Содержание
- 2. “Well, I’ll eat it,” said Alice, “and if it makes me grow larger, I can reach
- 3. #include String objects has several build-in functions. It can increase its length dynamically Strings
- 4. Moreover, it is possible to use a string object as an array of chars Nevertheless, it
- 5. A character array is simply an array of characters can terminated by a null character. A
- 6. 1. getline() :- This function is used to store a stream of characters as entered by
- 7. 4. find() :- Searches the string for the first occurrence of the sequence specified by its
- 8. Iterators are used to point at the memory addresses of STL containers. They are primarily used
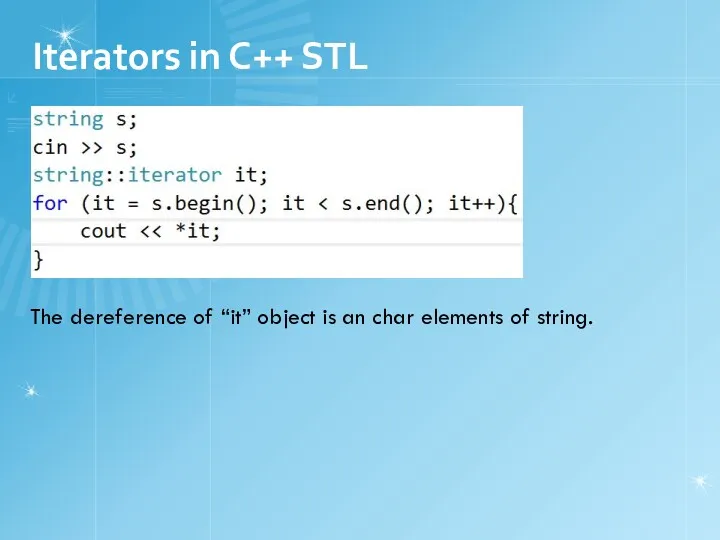
- 9. Iterators in C++ STL The dereference of “it” object is an char elements of string.
- 10. Array cannot change the length Vector the same purpose as arrays except can change length while
- 11. Vectors Library: #include Declaration: vector name; Example: vector v; vector v(10);
- 12. Vectors To add an element to a vector for the first time, you normally use the
- 13. Vectors The number of elements in a vector is called the size of the vector. The
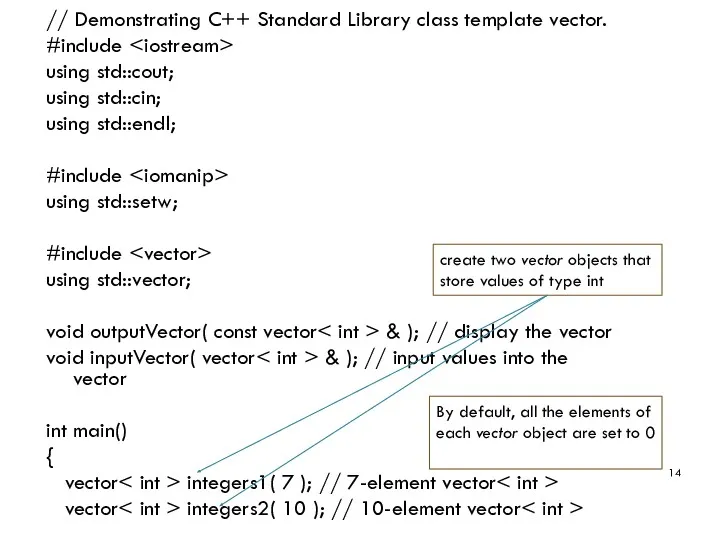
- 14. // Demonstrating C++ Standard Library class template vector. #include using std::cout; using std::cin; using std::endl; #include
- 15. // print integers1 size and contents cout outputVector( integers1 ); // print integers2 size and contents
- 16. // use inequality (!=) operator with vector objects cout if ( integers1 != integers2 ) cout
- 17. // use equality (==) operator with vector objects cout if ( integers1 == integers2 ) cout
- 18. // output vector contents void outputVector( const vector &array ) { size_t i; // declare control
- 19. Two / Three / Multi Dimensioned arrays using vector A two dimensional array is a vector
- 20. #include #include using namespace std; void main() { // Declare size of two dimensional array and
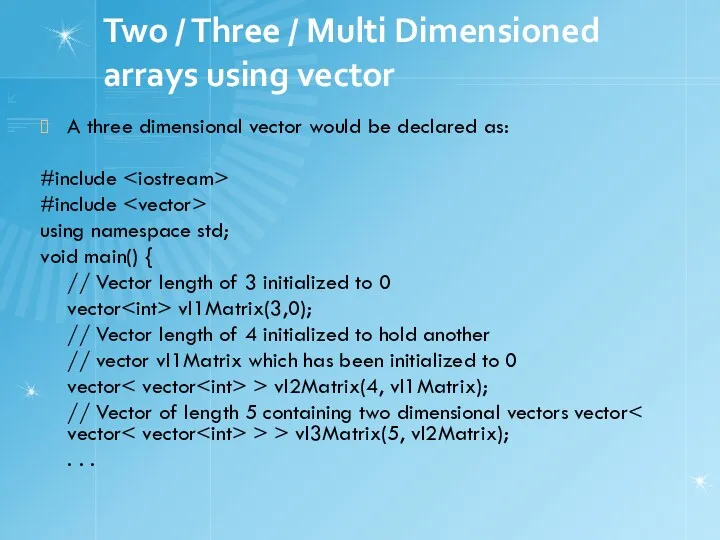
- 21. Two / Three / Multi Dimensioned arrays using vector A three dimensional vector would be declared
