Содержание
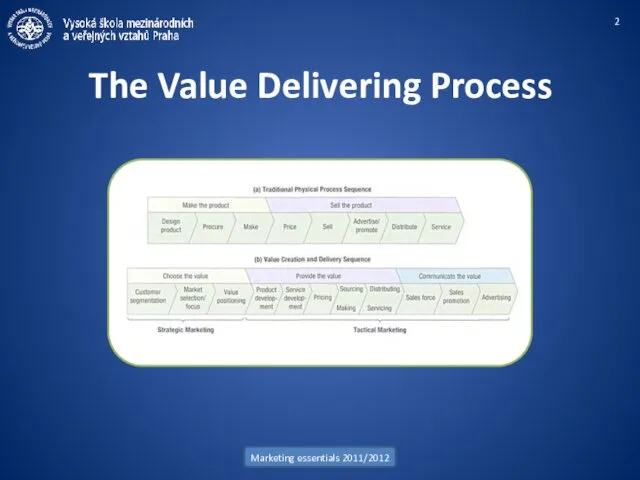
- 2. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 The Value Delivering Process
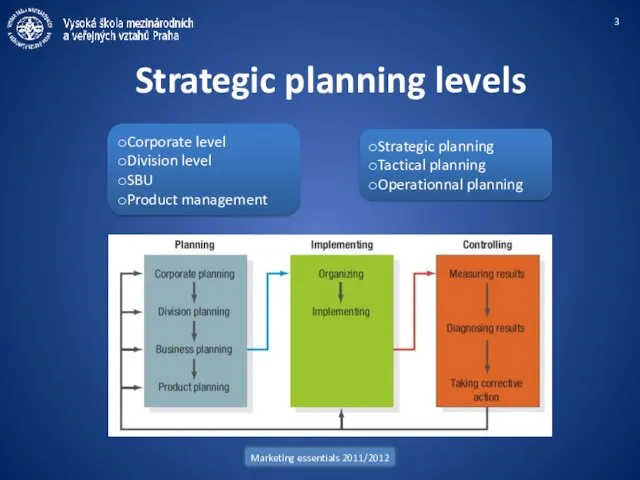
- 3. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Strategic planning levels Corporate level Division level SBU Product management Strategic planning Tactical
- 4. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Top management planning activities Mission statement Strategic audit Strategic business units management Business
- 5. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Mission statement articulation Enterprenneurs: Using product Using technology Using prospect market Non-profit subjects:
- 6. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Strategic marketing audit External audit: Markets Competition Business environment Ekonomic environment Internal audit:
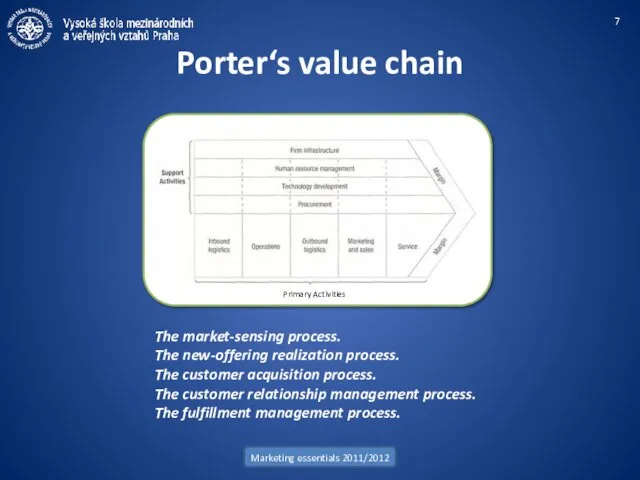
- 7. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Porter‘s value chain Primary Activities The market-sensing process. The new-offering realization process. The
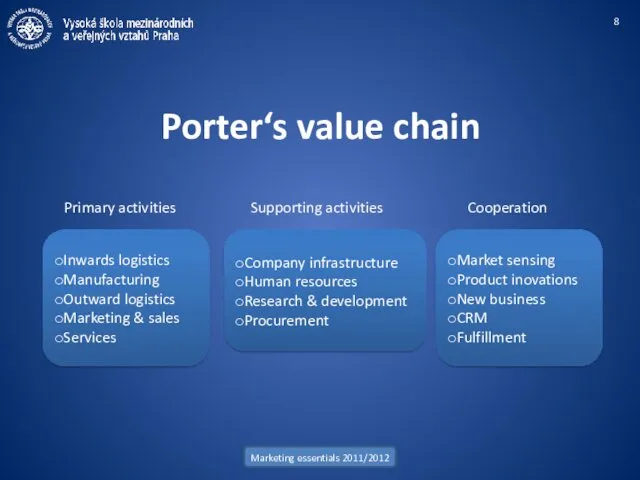
- 8. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Porter‘s value chain Inwards logistics Manufacturing Outward logistics Marketing & sales Services Primary
