Содержание
- 3. В разговорной форме в отрицательной форме обычно употребляются следующие сокращения: Can – cannot/can’t Could not –
- 4. Модальные глаголы - это глаголы, которые сами по себе не обозначают действие, а отражают отношение говорящего
- 5. Особенности модальных глаголов Не имеют формы инфинитива, т.е. не отвечают на вопрос «Что делать/ Что сделать?»
- 6. CAN/COULD can’t/couldn’t Умение, способность Разрешение Возможность, создаваемая обстоятельствами Сомнение (отрицательн. предл), Невероятрость, удивление (вопросит. предл.) He
- 7. 1) Underline the correct option. 1. Can/Could Sally learn a long poem by heart when she
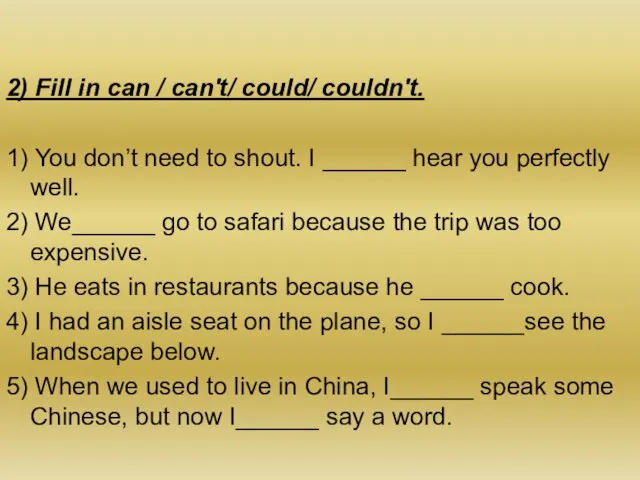
- 8. 2) Fill in can / can't/ could/ couldn't. 1) You don’t need to shout. I ______
- 9. 6) ______ you play the piano at the age of six? 7) He______ speak English so
- 10. MAY/MIGHT Разрешение. (May более официален, чем Can) Возможность (обычно фактическая, а не теоретическая) в утвердительных предложениях.
- 11. 3) Use may / might / may not/might not. 1) Sally isn't feeling very well. Sally
- 12. 4) ranslate the sentences. Используйте may / might. 1) Возможно, Вы встретите Салли на станции. 2)
- 13. Must Долженствование или необходимость в настоящем времени Предположение,основанное на уверенности ( в утвердительных предложениях) Запрет (mustn’t)
- 14. 5) Write in must or mustn't 1) Stop watching TV. You_______ do your homework. 2) I_______brush
- 15. 6) Write what you must or mustn't do when you travel. 1) You _________ drink dirty
- 16. SHOULD Личный совет, личное мнение, рекомендация, порицание. (следует, следовало бы, должен, нужно, нужно бы) He should
- 17. 7) Вставьте should или shouldn’t по смыслу. 1) The sun is really strong. He _______ put
- 18. OUGHT TO Совет, мнение (с простым инфинитивом) и порицание (перфектным инфинитивом). В отличие от Should, выражающего
- 20. Скачать презентацию
















 Развитие у детей дошкольного возраста элементарного творчества в процессе экспериментирования с разнообразным художественным материалом
Развитие у детей дошкольного возраста элементарного творчества в процессе экспериментирования с разнообразным художественным материалом ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ ЗРИТЕЛЬНАЯ ГИМНАСТИКА
ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ ЗРИТЕЛЬНАЯ ГИМНАСТИКА Тест. Решаем задачи по математике, 3 класс
Тест. Решаем задачи по математике, 3 класс Флювиальные процессы и формы рельефа
Флювиальные процессы и формы рельефа Мой любимый поэт Александр Сергеевич Пушкин
Мой любимый поэт Александр Сергеевич Пушкин Презентация по ОРКС на тему_ _Защита Отечества - долг и обязанность гражданина РФ_ (4 класс). (1)
Презентация по ОРКС на тему_ _Защита Отечества - долг и обязанность гражданина РФ_ (4 класс). (1) Организация сравнительных сценариев ТВ Samsung In-store
Организация сравнительных сценариев ТВ Samsung In-store Соғыстан кейінгі Сталиндік кезеңдегі Қазақстан
Соғыстан кейінгі Сталиндік кезеңдегі Қазақстан Тема №2. Планер. Занятие №3. Конструкция и компоновка крыла
Тема №2. Планер. Занятие №3. Конструкция и компоновка крыла Транспортные погрузочно-разгрузочные машины. Лекция 4
Транспортные погрузочно-разгрузочные машины. Лекция 4 Чалавечнасць - уласцівасць чалавечнага, гуманнасць,чалавекалюбства
Чалавечнасць - уласцівасць чалавечнага, гуманнасць,чалавекалюбства Список художественной литературы, рекомендованной для семейного чтения с учащимися 1 класса
Список художественной литературы, рекомендованной для семейного чтения с учащимися 1 класса Құрсақ ішілік инфекциялар. Инфекциялық процестің жастық ерекшеліктері
Құрсақ ішілік инфекциялар. Инфекциялық процестің жастық ерекшеліктері Карбоновые кислоты - союз двух групп(презентация)
Карбоновые кислоты - союз двух групп(презентация) Лакокрасочные материалы
Лакокрасочные материалы Лимерик, как часть английской поэзии
Лимерик, как часть английской поэзии Второе Пришествие
Второе Пришествие Электрошокер. Виды электрошокеров
Электрошокер. Виды электрошокеров Презентация:Формы взаимодействия с родителями в процессе музыкального воспитания детей раннего возраста
Презентация:Формы взаимодействия с родителями в процессе музыкального воспитания детей раннего возраста презентация Закон сохранения массы веществ
презентация Закон сохранения массы веществ Проект на тему: Сотрудничество педагога и родителей в процессе познания дошкольником семейной истории
Проект на тему: Сотрудничество педагога и родителей в процессе познания дошкольником семейной истории Практико -ориентированные задания при обучении химии
Практико -ориентированные задания при обучении химии Температура воздуха. Распределение солнечного тепла и света
Температура воздуха. Распределение солнечного тепла и света Ноніусні штангенглибиноміри
Ноніусні штангенглибиноміри Блок Настоящее искусство. (Текст 9.2)
Блок Настоящее искусство. (Текст 9.2) Санкт - Петербург - город трамваев.
Санкт - Петербург - город трамваев. Організація роботи лікаря мануальної терапії. Кабінет мануальної терапії
Організація роботи лікаря мануальної терапії. Кабінет мануальної терапії Массовая культура
Массовая культура