Содержание
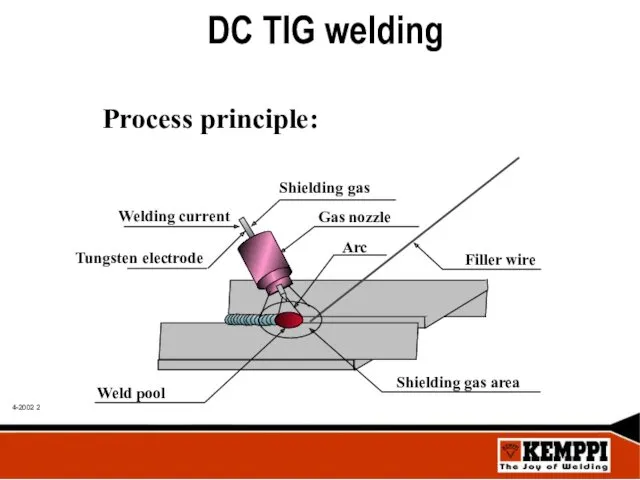
- 2. DC TIG welding
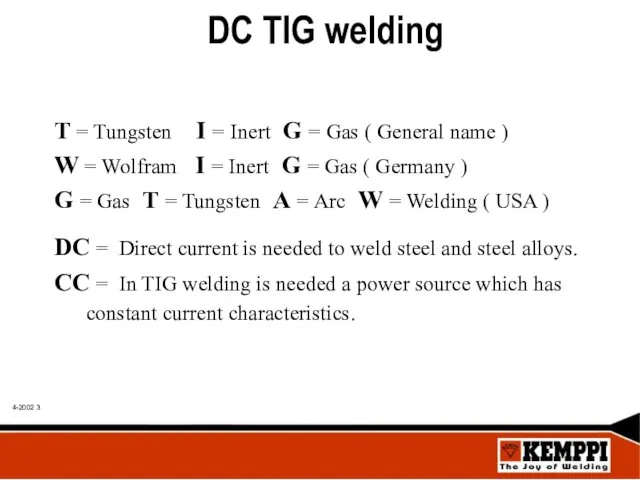
- 3. DC TIG welding T = Tungsten I = Inert G = Gas ( General name )
- 4. TIG benefits and features • Good visibility to the weld pool, no smoke or welding slag.
- 5. TIG process limitations Lower productivity than in MIG / MAG welding. Sensitive for base or filler
- 6. TIG applications TIG is suitable in steel welding cases where quality and visual appearance of weld
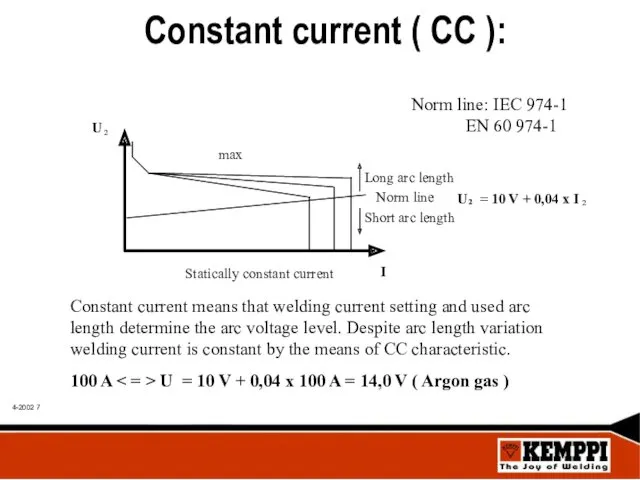
- 7. Constant current ( CC ):
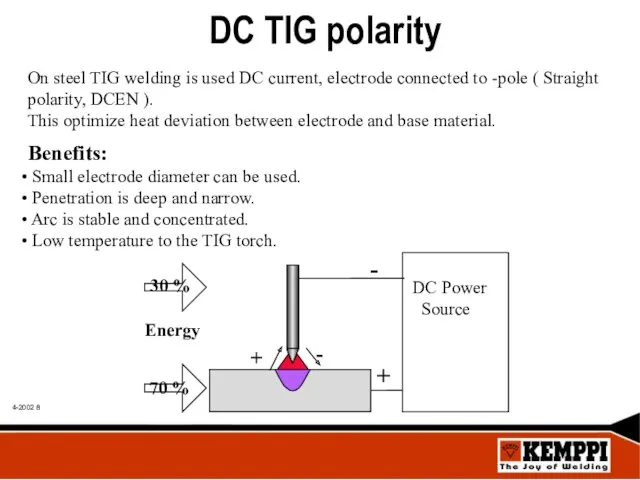
- 8. DC TIG polarity On steel TIG welding is used DC current, electrode connected to -pole (
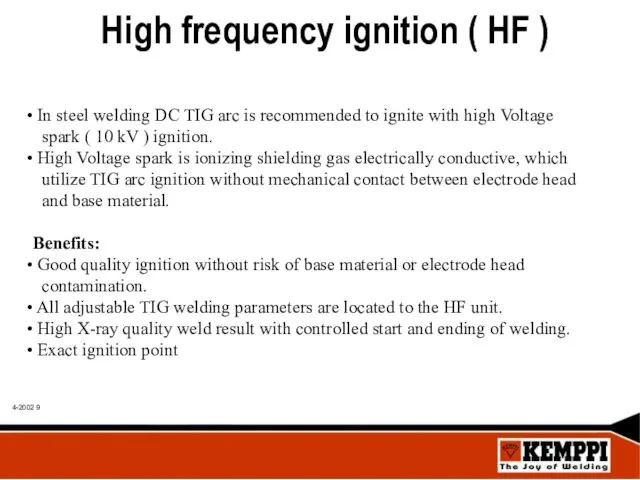
- 9. High frequency ignition ( HF ) In steel welding DC TIG arc is recommended to ignite
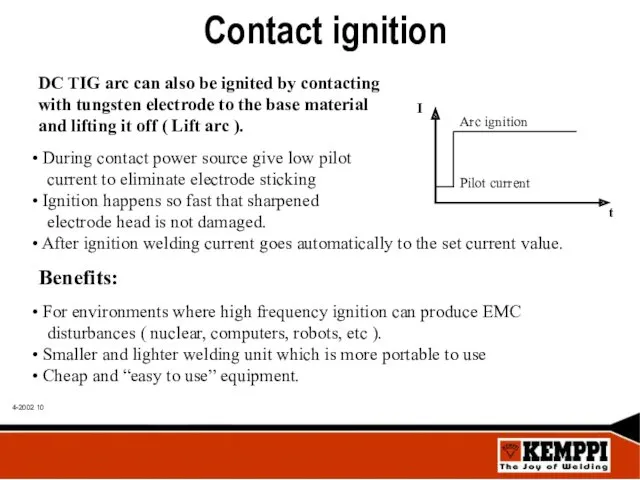
- 10. Contact ignition DC TIG arc can also be ignited by contacting with tungsten electrode to the
- 11. Welding preparations Steel is having normally on it´s surface slag coming from the material hot rolling