- 9. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Strategic Business Unit It is a single business, or a collection of related
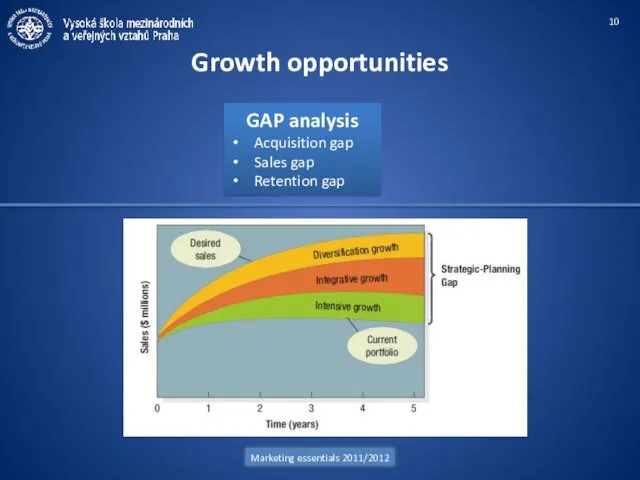
- 10. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Growth opportunities GAP analysis Acquisition gap Sales gap Retention gap
- 11. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Intensive growth: Ansoff's Product-Market Expansion Grid Growth opportunities Integrative growth: Diversification growth: Downsizing
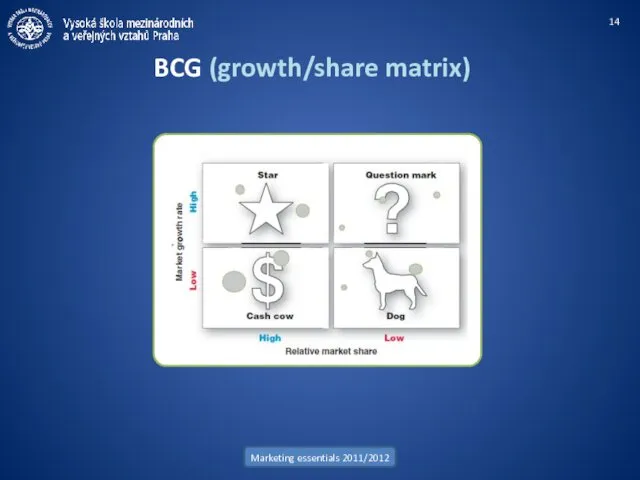
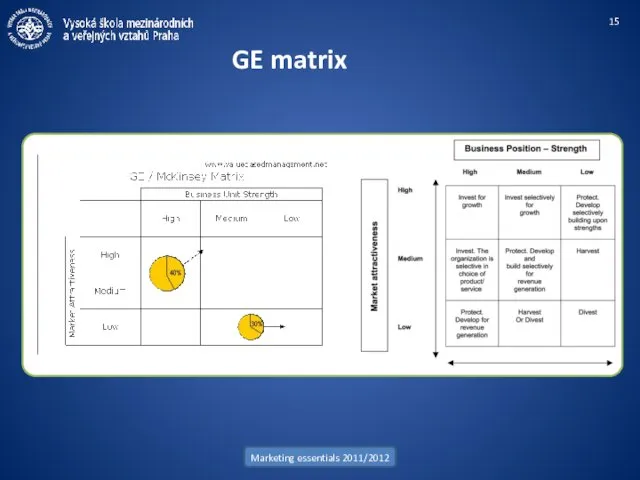
- 12. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Portfolio management BCG matrix (Boston Consulting Group) GE matrix (McKinsey) Shell directional policy
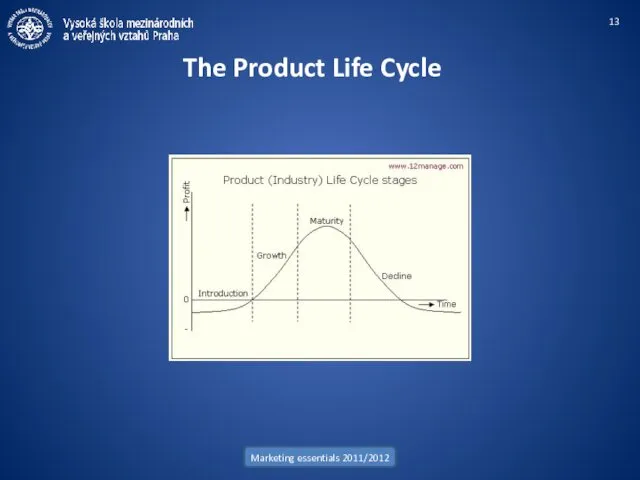
- 13. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 The Product Life Cycle
- 14. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 BCG (growth/share matrix)
- 15. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 GE matrix
- 16. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Shell directional policy matrix
- 17. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Industry Life Cycle Matrix A. D. Little SBU’s life cycle: Embryonic Growth Maturity
