Содержание
- 2. Review Term structure of interest rate Yield curve Expectations theory long-term interest rate = average of
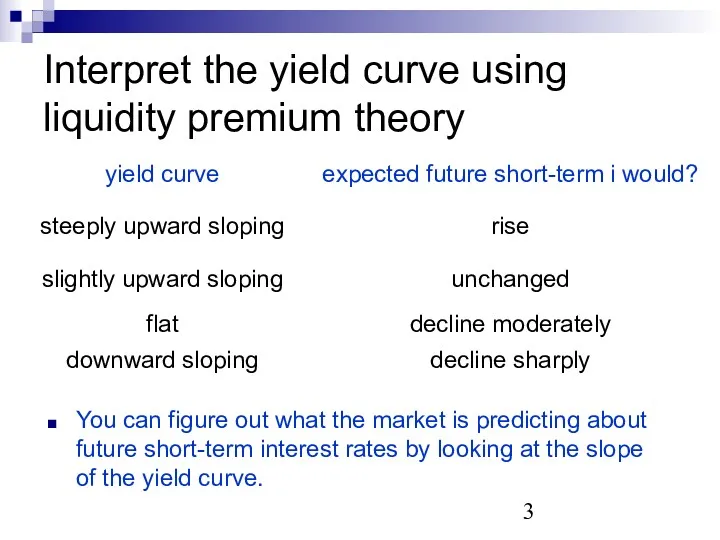
- 3. Interpret the yield curve using liquidity premium theory You can figure out what the market is
- 4. Stocks A share of stock is a claim on the net income and assets of the
- 5. Rights of shareholders Shareholders (stockholders) have ownership interest in the company proportional to shares owned. Large
- 6. Shareholders’ payoff possible income: dividends: payments made periodically, usually every quarter, to stockholders. Shareholders are eligible
- 7. Stock exchanges New York Stock Exchange (NYSE, "Big Board" ) NASDAQ (National Association of Securities Dealers
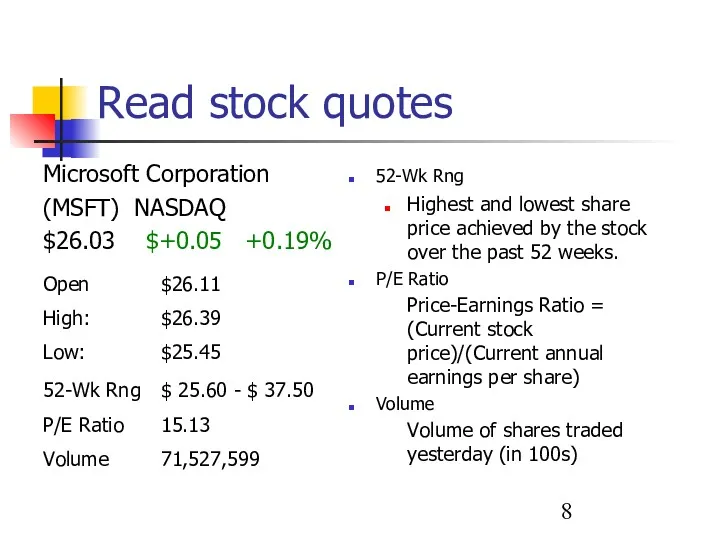
- 8. Read stock quotes 52-Wk Rng Highest and lowest share price achieved by the stock over the
- 9. Major events 1987 crash: total value of stocks fell by about a trillion dollars between August
- 10. If I could forecast stock price Fundamental analysis macro-econ and firm performance ? dividend ? stock’s
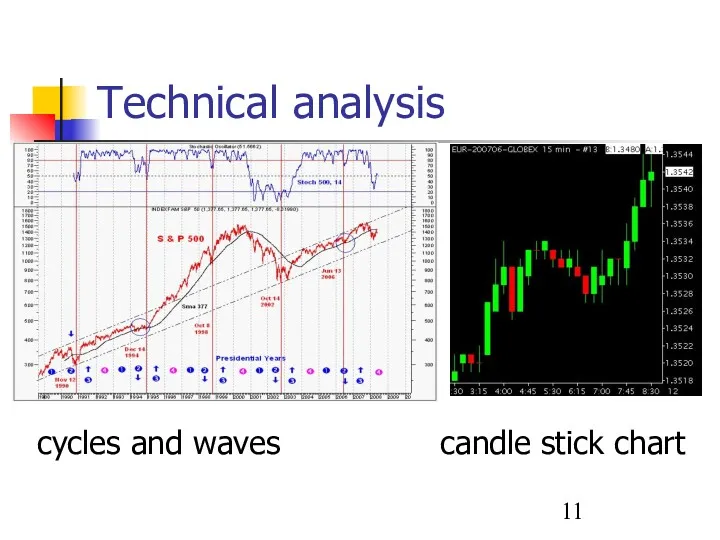
- 11. Technical analysis cycles and waves candle stick chart
- 12. Alternative views of stock pricing Fundamental Finance View: Stock prices are largely determined by the true
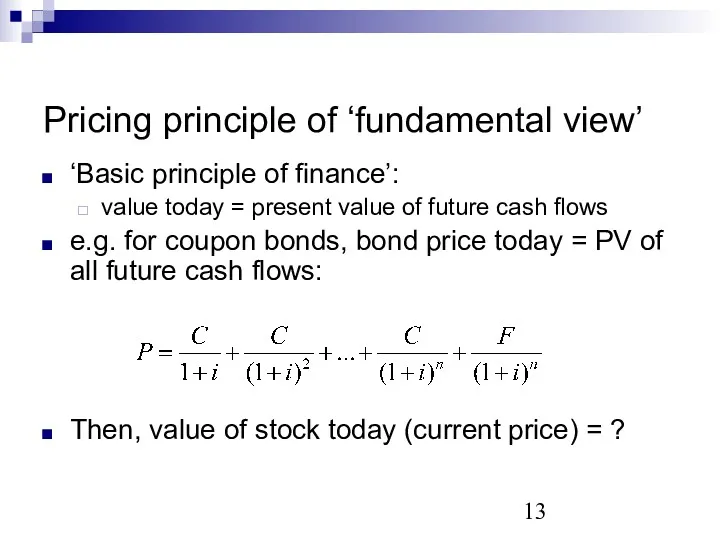
- 13. Pricing principle of ‘fundamental view’ ‘Basic principle of finance’: value today = present value of future
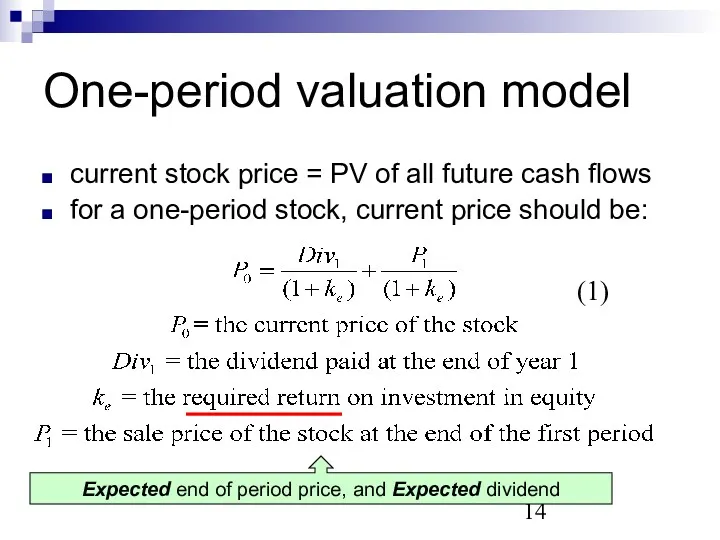
- 14. One-period valuation model current stock price = PV of all future cash flows for a one-period
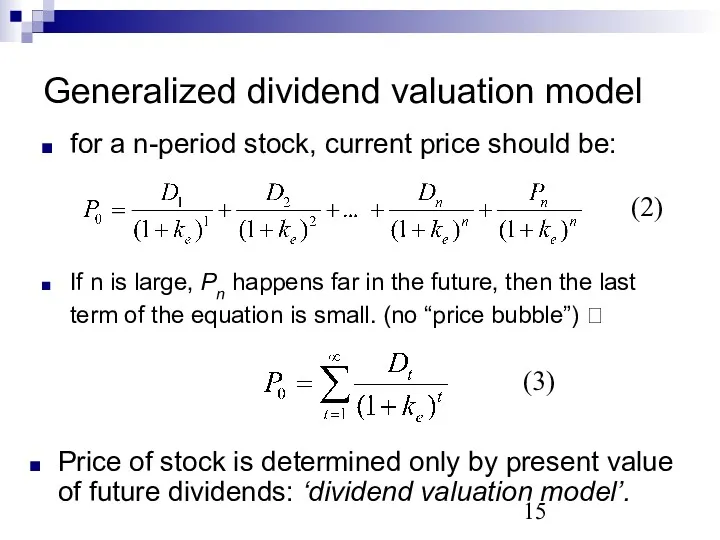
- 15. If n is large, Pn happens far in the future, then the last term of the
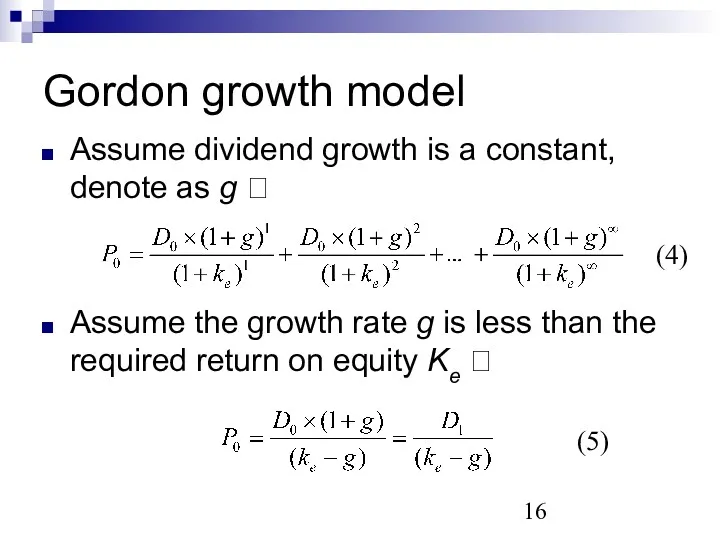