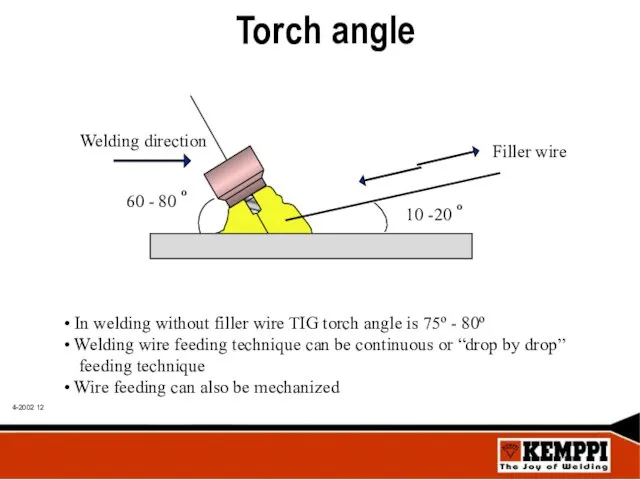
- 12. Torch angle In welding without filler wire TIG torch angle is 75º - 80º Welding wire
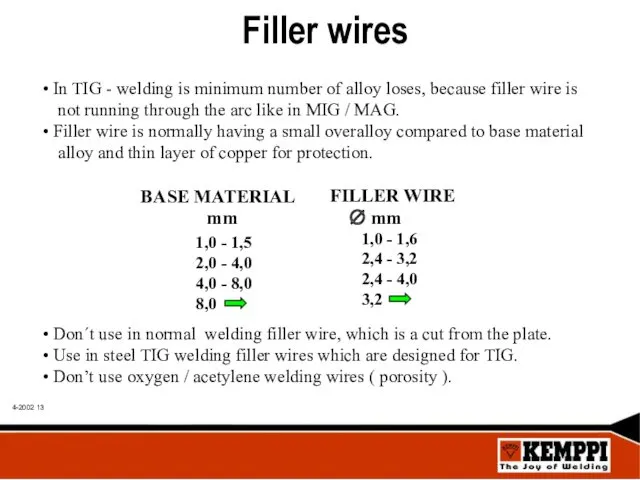
- 13. Filler wires In TIG - welding is minimum number of alloy loses, because filler wire is
- 14. Gas lens: Better gas shielding, no turbulence on gas flow Better visibility to the weld pool
- 15. Gas nozzle / lens inside diameter Gas nozzle / lens n:o is coming from 1/16” (
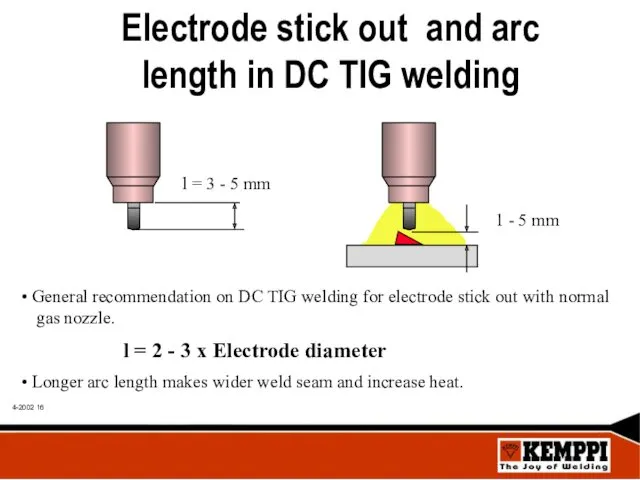
- 16. Electrode stick out and arc length in DC TIG welding General recommendation on DC TIG welding
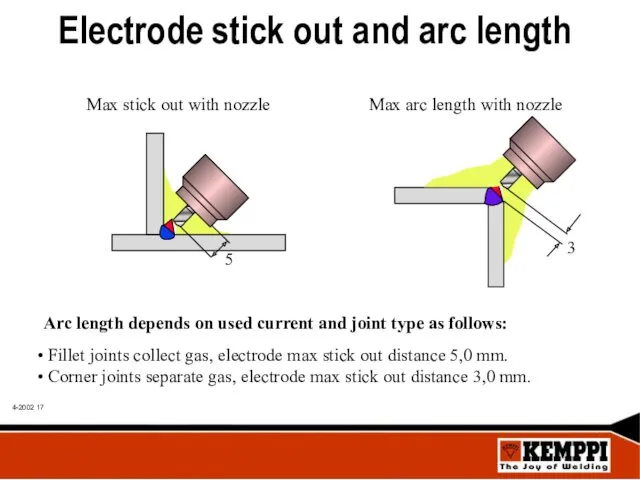
- 17. Arc length depends on used current and joint type as follows: Fillet joints collect gas, electrode
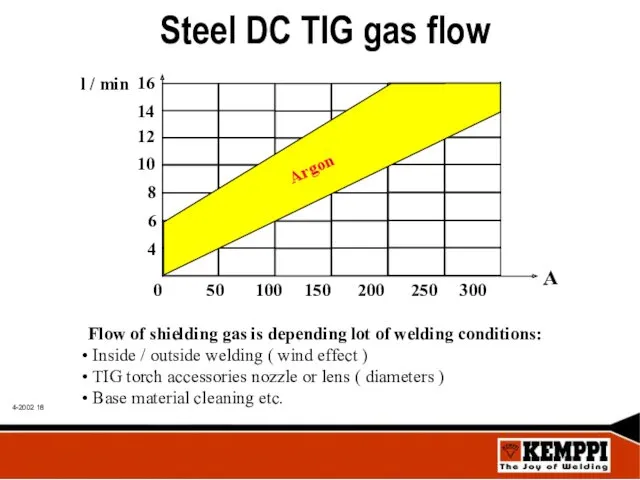
- 18. Steel DC TIG gas flow Flow of shielding gas is depending lot of welding conditions: Inside
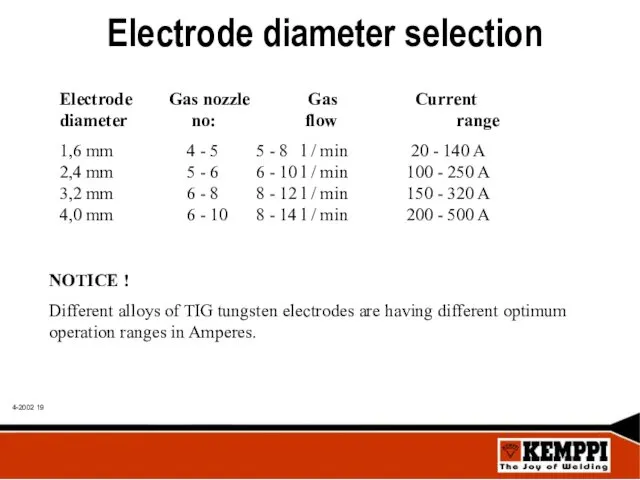
