Содержание
- 2. Macronutrients Proteins Carbohydrates Fats Macro nutrients
- 3. What is fat? It’s a combination of glycerin and fatty acids 1 g of fat =
- 4. What does fat do for us? Provide energy Carry fat-soluble nutrients (essential fat acids and vitamins
- 5. Classification Fat acids Saturated Unsaturated solid Animal fats liquid Plant oils exception:
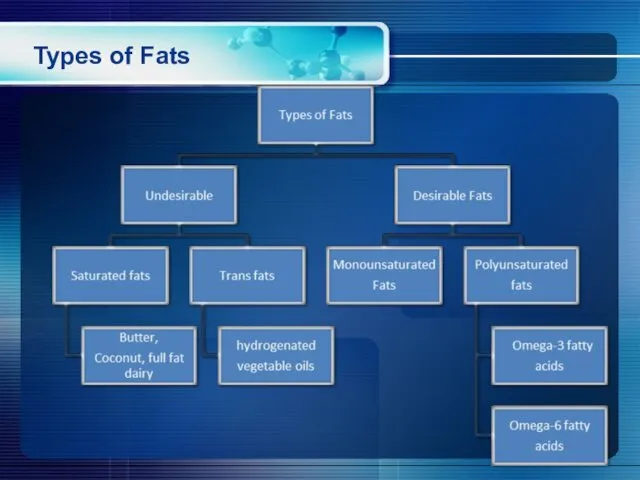
- 6. Types of Fats
- 7. Trans fats Trans fats, also known as partially hydrogenated oils), are unsaturated fats that are uncommon
- 8. Trans fats On 16 June 2015, the FDA finalized its determination that trans fats are not
- 9. «Street light» of fat usefulness Better to exclude: Transfats Limit: Saturated fats Omega 6 Increase: Omega
- 10. Transfats Margarine Butter with plant additives Cookies, candies Refines oils Mayonnaise Dried crust Fried potato Well
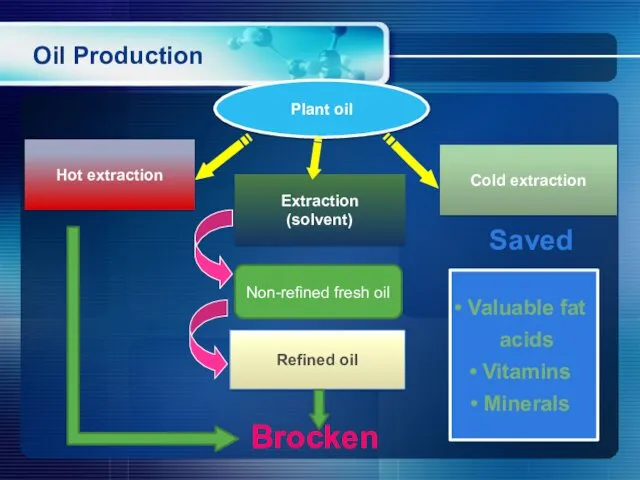
- 11. Oil Production Valuable fat acids Vitamins Minerals Cold extraction Plant oil Saved Brocken Refined oil Hot
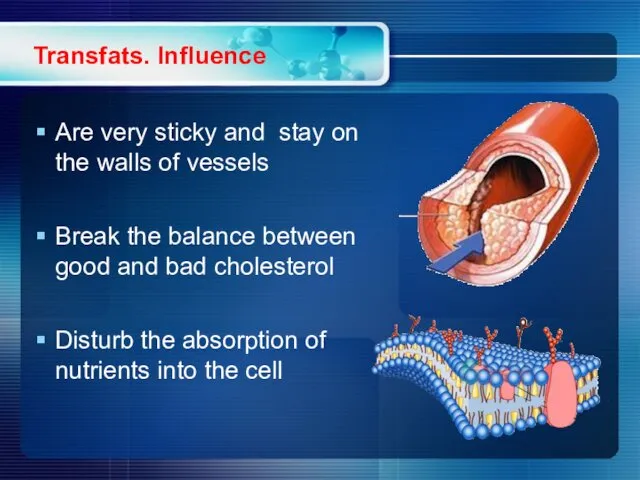
- 12. Transfats. Influence Are very sticky and stay on the walls of vessels Break the balance between
- 13. Saturated fats Are found in animal products (exception – palm oil) Transforms into energy Excesses plug
- 14. Omega-6 Essential fat acid (extra virgin oils) – building material Activate inflammations Excesses provoke tumors, autoimmune
- 15. Omega-3 Flax, hempseed, rape oil Seeds, grains Nuts Sea fish Fish oil in capsules
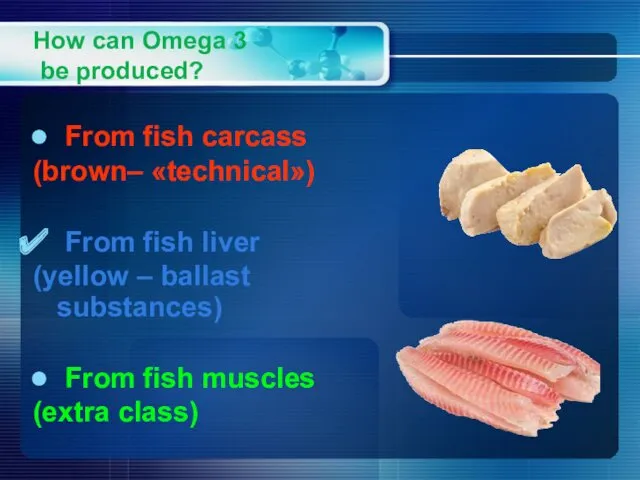
- 16. How can Omega 3 be produced? From fish carcass (brown– «technical») From fish liver (yellow –
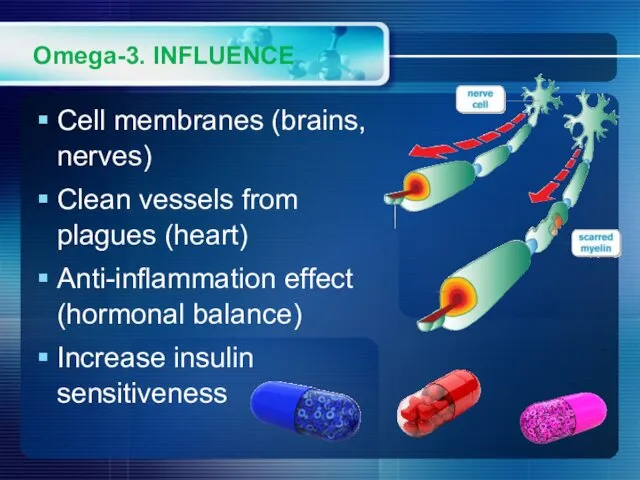
