Содержание
- 2. Characteristics 1. They are soft bodied, unsegmented worms. 2. They show bilateral symmetry and dorsiventrally flat
- 3. Characteristics cont. 8. Circulatory and respiratory systems are absent. 9. Nervous system and sense organs are
- 4. Phylum Platyhelminthes is divided into three classes: Class I:- TURBELLARIA Ex. Planaria sp. Class II:- TERMATODA
- 5. CLASS I: TURBELLARIA : 1. Mostly free - living forms found in fresh or sea waters
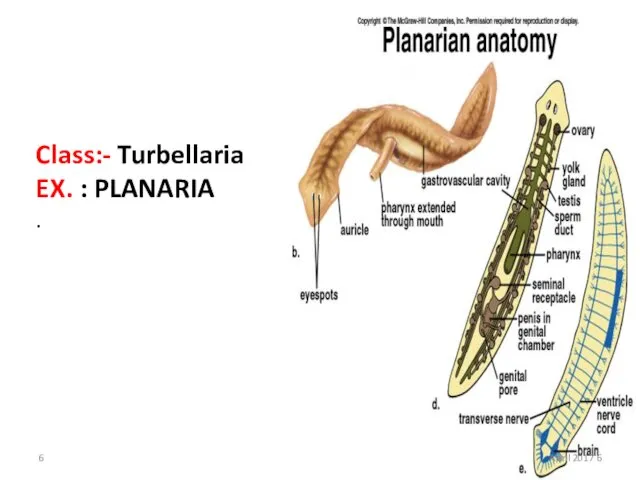
- 6. Class:- Turbellaria EX. : PLANARIA . 6 April 2017
- 7. 6 April 2017
- 8. CLASS II : TERMATODA : These are commonly known as flukes. These are ectoparasitic or endoparasitic