- 19. Electrode diameter selection Electrode Gas nozzle Gas Current diameter no: flow range 1,6 mm 4 -
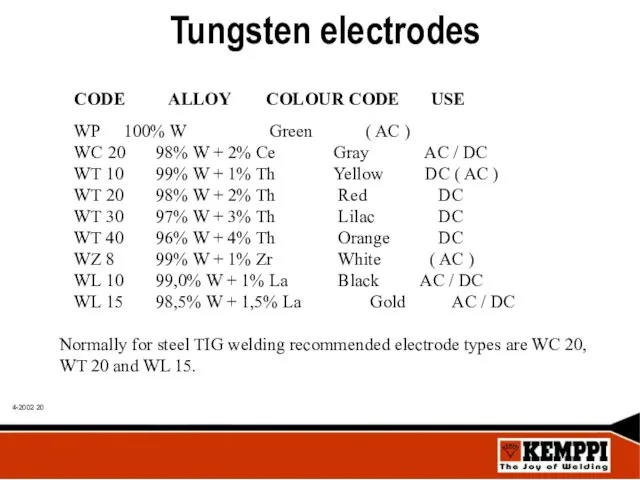
- 20. Tungsten electrodes CODE ALLOY COLOUR CODE USE WP 100% W Green ( AC ) WC 20
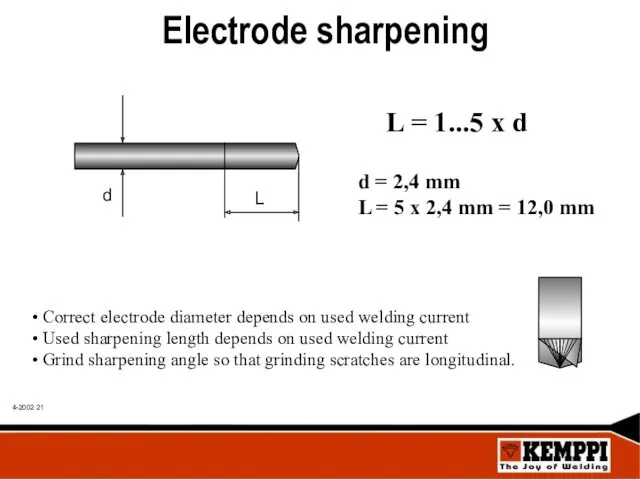
- 21. Electrode sharpening L = 1...5 x d d = 2,4 mm L = 5 x 2,4
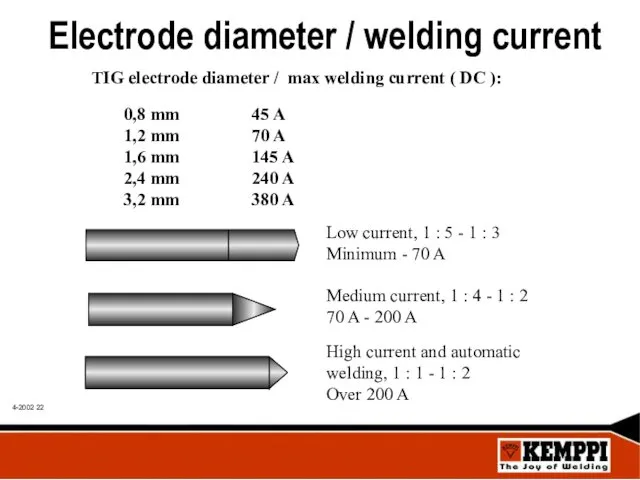
- 22. Electrode diameter / welding current TIG electrode diameter / max welding current ( DC ): 0,8
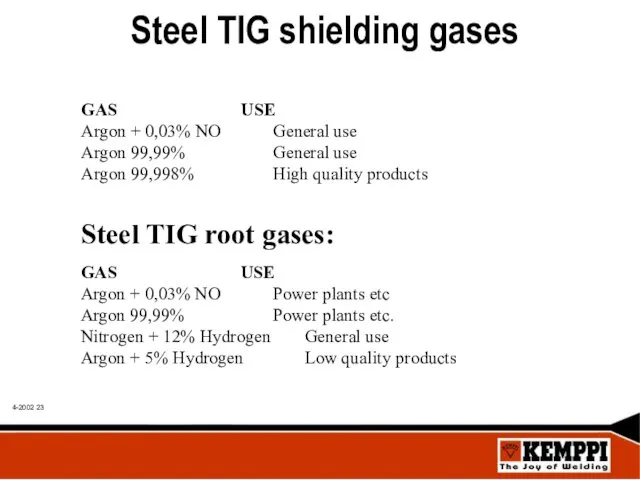
- 23. Steel TIG shielding gases GAS USE Argon + 0,03% NO General use Argon 99,99% General use
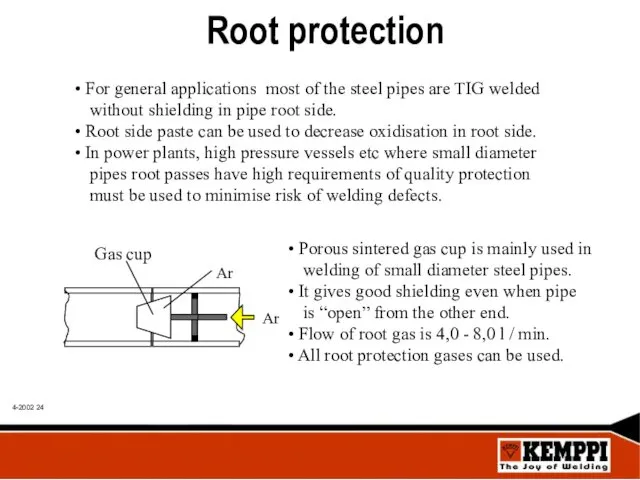
- 24. Root protection For general applications most of the steel pipes are TIG welded without shielding in
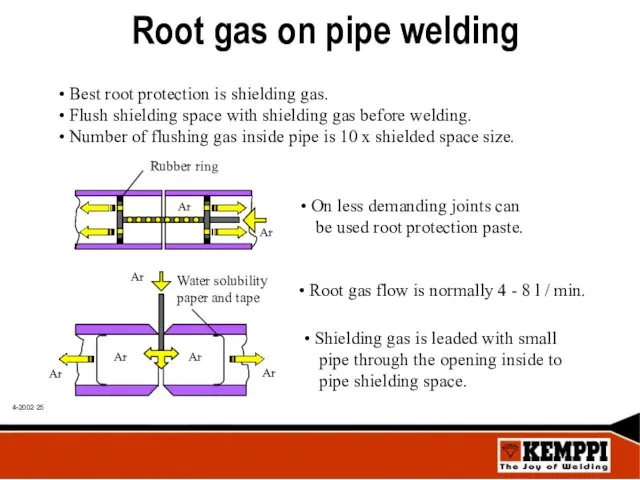
- 25. Root gas on pipe welding Best root protection is shielding gas. Flush shielding space with shielding
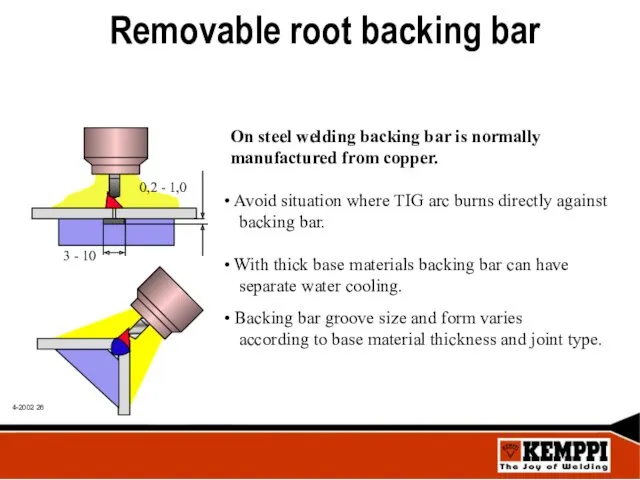
- 26. Removable root backing bar On steel welding backing bar is normally manufactured from copper. Avoid situation
