Содержание
- 2. Contents Ternary relationship Relational Model Relational Algebra
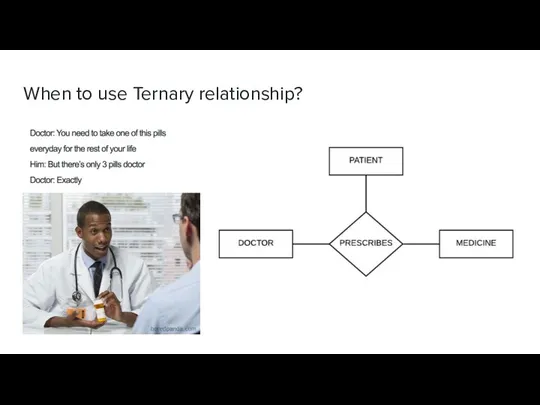
- 3. When to use Ternary relationship?
- 4. Examples Teachers teach Courses Courses use as material textbook Teachers use textbooks
- 5. Exercise Ternary Relationship One employee only works on one job One employee only works for one
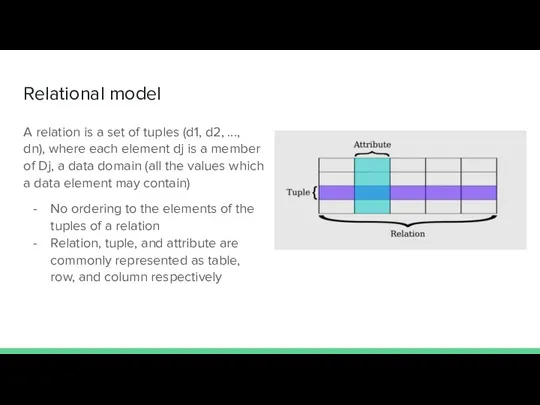
- 6. Relational model A relation is a set of tuples (d1, d2, ..., dn), where each element
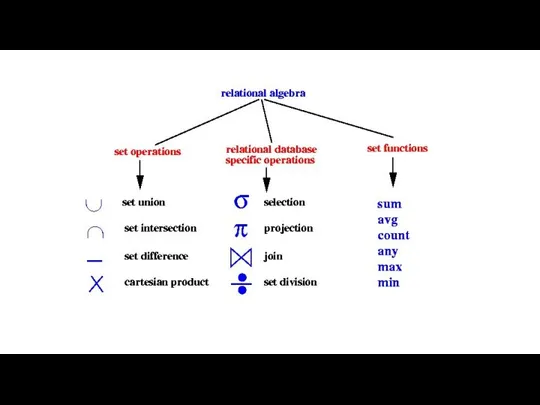
- 7. Relations Relations are sets, so we can apply set-theoretic operators + special relational operators Basic operators
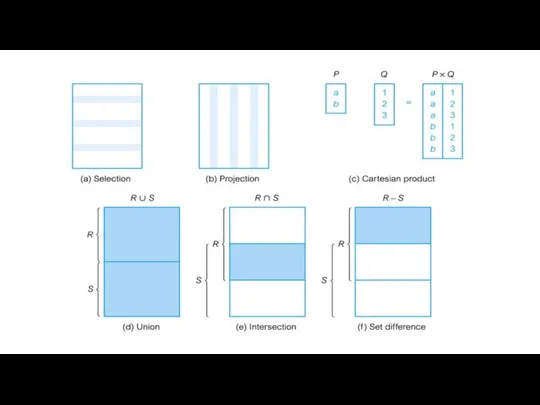
- 9. Operators
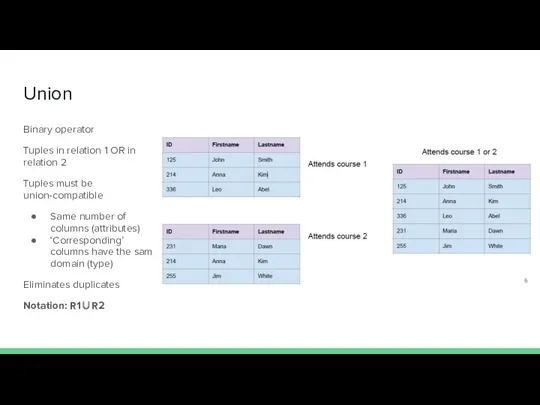
- 10. Union Binary operator Tuples in relation 1 OR in relation 2 Tuples must be union-compatible Same
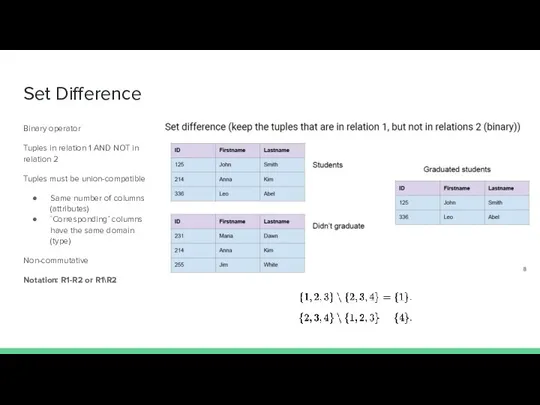