- 16. Gordon growth model Assume dividend growth is a constant, denote as g ? Assume the growth
- 17. Apply ‘Gordon growth model’ Gordon growth model predicts that current stock price P0 will be lower
- 18. Example - 9/11 attacks Fears led to downward revision of the growth prospects for U.S. companies
- 19. More about pricing formulas The current market price P0 is an equilibrium market price: Right side
- 21. Скачать презентацию











 Пётр Ильич Чайковский (1840–1893)
Пётр Ильич Чайковский (1840–1893) 1917 год: от февраля к октябрю
1917 год: от февраля к октябрю Опорно-двигательная система человека. Скелет головы
Опорно-двигательная система человека. Скелет головы Презентация Лащенко
Презентация Лащенко Оксиды серы (IV) и (VI). Производство серной кислоты
Оксиды серы (IV) и (VI). Производство серной кислоты Государственный фонд развития промышленности Московской области
Государственный фонд развития промышленности Московской области Наблюдение за насекомыми
Наблюдение за насекомыми 16 ноября- Международный день толерантности
16 ноября- Международный день толерантности Занятие по дополнительной образовательной программе Микробиология для школьников по теме: Водоросли, их строение. Биологические особенности
Занятие по дополнительной образовательной программе Микробиология для школьников по теме: Водоросли, их строение. Биологические особенности Загрязнение гидросферы. Материалы к урокам географии и экологии.
Загрязнение гидросферы. Материалы к урокам географии и экологии. Л_1_СТ_Фізико_технічні_основи_променевої_діагностики_
Л_1_СТ_Фізико_технічні_основи_променевої_діагностики_ Конфликты и способы их разрешения.
Конфликты и способы их разрешения. Мораль. Человек и общество
Мораль. Человек и общество Периодический закон и периодическая система химических элементов.