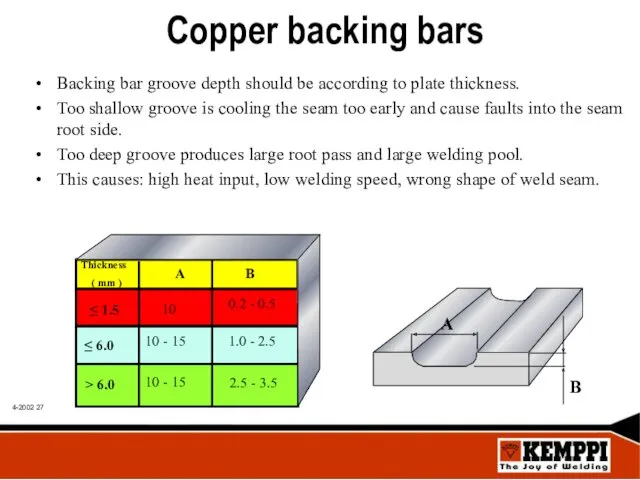
- 27. Copper backing bars Backing bar groove depth should be according to plate thickness. Too shallow groove
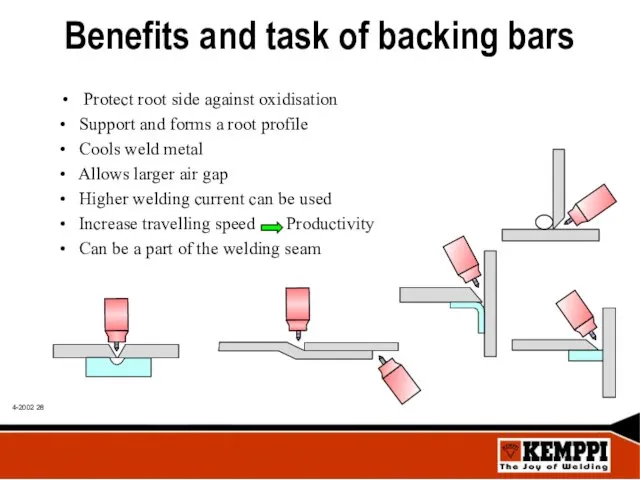
- 28. Benefits and task of backing bars Protect root side against oxidisation • Support and forms a
- 29. Pre gas / Post flow functions During Pre gas function shielding gas is flowing to the
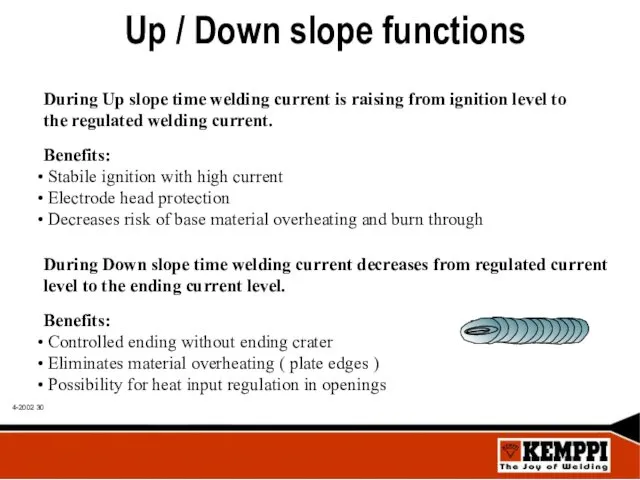
- 30. Up / Down slope functions During Up slope time welding current is raising from ignition level
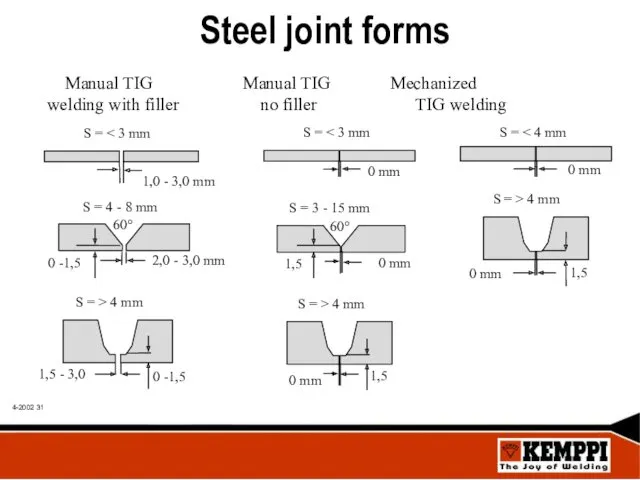
- 31. Steel joint forms
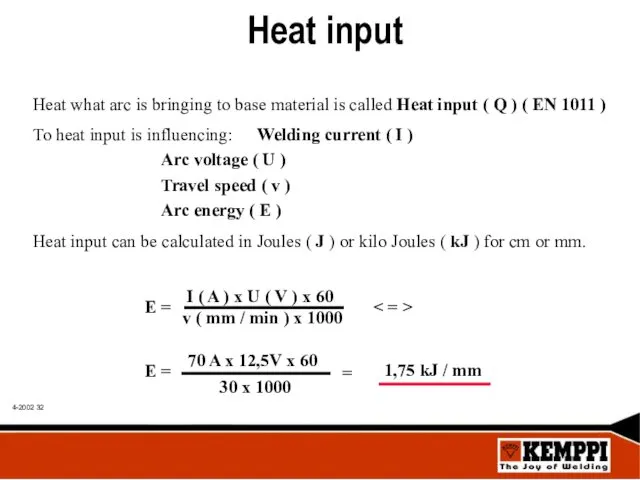
- 32. Heat input Heat what arc is bringing to base material is called Heat input ( Q
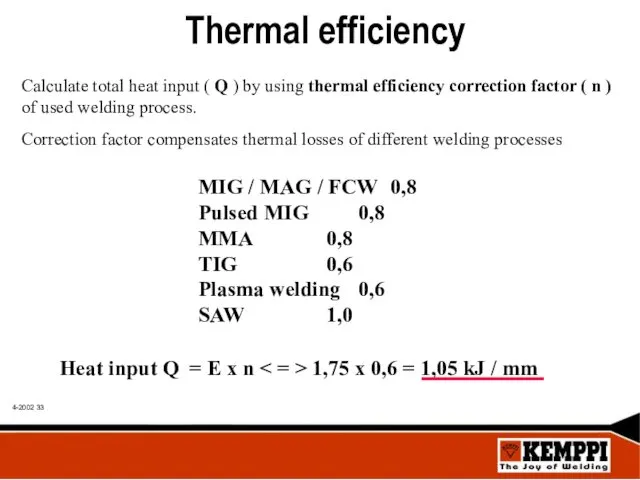
- 33. Thermal efficiency Calculate total heat input ( Q ) by using thermal efficiency correction factor (
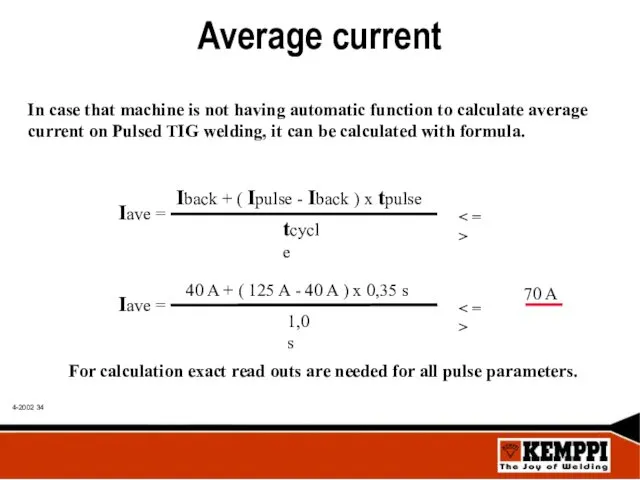
- 34. Average current In case that machine is not having automatic function to calculate average current on