- 11. Set Difference Binary operator Tuples in relation 1 AND NOT in relation 2 Tuples must be
- 12. Intersection Binary operator Tuples in relation 1 AND in relation 2 Tuples must be union-compatible Same
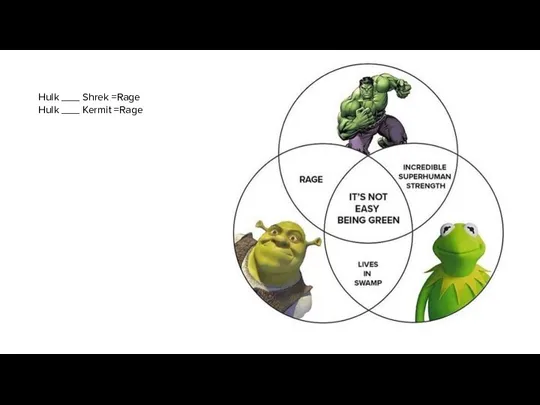
- 14. Hulk ___ Shrek =Rage Hulk ___ Kermit =Rage
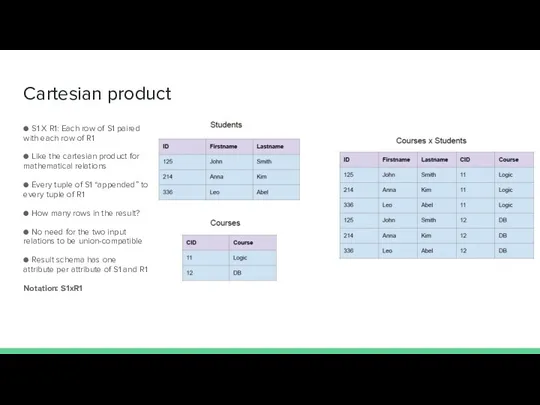
- 15. Cartesian product ● S1 X R1: Each row of S1 paired with each row of R1
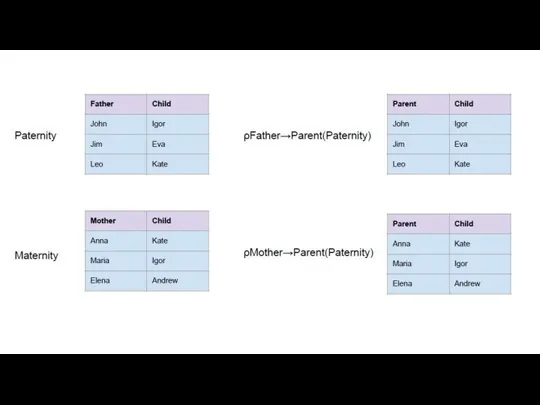
- 16. Renaming The problem: Father and Mother are different names, but both represent a parent. The solution:
- 17. Renaming Rename Unary operator Changes attribute names for a relation without changing any values Renaming removes
- 19. Select ● Unary operator ● Selects a subset of rows from a relation that satisfy selection
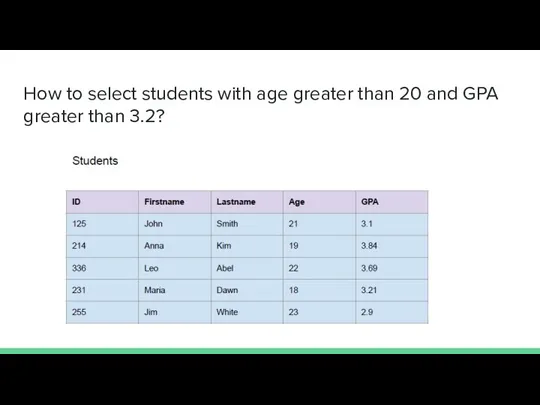
- 20. How to select students with age greater than 20 and GPA greater than 3.2?