- 9. CLASS Trematoda ORDER Digenea Fasciola sp. Schistosoma sp. ORDER Monogenea 6 April 2017
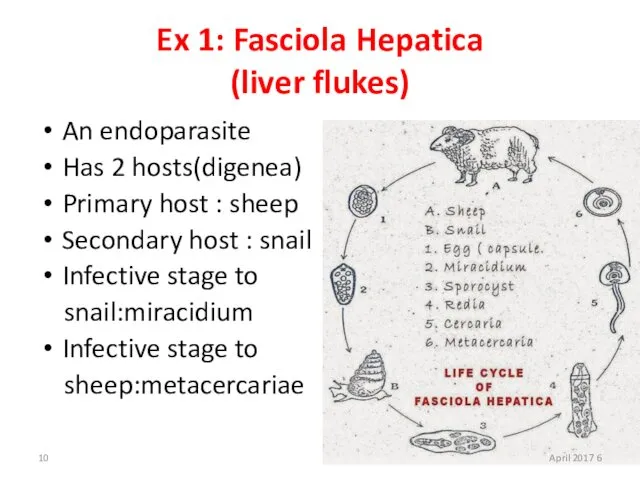
- 10. Ex 1: Fasciola Hepatica (liver flukes) An endoparasite Has 2 hosts(digenea) Primary host : sheep Secondary
- 11. 6 April 2017
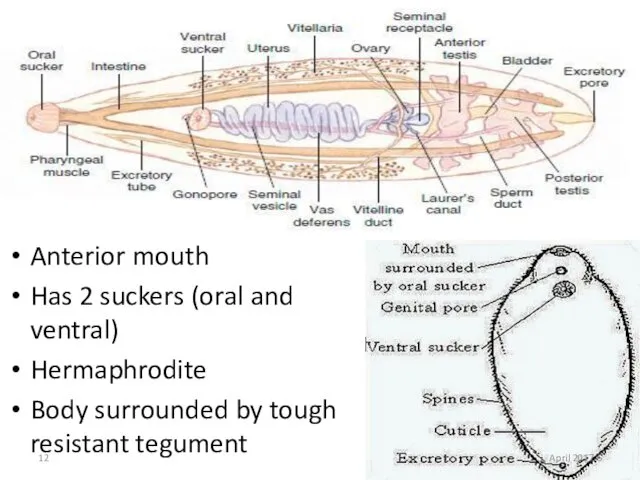
- 12. Anterior mouth Has 2 suckers (oral and ventral) Hermaphrodite Body surrounded by tough resistant tegument 6
- 13. 1-Digestive system Incomplete (has no anus) At the anterior end of the body a mouth opening
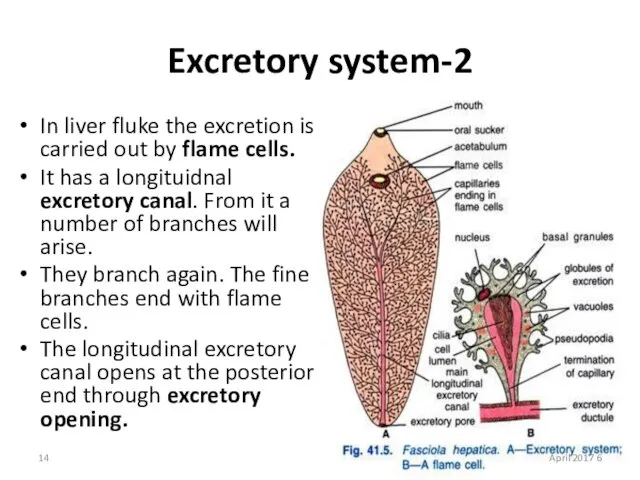
- 14. 2-Excretory system In liver fluke the excretion is carried out by flame cells. It has a