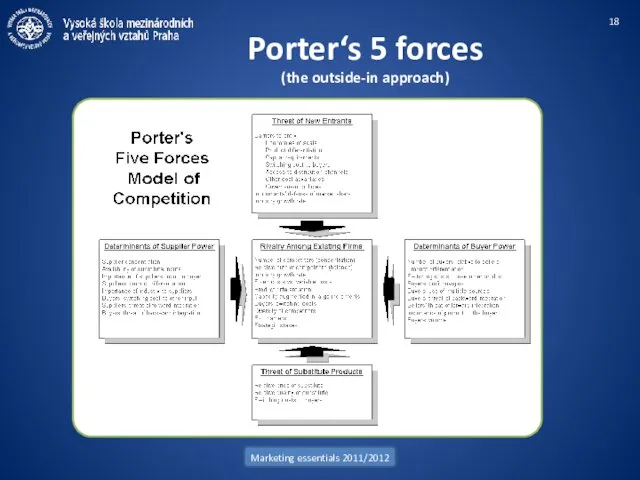
- 18. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Porter‘s 5 forces (the outside-in approach)
- 19. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Purchasing Portfolio Management Kraljic model „Purchasing must become Supply Management“ – P.Kraljic, HBR
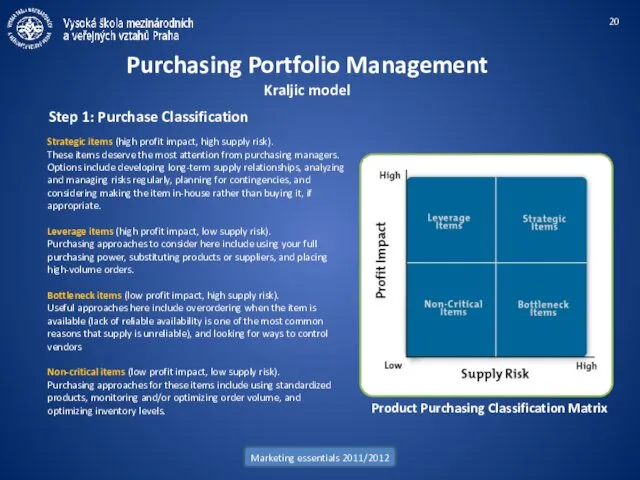
- 20. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Purchasing Portfolio Management Kraljic model Step 1: Purchase Classification Strategic items (high profit
- 21. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Purchasing Portfolio Management Kraljic model Step 3: Strategic Positioning Classify the products or
- 22. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Purchasing Portfolio Management Kraljic model Step 4: Action Plans Finally, develop action plans
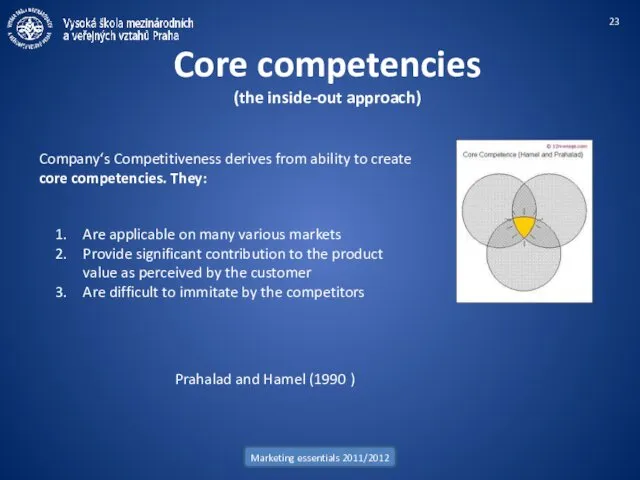
- 23. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Core competencies (the inside-out approach) Company‘s Competitiveness derives from ability to create core
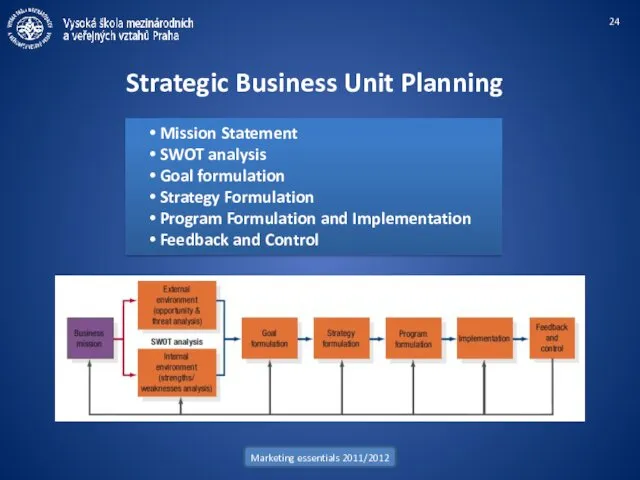
- 24. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Strategic Business Unit Planning Mission Statement SWOT analysis Goal formulation Strategy Formulation Program