- 22. #include #include using namespace std; void main() { vector > > vI3Matrix(2, vector > (3, vector
- 23. //Example of iterators used with a two dimensional vector. #include #include using namespace std; void main()
- 24. vI2Matrix.push_back(A); vI2Matrix.push_back(B); cout for(iter_ii=vI2Matrix.begin(); iter_ii!=vI2Matrix.end(); iter_ii++) { for(iter_jj=(*iter_ii).begin(); iter_jj!=(*iter_ii).end(); iter_jj++) { cout } } } Using
- 25. Readings: C++ How to Program, By H. M. Deitel Chapter 7. Arrays and Vectors
- 27. Скачать презентацию





















 Guess the Countries and Nationalities with profession
Guess the Countries and Nationalities with profession How to keep fit
How to keep fit Holidays in USA
Holidays in USA My school day. What school do you go to?
My school day. What school do you go to? Animals. Go Getter
Animals. Go Getter Summer camp “Discovery days”
Summer camp “Discovery days” Modal verbs
Modal verbs Урок грамматики
Урок грамматики Travelling Means of Transport
Travelling Means of Transport Practical pharmacology. Part 5. Dose response curve of acetylcholine
Practical pharmacology. Part 5. Dose response curve of acetylcholine Face. She’s got blue eyes
Face. She’s got blue eyes Conditionals
Conditionals The house of my dream
The house of my dream Modal verbs. Значение, использование, эквиваленты
Modal verbs. Значение, использование, эквиваленты My Family
My Family In the park. New words
In the park. New words Space programm of Russia
Space programm of Russia Generations
Generations Использование информационных технологий в преподавании иностранных языков
Использование информационных технологий в преподавании иностранных языков [ʤ] – перед гласными e, i, y
[ʤ] – перед гласными e, i, y Racism in Britain
Racism in Britain Finance 510: Microeconomic Analysis
Finance 510: Microeconomic Analysis Australia
Australia The sounds of language. Phonetics and phonology
The sounds of language. Phonetics and phonology Figure Skating
Figure Skating Роль музыки в изучении английского языка
Роль музыки в изучении английского языка Времена английского глагола
Времена английского глагола Irregular verbs
Irregular verbs