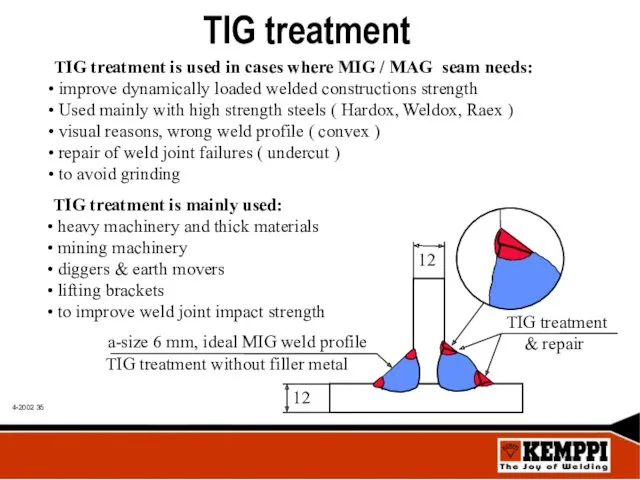
- 35. TIG treatment TIG treatment is used in cases where MIG / MAG seam needs: improve dynamically
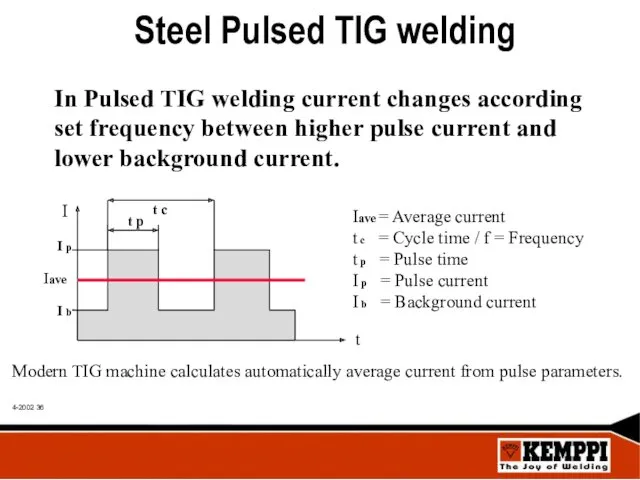
- 36. Steel Pulsed TIG welding In Pulsed TIG welding current changes according set frequency between higher pulse
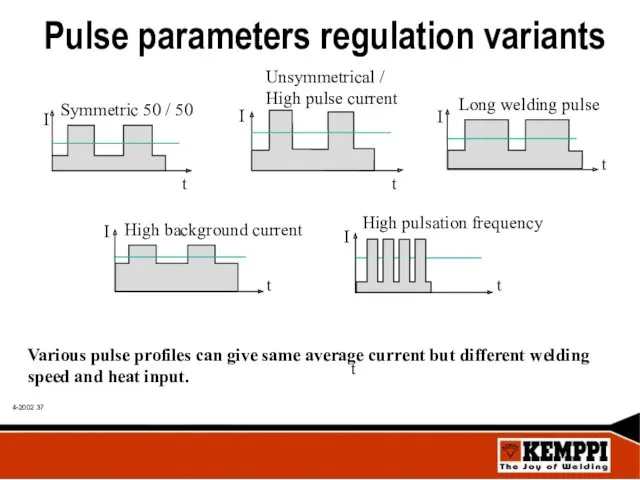
- 37. Pulse parameters regulation variants Various pulse profiles can give same average current but different welding speed
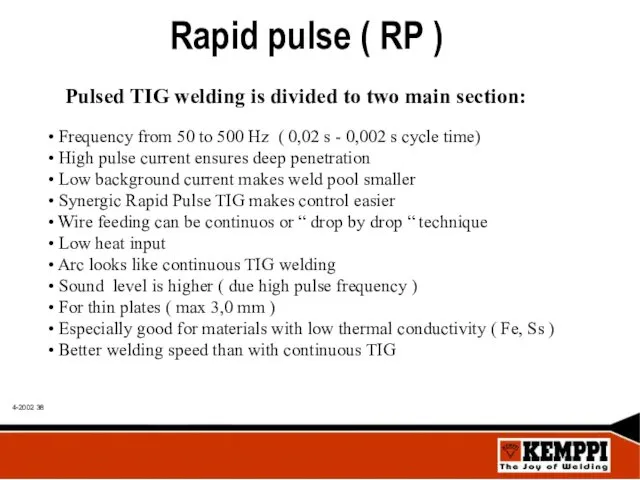
- 38. Rapid pulse ( RP ) Pulsed TIG welding is divided to two main section: Frequency from
- 39. Long pulse ( LP ) From 5 to 0,1 Hz ( 0,2 s - 10 s
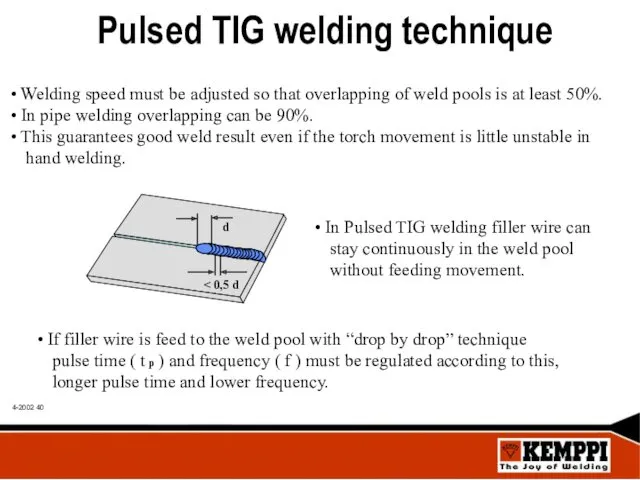
- 40. Pulsed TIG welding technique Welding speed must be adjusted so that overlapping of weld pools is
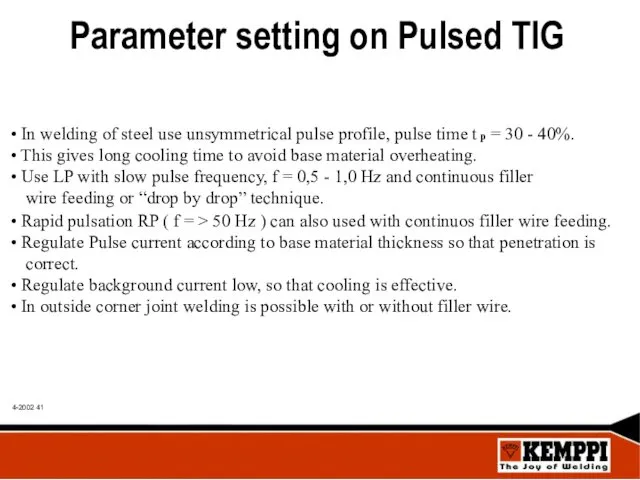
- 41. Parameter setting on Pulsed TIG In welding of steel use unsymmetrical pulse profile, pulse time t
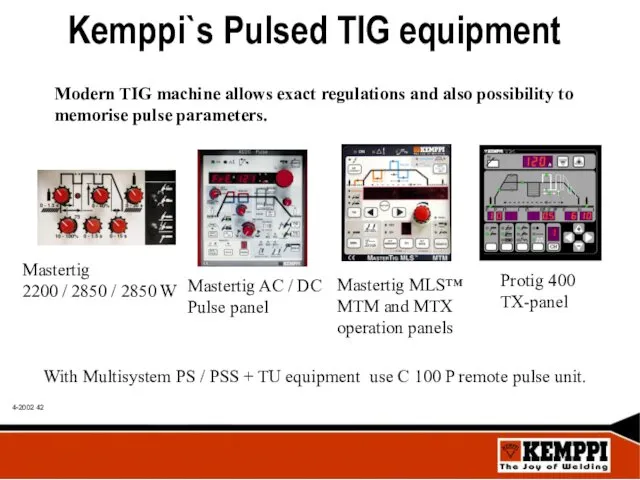
- 42. With Multisystem PS / PSS + TU equipment use C 100 P remote pulse unit. Kemppi`s
