Слайд 2

CONTENTS
Introduction
Hindu Law
History of ancient Law
Sources of Hindu Law
Indian Legal system
Classification
of legal system
Judiciary system
Conclusion
Слайд 3

Introduction
India has a Federal Constitution but does not have a dual
court system.
While there are State courts, they decide both Federal and State issues.
The Constitution provides for a High Court in each State, although Parliament may by law establish a common High Court for two or more States.
The Supreme Court, which has 18 judges including the Chief Justice, has original jurisdiction over disputes between the Government of India and States and States inter se and also has the power to issue writs and enforce Fundamental Rights.
Слайд 4

Hindu Law
Hindu law, as a historical term, refers to the code
of laws applied to Hindus, Buddhists, Jains and Sikhs in British India.
Hindu law, in modern scholarship, also refers to the legal theory, jurisprudence and philosophical reflections on the nature of law discovered in ancient and medieval era Indian texts.
It is one of the oldest known jurisprudence theories in the world.
Слайд 5

Слайд 6

History of Hindu Law
The ancient term in Indian texts is Dharma, which
means more than a code of law, though collections of legal maxims were compiled into works such as the Nāradasmṛti.
The term "Hindu law" is a colonial construction,and emerged after the colonial rule arrived in South Asia, and when in 1772 it was decided by British colonial officials, that European common law system would not be implemented in India, that Hindus of India would be ruled under their "Hindu law" and Muslims of India would be ruled under "Muslim law" (Sharia).
Слайд 7

In ancient Hindu jurisprudence texts, a number of Sanskrit words refer
to aspects of law.
Some of these includes Niyama (rule), Nyasa (justice), Yuktata (justice), Samya (equality and impartiality in law), Vidhi (rule), Vyavastha (regulation), Sambhasa (contract or mutual engagement), Prasamvida-Patra (written contract), Vivadayati (dispute), Adhivakta (lawyer), Nyayavadi (male lawyer), Nyayavadini (female lawyer), Nyayadata (judge), Danda (punishment / penalty), among others.
Слайд 8
Слайд 9
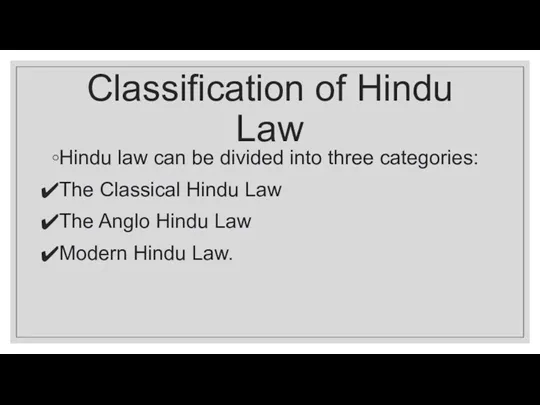
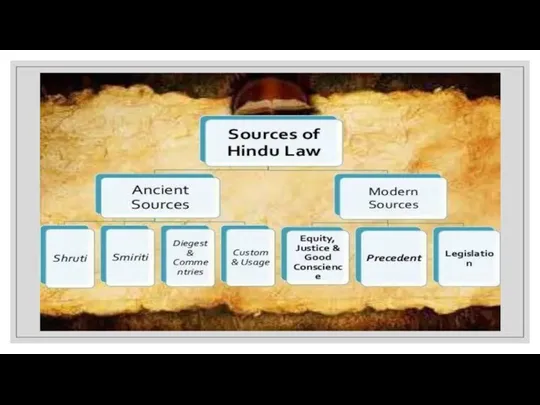
Classification of Hindu Law
Hindu law can be divided into three categories:
The
Classical Hindu Law
The Anglo Hindu Law
Modern Hindu Law.
Слайд 10

Indian Legal System
India has a federal judicial system which is primarily based on
mixed law i.e. based on parliamentary legislature, court laws, customary & religious laws as well.
The Indian Judicial System is developed by judges through their decisions, orders, and judgments.
In the constitution of India, every citizen has been given several rights and since the rights are provided, there will infringement of those rights as well.
Слайд 11
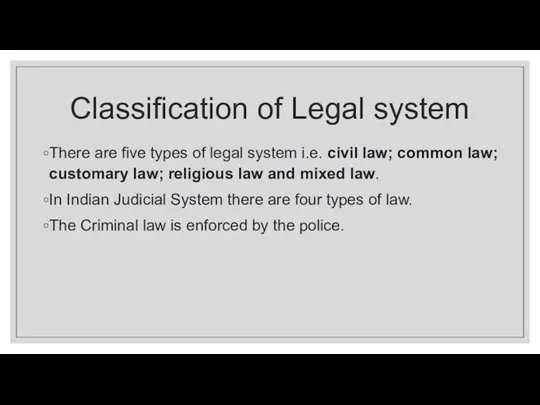
Classification of Legal system
There are five types of legal system i.e. civil
law; common law; customary law; religious law and mixed law.
In Indian Judicial System there are four types of law.
The Criminal law is enforced by the police.
Слайд 12