- 17. Omega-3. INFLUENCE Cell membranes (brains, nerves) Clean vessels from plagues (heart) Anti-inflammation effect (hormonal balance) Increase
- 18. Omega-9. INFLUENCE Doesn’t influence on hormonal balance Cleans vessels Doesn’t oxidize while cooking food
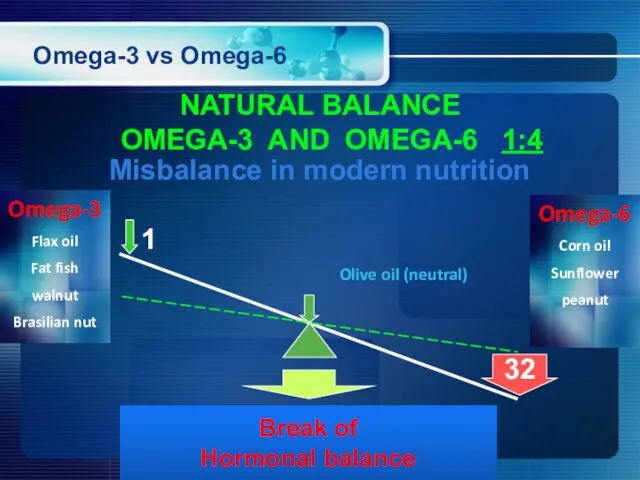
- 19. Omega-3 vs Omega-6 NATURAL BALANCE OMEGA-3 AND OMEGA-6 1:4 Omega-3 Flax oil Fat fish walnut Brasilian
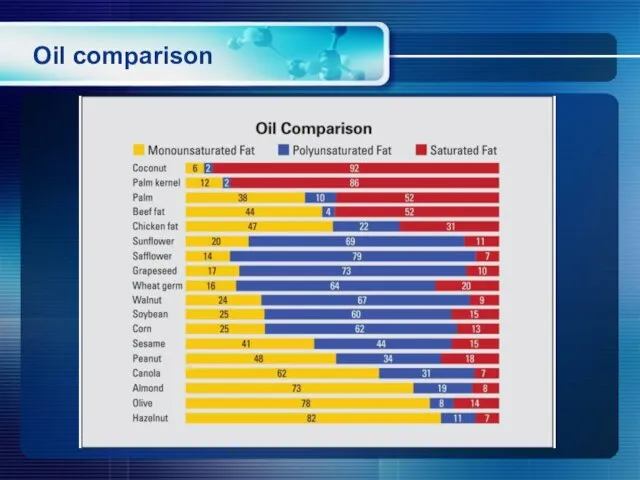
- 20. Oil comparison
- 21. Balance of Fats Fat acid Omega 3 should be in balance: 50% plant (oils, nuts, grains)
- 22. Herbalifeline THE COMPLEX OF POLIUNSATURATED FAT ACIDS Concentrate of fish oil «Extra class» - Omega-3 (contains
- 23. Strengthening of effect Vitamin Е (tocopherol) Antioxidant, prevent fats from oxidizing, protects vitamin A and amino-acids.
- 24. Functions of Omega-3 Builds and renews cell membranes Stimulates mental development in childhood Activates brain work
- 25. Day norm of Omega-3 To normalize cholesterol and strengthen health generally: 1-1,5 g. To increase muscles:
- 27. Скачать презентацию

















 Слухова сенсорна система
Слухова сенсорна система Плоды. Сухие плоды
Плоды. Сухие плоды Вестибулярный анализатор
Вестибулярный анализатор Адам ағзасындағы химиялық элементтер
Адам ағзасындағы химиялық элементтер Стра.ный гость
Стра.ный гость Надклас риби
Надклас риби Биологическая и психологическая подструктура личности (часть 1)
Биологическая и психологическая подструктура личности (часть 1) Царство Грибы. Общая характеристика и значение
Царство Грибы. Общая характеристика и значение Подготовка к Всероссийской проверочной работе по биологии. 5 класс
Подготовка к Всероссийской проверочной работе по биологии. 5 класс Нервная система. Спинной мозг