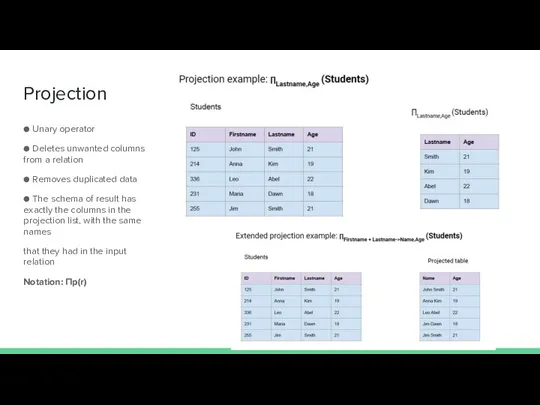
- 21. Projection ● Unary operator ● Deletes unwanted columns from a relation ● Removes duplicated data ●
- 22. Join ● Binary operator ● Allows us to establish connections among data in different relations, taking
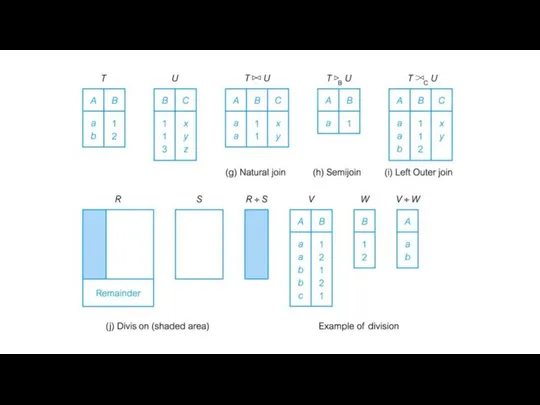
- 23. Natural join (or “just join”) ● Binary operator ● Select rows where attributes that appear in
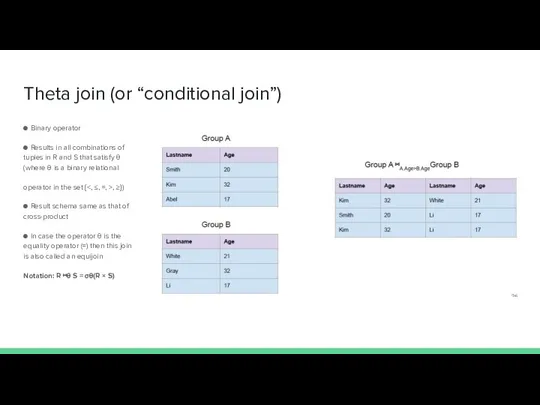
- 24. Theta join (or “conditional join”) ● Binary operator ● Results in all combinations of tuples in
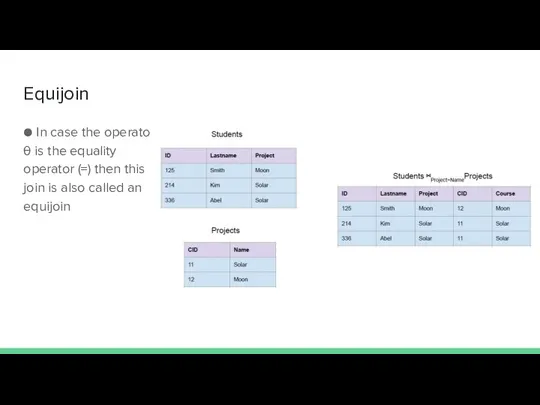
- 25. Equijoin ● In case the operator θ is the equality operator (=) then this join is
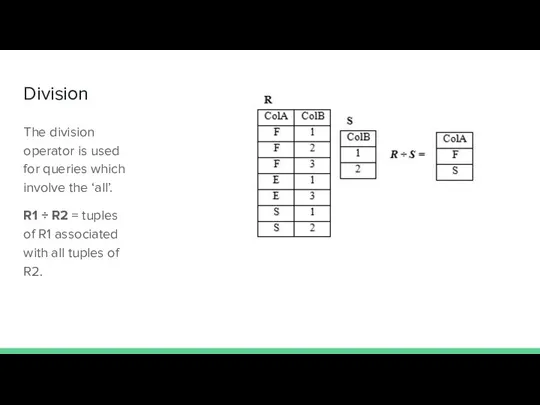
- 26. Division The division operator is used for queries which involve the ‘all’. R1 ÷ R2 =
- 29. Let us try together Suppliers (sid: integer, sname: string, address: string) Parts (pid: integer, pname: string,
- 30. Let us try together Suppliers (sid: integer, sname: string, address: string) Parts (pid: integer, pname: string,
- 31. Let us try together Suppliers (sid: integer, sname: string, address: string) Parts (pid: integer, pname: string,
- 33. Скачать презентацию















 Презентация по теме Основания
Презентация по теме Основания Что такое алкоголь?
Что такое алкоголь? Основы организации и деятельности центральных банков
Основы организации и деятельности центральных банков Холл’з Каф Рэнч (ранчо Холлов). Выращивание первоклассного ремонтного молодняка
Холл’з Каф Рэнч (ранчо Холлов). Выращивание первоклассного ремонтного молодняка родительское собрание август 2015
родительское собрание август 2015 Методическая разработка, презентация Организация развивающей предметно-пространственной среды в ДОУ в соответствии с ФГОС.
Методическая разработка, презентация Организация развивающей предметно-пространственной среды в ДОУ в соответствии с ФГОС. Облегченная кладка
Облегченная кладка Красная книга Краснодарского края
Красная книга Краснодарского края Тұрақсыз стенокардия
Тұрақсыз стенокардия Звукослоговой анализ слова