- 25. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Marketing environments
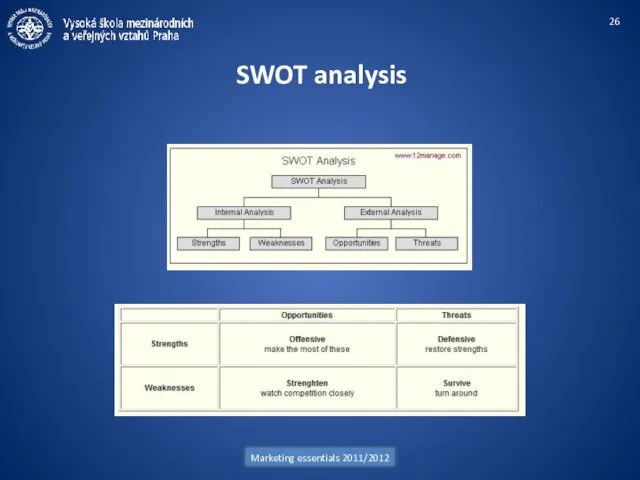
- 26. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 SWOT analysis
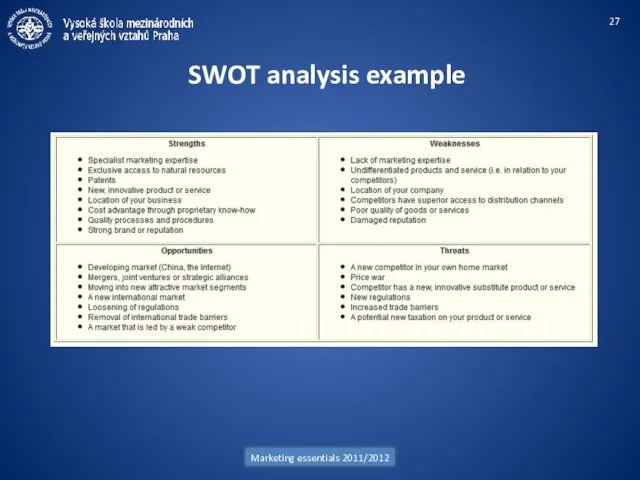
- 27. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 SWOT analysis example
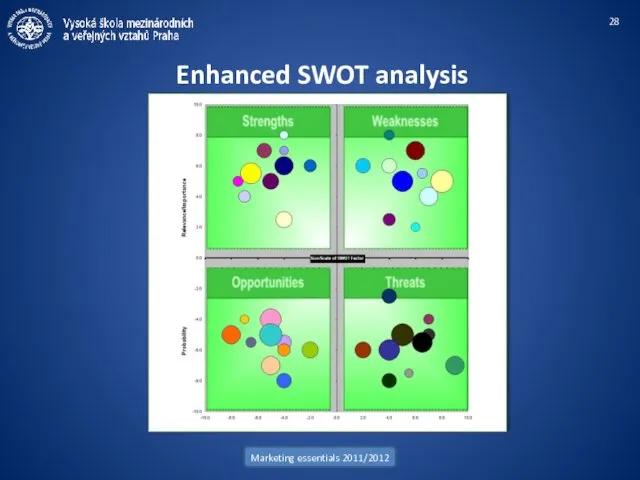
- 28. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Enhanced SWOT analysis
- 29. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Goals Formulation Specific Measurable Achiavable Realistic Time-related Profitability Market share Risk minimalization Innovations
- 30. Ansoff‘s grid Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Strategy Formulation Porter‘s Generic Strategies Kotler‘s Competitive Strategies
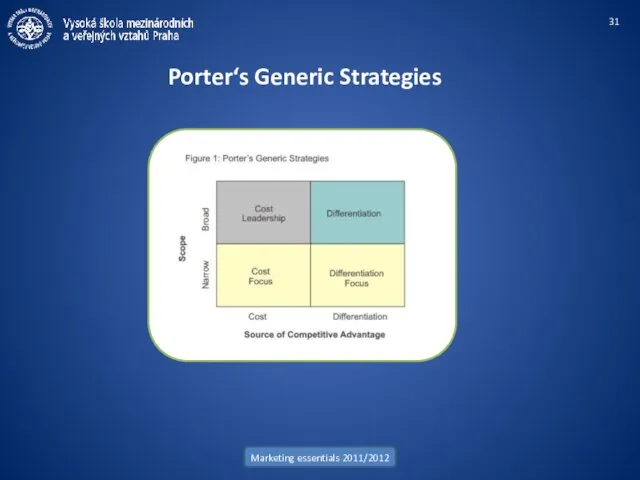
- 31. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Porter‘s Generic Strategies
- 32. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Kotler‘s Competitive Strategies Hypotetical market structure
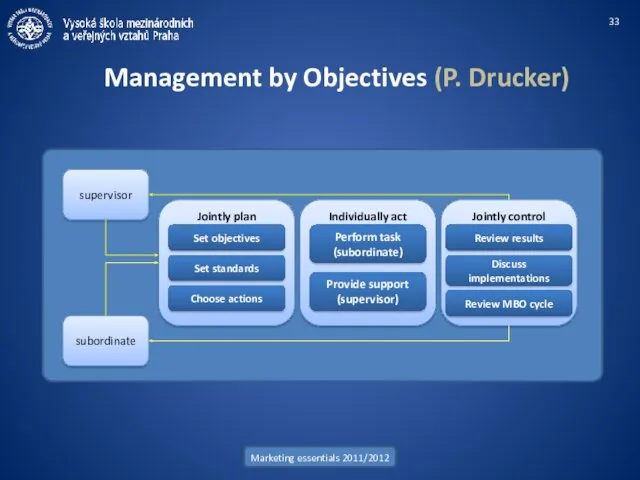
- 33. Marketing essentials 2011/2012 Management by Objectives (P. Drucker) supervisor subordinate Jointly plan Individually act Jointly control