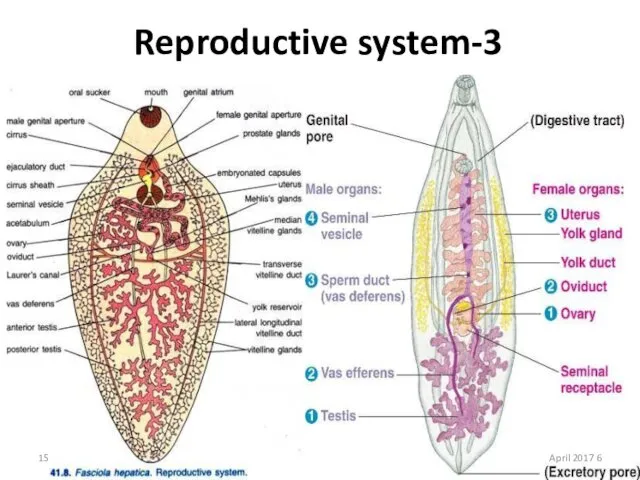
- 15. 3-Reproductive system 6 April 2017
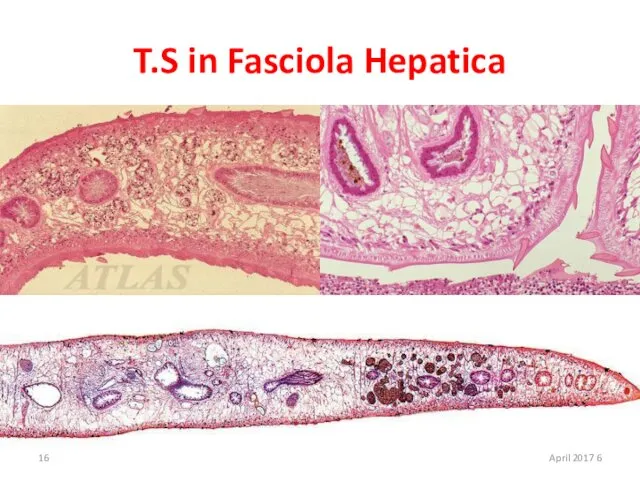
- 16. T.S in Fasciola Hepatica 6 April 2017
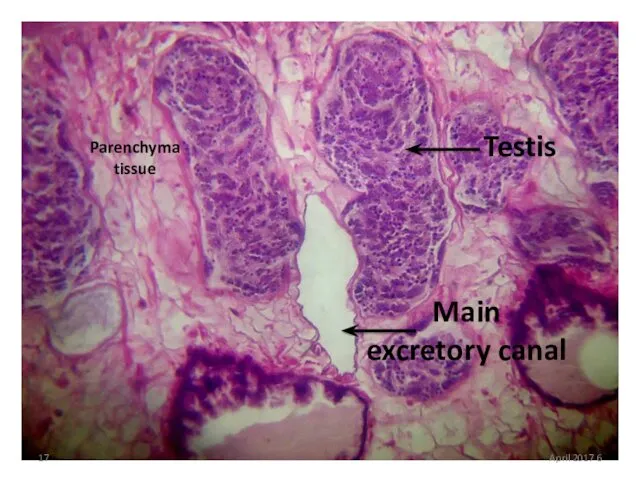
- 17. Testis Main excretory canal Parenchyma tissue 6 April 2017
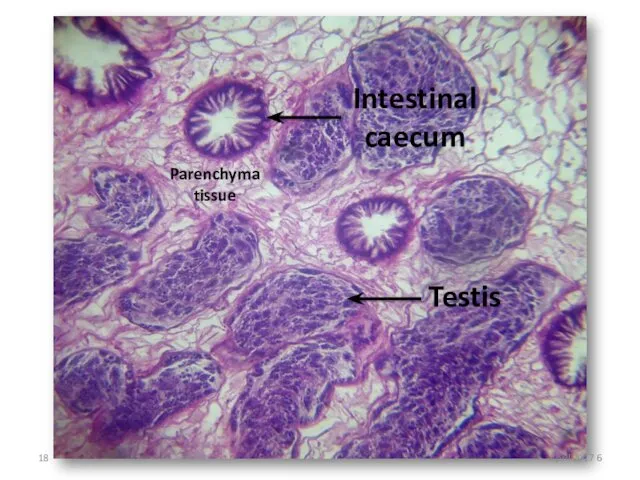
- 18. Intestinal caecum Testis Parenchyma tissue 6 April 2017
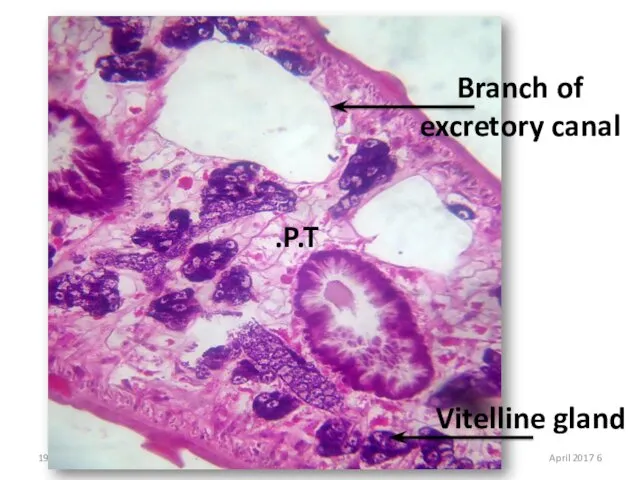
- 19. Branch of excretory canal Vitelline gland P.T. 6 April 2017
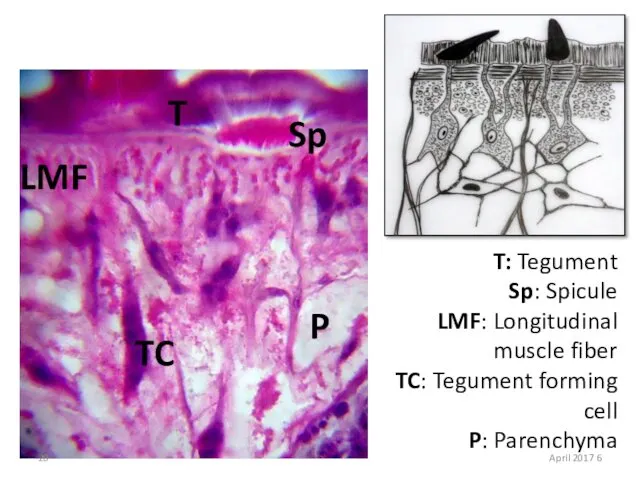
- 20. T Sp TC LMF P T: Tegument Sp: Spicule LMF: Longitudinal muscle fiber TC: Tegument forming