Нервная система. Спинной мозг Интерактивная игра Экологическое Ассорти
Интерактивная игра Экологическое Ассорти Игра В мире животных
Игра В мире животных Внутривидовые и межвидовые взаимодействия у грибов, водорослей, высших растений. (Часть 4)
Внутривидовые и межвидовые взаимодействия у грибов, водорослей, высших растений. (Часть 4) Выращивание огурцов из семян
Выращивание огурцов из семян Органи чуття та їх значення
Органи чуття та їх значення Формування знань у дітей про перелітніх птахів
Формування знань у дітей про перелітніх птахів Біологічні особливості і агротехніка вирощування зелених овочів
Біологічні особливості і агротехніка вирощування зелених овочів Красная книга
Красная книга Люминесцентная (флуоресцентная) микроскопия
Люминесцентная (флуоресцентная) микроскопия Анализаторы и органы чувств
Анализаторы и органы чувств Биологический объект как объект исследования (объект изучения и управления)
Биологический объект как объект исследования (объект изучения и управления) История первобытного общества. Антропосоциогенез. Лекция 1
История первобытного общества. Антропосоциогенез. Лекция 1 Презентация к уроку Эволюционное учение Ч. Дарвина
Презентация к уроку Эволюционное учение Ч. Дарвина Надцарство актиномицеты
Надцарство актиномицеты Тест-презентация Органы и системы органов животных.
Тест-презентация Органы и системы органов животных. Анаболизм. Автотрофное питание. Фотосинтез. Строение хлоропласта
Анаболизм. Автотрофное питание. Фотосинтез. Строение хлоропласта Жизнь организмов на планете Земля. Природные сообщества
Жизнь организмов на планете Земля. Природные сообщества Жануарлардың мінез-қылығы
Жануарлардың мінез-қылығы