Civil law
As the name suggests, Civil Law comprises of set of
rules and regulations which helps in resolving disputes which are non-criminal in nature.
The law in India is primarily governed by the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 (CPC) which is a procedural law pertaining to administration of civil proceedings in India.
Слайд 13

Common Law
Common law, also known as case law, is law developed
by judges through decisions of courts and similar tribunals.
A "common law system" is a legal system that gives great precedential weight to common law, on the principle that it is unfair to treat similar facts differently on different occasions.
Слайд 14

Customary Law
Customary right are specifically excluded from the purview of the Indian
Easement Act, 1882.
When the courts in India recognised customary rights based on long usage, they become customary laws.
These customary laws were the creation of Indian courts.
Customary law is a set of customs, practices and beliefs that are accepted as obligatory rules of conduct by indigenous peoples and local com- munities.
Customary law forms an intrinsic part of their social and economic systems and way of life.
Слайд 15

Religious Law
Freedom of religion in India is a fundamental right guaranteed by
Article 25-28 of the Constitution of India.
Modern India came into existence in 1947 and the Indian constitution's preamble was amended in 1976 to state that India is a secular state.
Religion is the very basis of human life which is not just following a belief but it is also a the way of living because the followers of a particular religion follows a definite kind of livelihood and with this moral duty
Слайд 16

Mixed Law
India maintains a hybrid legal system with a mixture of civil,
common law and customary, Islamic ethics, or religious law within the legal framework inherited from the colonial era and various legislation first introduced by the British are still in effect in modified forms today.
India has a federal judicial system which legal system based on mixed law i.e. based on parliamentary legislature, court laws, customary & religious laws as well.
Mixed legal systems refer to legal systems where two or more of the above legal systems work together.
Слайд 17

Judiciary System
The Judiciary is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements
and interprets, defends, and applies the law in legal cases.
The judiciary can also be thought of as the mechanism for the resolution of disputes.
The judiciary generally does not make statutory law or enforce law but rather interprets, defends, and applies the law to the facts of each case. However, in some countries the judiciary does make common law.
Courts with judicial review power may annul the laws and rules of the state when it finds them incompatible with a higher norm, such as primary legislation, the provisions of the constitution, treaties or international law.
Judges constitute a critical force for interpretation and implementation of a constitution, thus in common law countries creating the body of constitutional law.
















 Проблемы правового регулирования суррогатного материнства в России
Проблемы правового регулирования суррогатного материнства в России Новые документы
Новые документы Спортивное право
Спортивное право Система управления охраной труда в ОАО РЖД
Система управления охраной труда в ОАО РЖД Правила оформления документов
Правила оформления документов Правила вождения колесных машин. Закон Республики Казахстан
Правила вождения колесных машин. Закон Республики Казахстан Политика лицензирования программного обеспечения
Политика лицензирования программного обеспечения Человек и закон в стихах. По мотивам Уголовного кодекса Российской Федерации
Человек и закон в стихах. По мотивам Уголовного кодекса Российской Федерации Предмет теории государства и права. Методология теории государства и права. Лекции 1, 2, 3
Предмет теории государства и права. Методология теории государства и права. Лекции 1, 2, 3 Правовая охрана средств индивидуализации
Правовая охрана средств индивидуализации Виды и формы предпринимательской деятельности
Виды и формы предпринимательской деятельности Кедендік бақылау бөлімшесі, берілуі Қазақстан Республикасы Кедендік одақтың
Кедендік бақылау бөлімшесі, берілуі Қазақстан Республикасы Кедендік одақтың Права ребенка в картинках
Права ребенка в картинках Поверка водосчетчика
Поверка водосчетчика Врачебные ошибки
Врачебные ошибки Избирательное право. Понятие избирательного права
Избирательное право. Понятие избирательного права Статистикалық есептің мәні, міндеттері және ұйымдастырылуы
Статистикалық есептің мәні, міндеттері және ұйымдастырылуы Торгівля людьми. Масштаби проблеми. Основні дефініції поняття. Причини торгівлі людьми
Торгівля людьми. Масштаби проблеми. Основні дефініції поняття. Причини торгівлі людьми Контрольно-надзорная деятельность и административная практика. Россельхознадзор
Контрольно-надзорная деятельность и административная практика. Россельхознадзор Правовые основы операций с недвижимостью
Правовые основы операций с недвижимостью Agreement. Document. Covenant. Road map
Agreement. Document. Covenant. Road map Основы гражданского права. Лекция 5
Основы гражданского права. Лекция 5 Нормативно-правовые основы деятельности вожатого
Нормативно-правовые основы деятельности вожатого Система стандартов разработки и постановки продукции на производство (СРПП)
Система стандартов разработки и постановки продукции на производство (СРПП) Социальная защита военнослужащих
Социальная защита военнослужащих Итоги контрольно-надзорной деятельности
Итоги контрольно-надзорной деятельности Подготовка дела к судебному разбирательству. Судебное разбирательство
Подготовка дела к судебному разбирательству. Судебное разбирательство Общие положения административного права
Общие положения административного права