- 43. Pulsed DC TIG welding applications Pulsed DC TIG welding is a flexible welding process for all
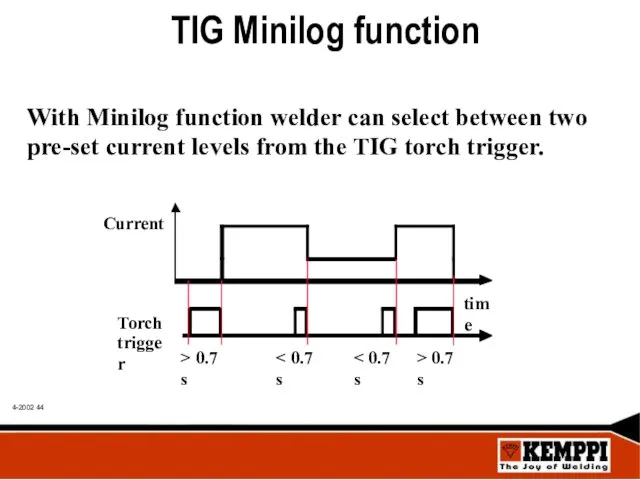
- 44. TIG Minilog function With Minilog function welder can select between two pre-set current levels from the
- 45. TIG Minilog benefits To avoid welding faults at starts Better weld pool control in positional welding
- 46. TIG Minilog applications Pre heat of base material before welding Starting from thin material or from
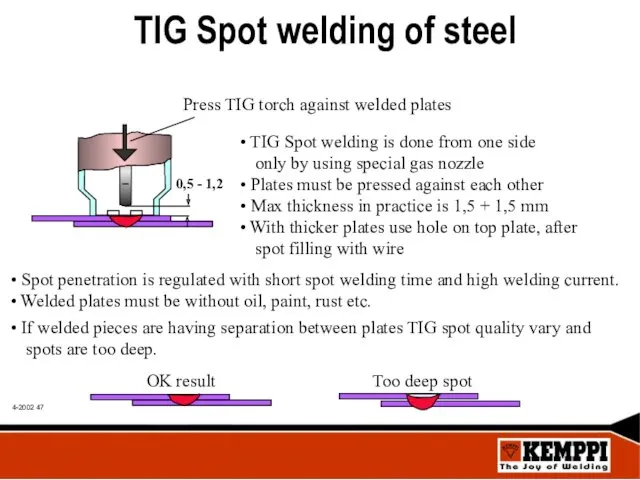
- 47. TIG Spot welding of steel Press TIG torch against welded plates TIG Spot welding is done
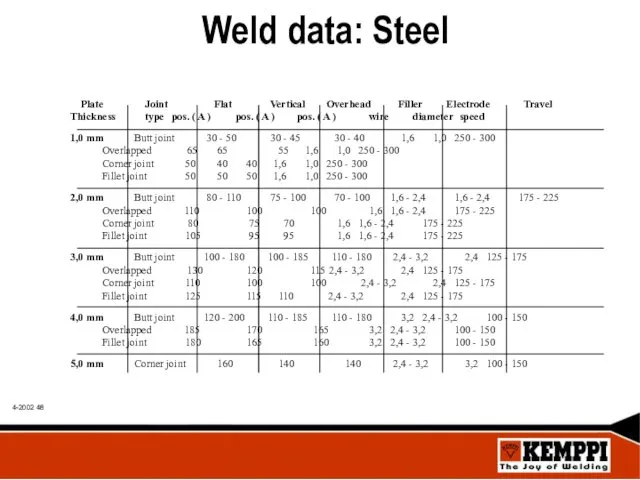
- 48. Weld data: Steel
- 50. Скачать презентацию











 Написание сочинения-рассуждения
Написание сочинения-рассуждения IVoice. Интеллектуальный голосовой помощник для вашего бизнеса
IVoice. Интеллектуальный голосовой помощник для вашего бизнеса Презентация к сценарию праздника Прощай, Букварь.