Звукослоговой анализ слова Образы русской природы. С.Я. Маршак Гроза днём, В лесу над росистой поляной
Образы русской природы. С.Я. Маршак Гроза днём, В лесу над росистой поляной Презентация к внеклассному занятию,посвящённому Дню победы.
Презентация к внеклассному занятию,посвящённому Дню победы. Инновационные приемы работы в рамках научно-исследовательской деятельности
Инновационные приемы работы в рамках научно-исследовательской деятельности Экспериментально-теоретические предпосылки механики грунтов. (Тема 2)
Экспериментально-теоретические предпосылки механики грунтов. (Тема 2) Вероятность случайного события
Вероятность случайного события Василь-Костянтин Острозький. Український православний князь, культурно-освітній діяч
Василь-Костянтин Острозький. Український православний князь, культурно-освітній діяч Современные теплоизоляционные материалы и их применение
Современные теплоизоляционные материалы и их применение Презентация к классному часу в 3 классе Здоровое питание
Презентация к классному часу в 3 классе Здоровое питание Презентация Животный мир Австралии
Презентация Животный мир Австралии Friendship and friends
Friendship and friends Презентация Мировой океан
Презентация Мировой океан Преимущества и недостатки систем охлаждения ПК
Преимущества и недостатки систем охлаждения ПК Праздник Страна Грамматика (начальная школа VIII вид)
Праздник Страна Грамматика (начальная школа VIII вид) Химическое многоборье
Химическое многоборье Роль подразделений медицинской профилактики в проведении осмотров и диспансеризации определенных групп взрослого населения
Роль подразделений медицинской профилактики в проведении осмотров и диспансеризации определенных групп взрослого населения Общественное движение при Александре I
Общественное движение при Александре I Презентация ко Дню конституции
Презентация ко Дню конституции Механические свойства горных пород. Деформирование и разрушение горных пород за пределом прочности
Механические свойства горных пород. Деформирование и разрушение горных пород за пределом прочности