- 35. Скачать презентацию












 20231211_matematicheskoe_kazino
20231211_matematicheskoe_kazino Триумфальная арка
Триумфальная арка Проект Книга Памяти 2013-2014 уч.год
Проект Книга Памяти 2013-2014 уч.год 20231120_urok_predstaviteli_sred_obitaniya_gotovyy
20231120_urok_predstaviteli_sred_obitaniya_gotovyy Основы финансовых вычислений
Основы финансовых вычислений Фотоколлаж с методическими рекомендациями Проектирование образовательного процесса по теме Цветы вокруг нас в условиях созданной предменно - развивающей среды
Фотоколлаж с методическими рекомендациями Проектирование образовательного процесса по теме Цветы вокруг нас в условиях созданной предменно - развивающей среды Educational system of Ukraine
Educational system of Ukraine Конспект занятия по безопасности жизнедеятельности дошкольников с включением компьютерной игры На тему опасности дома (+ презентация)
Конспект занятия по безопасности жизнедеятельности дошкольников с включением компьютерной игры На тему опасности дома (+ презентация) Сухие строительные смеси
Сухие строительные смеси Инновационный педагогический проект
Инновационный педагогический проект Трансцендентальна медитація
Трансцендентальна медитація Мы делили апельсин. Пальчиковая гимнастика.