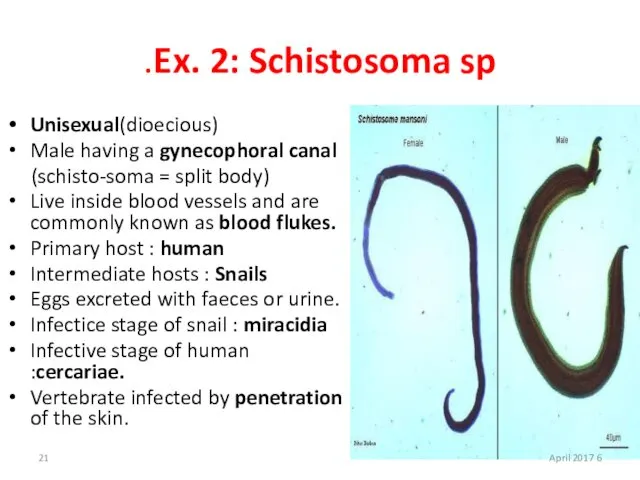
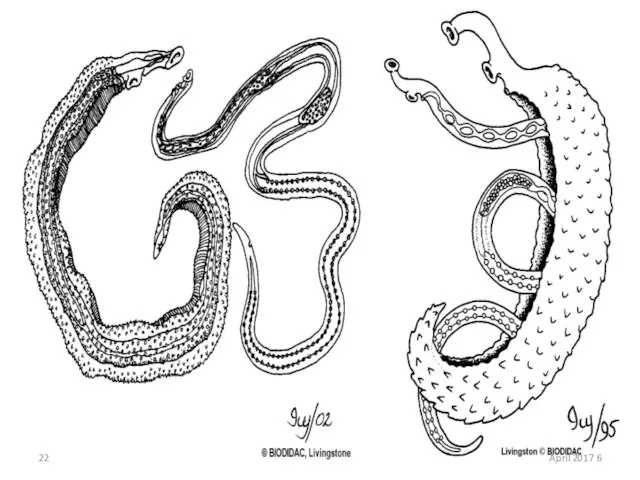
- 21. Ex. 2: Schistosoma sp. Unisexual(dioecious) Male having a gynecophoral canal (schisto-soma = split body) Live inside
- 22. 6 April 2017
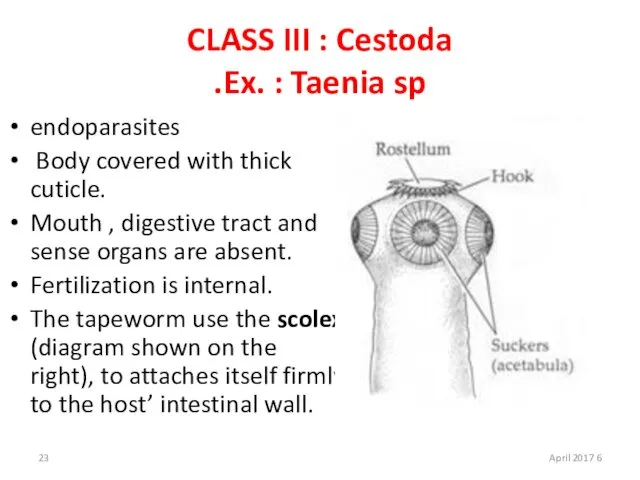
- 23. CLASS III : Cestoda Ex. : Taenia sp. endoparasites Body covered with thick cuticle. Mouth ,
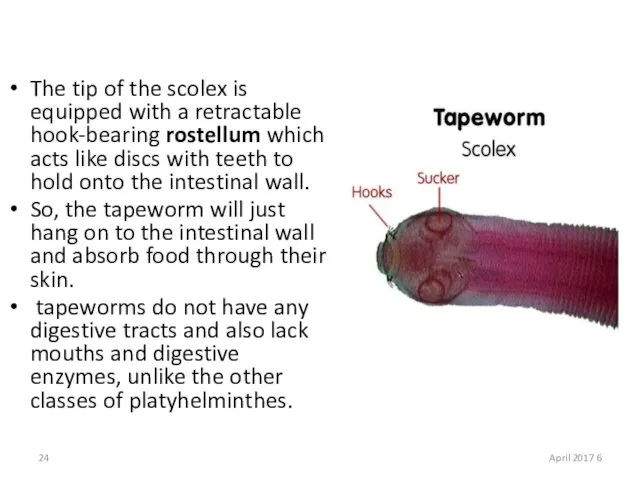
- 24. The tip of the scolex is equipped with a retractable hook-bearing rostellum which acts like discs
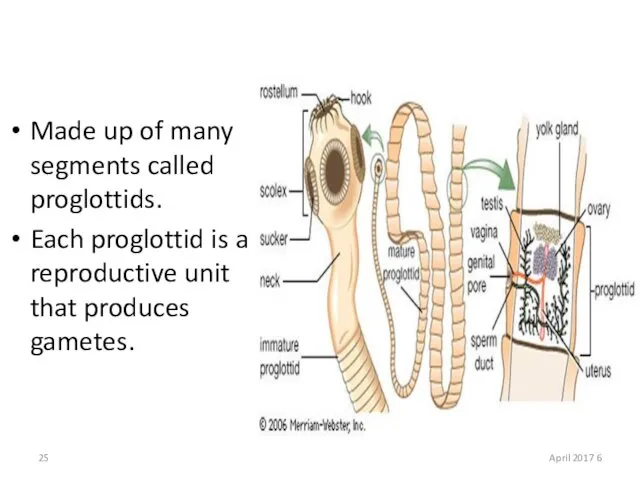
- 25. Made up of many segments called proglottids. Each proglottid is a reproductive unit that produces gametes.