Периодический закон и периодическая система химических элементов. Точность, взаимозаменяемость деталей и узлов столярных изделий
Точность, взаимозаменяемость деталей и узлов столярных изделий Podstawy finansów. Rachunek wyników
Podstawy finansów. Rachunek wyników Михаил Юрьевич Лермонтов 15 октября 1814 года – 27 июля 1841 года. Русский поэт, прозаик, драматург, художник
Михаил Юрьевич Лермонтов 15 октября 1814 года – 27 июля 1841 года. Русский поэт, прозаик, драматург, художник Денсаулық сақтауды жоспарлаудың, қаржыландырудың қазіргі кездегі проблемалары
Денсаулық сақтауды жоспарлаудың, қаржыландырудың қазіргі кездегі проблемалары Проект по строительству завода по производству высококачественных нефтепродуктов на территории Свердловской области
Проект по строительству завода по производству высококачественных нефтепродуктов на территории Свердловской области Згурський Петро. Студентський парламент
Згурський Петро. Студентський парламент Psikhologia_organizatsii_1
Psikhologia_organizatsii_1 Информационная система ЖИВУ.РФ
Информационная система ЖИВУ.РФ Отчёт о прохождении производственной практики в строительной компании ООО СК УРАЛПОЛ
Отчёт о прохождении производственной практики в строительной компании ООО СК УРАЛПОЛ Где логика? Интерактивная игра
Где логика? Интерактивная игра Роль и назначение международных стандартов финансовой отчетности (МСФО). Порядок создания МСФО
Роль и назначение международных стандартов финансовой отчетности (МСФО). Порядок создания МСФО Семь мудрецов Древней Греции
Семь мудрецов Древней Греции История престольного праздника День Святых Первоверховных апостолов Петра и Павла
История престольного праздника День Святых Первоверховных апостолов Петра и Павла Биологические науки. Интерактивный кроссворд
Биологические науки. Интерактивный кроссворд