Мы делили апельсин. Пальчиковая гимнастика. Кора́н-священная книга мусульман
Кора́н-священная книга мусульман Памятники знаменитым петербуржцам
Памятники знаменитым петербуржцам Природа России
Природа России Taboo professions
Taboo professions Презентация Праздник осени
Презентация Праздник осени Литературные памятники древних германцев
Литературные памятники древних германцев класс Изменение величин_Задания
класс Изменение величин_Задания Презентация к уроку трудового обучения Цветущий кактус (в технике торцевания)
Презентация к уроку трудового обучения Цветущий кактус (в технике торцевания) Общая физическая и спортивная подготовка студентов в образовательном процессе
Общая физическая и спортивная подготовка студентов в образовательном процессе Клининговая фирма ИП ФеяКрёстная
Клининговая фирма ИП ФеяКрёстная teoriya_avtomaticheskogo_upravleniya_Polulah_parth10
teoriya_avtomaticheskogo_upravleniya_Polulah_parth10 Наружные лестницы
Наружные лестницы 20231008_past_tenses
20231008_past_tenses 20191227_prishvin_lesnaya_kapel
20191227_prishvin_lesnaya_kapel Учебный мини-проект: поэтика числа пи
Учебный мини-проект: поэтика числа пи Презентация к классному часу 23 февраля
Презентация к классному часу 23 февраля