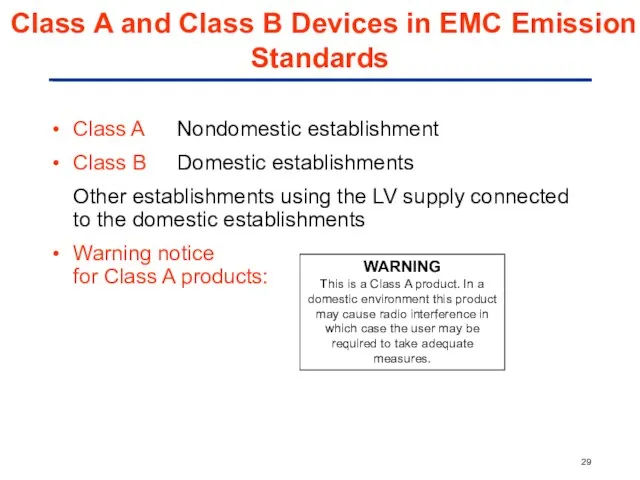
- 29. Class A and Class B Devices in EMC Emission Standards Class A Nondomestic establishment Class B
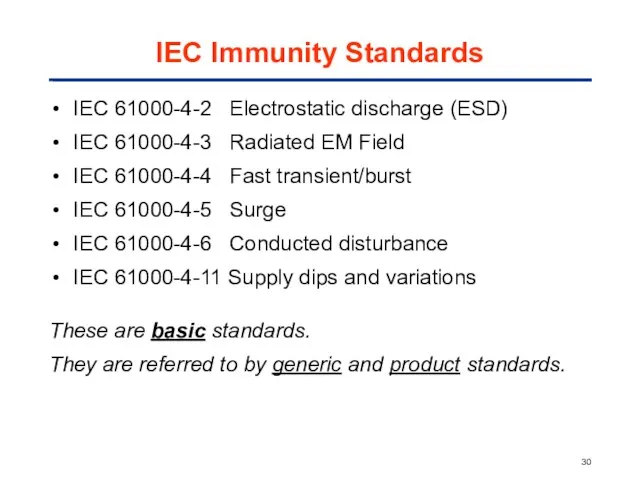
- 30. IEC Immunity Standards IEC 61000-4-2 Electrostatic discharge (ESD) IEC 61000-4-3 Radiated EM Field IEC 61000-4-4 Fast
- 32. Скачать презентацию





![[Source: Electronics Australia]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/432238/slide-7.jpg)
![What is EMC? EMC = Electromagnetic compatibility Definition [IEC 61000-1-1]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/432238/slide-8.jpg)




 Выбор и подготовка материалов для резки
Выбор и подготовка материалов для резки Изготовление цветка гвоздики
Изготовление цветка гвоздики Зороастризм
Зороастризм Дошкольное детство. Психология развития и возрастная психология
Дошкольное детство. Психология развития и возрастная психология Types of transport
Types of transport Стихи на уроках - 8
Стихи на уроках - 8 Механические методы индукции родов
Механические методы индукции родов Правила технической эксплуатации железных дорог Российской Федерации
Правила технической эксплуатации железных дорог Российской Федерации Распорный анкерный болт
Распорный анкерный болт Компьютерные технологий в обучении математике
Компьютерные технологий в обучении математике Международный день родного языка - 21 февраля. Викторина Я знаю удмуртский язык
Международный день родного языка - 21 февраля. Викторина Я знаю удмуртский язык Исследование и разработка системы автоматического управления процессом сушки аммиачной селитры
Исследование и разработка системы автоматического управления процессом сушки аммиачной селитры Гештальт-терапия как практико-ориентированный подход в психологии
Гештальт-терапия как практико-ориентированный подход в психологии Прекрасное Далеко. Слова Ю. Энтина. Музыка Е. Крылатова
Прекрасное Далеко. Слова Ю. Энтина. Музыка Е. Крылатова История возникновения образа Золотой век Голливуда 40-х годов
История возникновения образа Золотой век Голливуда 40-х годов В Новый год по странам мира
В Новый год по странам мира Winemaking In Russia
Winemaking In Russia Создание контента в Instagram
Создание контента в Instagram История происхождения и развития шрифтов
История происхождения и развития шрифтов Трудный диалог с учёбой, или как помочь своему ребёнку учиться
Трудный диалог с учёбой, или как помочь своему ребёнку учиться Симптомы поражения различных долей головного мозга, мозжечка, экстрапирамидных структур
Симптомы поражения различных долей головного мозга, мозжечка, экстрапирамидных структур Регистры
Регистры Зимние Олимпийские игры XX - XXII
Зимние Олимпийские игры XX - XXII ЛДО Прикамье отряд: Еще не взрослые! 5-7 классы
ЛДО Прикамье отряд: Еще не взрослые! 5-7 классы Бытие. Развитие. Детерминизм. Тема №5
Бытие. Развитие. Детерминизм. Тема №5 Река и ее части
Река и ее части Кордиц совет (1)
Кордиц совет (1) Клиническая физиология кислотно-щелочного равновесия
Клиническая физиология кислотно-щелочного равновесия