- 26. The neck produces segments called proglottids which make up the body and tail. Each segment has
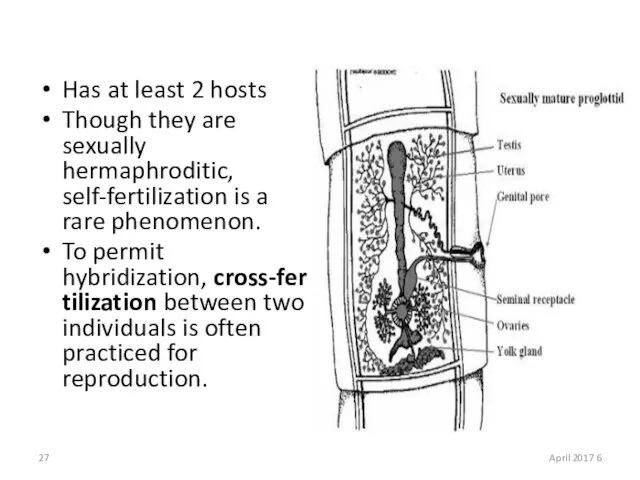
- 27. Has at least 2 hosts Though they are sexually hermaphroditic, self-fertilization is a rare phenomenon. To
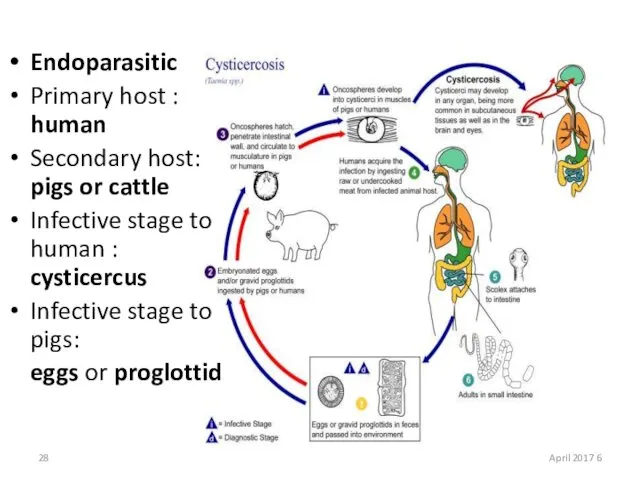
- 28. Endoparasitic Primary host : human Secondary host: pigs or cattle Infective stage to human : cysticercus
- 30. Скачать презентацию








 Сущность и стратегии устойчивого развития
Сущность и стратегии устойчивого развития Биотехнология. Вектора. Метод Максама—Гилберта
Биотехнология. Вектора. Метод Максама—Гилберта Анатомо-физиологические аспекты саморегуляции функций организма
Анатомо-физиологические аспекты саморегуляции функций организма Красная книга
Красная книга Папоротникообразные растения
Папоротникообразные растения Дигибридное скрещивание. Третий закон Менделя
Дигибридное скрещивание. Третий закон Менделя Строение растительной клетки
Строение растительной клетки Химия и обмен углеводов. Классификация
Химия и обмен углеводов. Классификация Эволюция систем органов
Эволюция систем органов Аквариум как химико-биологический объект исследования
Аквариум как химико-биологический объект исследования Из опыта работы Проектно – исследовательская деятельность на уроках биологии
Из опыта работы Проектно – исследовательская деятельность на уроках биологии Генетика человека
Генетика человека Редис. Биологические особенности
Редис. Биологические особенности Thoroughbred horse
Thoroughbred horse Патофизиология апоптоза
Патофизиология апоптоза ДЕЛОВАЯ ИГРА АУКЦИОН ЗНАНИЙ
ДЕЛОВАЯ ИГРА АУКЦИОН ЗНАНИЙ Дикие животные. Амфибии. Земноводные
Дикие животные. Амфибии. Земноводные Мышечная система человека
Мышечная система человека Презентация лекции по теме Пластиковая бомба
Презентация лекции по теме Пластиковая бомба Анализ красителей и консервантов, входящих в состав безалкогольных газированных и негазированных напитков
Анализ красителей и консервантов, входящих в состав безалкогольных газированных и негазированных напитков Мінливість. Типи мінливості. Мутації і модифікації. Тема 7
Мінливість. Типи мінливості. Мутації і модифікації. Тема 7 Интерактивная игра Кто? Как? Почему? Играя, вспоминаем для 9 класса (по материалу I полугодия)
Интерактивная игра Кто? Как? Почему? Играя, вспоминаем для 9 класса (по материалу I полугодия) Ядовитые растения Курганской области
Ядовитые растения Курганской области Тип Губки
Тип Губки Бізон європейський, або зубр
Бізон європейський, або зубр Регуляция водно-солевого и минерального обмена
Регуляция водно-солевого и минерального обмена Высшая нервная деятельность человека
Высшая нервная деятельность человека Удаление продуктов обмена. Обмен веществ
Удаление продуктов обмена. Обмен веществ