Презентация к сценарию праздника Прощай, Букварь. Проектирование блочной котельной для гостиницы
Проектирование блочной котельной для гостиницы Путешествие в страну Морфемика. (5 класс)
Путешествие в страну Морфемика. (5 класс) Ислам. Догматика ислама
Ислам. Догматика ислама Применение подобия треугольников в жизни. Измерительные работы на местности
Применение подобия треугольников в жизни. Измерительные работы на местности Научно-исследовательская работа в группе Следопыт
Научно-исследовательская работа в группе Следопыт Цифровые данные. Цифровая технология. Цифровая революция
Цифровые данные. Цифровая технология. Цифровая революция Гипотезы возникновение жизни на Земле
Гипотезы возникновение жизни на Земле Кодирование и обработка графической информации
Кодирование и обработка графической информации Европейские нормативы теплозащиты зданий. Технологии теплозащиты и естественной вентиляции архитектурных сооружений в Казахстане
Европейские нормативы теплозащиты зданий. Технологии теплозащиты и естественной вентиляции архитектурных сооружений в Казахстане Вода
Вода Маленькие герои большой войны. Кто такие пионеры?
Маленькие герои большой войны. Кто такие пионеры? Таблица умножения для младших школьников (тренажер)
Таблица умножения для младших школьников (тренажер) Людовик ван Бетховен
Людовик ван Бетховен Моя театральная деятельность Диск
Моя театральная деятельность Диск Государства на политической карте мира
Государства на политической карте мира Благоустройство объекта Свиридовский пруд
Благоустройство объекта Свиридовский пруд Countable nouns
Countable nouns Опиливание заготовок из сортового проката
Опиливание заготовок из сортового проката Органическая архитектура
Органическая архитектура Уровень и качество жизни населения
Уровень и качество жизни населения Виды треугольников. Логическая задача
Виды треугольников. Логическая задача Затратный подход к оценке собственности
Затратный подход к оценке собственности Презентация Играем вместе
Презентация Играем вместе Михаил Лямин
Михаил Лямин Как стать личностью
Как стать личностью